Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Abstract English
Uploaded by
Milton VimosOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Abstract English
Uploaded by
Milton VimosCopyright:
Available Formats
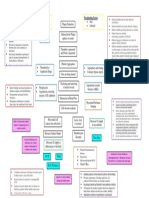
An indigenous female patient, of 80 years old, is brought to the emergency
room of Coltas hospital with a continous abdominal pain, located in the
epigastrium and right hipocondrio, that irradiates to the back, of moderate
intensity, that gets worse 6 hours ago, without any apparent reason.
Nothings seems to bring it up, like food, or any special position. The patient
also presents nausea that does not lead to vomiting, and constipation 6
days ago, also anorexy. Along side this symptoms, she presents severe
jaundice 4 weeks ago, and finally progressive weight loss during the last
months. The patient does not have any other importance atnecedents.
At the physical exam could be found: non distended abdomen, present
hydroaereal sounds, painful to te deep palpation. Positive Murphys and
Desjardins signs. A mass can e located in the epigastrium. To the percussion
mate sound could be found. Kidney percussion negative. No edema in the
patients limbs.
The patient gets hospitalized on October 30th of 2014, lab exams as well as
a chest x ray get done, which didnt allow the doctors to get to the diagnose.
An abdomen ultrasound was realized where doctors could see gallblader
pathology as well as an unidentified mas son the pncreas. That is why a
ACT was done on November 3rd of 2015, where bile dicts were dilated with
a diameter of 23 mm, the pncreas showed a mass of 50mm by 33 mm as
well as pancreatic calcifications.
Biopsy and surgicall extraction could not be made, so a transfer to intesive
care was made.
The patient enters intesive care unit after 4 days of hospitalization, artificial
breathing methods were used. After this the patient died due to a depletion
of the cardiorespiratory function.
Pancreatic cncer does not have a high prevalence in population. However
its mortality is very high. In Europe almost 78 000 cases were reported and
32 000 cases in USA. In spain 2 400 men and 2 000 women die due to this
cncer.
Pancreatic cncer ussually appears between 65 and 70 years, and is very
rare under 60 years. In the momento of the diagnose less tan 20% of the
patient would susceptible for operation due to the advanced stage of the
disease.
Ethiology of this cncer is unkkown but some risk factors can be identified:
Genetics.
Age.
Sex.
Ethie.
Tobacco consuption
Diet habits
Diabetes.
The symptomatology can be very different deppending on where the tumor
would be located.
According to some speciallists there are two types of cncer:
Exocrine pncreas cncer
Endocrine pncreas cncer.
The Spanish Oncology society says that when a patient presents jaundice,
altered glucose levels, and abdominal pain, tests should be done to
investigate this pathology.
Bilirubin levels should be analyzed to detect any alteration in bilirubin
elimination.
Secondly, tumoral markers should be checked like CA 19,9, Isolated
elevations dont make the diagnose but can make suspect of the pathology.
The third test should be a thoracoabdominal CT, and finally a magentic
resonance.
Patients with pancreatic cncer can recieve trhee types of treatment.
1. Surgery: Surgery has two main objectives, partially extract tumors
located in the head of the pncreas by doing a cephalic
duodeopancreatectomy, and extract those located in the body and
tail of the pacnreas by a partial pancreatectomy.
2. Chemotherapy.
3. Radiotherapy.
You might also like
- CORONAVIRUSDocument13 pagesCORONAVIRUSMilton VimosNo ratings yet
- Covid MbeDocument64 pagesCovid MbeMilton VimosNo ratings yet
- DeSocio2021 Article NationalEarlyWarningScore2NEWSDocument6 pagesDeSocio2021 Article NationalEarlyWarningScore2NEWSMilton VimosNo ratings yet
- Covid y EmbarazoDocument24 pagesCovid y EmbarazoMilton VimosNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Bibliografia 2222Document28 pagesBibliografia 2222francivan111No ratings yet
- Practicing Clinical Instructor (PCI) Evaluation Form: College of NursingDocument1 pagePracticing Clinical Instructor (PCI) Evaluation Form: College of NursingJoe RealNo ratings yet
- Occupational Hazards in Health Care ProfessionalsDocument33 pagesOccupational Hazards in Health Care Professionalsdocshirin100% (1)
- Stock Per 2 Nov 20 HargaDocument13 pagesStock Per 2 Nov 20 HargaLutfi QamariNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing TestDocument21 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing TestAt Day's Ward50% (2)
- A Brief Review On Foeniculum Vulgare Mill Highlighting Gastroprotective ActivityDocument2 pagesA Brief Review On Foeniculum Vulgare Mill Highlighting Gastroprotective ActivityInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Navjaat Shishu Suraksha Karyakram: Training ManualDocument99 pagesNavjaat Shishu Suraksha Karyakram: Training ManualBiswaranjan Padhy100% (1)
- Leaflet of Bach Therapy PDFDocument2 pagesLeaflet of Bach Therapy PDFPrakash VerekarNo ratings yet
- Point of CareDocument5 pagesPoint of CareDaniela RochaNo ratings yet
- Moran CORE - How To Use The Direct OphthalmoscopeDocument1 pageMoran CORE - How To Use The Direct OphthalmoscopeSamsung M20APNo ratings yet
- Client Choice Plus Key FactsDocument4 pagesClient Choice Plus Key Factsjudge101No ratings yet
- Recovery From Tactile AgnosiaDocument12 pagesRecovery From Tactile AgnosiaIsaac Saucedo FloresNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome - Concept MapDocument1 pageAcute Coronary Syndrome - Concept MapWyen CabatbatNo ratings yet
- Fiji Times Jan 7Document48 pagesFiji Times Jan 7fijitimescanadaNo ratings yet
- 36450378Document109 pages36450378Seiba PerezNo ratings yet
- Do Psychedelics Mimic KundaliniDocument10 pagesDo Psychedelics Mimic KundaliniGabriel MarquesNo ratings yet
- QC1 Prelims 2019 HandoutsDocument202 pagesQC1 Prelims 2019 HandoutsFrances Salud40% (5)
- What Is CelecoxibDocument3 pagesWhat Is CelecoxibKevin LabbeikNo ratings yet
- Intrathecal Morphine Single DoseDocument25 pagesIntrathecal Morphine Single DoseVerghese GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 014 Student HandoutsDocument16 pagesChapter - 014 Student Handoutsebiniyam2021No ratings yet
- Assessment of Time Perception The Effect of AgingDocument10 pagesAssessment of Time Perception The Effect of AgingYuki ChongNo ratings yet
- Case Study On SyphillisDocument18 pagesCase Study On Syphillisdia_pee100% (1)
- Primary Awards 2012-2014 - CaribbeansDocument7 pagesPrimary Awards 2012-2014 - CaribbeansGuillaume PrefolNo ratings yet
- Research EssasyDocument9 pagesResearch Essasyapi-279881900No ratings yet
- CystosDocument1 pageCystosgeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa InggrisDocument15 pagesMakalah Bahasa Inggrisfera kartikaNo ratings yet
- Contents (Continued) : Chapter 5. Nondestructive Inspection (Ndi)Document3 pagesContents (Continued) : Chapter 5. Nondestructive Inspection (Ndi)blackhawkNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Peritoneal Lavage (DPL)Document10 pagesDiagnostic Peritoneal Lavage (DPL)hatem alsrour100% (2)
- WarfarinDocument2 pagesWarfarinWAHYU NOFANDARI HERDIYANTINo ratings yet
- Efficacy and Adverse Events of Oral Isotretinoin For Acne: A Systematic ReviewDocument10 pagesEfficacy and Adverse Events of Oral Isotretinoin For Acne: A Systematic ReviewFerryGoNo ratings yet