Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How Does A Thermal Power Plant Work - Learn Engineering PDF
Uploaded by
ferayiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How Does A Thermal Power Plant Work - Learn Engineering PDF
Uploaded by
ferayiCopyright:
Available Formats
Home
About us
Contact us
Get your project done
SearchthisSite...
Home
Electrical Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
Civil Engineering
Miscellaneous
Support us
How does a Thermal Power Plant Work ?
| | Power Plant, Thermal Engineering
LearnEngineering
17Binbeenme
The purpose of this video is to give you a conceptual introduction on working of thermal power plants. Here working of a
thermal power plant is explained in a logical step by step manner.
SayfayBeen
How does a Thermal power plant work ?
Arkadalarnarasndabunuilk
beenensenol
2.6k
Translate
DiliSein
A detailed analysis of thermal power plants based on it's thermodynamic cycle is given below.
You may also like
Thermal Power Plants
Thermal power plants use water as working fluid. Nuclear and coal based power plants fall under this category. The way
energy from fuel gets transformed into electricity forms the working of a power plant. In a thermal power plant a steam
turbine is rotated with help of high pressure and high temperature steam and this rotation is transferred to a generator
to produce electricity.
Jet Engine, How it works ?
How does a Diesel Engine
work ?
Working of Refrigerator &
Refrigera...
Working of Centrifugal
Pumps
Working of Steam Turbine
Fig.1 Power is produced in thermal power plants by rotating steam turbine
Energy absorption from steam
When turbine blades get rotated by high pressure high temperature steam, the steam loses its energy. This in turn will
result in a low pressure and low temperature steam at the outlet of the turbine. Here steam is expanded till saturation
point is reached. Since there is no heat addition or removal from the steam, ideally entropy of the steam remains same.
This change is depicted in the following pv and Ts diagrams. If we can bring this low pressure, low temperature steam
back to its original state, then we can produce electricity continuously.
Diesel Engine vs Petrol
Engine
Template Hits
4,736,578
Fig.2 Pressure and temperature drop of steam when turbine absorbs energy from it
Use of Condenser
Compressing a fluid which is in gaseous state requires a huge amount of energy,so before compressing the fluid it should
be converted into liquid state. A condenser is used for this purpose, which rejects heat to the surrounding and converts
steam into liquid. Ideally there will not be any pressure change during this heat rejection process, since the fluid is free
to expand in a condenser. Changes in fluid are shown in the pv and Ts diagram below.
Fig.3 Use of condenser in order to transform vapor into liquid state
Pump
At exit of the condenser fluid is in liquid state, so we can use a pump to raise the pressure.During this process the
volume and temperature (23 deg.C rise)of fluid hardly changes, since it is in liquid state. Now the fluid has regained its
original pressure.
Fig.4 Compressor pumps the fluid to its original pressure
Heat Addition in Boiler & Rankine Cycle
Here external heat is added to the fluid in order to bring fluid back to its original temperature. This heat is added
through a heat exchanger called a boiler. Here the pressure of the fluid remains the same, since it is free to expand in
heat exchanger tubes. Temperature rises and liquid gets transformed to vapor and regains its original temperature. This
completes the thermodynamic cycle of a thermal power plant, called Rankine Cycle. This cycle can be repeated and
continuous power production is possible.
Fig.5 Heat addition at boiler brings the fluid to its original temperature
Condenser Heat Rejection - Cooling Tower
In order to reject heat from the condenser a colder liquid should make contact with it. In a thermal power plant
continuous supply of cold liquid is produced with the help of a cooling tower. Cold fluid from the cooling tower absorbs
heat from a condenser and gets heated, this heat is rejected to the atmosphere via natural convection with the help of a
cooling tower.
Boiler furnace for Heat Addition
Heat is added to the boiler with help of a boiler furnace. Here fuel reacts with air and produces heat. In a thermal power
plant, the fuel can be either coal or nuclear. When coal is used as a fuel it produces a lot of pollutants which have to be
removed before ejecting to the surroundings. This is done using a series of steps, the most important of them is an
electro static precipitator (ESP) which removes ash particles from the exhaust. Now much cleaner exhaust is ejected into
the atmosphere via a stack.
Fig.6 Main accessories of Rankine cycle Cooling tower, Boiler furnace, ESP & Chimney
Optimizing a Thermal plant performance
There are various flow parameters which have to be finetuned in order to get optimum performance from a thermal
power plant.Lowering the condenser temperature or raising the average boiler temperature will result in a high efficiency
power plant cycle according to the 2nd law of thermodynamics (Carnot efficiency),most of the performance improving
technologies are working on this idea. Some latest trends are listed below.
1. Expanding Turbine After Saturation
Expanding the steam in the turbine even after reaching the saturation point may be a dangerous affair. As the
steam goes below saturation, wetness of the steam increases. These condensed water droplets collide with the
turbine blades rotating at a high speed, thus it can cause extreme tip erosion to the blades. Turbine blade tip
erosion is shown in figure below. But as you expand more you will be able to absorb more energy from the steam,
thus increasing power plant efficiency. Up to 15% wetness level is considered to be safe for steam turbine
operation. So most of the steam turbine will expand up to this point in order to extract maximum energy from the
fluid. This is shown in figure below.
Fig.7 Expanding turbine below saturation point in order to gain maximum power from steam
2. Raising average boiler temperature
If you can increase the average heat addition temperature of the boiler, that will result in a power plant with
higher efficiency. One way to do this is to increase the compressor pressure. This will shift the saturation point of
the fluid to a higher level, thus providing higher average temperature of heat addition. This is shown in the figure
below. The blue line represents change in the cycle after raising the compressor pressure.
Fig.8 Raising compressor pressure in order achieve higher average boiler temperature
LocalFurnaceExperts
FindTopRatedProsInYourArea.EnterYourZip&Get4FreeBids!Goto
homeadvisor.com
Newer Post
Home
Older Post
2012-2013 Imajey. The content is copyrighted to LearnEngineering.org & Imajey Consulting Engineers Pvt. Ltd. and may not be reproduced without consent.
Learn Engineering Designed by PSD Style 2011 All Rights Reserved.
Blogger Template by Way2blogging
You might also like
- Experiment No 1: Categories For Conventional Power Plants 1. Fossil Fuel Power Plants or Thermal PlantDocument8 pagesExperiment No 1: Categories For Conventional Power Plants 1. Fossil Fuel Power Plants or Thermal Plantmughees khanNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Plant Components & ProcessesDocument37 pagesSteam Power Plant Components & ProcessessureshlalNo ratings yet
- Vapor Power Cycle Lecture2Document32 pagesVapor Power Cycle Lecture2Abdur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Turbine Is A Rotary Machine With Vanes or Blades Around ItDocument10 pagesTurbine Is A Rotary Machine With Vanes or Blades Around ItTalha AhmadNo ratings yet
- AES Thermal Power Plant, Lalpir, District Muzaffargarh: Prepared byDocument25 pagesAES Thermal Power Plant, Lalpir, District Muzaffargarh: Prepared byIrfan UllahNo ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantDocument9 pagesSteam Power PlantAnne Gabrielle DavidNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument36 pagesThermal Power PlantAshvani Shukla100% (1)
- Thermal Power Plant Diagram All You Need To Know About ItDocument7 pagesThermal Power Plant Diagram All You Need To Know About Itngoc hoangNo ratings yet
- Vapor Power Cycle Lecture2Document36 pagesVapor Power Cycle Lecture2Zain Ul AbideenNo ratings yet
- GENERATING ELECTRICITYDocument34 pagesGENERATING ELECTRICITYAdeniji OlusegunNo ratings yet
- Me152l - Experiment 6 - AmahmudDocument25 pagesMe152l - Experiment 6 - AmahmudAli Requiso MahmudNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 STEAM GENERATION (Complete Slide)Document25 pagesCHAPTER 1 STEAM GENERATION (Complete Slide)nisasoberiNo ratings yet
- Write Up For Voc TRGDocument12 pagesWrite Up For Voc TRGPritish MohanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Job Questions:Thermal Power Plant (Set 1) : AnswerDocument11 pagesElectrical Job Questions:Thermal Power Plant (Set 1) : AnswerNitin NaharNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument12 pagesLab ReportFaisal ArslanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power StationsDocument83 pagesThermal Power StationschdiNo ratings yet
- تقرير محطات الطاقهDocument45 pagesتقرير محطات الطاقهعبد الرحمن إبراهيمNo ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantDocument10 pagesSteam Power PlantJoel DaleNo ratings yet
- Generation of Electric PowerDocument108 pagesGeneration of Electric Powermausam sharmaNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Steam Power Plant EquipmentDocument102 pagesEssentials of Steam Power Plant EquipmentPrakhar Shukla100% (1)
- Steam Power Plant PresentationDocument37 pagesSteam Power Plant PresentationsharenslaNo ratings yet
- Expt. # 03 Study of A Steam Turbine Power PlantDocument6 pagesExpt. # 03 Study of A Steam Turbine Power PlantSajeeb SarkerNo ratings yet
- PGD 161018125619 PDFDocument47 pagesPGD 161018125619 PDFveerchetan007No ratings yet
- Steam Power Plant Components and FunctionsDocument47 pagesSteam Power Plant Components and FunctionsSandeep Gupta100% (1)
- Heatpump PDFDocument17 pagesHeatpump PDFJulio RicardoNo ratings yet
- محطة شبرا الخيمةDocument15 pagesمحطة شبرا الخيمةعبدالله عبدالمنعم100% (1)
- Jagan Steam Power PlantDocument101 pagesJagan Steam Power PlantMahender VangalaNo ratings yet
- Experiment NoDocument5 pagesExperiment NoAbdullah UsmaniNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics - Steam TurbineDocument8 pagesThermodynamics - Steam TurbineSaiful ZakwanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plants: Key Components and Working PrincipleDocument157 pagesThermal Power Plants: Key Components and Working Principlegteklay100% (1)
- 2013edusat Lecture On STEAM PLANTDocument101 pages2013edusat Lecture On STEAM PLANTKishore KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Amulya Gaikwada ProjectDocument34 pagesAmulya Gaikwada ProjectHarikrishna NethaNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engineering BasicsDocument21 pagesPower Plant Engineering BasicsSiman NapstervkkNo ratings yet
- Abhishek Kumar Asif Ahmad Niket Rakeshan Zeeshan AliDocument21 pagesAbhishek Kumar Asif Ahmad Niket Rakeshan Zeeshan AliSuphi YükselNo ratings yet
- Iare Epgs LNDocument53 pagesIare Epgs LNPrema MahadikNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbines Definition Applications Working Components Types Design Advantages PDFDocument13 pagesGas Turbines Definition Applications Working Components Types Design Advantages PDFSaadi DzNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EquipmentDocument54 pagesPower Plant EquipmentJoy PalitNo ratings yet
- Vapor and Combined Power Cycles: Mehmet KanogluDocument27 pagesVapor and Combined Power Cycles: Mehmet KanogluRodrigo Patiño100% (1)
- Detailed Crank Shaft DescriptionDocument110 pagesDetailed Crank Shaft DescriptionDharmendra PalNo ratings yet
- Bme NotesDocument34 pagesBme NotesAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Revealing The Secrets - How To Design A Heat Recovery Compression Refrigeration SystemDocument6 pagesRevealing The Secrets - How To Design A Heat Recovery Compression Refrigeration SystemCharlieDeppNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power StationDocument13 pagesThermal Power StationUdayNo ratings yet
- Conventional Power Generation Systems ExplainedDocument44 pagesConventional Power Generation Systems ExplainedGunjan VijayVargiyaNo ratings yet
- Diesel Power Plant EngineeringDocument27 pagesDiesel Power Plant EngineeringDexter Baret0% (1)
- A Tutorial On Power Generation From Thermal Power PlantsDocument326 pagesA Tutorial On Power Generation From Thermal Power Plantslaloo01No ratings yet
- Assignment in ME 312Document23 pagesAssignment in ME 312jasperNo ratings yet
- Nozzles Notes PDFDocument83 pagesNozzles Notes PDFAbubakkar Siddiq83% (6)
- How to Increase Efficiency of Rankine Cycle Power PlantsDocument11 pagesHow to Increase Efficiency of Rankine Cycle Power Plantsgjanklesaria100% (1)
- Industrial Training AT: Submitted By: Rishikesh (11-1-6-002) NIT, SilcharDocument26 pagesIndustrial Training AT: Submitted By: Rishikesh (11-1-6-002) NIT, SilcharRakesh Roshan KeshriNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Power PlantsDocument22 pagesUnit-I Power Plantsamsk24_24No ratings yet
- Essential Equipment of Steam Power PlantsDocument101 pagesEssential Equipment of Steam Power Plantsjamunaa83100% (1)
- Vapor and Combined Power Cycles: Mehmet KanogluDocument22 pagesVapor and Combined Power Cycles: Mehmet Kanogluichig0_89No ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant: Gaini Zail Singh Punjab Technical University Campus (Bathinda)Document30 pagesThermal Power Plant: Gaini Zail Singh Punjab Technical University Campus (Bathinda)Sriram ramsNo ratings yet
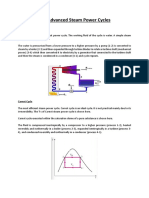
- 1-3 Advanced Steam Power CyclesDocument14 pages1-3 Advanced Steam Power CyclesGeethika NayanaprabhaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant Project ReportDocument63 pagesThermal Power Plant Project Reportasutoshjena28174% (23)
- Working Principle Gas Turbine and Combined Cycles, Auxiliary SystemsDocument27 pagesWorking Principle Gas Turbine and Combined Cycles, Auxiliary SystemsRey Danielle Navea100% (2)
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Instructions for fitting SSS clutchDocument4 pagesInstructions for fitting SSS clutchferayiNo ratings yet
- M Hendry SSS Clutch Frm6UG07 Clutch DesignDocument37 pagesM Hendry SSS Clutch Frm6UG07 Clutch Designchugo02No ratings yet
- MC - 60 70 en 042003Document6 pagesMC - 60 70 en 042003ferayiNo ratings yet
- Replacing Jaw Clutches - Welcome To Combined Cycle Journal PDFDocument3 pagesReplacing Jaw Clutches - Welcome To Combined Cycle Journal PDFferayiNo ratings yet
- Links To SSS DriveDocument1 pageLinks To SSS DriveferayiNo ratings yet
- Turb Start ImpDocument4 pagesTurb Start ImppramodtryNo ratings yet
- SSS Clutch - AMP Maintenance ForumsDocument4 pagesSSS Clutch - AMP Maintenance ForumsferayiNo ratings yet
- Morton EffectDocument8 pagesMorton EffectWalid FattahNo ratings yet
- SSS Clutch Operating Principles PDFDocument4 pagesSSS Clutch Operating Principles PDFferayi100% (3)
- Thermal Spray ProcessesDocument15 pagesThermal Spray Processesapi-3766939100% (2)
- SSS Clutch PrinciplesDocument4 pagesSSS Clutch PrinciplesmuddasirmasoodNo ratings yet
- Fe C Phase DiagramDocument12 pagesFe C Phase DiagramferayiNo ratings yet
- 5192120Document6 pages5192120ferayiNo ratings yet
- Power Valve La Re95514 - 2010 04Document4 pagesPower Valve La Re95514 - 2010 04Eric CNo ratings yet
- Alfa Laval PHE Part Numbers PDFDocument686 pagesAlfa Laval PHE Part Numbers PDFcbienst0% (1)
- Experiment 1 RefrigerationDocument4 pagesExperiment 1 RefrigerationErlangga Sulaiman Razak100% (1)
- The New Evolution in Open Gear Lubrication: Logomarca Do PatrocinadorDocument14 pagesThe New Evolution in Open Gear Lubrication: Logomarca Do PatrocinadorJako MishyNo ratings yet
- The Computer Simulation of Dispersed Two Phase Flows David Hill PHD 1998Document371 pagesThe Computer Simulation of Dispersed Two Phase Flows David Hill PHD 1998AghajaniNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet: 25cm Single Acting Handpump AssembliesDocument6 pagesTechnical Data Sheet: 25cm Single Acting Handpump AssembliesngazawooNo ratings yet
- Thompson'S Station - Regional Wastewater Treatment Plant UpgradesDocument30 pagesThompson'S Station - Regional Wastewater Treatment Plant UpgradesLy Duc TrungNo ratings yet
- Sullair Compressed Air Filtration and Mist EliminatorsDocument12 pagesSullair Compressed Air Filtration and Mist EliminatorsganiablachimNo ratings yet
- Bearing Details For Pump and Motor DataDocument1 pageBearing Details For Pump and Motor DataHarish UpretiNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Introduction To HydraulicsDocument20 pagesModule 1 Introduction To Hydraulicsoluja93No ratings yet
- UG Question Papers & Answer Keys 17.01.2019Document837 pagesUG Question Papers & Answer Keys 17.01.2019smcyber0% (1)
- Compressed Air DryersDocument15 pagesCompressed Air Dryersmanpreetsodhi08100% (1)
- Cranfield Flow Assurance MSCDocument12 pagesCranfield Flow Assurance MSCJamesGascoineNo ratings yet
- Geared Drive Mixer: Mobile: +91 9820268595Document1 pageGeared Drive Mixer: Mobile: +91 9820268595Anil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Flow Sheet Sorbitol Dari Tepung Tapioka FIXDocument1 pageFlow Sheet Sorbitol Dari Tepung Tapioka FIXfidelisboymanurungNo ratings yet
- Piping Cog Report: OID Pipeline Name Component NameDocument2 pagesPiping Cog Report: OID Pipeline Name Component NamemanhngoducNo ratings yet
- Objective: Find The Displacement and Stress Fields. Problem Definition: Consider An Ideal Flow of Air Around A Cylinder, As Shown in Figure. TheDocument1 pageObjective: Find The Displacement and Stress Fields. Problem Definition: Consider An Ideal Flow of Air Around A Cylinder, As Shown in Figure. ThepmagrawalNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document3 pagesTutorial 3Andrew0% (1)
- RH200 Cooling SystemDocument14 pagesRH200 Cooling SystemLuis jopi100% (3)
- Changes in Materials QuizDocument1 pageChanges in Materials QuizMa Victoria Elizabeth MaraseNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Energy Dissipation StructureDocument15 pagesChapter-2 Energy Dissipation StructureGoytom yigezuNo ratings yet
- Charles' Law - The Temperature-Volume RelationshipDocument19 pagesCharles' Law - The Temperature-Volume Relationshipshort bondpaperNo ratings yet
- Gi v4 n3Document14 pagesGi v4 n3juanva_123No ratings yet
- Handout 4A Heat TransferDocument19 pagesHandout 4A Heat TransferRobyn GautamNo ratings yet
- Effect of MLSS on Start-Up of Submerged Membrane BioreactorDocument8 pagesEffect of MLSS on Start-Up of Submerged Membrane BioreactorTanmay MajhiNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics I: Chapter 2 HydrostaticsDocument14 pagesHydraulics I: Chapter 2 HydrostaticsKubaNo ratings yet
- Fick's Law Explained: Diffusion, Flux, and Mass TransportDocument107 pagesFick's Law Explained: Diffusion, Flux, and Mass TransportYasir AliNo ratings yet
- Guide Document GE P312 4.1.2 I General ConsiderationsDocument31 pagesGuide Document GE P312 4.1.2 I General ConsiderationsDiarista Thoma SaputraNo ratings yet
- GRE Pipe Testing MethodDocument3 pagesGRE Pipe Testing MethodVanaa MohanNo ratings yet
- Cre IDocument2 pagesCre IJdNo ratings yet