Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture30 PDF
Uploaded by
Ankan GayenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture30 PDF
Uploaded by
Ankan GayenCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture-2
Example-1:
Obtain the pattern of two isotropic point sources with identical amplitude and phase currents, and spaced
one-half wavelength apart.
Ans:
X
Add: Double
Z
Cancel: Zero
Cancel: Zero
Add: Double
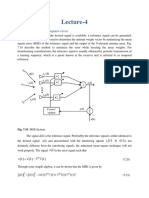
Fig 6.3 Two element array
The two isotropic antennas are placed on the z-axis with equal distance apart from the origin. The pattern
of this array can be approximated by simple observations.The points in the far field along the
perpendicular bisector of the line joining the point sources, the path lengths from each point sources are
equal. As the point sources are of identical amplitude and phase, the waves arrive in phase and equal in
amplitude in the far field along the x-axis and y-axis. So the total field is double that of the single source.
Along the z-axis, the scenario is different. If we move along the +z axis, the wave coming from th left
source must travel one half wavelength before reaching the source on the right. This amounts to a 1800
phase lag. The waves then continue traveling to the right +z axis and maintain the same phase
relationship. Thus in the far field, the waves from the two sources traveling in +z directions are 1800 out
of phase, so the total field is zero. The same reasoning can be used to see the effects in the -z direction.
The total pattern has a relative value of 2 in the x- direction, 0 in z-direction and a smooth variation in
between.
In a mathematical form the AF is
AF E 0 e j kd cos / 2 E 0 e j kd cos / 2
kd cos
( AF ) n cos
Distance between the two elements d = /2
= 0, as both the elements have the identical phase.
So kdcos = (2/) (/2) cos = cos
cos
AF cos
So AF is maximum for = /2 and 0 for = 0.
/2
/3
AF
1/2
Example-2:
Obtain the pattern of two isotropic point sources with identical amplitude and opposite phase currents,
and spaced one-half wavelength apart.
Ans:
AF E0 e j kd cos / 2 E0 e j kd cos / 2
(-ve sign due to the opposite phase)
kd cos
AF 2 jE 0 sin
The normalized array factor will be
( AF ) n sin cos( ) (For d = /2)
2
0
1
AF
/2
/3
1/2
Example-3:
Obtain the pattern of two isotropic point sources with identical amplitude and in phase quadrate currents,
and spaced (i) one-half wavelength, (ii) quarter wavelength apart .
Ans:
(i) Isotropic point sources at one-half wavelength apart
AF E 0 e j kd cos / 2 E 0 e j kd cos / 2
Here the value of is /2 and d = /2
So AF E 0
j cos
2
4
E0
AF 2 E 0 cos cos
4
2
AF n cos
cos
j cos
2
4
/3
/2
2/3
AF
1/2
1/2
1/2
(ii) Isotropic point sources at quarter wavelength apart
Similarly the array factor can be obtained by putting d = /4.
AF n cos
cos
/2
2 /3
5/6
AF
1/2
0.9239
0.9945
Example-4 ( Principle of Pattern Multilpcation)
An array consists of two horizontal dipoles located along z-axis at one-half wavelength apart. If the
excitation magnitudes and phases are same, then obtain the shape of the radiation pattern.
Ans:
The total field radiated by the array can be expressed as
E t a j
kI o le jkr
cos e j kd cos / 2 e j kd cos / 2
4r
E (total ) ESingle Element AF
The field due to the single element at the origin is
jkI o le jkr
E
cos a
4r
E n cos a and it does not depend on .
The AF of the dipole array can be obtained similar to Example-1. So the total field of the array is
cos
E t cos cos
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Lecture42 PDFDocument3 pagesLecture42 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- MSE Minimization BeamformingDocument3 pagesMSE Minimization BeamformingAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Lecture38 PDFDocument4 pagesLecture38 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Lecture36 PDFDocument3 pagesLecture36 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Lecture39 PDFDocument4 pagesLecture39 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Dolph-Chebyshev Array Design Uses Chebyshev Polynomials to Approximate Array PatternsDocument2 pagesDolph-Chebyshev Array Design Uses Chebyshev Polynomials to Approximate Array PatternsAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Lecture34 PDFDocument4 pagesLecture34 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Lecture43 PDFDocument2 pagesLecture43 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Lecture37 PDFDocument3 pagesLecture37 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Lecture40 PDFDocument6 pagesLecture40 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- Lecture32 PDFDocument7 pagesLecture32 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- Lecture33 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture33 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Lecture24 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture24 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Lecture28 PDFDocument6 pagesLecture28 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Lecture31 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture31 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Rectangular Patch Cavity Model ExplainedDocument5 pagesRectangular Patch Cavity Model ExplainedAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- ANTENNA ARRAY LECTURE-1Document4 pagesANTENNA ARRAY LECTURE-1GaneshVenkatachalamNo ratings yet
- Lecture26 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture26 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- Lecture22 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture22 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- Lecture21 PDFDocument3 pagesLecture21 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Lecture17 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture17 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Lecture13 PDFDocument3 pagesLecture13 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- Lecture23 PDFDocument3 pagesLecture23 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- Lecture20 PDFDocument4 pagesLecture20 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Lecture16 PDFDocument4 pagesLecture16 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- Lecture19 PDFDocument4 pagesLecture19 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- Lecture14 PDFDocument3 pagesLecture14 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- Lecture15 PDFDocument3 pagesLecture15 PDFAnkan GayenNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Blast Pressure ExampleDocument14 pagesBlast Pressure ExamplekeshavnvaityNo ratings yet
- CH 9 Flow Over Immersed BodiesDocument165 pagesCH 9 Flow Over Immersed BodiesMujtaba Rizvi67% (3)
- TITLE: Momentum PURPOSE: To Experimentally Find The Relationships Between Mass, Velocity, and Momentum. To Look at The LawDocument3 pagesTITLE: Momentum PURPOSE: To Experimentally Find The Relationships Between Mass, Velocity, and Momentum. To Look at The LawreynanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report. 09: HY - 1104 Hysics AboratoryDocument6 pagesLab Report. 09: HY - 1104 Hysics AboratoryZulfiqar SakibNo ratings yet
- Development of A Single Axis Tilting QuadcopterDocument4 pagesDevelopment of A Single Axis Tilting QuadcopterbasavasagarNo ratings yet
- Phys 104 Practice Midterm SolutionsDocument5 pagesPhys 104 Practice Midterm SolutionsHenry JurneyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3-Solutions PDFDocument6 pagesAssignment 3-Solutions PDFNickson KomsNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Pacejka's AnalyticalDocument42 pagesImplementation of Pacejka's AnalyticalRenan AlvesNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper-1 With Effect From 2020-21 (CBCS Scheme)Document6 pagesModel Question Paper-1 With Effect From 2020-21 (CBCS Scheme)Preetham PreethuNo ratings yet
- Q1 Week 4 - Module 9 Sound and TemperatureDocument20 pagesQ1 Week 4 - Module 9 Sound and TemperatureAbigail M. Moreno-SapaulaNo ratings yet
- T 3.67 S and The: SolutionDocument11 pagesT 3.67 S and The: SolutionabealNo ratings yet
- File 68244Document25 pagesFile 68244Atul SinghNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Understanding Polarization in 40 CharactersDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Polarization in 40 CharactersShaswath SasiNo ratings yet
- Subsonic Compressible Flow Over AirfoilDocument34 pagesSubsonic Compressible Flow Over AirfoilJagsahil SainiNo ratings yet
- Bicycle Wind Turbine PDFDocument7 pagesBicycle Wind Turbine PDFtokagkeloNo ratings yet
- Sample Chapter5 Basic Skills Test f19 SolnsDocument7 pagesSample Chapter5 Basic Skills Test f19 SolnsbilqistazNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Course OverviewDocument2 pagesEngineering Mechanics Course OverviewDil KumNo ratings yet
- Boundary Layer TheoryDocument2 pagesBoundary Layer TheoryHariz MiorNo ratings yet
- Momentum and ImpulseDocument21 pagesMomentum and Impulse황동현No ratings yet
- Swan TechDocument149 pagesSwan TechSantiago ReynosoNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 - Group 1Document4 pagesAP Physics 1 - Group 1Maja BolesnikovNo ratings yet
- Gravitation and Kepler's LawsDocument18 pagesGravitation and Kepler's LawsAaditya Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3-Quantum PhysicsDocument31 pagesLesson 3-Quantum Physicsabdulrahman alalawiNo ratings yet
- Dynamics worksheet forces momentum collisionsDocument3 pagesDynamics worksheet forces momentum collisionsJoe WestNo ratings yet
- Structured Questions-Wave: 1. This Question Is About The Superposition of WavesDocument6 pagesStructured Questions-Wave: 1. This Question Is About The Superposition of WavesZero TwoNo ratings yet
- Measuring Absorption CoefficientsDocument73 pagesMeasuring Absorption CoefficientsSeddik MaarfiNo ratings yet
- GR 9 ICSE Final Exam Question Paper PhysicsDocument4 pagesGR 9 ICSE Final Exam Question Paper PhysicsanjalimenonNo ratings yet
- Moment of Inertia of Flywheel LabDocument8 pagesMoment of Inertia of Flywheel LabLaith MarzoukaNo ratings yet
- Worked Out Examples (External Flows) : Example 1 (Velocity Profiles)Document23 pagesWorked Out Examples (External Flows) : Example 1 (Velocity Profiles)Rockerss RockerssNo ratings yet
- Computational Fluid Dynamics-Based System Identification of Marine VehiclesDocument19 pagesComputational Fluid Dynamics-Based System Identification of Marine Vehiclesinsiderr100% (1)