Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes
Uploaded by
api-330050027Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes
Uploaded by
api-330050027Copyright:
Available Formats
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes
480
page
Do not write on this copy. Transfer the questions into your notebook in Cornell style and
use your book to find the answers.
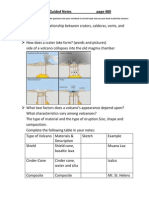
What is the relationship between craters, calderas,
vents, and magma? The vent connects to the crater
which is the top of the volcano and the larger
depressions of the calderas can form at the summit.
The magma flows through out
How does a crater lake form? (words and pictures)
crater lakes can form when the summit or side of a
volcano collapses into the magma chamber that once
fueled the volcano.
What two factors does a volcanos appearance
depend upon? The 2two factors that can influence
the appearance of a volcano depends on the type of
material that forms the volcano and the type of
eruptions.
What characteristics vary among volcanoes? Size,
shape, and composition vary between volcanoes.
Complete the following table in your notes:
Type of
Volcano
Shield
Materials &
Sketch
Description
Broad, gently
sloping sides
and a nearly
circular base
Example
Cinder-Cone
Small in size,
steep slope
angle, built
from ejected
Paricutin
Mauna Loa
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes
480
page
Do not write on this copy. Transfer the questions into your notebook in Cornell style and
use your book to find the answers.
lava
fragments
Composite
Symmetrical
(Stratovolcano cone, located
)
in Pacific ring
of fire,
composed of
interbedded
lava flows
and layers on
pyroclastic
debris.
Mount fuji
How do the volcanoes compare in terms of size and
slope? volcanoes compare in terms of sizes because
they all have different sides and one volcano could
be a steep slope and another could not be very
steep.
What factors cause differences in size and slope?
There are many factors that go into the size and
slope of a volcano but the main elements are the
variety of eruption types. Composition of the
volcano, the volume of the volcanic products, and
the environment that is around the volcano.
What is tephra? Tephra is the rock fragments and
particles ejected by a volcano.
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes
480
page
Do not write on this copy. Transfer the questions into your notebook in Cornell style and
use your book to find the answers.
What is a pyroclastic flow? Pyroclastic flow is a
dense, destructive mass of very hot ash, lava
fragments, and gases ejected explosively from a
volcano and typically flowing downward at a great
speed.
Where are most volcanoes found? Theyre found at
convergent and divergent volcanoes.
Use the maps provided to show: (1) the Circum Pacific
Belt and the Mediterranean Belt where convergent
volcanism occurs and (2) the Hawaiian Emperor
Volcanic Chain.
How do hotspots form? Hotspots form when heat
rises in the mantle as thermal plume from deep in
the earth (core). High heat and lower pressure at a
base of the lithosphere (tectonic plate) facilitates
melting the rock.
What do hotspots tell us about tectonic plates? Hot
spots are places where tectonics, especially
volcanic activity is especially strong, often
breaking though a plate even though its not at the
juncture of two plates.
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes
480
page
Do not write on this copy. Transfer the questions into your notebook in Cornell style and
use your book to find the answers.
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes
480
page
Do not write on this copy. Transfer the questions into your notebook in Cornell style and
use your book to find the answers.
You might also like
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument4 pagesTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330085018No ratings yet
- Volcanoes The Ultimate Book: Experience the Heat, Power, and Beauty of VolcanoesFrom EverandVolcanoes The Ultimate Book: Experience the Heat, Power, and Beauty of VolcanoesNo ratings yet
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument3 pagesTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-264090670No ratings yet
- Volcano Guided NotesDocument4 pagesVolcano Guided Notesapi-330490538100% (1)
- The Explosive World of Volcanoes with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Explosive World of Volcanoes with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument5 pagesTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330464848No ratings yet
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument5 pagesTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330049903No ratings yet
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument2 pagesTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-264220672No ratings yet
- Volcanoes NotesDocument4 pagesVolcanoes Notesapi-264874516No ratings yet
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument5 pagesTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330050095No ratings yet
- Types of VolcanoesDocument3 pagesTypes of Volcanoesapi-265544103No ratings yet
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument4 pagesTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330049909No ratings yet
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument4 pagesTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330042011No ratings yet
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument5 pagesTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330092916No ratings yet
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument3 pagesTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-264099976No ratings yet
- Voolcanoes Guided NotesDocument3 pagesVoolcanoes Guided Notesapi-264885511No ratings yet
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument4 pagesTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330102217No ratings yet
- Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes 1Document4 pagesTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notes 1api-330067833No ratings yet
- Volcano WebquestDocument3 pagesVolcano WebquestRichard Muchow100% (1)
- Volcanoes EarthquakeDocument83 pagesVolcanoes EarthquakeMeshal M ManuelNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 - Module 1 VOLCANOESDocument39 pagesQuarter 3 - Module 1 VOLCANOESRubeliza LawengNo ratings yet
- Volcanic EruptionsDocument7 pagesVolcanic EruptionsmusicatworkNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument8 pagesVolcanoesShah KhanNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes PDF Format 5912b8dcDocument4 pagesVolcanoes PDF Format 5912b8dcsukesh sNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Tarbuck 14th Edition Solutions ManualDocument11 pagesEarth Science Tarbuck 14th Edition Solutions ManualAntonioCohensirt100% (32)
- Volcanic LandformDocument12 pagesVolcanic LandformJoseph ZotooNo ratings yet
- VolcanoDocument84 pagesVolcanoJM LomoljoNo ratings yet
- Byjus Com Physics Types of VolcanoesDocument6 pagesByjus Com Physics Types of VolcanoesEren YeagerNo ratings yet
- Mary Drury - VOLCANOES TemplateDocument11 pagesMary Drury - VOLCANOES TemplateMary DruryNo ratings yet
- VolcanoDocument8 pagesVolcanoaditya2053No ratings yet
- Forces Within The EarthDocument56 pagesForces Within The EarthTHE HATE FARMERNo ratings yet
- Science Power PointDocument18 pagesScience Power PointpatriciangbenaohanNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Pt3 VolcanoesDocument16 pagesPlate Tectonics Pt3 VolcanoesDemon bbyNo ratings yet
- VOLCANOESDocument10 pagesVOLCANOESYesha ShahNo ratings yet
- Types of VolcanoesDocument26 pagesTypes of VolcanoesMatt PayawalNo ratings yet
- VolcanoDocument3 pagesVolcanoRhienzane L. MarasiganNo ratings yet
- P PPPPPP P: P PP PP P' P P PP' P $P' P P ('P P"Document4 pagesP PPPPPP P: P PP PP P' P P PP' P $P' P P ('P P"bpmojapeloNo ratings yet
- 5b. VolcanismDocument44 pages5b. VolcanismGaurav KapseNo ratings yet
- Science9 Q3 Week1 Romo AmabelleDocument18 pagesScience9 Q3 Week1 Romo AmabelleGrace OroNo ratings yet
- Volcanic Eruptions and HazardsDocument44 pagesVolcanic Eruptions and HazardsLevy GerpacioNo ratings yet
- Volcano WebquestDocument4 pagesVolcano Webquesttristan p100% (1)
- Earth Science Reviewer VolcanoesDocument7 pagesEarth Science Reviewer VolcanoesAndrea Grace Bayot AdanaNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Pt3 VolcanoesDocument17 pagesPlate Tectonics Pt3 VolcanoesChristle NgoveNo ratings yet
- Volcano TriviaDocument22 pagesVolcano TriviaEman VidalloNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Study Guide: Volcanoes and Volcanic Activity: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesLecture Notes Study Guide: Volcanoes and Volcanic Activity: ObjectivesRonaldo ManaoatNo ratings yet
- Pre-Assessment: Choose The Letter of The Best AnswerDocument60 pagesPre-Assessment: Choose The Letter of The Best AnswerheartNo ratings yet
- For Earth Science !! 33Document91 pagesFor Earth Science !! 33art2rugraceNo ratings yet
- Volcanic Activity محاضره 4و5Document12 pagesVolcanic Activity محاضره 4و5Hanna AngelaNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan in Science 10: Unit Topic: Content Standard: Performance Standard: Learning CompetenciesDocument7 pagesLearning Plan in Science 10: Unit Topic: Content Standard: Performance Standard: Learning CompetenciesSarah FranciscoNo ratings yet
- This Article Is About The Geological Feature. For Other Uses, See and - For Broader Coverage of This Topic, SeeDocument27 pagesThis Article Is About The Geological Feature. For Other Uses, See and - For Broader Coverage of This Topic, SeeMichael FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Types of VolcanoesDocument21 pagesTypes of VolcanoesAgaManlapazMacasaquitNo ratings yet
- VOLCANESDocument10 pagesVOLCANESJahnisel A. CordovaNo ratings yet
- VOLCANOESDocument65 pagesVOLCANOESPrincess Alyssa BarawidNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Mrs. Amany Adel Gaber HussienDocument127 pagesPrepared By: Mrs. Amany Adel Gaber Hussienmalakelghamry743No ratings yet
- Strategic Intervention Material (Volcano)Document25 pagesStrategic Intervention Material (Volcano)Aaron Cafe69% (13)
- What Is A Volcano?Document26 pagesWhat Is A Volcano?Muhammad Faisal GauheerNo ratings yet
- Science-6 Q4 W2 The Effects of Volcanic EruptionDocument8 pagesScience-6 Q4 W2 The Effects of Volcanic Eruptionkiandizon12No ratings yet
- VolcanoDocument18 pagesVolcanoVIJAY KRISHNANo ratings yet
- What Is MeteorologyDocument4 pagesWhat Is Meteorologyapi-330050027No ratings yet
- Atmosphere Basics WebsquestDocument2 pagesAtmosphere Basics Websquestapi-264090085No ratings yet
- Atmosphere Basics NotesDocument3 pagesAtmosphere Basics Notesapi-330050027No ratings yet
- MeatrixDocument2 pagesMeatrixapi-330050027No ratings yet
- The Lorax Honors Ees 1Document1 pageThe Lorax Honors Ees 1api-330050027No ratings yet
- Earthquake Guided NotesDocument2 pagesEarthquake Guided Notesapi-330050027No ratings yet
- 3.6 Környezetvédelem - Angol Szóbeli Témakör B2Document4 pages3.6 Környezetvédelem - Angol Szóbeli Témakör B2Nagyné KingaNo ratings yet
- Before A Volcanic EruptionDocument4 pagesBefore A Volcanic EruptionUnknownNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and Volcanoes The Restless Earth PDFDocument121 pagesEarthquakes and Volcanoes The Restless Earth PDFAri Yusliandi50% (2)
- Merged 20231202 1547Document199 pagesMerged 20231202 1547titobright312No ratings yet
- 21st Century Lit-50f9f PDFDocument4 pages21st Century Lit-50f9f PDFGrace BayauaNo ratings yet
- Kingsway Christian Academy: WWW - Kingsway.edu - PHDocument4 pagesKingsway Christian Academy: WWW - Kingsway.edu - PHAldrin CastanetoNo ratings yet
- Volcano Paper Mache ModelDocument7 pagesVolcano Paper Mache ModelSabrina LavegaNo ratings yet
- The Mountain and River Systems in The PhilippinesDocument7 pagesThe Mountain and River Systems in The PhilippinesRose Sauler ServidaNo ratings yet
- CAPE Geography Unit 1 Specimen Multiple ChoiceDocument10 pagesCAPE Geography Unit 1 Specimen Multiple ChoiceDaniel Joseph100% (2)
- Earth Science S1Q2 Quiz 1 (Weathering+Erosion) ReviewerDocument3 pagesEarth Science S1Q2 Quiz 1 (Weathering+Erosion) ReviewerSunNo ratings yet
- KS - C - Assessment 8thDocument208 pagesKS - C - Assessment 8thZULY TATIANA DIAZ LOPEZNo ratings yet
- (123doc - VN) - 41-De-Thi-Thu-Trac-Nhiem-Dai-Hoc-Tieng-Anh-Co-Dap-An PDFDocument248 pages(123doc - VN) - 41-De-Thi-Thu-Trac-Nhiem-Dai-Hoc-Tieng-Anh-Co-Dap-An PDFTrang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Insights On The Formation of Vapor-Dominated Geothermal SystemsDocument8 pagesInsights On The Formation of Vapor-Dominated Geothermal SystemsDanis WaraNo ratings yet
- Teens Intermediate 5 (4 - 6)Document5 pagesTeens Intermediate 5 (4 - 6)UserMotMooNo ratings yet
- Countries and Nationalities: Vocabulary 1Document31 pagesCountries and Nationalities: Vocabulary 1Ivan Austin GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Disaster PreparednessDocument23 pagesDisaster PreparednessIslein DevaugnNo ratings yet
- 362 Volcanic Rifted MarginsDocument231 pages362 Volcanic Rifted MarginsEdwin Yudha NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Effects of VolcanoesDocument38 pagesEffects of Volcanoesmonch1998No ratings yet
- LISTENING SCRIPT Pathway To English 3 WajibDocument16 pagesLISTENING SCRIPT Pathway To English 3 WajibELa Noviana57% (21)
- Reading Adventures 1 SyllabusDocument3 pagesReading Adventures 1 SyllabusJose Eduardo Saurith Escobar100% (1)
- School of Saint Joseph (Naguilian, Isabela), IncDocument4 pagesSchool of Saint Joseph (Naguilian, Isabela), IncYvette Marie Yaneza NicolasNo ratings yet
- M4 Lecture Notes The DRMAPS Case Study Proposal - Acm - 2122-2Document10 pagesM4 Lecture Notes The DRMAPS Case Study Proposal - Acm - 2122-2Maria VirtzNo ratings yet
- Lahars Are A Specific Kind of Mudflow Made Up of Volcanic Debris Composed of A Significant Component of Volcanic MaterialsDocument5 pagesLahars Are A Specific Kind of Mudflow Made Up of Volcanic Debris Composed of A Significant Component of Volcanic MaterialsLorena BoteroNo ratings yet
- EST 1103: Earth Science IDocument1 pageEST 1103: Earth Science IRezaul KarimNo ratings yet
- Soal Dan Pembahasan Utbk Inggris 2019 - Rukim - IdDocument6 pagesSoal Dan Pembahasan Utbk Inggris 2019 - Rukim - IdEkiBheBheNo ratings yet
- Niña P. Cochingco Humss 11-ADocument1 pageNiña P. Cochingco Humss 11-AWillie Anne Chan UyNo ratings yet
- 1st Grading Exam Science Grade 10Document2 pages1st Grading Exam Science Grade 10Ann Necdote100% (2)
- 1991 PinatuboDocument1 page1991 PinatuboClaudetteNo ratings yet
- G12 Makabansa (Stem) 2 Semester Q2: Written and Performance ActivityDocument13 pagesG12 Makabansa (Stem) 2 Semester Q2: Written and Performance ActivityFritzie Corpuz0% (1)
- Global Catastrophic RiskDocument16 pagesGlobal Catastrophic RiskSajjad WarsiNo ratings yet
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessFrom EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNo ratings yet
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (597)
- Water to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesFrom EverandWater to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (21)
- Smokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersFrom EverandSmokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersNo ratings yet
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (812)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutFrom EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (142)
- The Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterFrom EverandThe Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterNo ratings yet
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorFrom EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (137)
- Come Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogFrom EverandCome Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- Darwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignFrom EverandDarwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (19)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsFrom EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (223)
- When You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsFrom EverandWhen You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (13)
- Remnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsFrom EverandRemnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- Spoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeFrom EverandSpoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (19)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)