Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Points About Medical Topics Sample
Uploaded by
medpgnotesCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Points About Medical Topics Sample
Uploaded by
medpgnotesCopyright:
Available Formats
POINTS ABOUT
MEDICAL TOPICS
medpgnotes
POINTS ABOUT MEDICAL TOPICS
Contents
AMYLOID............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 3
APOPROTEIN ....................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 3
ARTHRITIS ........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 4
AVASCULAR NECROSIS ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 4
BONE GRAFT ....................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 5
BRAIN ..................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 5
BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA ..................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 7
CENSUS .................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 7
CLOTTING FACTORS ........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 8
CONTRACEPTION .............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 9
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE ......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 11
CEREBROSPINAL FLUID .............................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 12
CULTURE MEDIA ............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 13
DEMENTIA......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 15
ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAM ..................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 16
ENGAGING DIAMETER ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 16
ESTROGEN ......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 17
FAMILIAL HYPERLIPOPROTEINEMIA.................................................................................................................................................................................................... 17
FEATURES OF FIBROID ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 18
FIREARM ............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 19
GASTRIC MOTILITY ....................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 20
ABSORPTION IN GUT AND NEPHRON.................................................................................................................................................................................................... 21
HORMONES ....................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 23
HYPERSENSITIVITY ....................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 24
IMMUNOGLOBULIN ....................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 24
INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM AND DEFICIENT ENZYMES ................................................................................................................................................ 25
KIDNEY STONES.............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 28
LITHIUM ............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 29
LUNG VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES .......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 30
METABOLIC ACIDOSIS.................................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 31
MOSQUITO......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 31
NERVE FIBERS ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 32
MUSCLES AND NERVE SUPPLY ................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 33
CHANGES IN PREGNANCY .......................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 41
METHODS FOR PROTEINS .......................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 42
PROTOONCOGENES AND TUMOR SUPPRESSOR GENES ................................................................................................................................................................ 43
RADIOISOTOPES ............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 44
RICKETTSIAL ZOONOSES ............................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 45
ROOT VALUES FOR REFLEXES .................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 45
RAPIDLY PROGRESSING GLOMERULONEPHRITIS ........................................................................................................................................................................... 45
www.medpgnotes.com
POINTS ABOUT MEDICAL TOPICS
SMALL INTESTINAL BIOPSY ...................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 46
SPECIMEN PRESERVATION IN POISONING ......................................................................................................................................................................................... 46
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES .................................................................................................................................................................................................... 47
STERILIZATION AND DISINFECTION ..................................................................................................................................................................................................... 47
TETANUS............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 48
TOXINS IN FOOD ............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 48
MANAGEMENT OF POISONING ................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 49
VACCINATION .................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 50
VAGINAL CYTOLOGY ..................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 52
VITAMINS .......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 53
www.medpgnotes.com
AMYLOID
POINTS ABOUT MEDICAL TOPICS
AMYLOID
AL
Primary Amyloidosis
(multiple Myeloma/B-Cell Neoplasm)
Secondary Amyloidosis (MC Rheumatoid arthritis)
Hemodialysis Associated Amyloidosis
Familial Mediterranean Fever
AA
A2m
AA
(Pyrin)
A
ACal
ATTR
AIAPP
AANF
A
Electron microscopic finding of amyloid
X ray Crystallographic finding of amyloid
Characteristic feature of long standing type II DM
Protein affected in Alzheimers disease
Most Specific feature of AL type of amyloidosis
Alzemiers disease
Medullary Carcinoma Thyroid
Familial Amyloidotic Neuropathy
Systemic Senile Amyloidosis
Type II diabetes
Isolated Atrial Amyloidosis
Familial Renal amyloidosis
Non branching fibrils
Cross pleated sheet conformation
Islet amyloid protein (amylin)
-amyloid
Macroglossia
APOPROTEIN
LDL
VLDL
Chylomicron
HDL
Cofactor for Lipoprotein Lipase
Inhibitor for Lipoprotein Lipase
Lipoprotein increases risk of
Lipoprotein not showing Electrophoretic mobility
Lipoprotein having maximum triacylglycerol
Maximum exogenous triacylglycerol
Lipoprotein having maximum Cholesterol
Lipoprotein having maximum protein & Phospholipid
Exogenous trigylcerides maximum in
Endogenous triglycerides maximum in
Apo B-100
Apo E
Apo B-100
Apo B-48
Apo A I
Apo A II
Apo C II (Main)
Apo C I
Apo A II (Main)
Apo C III
CHD & Atherosclerosis
Chylomicron
Chylomicron
Chylomicron
LDL
HDL
Chylomicrons
VLDL
www.medpgnotes.com
ARTHRITIS
POINTS ABOUT MEDICAL TOPICS
ARTHRITIS
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS & VARIANTS
Symmetrical
Small Joint
More Osteoporosis
Erosions
RA
SLE
Scleroderma
Dermatomyositis
SERONEGATIVE ARTHRITIS
Asymmetrical
Large Joints
Less Osteoporosis
Periostitis,Syndesmophytes
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Psoriatric arthropathy
Reiter Syndrome
Enteropathic Arthritis
ARTHRITIS
OSTEOARTHRITIS
st
PIP,DIP,1 CMC
Sparing of MCP joint
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
Any Small joint
Sparing of DIP
MC connective tissue disorder associated with Scleritis
MC Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome occurs in
(Compression of Tibial Nerve)
MC weakened muscle in Osteoarthritis
MC Late Complication of Acetabular Fracture
MC type of Anaemia in Rheumatoid arthritis
PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS
PIP,DIP,MCP,Wrist
NO SPARING
Rheumatoid arthritis
st
1 Rheumatoid arthritis
nd
2 Ankylosing Spondylitis
rd
3 Osteoarthritis
Quadriceps
Secondary Osteoarthritis
(Post traumatic Osteoarthritis)
Normochromic Normocytic Anaemia
AVASCULAR NECROSIS
BONE
Lower pole of Patella
Tibial Tuberosity
Calcaneum
Navicular
nd
2 Metatarsal
th
5 Metatarsal
Capitulum
Ring epiphysis of Vertebra
Central Nucleus of Vertebral Body
Lunate
Proximal Pole of Scaphoid
Femoral Head
DISEASE
Synding Larsen Joharresen Disease
Osgood Shlatter Disease
Severs Disease
Kohlers Disease
Freibergs Disease
Islene Disease
Panners Disease
Scheurmanns Disease
Calves Disease
Keinbochs Disease
Preisers Disease
Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease
Those written in ITALICS are TRACTION/PULLING APOPHSITIS
All the others are crushing type
www.medpgnotes.com
BONE GRAFT
POINTS ABOUT MEDICAL TOPICS
BONE GRAFT
Ideal Source of bone Graft
Commonest Source of Cortical Bone Graft
Best source for Cortical/Corticocancellous bone Graft
Best Source for Cancellous bone Graft
Ilium
Fibula
Anterior Iliac Crest
Posterior Iliac Crest
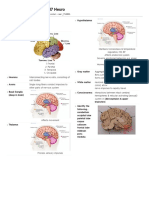
BRAIN
ANTERIOR HYPOTHALAMUS
Paraventricular Nucleus
Supraoptic Nucleus
Medial Preoptic Nucleus
Oxytocin release
Vasopressin release
Sexual drive in Males
POSTERIOR HYPOTHALAMUS
Lateral area
Ventromedial Nucleus
Mamillary body
Dorsomedial Nucleus
Arcurate Nucleus &
Periventricular Zone
Thirst & Hunger
Satiety centre
Feeding Reflexes
GI Stimulation
Neuroendocrinal Control
Structure of brain involved in emotion
Sensory action of emotion
Expressive action of emotion
Osmoreceptors are located in
Consolidation of long term memory
Window of Limbic system
Reward centre
Functions of Limbic system
Addiction associated with
Conation means
Longetrm memory stored in
Memory doesnot involve processing in Hippocampus
Nucleus controlling Circadian Rhythm
Blobs of visual cortex a/w
Parvocellular pathway carry signal for detection of
Two main afferent to cerebellar cortex
Only output from cerebellar cortex
Neocerebellum to Ventral lateral nucleus of thalamus
through
Largest & most lateral cerebellar peduncle
Afferent tract to middle cerebellar peduncle
Posterior perforated substance located in
Pain sensitive cranial nerve
Vertical & Upside down cortical representation of body
Hypothalamus, Limbic system
Limbic system
Hypothalamus
Anterior Hypothalamus
Hippocampus
Amygdala
Medial forebrain bundle
Emotion, Memory, Higher function
Reward Centre
Desire to take action
Various part of Neocortex
Implicit/Non destructive skill
Suprachiasmatic nucleus
Colour Processing
Colour vision, shape, Fine details
Climbing fibres & Mossy fibres
Purkinje cells
Dentate nucleus
Middle cerebellar peduncle
Pontocerebellar
Floor of interpeduncular fossa
2,3,5,7,9,10
Homunculus
www.medpgnotes.com
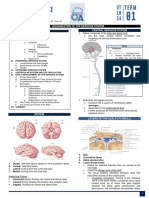
BRAIN
POINTS ABOUT MEDICAL TOPICS
inCerebrum
Anterior perforated area bounded laterally by
White fibres connecting cortical areas in Same
hemisphere
White fibres connecting corresponding cortical fibres
crossing midline
Cerebral cortex connected to lower levels of brain by
Fibres of genu of corpus callosum curve forward into
frontal lobes to form
Intracellular inclusion bodies found in choroid plexus
Main afferent to basal ganglia
Tightness of blood brain barrier
Vestibular nucleus location
Largest sensory root of trigeminal nerve composed of
LMN includes
Anterior & Lateral spinothalamic tract ends in
Uncrossed ascending tracts
Filum terminale mainly composed of
Ventral roots of spinal nerve contains
Anterior & Posterior gray columns united by
Cranial nerves entrapped in apex of Petrous bone
Parasympathetic Cranial Nerves
Initiation of Voluntary movements by
Maintenance of posture in normal adult depends on
Cell bodies of Orexinergic neurons present in
Function of Microglia
Function of Oligodendrocytes
Function of Astrocyte
Neuroglial cells of ectodermal origin
Neuroglial cells of mesodermal origin
Fibrous astrocyte found in
Protoplasmic astrocytes found in
Repetetive stimulus increase pain means
Pain receptors
Ascending pain pathway in dorsal midbrain inhibited by
Afferent fibres from Lateral geniculate body end in
DOMINANT HEMISPHERE
CATEGORIAL HEMISPHERE
Language Function
Mathematical & scientific Skills
LEFT SIDED OLFACTION
Limen Insulae (Gyrus ambiens)
Association fibres
Commisural fibres
Projection fibres
Forceps minor
Bionds ring tangles
Corticostriate projection
Close apposition of astrocyte
th
Beneath floor of 4 ventricle
Pseudounipolar neurons
Anterior horn cells,Anterior spinal root,Peripheral nerve
Ventral Posterolateral nucleus of thalamus
Nucleus gracilis,cuneatus,Spinoolivary
Piamater
Somatic efferent
Grey commissure
5,6
3,7,9,10
Corticospinal & corticobulbar
Integrity of Reflex arc
Lateral hypothalamic area
Phagocytosis
Myelin formation
Blood Brain barrier
Astrocyte,Oligodendrocytes
Microglia
White matter
Grey matter
Hypersensitisation
Nociceptors (Free nerve endings)
Enkephalin,Seratonin
Layer 4 of Visual Cortex
NON DOMINANT HEMISPHERE
REPRESENTATIONAL HEMISPHERE
Music & Art awareness
Visuospatial Orientation
Form,Shape,Faces,Body images
RIGHT SIDED OLFACTION
www.medpgnotes.com
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- General Embryology PDFDocument9 pagesGeneral Embryology PDFmedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- General Physiology PDFDocument11 pagesGeneral Physiology PDFmedpgnotes100% (4)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Female Reproductive System SampleDocument15 pagesFemale Reproductive System SamplemedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- Long Test No. 4 (Nervous System) Ready To PrintDocument3 pagesLong Test No. 4 (Nervous System) Ready To Printjayrald cruzada100% (1)
- Sci 10 Week 3 Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesSci 10 Week 3 Nervous SystemNikkha elle Teleron100% (1)
- Atrial Systole: The End of DiastoleDocument9 pagesAtrial Systole: The End of DiastoleSophia MahboobNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 - Anatomy and Electrophysiology of The Heart: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument17 pagesChapter 01 - Anatomy and Electrophysiology of The Heart: Multiple Choice QuestionsyebegashetNo ratings yet
- Social and Preventive Medicine SampleDocument11 pagesSocial and Preventive Medicine SamplemedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- Microbiology PDFDocument103 pagesMicrobiology PDFmedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- RossDocument436 pagesRossAna Ion100% (1)
- Respiratory System SampleDocument18 pagesRespiratory System SamplemedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- Medical InvestigationsDocument7 pagesMedical InvestigationsmedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- Medical NuggetsDocument8 pagesMedical NuggetsDrGandhi Bhaskar Patrudu LankaNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry SampleDocument8 pagesPsychiatry SamplemedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- General Pathology SampleDocument10 pagesGeneral Pathology SamplemedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology SampleDocument14 pagesOphthalmology SamplemedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- Nutrition SampleDocument6 pagesNutrition SamplemedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- Genetics SampleDocument7 pagesGenetics SamplemedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- Otorhinolaryngology SampleDocument9 pagesOtorhinolaryngology SamplemedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- Nervous System SampleDocument18 pagesNervous System SamplemedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics SampleDocument14 pagesObstetrics SamplemedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- Radiology Sample PDFDocument5 pagesRadiology Sample PDFmedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- Orthopedics SampleDocument14 pagesOrthopedics Samplemedpgnotes100% (1)
- Male Reproductive System SampleDocument4 pagesMale Reproductive System SamplemedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- General Pharmacology SampleDocument13 pagesGeneral Pharmacology SamplemedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- General Surgery SampleDocument9 pagesGeneral Surgery Samplemedpgnotes100% (1)
- Immunology SampleDocument7 pagesImmunology SamplemedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- General Pediatrics SampleDocument7 pagesGeneral Pediatrics SamplemedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- Forensic Medicine and Toxicology SampleDocument9 pagesForensic Medicine and Toxicology SamplemedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System SampleDocument14 pagesGastrointestinal System SamplemedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolyte Abnormalities SampleDocument7 pagesFluids and Electrolyte Abnormalities SamplemedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System SampleDocument12 pagesCardiovascular System SamplemedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- Excretory System SampleDocument13 pagesExcretory System SamplemedpgnotesNo ratings yet
- Conduction System of The HeartDocument1 pageConduction System of The HeartJulie AnnNo ratings yet
- AmenorrheaDocument51 pagesAmenorrheabisharatNo ratings yet
- Fungsi GinjalDocument21 pagesFungsi GinjalA1205Angelica GloryNo ratings yet
- Diagnosa Icd 10Document424 pagesDiagnosa Icd 10Sinta FiraniNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and PhydudzNo ratings yet
- Zuqiaoyin Gb-44: Yin Portals of The FootDocument2 pagesZuqiaoyin Gb-44: Yin Portals of The Footray72roNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Brain Anatomy: Wieslaw L. NowinskiDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Brain Anatomy: Wieslaw L. NowinskiAditya Rama DevaraNo ratings yet
- Bates CH 17 NeuroDocument11 pagesBates CH 17 NeurokandeeNo ratings yet
- OT1024 - 1S1L - Organization of The Nervous System-CompressedDocument14 pagesOT1024 - 1S1L - Organization of The Nervous System-CompressedRidz FNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy Digestive Systemtimmieb_1No ratings yet
- Biomarkers of Male Hypogonadism in Childhood and AdolescenceDocument13 pagesBiomarkers of Male Hypogonadism in Childhood and AdolescenceScott LoveNo ratings yet
- Lymph NodesDocument6 pagesLymph NodesIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Group 4 GCS Type II Diabetes Mellitus With Stage 1 Renal Failure NCM 116 RLEDocument67 pagesGroup 4 GCS Type II Diabetes Mellitus With Stage 1 Renal Failure NCM 116 RLEAriane Gay DuranNo ratings yet
- 16-Acute AbdomenDocument32 pages16-Acute AbdomenAiden JosephatNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Blood Pressure Regulation - 10Document31 pagesDisorders of Blood Pressure Regulation - 10Cres Padua QuinzonNo ratings yet
- Hydrocephalus PresDocument14 pagesHydrocephalus Presapi-610861419No ratings yet
- (Five Minute Veterinary Consult) Morrison, Jo Ann - Mott, Jocelyn - Blackwell's Five-Minute Veterinary Consult Clinical Companion. Small Animal Gastrointestinal Diseases-Wiley-Blackwell (2019)Document982 pages(Five Minute Veterinary Consult) Morrison, Jo Ann - Mott, Jocelyn - Blackwell's Five-Minute Veterinary Consult Clinical Companion. Small Animal Gastrointestinal Diseases-Wiley-Blackwell (2019)Eduardo SantamaríaNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy (Rai) : GoalsDocument6 pagesRadioactive Iodine Therapy (Rai) : GoalsFirras SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class Ix Animal Tissue Flow ChartDocument1 pageCbse Class Ix Animal Tissue Flow ChartAMit100% (1)
- BIBLIOGRAFIE Neural Conduction Synaptic TransmisionDocument16 pagesBIBLIOGRAFIE Neural Conduction Synaptic TransmisionMirela GiurgeaNo ratings yet
- Faktor-Faktor Risiko Hipertensi Intrahemodialisis Pada Pasien Gagal Ginjal Kronis Stadium 5 Di RSUD Al-Ihsan BandungDocument6 pagesFaktor-Faktor Risiko Hipertensi Intrahemodialisis Pada Pasien Gagal Ginjal Kronis Stadium 5 Di RSUD Al-Ihsan BandungmayyfajrianiiNo ratings yet
- Salivary Secretion: Chapter OutlineDocument9 pagesSalivary Secretion: Chapter OutlineJoshika MahendranNo ratings yet
- Kulpak UPN - AnatomiDocument21 pagesKulpak UPN - AnatomigresiasallyNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Professor René AdamDocument4 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Professor René AdamdoctorNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue - 1Document3 pagesAnimal Tissue - 1Kb AshishNo ratings yet