Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earthquake Guided Notes
Uploaded by
api-330050027Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Earthquake Guided Notes
Uploaded by
api-330050027Copyright:
Available Formats
Earthquake Guided Notes
page494
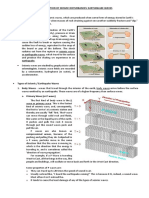
What is stress? The forces per unit area acting upon
a material. What is strain? The deformation of
materials in response to stress. How to they compare
and contrast? (make a Venn diagram)
Stress
Force
acting
upon a
materi
al
strain
Stress
must
occur
for
strain to
arehappen
the 3
Deformati
on in
response
to stress
What
different types of faults? Describe
each. Reverse fault: fractures that form as a result of
horizontal compression. Normal fault: fractures
caused by horizontal tension. Strike-slip fault: san
Andreas fault
Type of
waves
Primary
Secondary
Materials &
Description
Sketch
With the
ocean wave
Squeeze and
pull rocks
the same
direction as
the waves.
Cause rocks
to move at
right angles
in relation to
Movement
^^^
In relation to
Earthquake Guided Notes
page494
Surface
the direction
of waves
An up and
down
movement
similar to an
ocean wave
Up and down
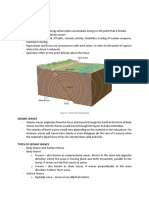
How do the focus and the epicenter of earthquakes
compare and contrast? contrast: focus is where the
earthquake originates from, epicenter is the point
directly above the focus. Compare: they fall in line
with one another
The greater the distance between P and S waves
on a seismograph the (longer or shorter) distance
away from the epicenter.
What is the name of the scale used to measure the
energy released during an earthquake? What is the
range of the scale?
Seismograph, 1-10
What is the name of the scale used to measure the
intensity (damage done) during an earthquake?
What is the range of the scale? Richter
Describe the damage caused by earthquakes for a
level 1, 5, and 10 level 1 earthquake damage is
almost nothing, level five is some damage but not
much, level 10 is a lot of damage.
You might also like
- Earthquake Guided NotesDocument2 pagesEarthquake Guided Notesapi-330300646No ratings yet
- Earthquake Guided NotesDocument3 pagesEarthquake Guided Notesapi-264885511No ratings yet
- Earthquake Guided NotesDocument3 pagesEarthquake Guided Notesapi-264756260No ratings yet
- Earthquake Guided NotesDocument3 pagesEarthquake Guided Notesapi-330037580100% (1)
- Earthquake Guided NotesDocument3 pagesEarthquake Guided Notesapi-335690255No ratings yet
- Earthquake Guided NotesDocument3 pagesEarthquake Guided Notesapi-264090670No ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument1 pageEarthquakeapi-269485108No ratings yet
- Earthquake Guided NotesDocument3 pagesEarthquake Guided Notesapi-330050095No ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument25 pagesEarthquakeSyafiqah AimanNo ratings yet
- Seismic Refraction SurveyingDocument58 pagesSeismic Refraction SurveyingMohammadFaisalQureshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Propagation of Seismic DisturbanceDocument7 pagesChapter 4 Propagation of Seismic DisturbanceGabriel LopezNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and Seismic Waves MOTIVATIONDocument50 pagesEarthquakes and Seismic Waves MOTIVATIONjacoblaureta1108No ratings yet
- Earthquake ReadingsDocument16 pagesEarthquake Readingsapi-251355123No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document22 pagesChapter 3Wubayehu DessalegnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Earthquake and Its Impact On Roads and BuildingsDocument9 pagesChapter 1 Earthquake and Its Impact On Roads and BuildingsVivek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1B - Earth QuakeDocument32 pagesTopic 1B - Earth QuakeXver MLNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes PDFDocument6 pagesEarthquakes PDFRaphael Ivan FernandezNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant Design: Seismological AspectsDocument49 pagesEarthquake Resistant Design: Seismological AspectserjuniorsanjipNo ratings yet
- Concept of Stress and Strain AssignmentDocument17 pagesConcept of Stress and Strain AssignmentBirwa GandhiNo ratings yet
- Types of Earthquake WavesDocument276 pagesTypes of Earthquake WavesAndoryuuBanRaianNo ratings yet
- Geo FinalsDocument176 pagesGeo FinalsRizette PaloganNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Engineering2Document147 pagesEarthquake Engineering2Mariz Ellaine Baltazar83% (6)
- EarthquakeDocument177 pagesEarthquakebharasha mahantaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Causes and MeasurementsDocument16 pagesEarthquake Causes and MeasurementsMahfuzul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Week 4Document20 pagesModule 4 - Week 4Alice ChanNo ratings yet
- Introduction Seismic Methods - Refraction SeismicDocument107 pagesIntroduction Seismic Methods - Refraction SeismicMohammed AmerNo ratings yet
- Friction: Classical MechanicsDocument12 pagesFriction: Classical MechanicsAhmad KoujanNo ratings yet
- Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering MCQDocument11 pagesStructural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering MCQKaushik GondaliyaNo ratings yet
- Deformation Stress and Strain NotesDocument19 pagesDeformation Stress and Strain NotesPrasoon ShuklaNo ratings yet
- EarthquakesDocument73 pagesEarthquakesMuhammad KhanNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Source MechanicsDocument37 pagesEarthquake Source MechanicsLiam NellNo ratings yet
- Chapt 10 MarshakDocument24 pagesChapt 10 Marshak周牮No ratings yet
- Refraction SurveyDocument37 pagesRefraction SurveyRomeo LourdurajNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Year 3-TidesDocument8 pagesLecture 3 Year 3-Tideslegendibra8No ratings yet
- Friction & Its TypesDocument4 pagesFriction & Its TypesJannatul Ferdoush SadiaNo ratings yet
- Earth Quake DesignDocument13 pagesEarth Quake DesignRanie boy CabanillaNo ratings yet
- Propagation of Seismic DisturbancesDocument6 pagesPropagation of Seismic DisturbancesEM SimonNo ratings yet
- Waves: Gravity Waves - These Are Waves That Are Formed in A Fluid (Ie. TheDocument1 pageWaves: Gravity Waves - These Are Waves That Are Formed in A Fluid (Ie. TheVinal PatelNo ratings yet
- Every Day ForcesDocument40 pagesEvery Day ForcesHaneen DweikatNo ratings yet
- Solid MechanicsDocument8 pagesSolid MechanicsMilan GhoshNo ratings yet
- Types of FrictionDocument3 pagesTypes of FrictionCathyNo ratings yet
- Structural Geology UWIDocument76 pagesStructural Geology UWIshayndellNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and FaultsDocument4 pagesEarthquakes and FaultsChloe De LeonNo ratings yet
- E102 - AgustinDocument20 pagesE102 - AgustinSeth Jarl G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions For EarthDocument5 pagesMultiple Choice Questions For EarthShaukat Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Notes 1 Seimology Civl7119Document83 pagesNotes 1 Seimology Civl7119Sergio Rojas ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Seismic WaveDocument2 pagesSeismic WaveAlessandra Lei AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Seismic Stag 6343Document67 pagesSeismic Stag 6343akujeeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 Tectonic Plates and Earths Internal Structure CSS PMS General Science and AbilityDocument46 pagesLecture 14 Tectonic Plates and Earths Internal Structure CSS PMS General Science and AbilityAsif SardarNo ratings yet
- 8.00 Seismic WavesDocument36 pages8.00 Seismic WavesMohammad AlhajNo ratings yet
- Earth Sesemic ProfilingDocument13 pagesEarth Sesemic ProfilingNinni SinghNo ratings yet
- Basics of TidesDocument11 pagesBasics of TidesHarikrishnaNo ratings yet
- Faults - LectDocument39 pagesFaults - LectMarshall NhodzaNo ratings yet
- Assignment On EarthquakeDocument14 pagesAssignment On EarthquakeAkash Sahu100% (2)
- Earthquakes-And-Faults PPT 2014Document33 pagesEarthquakes-And-Faults PPT 2014api-269185515No ratings yet
- Earthquakefaults BackgroundDocument3 pagesEarthquakefaults Backgroundapi-323743823No ratings yet
- Waves, Tides (Classwork, Homework)Document9 pagesWaves, Tides (Classwork, Homework)api-262318021No ratings yet
- Rock Blasting 16Document75 pagesRock Blasting 16llllcesarllllNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and Seismic WavesDocument36 pagesEarthquakes and Seismic WavesTeena SeiclamNo ratings yet
- What Is MeteorologyDocument4 pagesWhat Is Meteorologyapi-330050027No ratings yet
- Atmosphere Basics WebsquestDocument2 pagesAtmosphere Basics Websquestapi-264090085No ratings yet
- Atmosphere Basics NotesDocument3 pagesAtmosphere Basics Notesapi-330050027No ratings yet
- MeatrixDocument2 pagesMeatrixapi-330050027No ratings yet
- The Lorax Honors Ees 1Document1 pageThe Lorax Honors Ees 1api-330050027No ratings yet
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument5 pagesTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330050027No ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument3 pagesDaftar PustakaWisnu PerdanaNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument17 pagesEarthquakeAbhita DaffaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake and Faults Summative TestDocument2 pagesEarthquake and Faults Summative TestDha Wafu96% (24)
- DRRRDocument2 pagesDRRRJoyce Dela Rama JulianoNo ratings yet
- Seismic Risk Assessment of A 42-Story Reinforced Concrete Dual-System Building Considering Mainshock and Aftershock HazardDocument16 pagesSeismic Risk Assessment of A 42-Story Reinforced Concrete Dual-System Building Considering Mainshock and Aftershock HazardQorry OktaliaNo ratings yet
- Common Earthquake Effects: 3.2.1 DescriptionDocument13 pagesCommon Earthquake Effects: 3.2.1 DescriptionAnabel Perez CuetoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet: Name: Teacher: Grade Level / Section: VI-Week 1 Activity 1 Q4 - MELCDocument3 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: Name: Teacher: Grade Level / Section: VI-Week 1 Activity 1 Q4 - MELCxannah silvaNo ratings yet
- Kobe Earthquake Case StudyDocument3 pagesKobe Earthquake Case StudySara Vawser LiversidgeNo ratings yet
- Earthquake!pptDocument15 pagesEarthquake!pptPrincess Shynne MercadoNo ratings yet
- European Seismic Hazard MapDocument1 pageEuropean Seismic Hazard MapDaiuk.DakNo ratings yet
- Haiti Earthquake HomeworkDocument9 pagesHaiti Earthquake Homeworkh00etde1100% (1)
- Case Ctudy of Bhuj EarthquakeDocument11 pagesCase Ctudy of Bhuj EarthquakeRudra HalderNo ratings yet
- Earthquake, Earthquake Preparedness and MitigationDocument16 pagesEarthquake, Earthquake Preparedness and MitigationTricia Fern MadayagNo ratings yet
- Report Eefit Kobe Japan 20190814 PDFDocument278 pagesReport Eefit Kobe Japan 20190814 PDFAlessandra Jara ChavezNo ratings yet
- Unesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Geological Hazards: Earthquakes, Landslides, and TsunamisDocument9 pagesUnesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Geological Hazards: Earthquakes, Landslides, and TsunamisMarifeNo ratings yet
- Consolidation Template (EQ Preparedness)Document12 pagesConsolidation Template (EQ Preparedness)Angeline S. Cherweg0% (1)
- Seismic Waves and Earths InteriorDocument6 pagesSeismic Waves and Earths InteriorKesha Ann Ferraren Aquino0% (1)
- Earthquake Morocco - Google SearchDocument1 pageEarthquake Morocco - Google SearchflyinzeskyNo ratings yet
- Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Assessment For Albania, Macedonia and SerbiaDocument10 pagesProbabilistic Seismic Hazard Assessment For Albania, Macedonia and Serbiasofronije2005100% (1)
- Earthquake Family Preparedness QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesEarthquake Family Preparedness QuestionnaireGracey PelagioNo ratings yet
- Study On The Risk of Collapse of Block Walls in Japan During EarthquakesDocument12 pagesStudy On The Risk of Collapse of Block Walls in Japan During EarthquakesIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Ecological DisastersDocument15 pagesEcological DisastersamartyaNo ratings yet
- Recorded Accelerograms As An Alternative Description of The Seismic Action in The P 100-1 / 2006 Romanian Seismic Design CodeDocument10 pagesRecorded Accelerograms As An Alternative Description of The Seismic Action in The P 100-1 / 2006 Romanian Seismic Design CodeIonut Narcis IugaNo ratings yet
- Strong-Motion Parameters: Definition, Usefulness and PredictabilityDocument8 pagesStrong-Motion Parameters: Definition, Usefulness and PredictabilitySadeghMahmoudkhaniNo ratings yet
- SeizmikaDocument12 pagesSeizmikakalosevicNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument10 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word Documentprithviraj1990100% (1)
- Nama: Jaka Prasetya NIM: 5150811249 Kelas: D Judul: Innovations in Earthquake Resistant Steel Structures ReferencesDocument3 pagesNama: Jaka Prasetya NIM: 5150811249 Kelas: D Judul: Innovations in Earthquake Resistant Steel Structures Referencesjaka prasetyaNo ratings yet
- The Lisbon Earthquake of 1 November 1755Document2 pagesThe Lisbon Earthquake of 1 November 1755Richter, JoannesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Types of Plate BoundariesDocument21 pagesLesson 2 Types of Plate BoundariesVergil S.YbañezNo ratings yet
- Manvi Sharma Apeejay School, Noida: Japan: Earthquake, Tsunami, Nuclear DisasterDocument16 pagesManvi Sharma Apeejay School, Noida: Japan: Earthquake, Tsunami, Nuclear DisasterprakrutisNo ratings yet