Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gene Mutation 333
Uploaded by
Mahrose Nawaz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views2 pagesbrief discription
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentbrief discription
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views2 pagesGene Mutation 333
Uploaded by
Mahrose Nawazbrief discription
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
GENE MUTATION:
Gene mutation is abrupt inheritable qualitative or
quantitative change in the genetic material of an
organism.
Since in most organisms genes are segments of DNA molecule,
so a mutation can be regarded as a change in the DNA sequence
which is reflected in the change of sequence of corresponding
RNA or protein molecules. Such a change may involve only one
base/base pair or more than one base pair of DNA.
Mutations occur in a random manner, i.e., they are not directed
according to the requirements of the organism. Most mutations
occur spontaneously by the environmental effect ,however,
they can be induced in the laboratory either by radiations,
physical factors or chemicals (called mutagens). A unicellular
organism is more subjected to environmental on-slaughts since it
is at the same time a somatic or germ cell.
In multi cellular organisms the germ cells are distinct cells, and
are relatively protected from the environment. Mutation has a
significant role to play in the origin of species or evolution
Historical Background
The earliest record of point mutations dates back to 1791,
when Seth Wright noticed a lamb with exceptionally short legs
in his flock of sheep. Visualising the economic significance of this
short-legged sheep. i.e., short legged sheep could not cross the
low stone fence and damage the crop fields in the vicinity, he
produced a flock of sheep, each of which having short legs by
employing artificial breeding techniques. The short legged breed
of sheep was known as Ancon breed. Later on, the trait of short
legs was found to be resulted from a recessive mutation and the
short legged individuals were found to be homozygous recessive
OCCURANCE
Mutations occur frequently in the nature and have been reported
in many organisms, e.g. Drosophila, mice and other rodents, rats,
rabbits, guinea pigs and man. In the Drosophila, mutation causes
white and pink eyes, black and yellow body colors, and vestigial
wings. In rodents the mutations are responsible for black, white
and brown coats. In man, the mutations cause variation in hair
color, eye color, skin pigmentation and several somatic
malformations. Various genetical diseases of human beings such
as haemophila color blindness, phenyl ketonuria, etc., form
other examples of mutation in human beings.
How does a mutation act?
Any change in sequence of nucleotides in the DNA will result in
the corresponding change in the nucleotide sequence of mRNA.
This may result in alignment of different tRNA molecules on
mRNA (during protein synthesis). Thus, the amino acid sequence,
and, hence, the structure and properties of the enzyme formed
will be changed. This defective enzyme or structural protein may
adversely affect the trait controlled by the protein. In
consequence, a mutant phenotype makes its expression.
You might also like
- Gene MutationDocument22 pagesGene MutationMahrose NawazNo ratings yet
- Genes and Proteins: What Do Genes Do?Document27 pagesGenes and Proteins: What Do Genes Do?Jonathon HartNo ratings yet
- Evolution: - Evolution Means Change Over Time Changes in Species Over Long Periods of TimeDocument29 pagesEvolution: - Evolution Means Change Over Time Changes in Species Over Long Periods of TimeMalik FhaimNo ratings yet
- Heredity and EvolutionDocument8 pagesHeredity and EvolutionAtharv ChhabraNo ratings yet
- 1.heredity and EvolutionDocument22 pages1.heredity and Evolutionvirotix812No ratings yet
- Ch. 23 Lecture Outline PDFDocument15 pagesCh. 23 Lecture Outline PDFCSERM UNASNo ratings yet
- E Volution by Means of Natural SelectionDocument3 pagesE Volution by Means of Natural SelectionNurul HidayahNo ratings yet
- Transposons An Introduction To Transposons: Figure Showing Simple TransposonsDocument8 pagesTransposons An Introduction To Transposons: Figure Showing Simple TransposonsMudit MisraNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument8 pagesAnatomyaminmofrehNo ratings yet
- Mutations NotesDocument8 pagesMutations NotesHarini anuNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes - Blueprint of LifeDocument31 pagesBiology Notes - Blueprint of Lifecody jamesNo ratings yet
- Notes On Micro and Macro EvolutionDocument5 pagesNotes On Micro and Macro EvolutionObaiah JamakalaNo ratings yet
- Evolution: An Overview Based on Genetic Characters and BirdsFrom EverandEvolution: An Overview Based on Genetic Characters and BirdsNo ratings yet
- What Is A Genetic Mutation?: Gene Mutations Can Be Classified in Two Major WaysDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Genetic Mutation?: Gene Mutations Can Be Classified in Two Major WaysStephanie BulusanNo ratings yet
- Evolution MergedDocument80 pagesEvolution MergedSasuke UchihaNo ratings yet
- MutationsDocument6 pagesMutationsGargee MohantyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document6 pagesChapter 7olivia majcherNo ratings yet
- Molecular Genetics: Topic: Gene MutationDocument28 pagesMolecular Genetics: Topic: Gene MutationJannifer Andrew100% (2)
- Genetic MutationDocument27 pagesGenetic MutationKathleen JOy BiasUraNo ratings yet
- Essay 34Document2 pagesEssay 34api-213708874No ratings yet
- Descent With ModificationDocument38 pagesDescent With ModificationRhea GulayNo ratings yet
- VaniDocument17 pagesVanipagoti mohanraoNo ratings yet
- MutationDocument12 pagesMutationSamuelNo ratings yet
- The Role of Chromatin and Epigenetics in The Polyphenisms of Ant CastesDocument11 pagesThe Role of Chromatin and Epigenetics in The Polyphenisms of Ant CastesNina ČorakNo ratings yet
- Module 13Document13 pagesModule 13John Bernard VeloriaNo ratings yet
- What Are The Most Common Blood Types of A Child From Any Two Parents?Document5 pagesWhat Are The Most Common Blood Types of A Child From Any Two Parents?Christine Joyce Toledo VasquezNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 NotesDocument97 pagesGeneral Biology 2 NotesMacky NohayNo ratings yet
- Evidences of EvolutionDocument5 pagesEvidences of EvolutionAnthony CreationNo ratings yet
- Bio and GlucoseDocument21 pagesBio and Glucosesaga.a.mNo ratings yet
- W2 Genetic DiversityDocument29 pagesW2 Genetic DiversityMammoth CoffeeNo ratings yet
- Variation F 5Document8 pagesVariation F 5Angie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- The Long Journey of My Little Y Chromosomes: The Origins of One Viking FamilyFrom EverandThe Long Journey of My Little Y Chromosomes: The Origins of One Viking FamilyNo ratings yet
- Lect 3-4 PDFDocument34 pagesLect 3-4 PDFMohd BabarNo ratings yet
- Biology Summaries: CO MethaneDocument25 pagesBiology Summaries: CO MethaneMariam Abdel-RazekNo ratings yet
- Heredity and Evolution NotesDocument5 pagesHeredity and Evolution NotesCapt Pradeep kumarNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of EvolutionDocument4 pagesMechanisms of Evolutionchristopher daniolcoNo ratings yet
- Chaprter 5 Environmental ScienceDocument6 pagesChaprter 5 Environmental Sciencejeboy DaquizNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument21 pagesQuestionsNikhil ShahNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in General BiologyDocument6 pagesReviewer in General BiologyArlynKaren VargasNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 - The Origin and Diversity of LifeDocument33 pagesGeneral Biology 2 - The Origin and Diversity of LifeJohn OliquianoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GeneticsDocument25 pagesIntroduction To GeneticsBella VengcoNo ratings yet
- The Braconid and Ichneumonid Parasitoid Wasps: Biology, Systematics, Evolution and EcologyFrom EverandThe Braconid and Ichneumonid Parasitoid Wasps: Biology, Systematics, Evolution and EcologyNo ratings yet
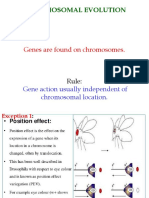
- Chromosomal Evolution: Genes Are Found On ChromosomesDocument28 pagesChromosomal Evolution: Genes Are Found On ChromosomesDibbyangana MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Change and MutabilityDocument11 pagesChange and Mutabilityrey_fremyNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of EvolutionDocument23 pagesMechanisms of EvolutionVeancy WangNo ratings yet
- 10.1007@s11427 020 1709 6Document4 pages10.1007@s11427 020 1709 6Nouri RaidNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Population ChangeDocument47 pagesMechanisms of Population ChangeNicole DennillNo ratings yet
- Aakaash Bio ProjectDocument7 pagesAakaash Bio ProjectHASHIRANo ratings yet
- Genetics in OrthodonticsDocument63 pagesGenetics in OrthodonticsPrachi Madan100% (20)
- Form 4 Biology Notes LatestDocument104 pagesForm 4 Biology Notes LatestElvis KemboiNo ratings yet
- Human Genetics Lecture #1 Autor Cristina de Guzman Strong, Ph.D.Document97 pagesHuman Genetics Lecture #1 Autor Cristina de Guzman Strong, Ph.D.Лион ГоровецNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Genetic: PolymorphismDocument14 pagesAn Introduction To Genetic: PolymorphismKishore ReddyNo ratings yet
- Heredity and Evolution HeredityDocument9 pagesHeredity and Evolution HeredityManikandan SNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Evolution - IDocument34 pagesMechanisms of Evolution - IVaibhav KumarNo ratings yet
- 3 Model GenomesDocument4 pages3 Model GenomesParisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Gene & Genome Evolution: Kevin Duh Molecular Biology Reading GroupDocument23 pagesGene & Genome Evolution: Kevin Duh Molecular Biology Reading Groupvallabhaneni rajeshNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of GeneticsDocument16 pagesFundamentals of GeneticsshriNo ratings yet
- Heredity and EvolutionDocument4 pagesHeredity and EvolutionSneha GoyalNo ratings yet
- 12th Bio QB Chap5Document13 pages12th Bio QB Chap5Vivek KasarNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Analysis by X-Ray FluorescenceDocument9 pagesQuantitative Analysis by X-Ray FluorescenceMahrose NawazNo ratings yet
- Analytical AssignmentDocument9 pagesAnalytical AssignmentMahrose NawazNo ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGYDocument9 pagesMICROBIOLOGYMahrose NawazNo ratings yet
- OriginalDocument47 pagesOriginalMahrose NawazNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument32 pagesMicrobiologyMahrose NawazNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument29 pagesGeneticsMahrose NawazNo ratings yet
- Age and Sex Structure of PopulationDocument11 pagesAge and Sex Structure of PopulationMahrose NawazNo ratings yet
- HypothyrodismDocument15 pagesHypothyrodismMahrose NawazNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument20 pagesHydrocarbonsMahrose NawazNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in Chemical BondsDocument19 pagesBasic Concepts in Chemical BondsMahrose NawazNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument28 pagesMicrobiologyMahrose NawazNo ratings yet
- Classification of Mutation According To Magnitude of Phenotypic Effect-1-1Document4 pagesClassification of Mutation According To Magnitude of Phenotypic Effect-1-1Mahrose NawazNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument20 pagesGeneticsMahrose Nawaz100% (1)
- History of ComputerDocument13 pagesHistory of ComputerMahrose NawazNo ratings yet
- PRW - Recommendations - SAU - Chemistry - Grade 11-12Document15 pagesPRW - Recommendations - SAU - Chemistry - Grade 11-12Talpyn RakhymNo ratings yet
- Single ReplacementDocument3 pagesSingle ReplacementJeianne Decerie MiguelNo ratings yet
- TCVN 6260-2009 - Portland Blended Cement (E)Document4 pagesTCVN 6260-2009 - Portland Blended Cement (E)Long LêNo ratings yet
- Phyto-Mediated Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles of BerberisDocument31 pagesPhyto-Mediated Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles of BerberisRabeea NasirNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 01Document5 pagesScience Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 01hweta173No ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - States of Matter and Separation TechniquesDocument12 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - States of Matter and Separation TechniquesChemistryKlipz100% (24)
- ProjectDocument10 pagesProjectMuhammad JafarNo ratings yet
- TEST BANK FinalDocument220 pagesTEST BANK FinalPrabhjot MundiNo ratings yet
- Soap - WikipediaDocument54 pagesSoap - WikipediaArun SinghNo ratings yet
- A Level Chap 5 EOCDocument4 pagesA Level Chap 5 EOCTrúc Hồ100% (1)
- 2013 RI H2 Chem P1 QP PDFDocument23 pages2013 RI H2 Chem P1 QP PDFsaffronNo ratings yet
- NANOCHEMISTRYDocument11 pagesNANOCHEMISTRYKrithigasri Murugesan100% (1)
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology 5.12, Spring 2005: Problem Set #4Document9 pagesMassachusetts Institute of Technology 5.12, Spring 2005: Problem Set #4KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Coordination Number - HCPDocument12 pagesCoordination Number - HCPDrRoja A RNo ratings yet
- MasterGlenium SKY 8233 v2 PDFDocument3 pagesMasterGlenium SKY 8233 v2 PDFRaju VeeraNo ratings yet
- Sikafloor 92EGDocument2 pagesSikafloor 92EGthe pilotNo ratings yet
- Chemical Weathering of Lime Mortars From The JahanDocument10 pagesChemical Weathering of Lime Mortars From The JahanVornicu NicoletaNo ratings yet
- Bioknowledgy Quick Quiz On The Origin of Cells (1.5) : (19 Marks)Document3 pagesBioknowledgy Quick Quiz On The Origin of Cells (1.5) : (19 Marks)iomaNo ratings yet
- Nanophase Ceramics: The Future Orthopedic and Dental Implant MaterialDocument42 pagesNanophase Ceramics: The Future Orthopedic and Dental Implant MaterialDario Bejarano RojasNo ratings yet
- Lowell Guilbert On Porphyry Cu (36 Pags)Document36 pagesLowell Guilbert On Porphyry Cu (36 Pags)rmiguelmera4733100% (1)
- Bohr EffectDocument3 pagesBohr EffectRendi Nak SepusatNo ratings yet
- Microbiology & Parasitology - LAB-MIDTERM-REVIEWERDocument9 pagesMicrobiology & Parasitology - LAB-MIDTERM-REVIEWERShene Claire VigillaNo ratings yet
- Classification of ElementsDocument17 pagesClassification of Elementsaaranyaka shobinNo ratings yet
- ExamView - CHP 3 QuizDocument5 pagesExamView - CHP 3 Quizkylev100% (1)
- General Chemistry Ebbing Gammon Ch. 15Document22 pagesGeneral Chemistry Ebbing Gammon Ch. 15Zara V. Feldman100% (3)
- Kimia f4 k3 2014 PPDJJ (Skema)Document14 pagesKimia f4 k3 2014 PPDJJ (Skema)comi_natchaNo ratings yet
- Hand BookDocument251 pagesHand Bookvarunn3110No ratings yet
- Felder 1938483Document21 pagesFelder 1938483Nick Renzo Barzola YauceNo ratings yet
- Chemical DosingDocument3 pagesChemical DosingMasoodyNo ratings yet
- Lanolin ADocument3 pagesLanolin ASanddmanrs Port Sanddmanrs100% (1)