Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial Rotational Motion
Uploaded by
eyfa firdausCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial Rotational Motion
Uploaded by
eyfa firdausCopyright:
Available Formats
EXERCISE/ROTATIONAL MOTION
ROTATIONAL & CIRCULAR MOTION
1. A computer hard disk normally spins at 7000 rpm. If the hard disk takes
5.0 s to reach this angular velocity staring from rest, calculate:
a) The hard disks angular acceleration in rad/s 2.
( 146.61 rad/s2 )
b) The angular displacement of the disk.
( 1832.58 rad )
2. A wheel of radius 50 cm is speeded up uniformly from rest to a speed of
1200 rpm in 30 s. Calculate:
a) The angular acceleration of the wheel
( 4.19 rad/s2 )
b) The tangential acceleration of a point on its rim.
( 2.10 m/s2 )
3. The tires of a Myvis car makes 65 revolutions as the car reduces its speed
uniformly from 80 km/h to 30 km/h. The tires have a diameter of 0.8 m.
What was the angular acceleration of the tires?
( -3.25 rad/s2 )
4. A wheel of radius 0.40 m starts rotating from rest and after 6.0 s its
angular velocity is 3.6 rad/s. What is:
a) The angular acceleration of the wheel?
( 0.6 rad/s2 )
b) The angular velocity after 3.0 s?
( 1.8 rad/s )
c) The tangential acceleration?
( 0.24
m/s2 )
5. A wheel starts rotating initially from rest with a uniform angular
acceleration and complete 1 revolution after t = 6.0 s. Determine:
a) The angular velocity after 6.0 s.
b) The angular acceleration.
c) The angular velocity after 2 revolutions.
d) The time taken for the second revolution.
( 2.09 rad/s , 0.35 rad/s2 , 2.97 rad/s , 8.47 s )
6. Marilyn is riding in a merry-go-round which is initially at rest. The distance
between Marilyn to the center of the merry-go-round is 3.0 m. At t = 0 s is
given a constant angular acceleration a = 0.08 rad/s 2 for 10.0 s. At t =
10.0 s, find
a) The angular velocity of the merry-go-round
b) The linear velocity that Marilyn felt
c) The tangential acceleration of Marilyn
d) The centripetal acceleration of Marilyn
e) The total linear acceleration of Marilyn
( 0.8 rad/s, 2.4 m/s, 0.24 m/s2, 1.92 m/s2, 1.93 m/s2 )
ENGINEERING SCIENCE/LGB10203
EXERCISE/ROTATIONAL MOTION
7. A disk has a moment of inertia of 3.0 10-4 kg m2 and is rotating with an
angular speed of 3.5 rad/s. What net torque must be applied to bring it to
rest within 3 s?
( 3.5 10-4 Nm )
8. A wheel is rotating at 2 rad/s when it starts to experience a constant
angular acceleration of 3.5 rad/s2. Calculate the number of revolutions it
makes in 2 s.
( 1.75 rev )
9. An airplane propeller has a mass of 70 kg and a radius of 75 cm. Find its
moment of inertia. How large a torque is needed to give it an angular
acceleration of 4.0 rev/s2 ?
(0.99 kNm)
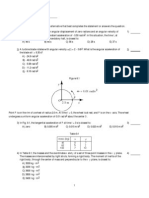
10.
As shown in figure below, a constant force of 40 N is applied
tangentially to the rim of a wheel with radius 20 cm. The wheel has a
moment of inertia of 30 kgm2. Find :
a) The angular acceleration
b) The angular speed after 4.0 s from rest
c) The number of revolutions made in that 4.0 s
(0.267 rad/s2, 1.1 rad/s, 0.34 rev)
11.The wheel on a grinder is a uniform 0.90 kg disc of 8.0 cm radius. It coasts
uniformly to rest from 1400 rpm in a time of 35 s. How large a friction
torque slows its motion?
(-1.2 x 10-2 Nm)
12.A shown in figure 1, a mass m = 400 g hangs from the rim of a wheel of
radius r = 15 cm. When released from rest, the mass falls 2.0 m in 6.5 s.
Find the moment of inertia of the wheel.
(0.93 kg m2)
ENGINEERING SCIENCE/LGB10203
EXERCISE/ROTATIONAL MOTION
13.
As shown in figure below, a uniform solid sphere rolls on a
horizontal surface at 20 m/s and the rolls up the incline. If the friction
losses are negligible, what will be the value of h where the ball stops?
(h = 29 m)
14.An object with a weight of 50.0 N is attached to the free end of a light
string wrapped around a pulley of radius 0.250 m and mass 3.00 kg. The
reel is a solid disk, free to rotate in a vertical plane about the horizontal
axis passing through its center. The suspended object is released 6.00 m
above the floor as shown in figure below.
a)
Determine the tensional string and acceleration of the system?
b)
Determine the speed of the object when hits the floor.
c)
Compare your answer (b) by using the principle of conservation of
energy to find
the speed with which the object hits the floor.
( 11.4 N. 9.53 m/s, 9.53 m/s )
15.A cylinder of radius 100 mm and mass 20 kg rolls from rest a distance of
10 m down an inclined plane and in doing so its vertical height decreases
by 5 m. What will be the linear velocity of the cylinder after this ?
( 8.1 m/s)
ENGINEERING SCIENCE/LGB10203
EXERCISE/ROTATIONAL MOTION
16.A hollow sphere of mass M = 6.0 kg and radius, R = 0.15m rolls without
slipping up a ramp at angle =30 .The sphere has moved 2.0 m up along
the incline before it stop. Find the initial speed of the sphere ?
(3.43 m/s)
17.Calculate the force of the Earths gravity on a spacecraft 12800 km above
the Earth surface if its mass is 1350 kg.
( mE = 5.98 x 1024 kg, rE = 6380 km )
( 1.48 x 103 N )
18.Calculate the acceleration due to gravity on the Moon. The Moons radius
is 1.74 x 106 m and its mass is 7.35 x 1022 kg.
( 1.62 m/s2 )
19.A satellite is placed in a circular orbit to observe the surface of Mars from
an altitude of 144 km. The equatorial radius of Mars is 3397 km. If the
speed of the satellite is 3480 m/s, what is the magnitude of the centripetal
acceleration of the satellite?
( 3.42 m/s2)
20.Callisto and Io are two of Jupiter's satellites. The distance from Callisto to
the center of Jupiter is approximately 4.5 times farther than the distance
ENGINEERING SCIENCE/LGB10203
EXERCISE/ROTATIONAL MOTION
from Io to the center of Jupiter.
compare to that of Io, TI?
How does Callisto's orbital period, TC,
(TC = 9.5 TI)
ENGINEERING SCIENCE/LGB10203
You might also like
- Unit 6 ExercisesDocument4 pagesUnit 6 Exercises张书No ratings yet
- Computer Keyboard Shortcut Keys PDFDocument7 pagesComputer Keyboard Shortcut Keys PDFmuhammad sohail janjuaNo ratings yet
- A Brand Building Literature ReviewDocument17 pagesA Brand Building Literature ReviewUdaya Kumar SNo ratings yet
- MercerDocument33 pagesMercersadir16100% (4)
- AnswersDocument15 pagesAnswersjrence33% (3)
- Chapter 10-Rotation of A Rigid Object About A Fixed Axis: Multiple ChoiceDocument23 pagesChapter 10-Rotation of A Rigid Object About A Fixed Axis: Multiple ChoiceMerlin Trochez 504No ratings yet
- A Presentation ON Office Etiquettes: To Be PresentedDocument9 pagesA Presentation ON Office Etiquettes: To Be PresentedShafak MahajanNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Physics For Scientists and Engineers With Modern Physics 10th Edition Raymond A Serway John W JewettDocument29 pagesTest Bank For Physics For Scientists and Engineers With Modern Physics 10th Edition Raymond A Serway John W Jewettguyzunigaiadzrbpfes100% (21)
- Injection Machine RobotDocument89 pagesInjection Machine Robotphild2na250% (2)
- Data MiningDocument14 pagesData MiningRavi VermaNo ratings yet
- EFQM Excellence Model TeaserDocument5 pagesEFQM Excellence Model TeaserMehmet SinanNo ratings yet
- Test116 3 PlusansDocument5 pagesTest116 3 PlusansAvnish GargNo ratings yet
- Accounting Chapter 08Document12 pagesAccounting Chapter 08Melody SanchezNo ratings yet
- ANSWER: (A) 30 S (B) 1.8Document2 pagesANSWER: (A) 30 S (B) 1.8Thu HòaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Week 1 Phy210Document2 pagesTutorial Week 1 Phy210NUR ALIAH IRDINA MOHD FADZLINo ratings yet
- Practice Set 2phy11Document2 pagesPractice Set 2phy11Vince Rabin CandidatoNo ratings yet
- Saint Joseph Catholic School-Adama: Grade 11 Physics Worksheet April 2012 (2020)Document3 pagesSaint Joseph Catholic School-Adama: Grade 11 Physics Worksheet April 2012 (2020)Nardos AlemayewNo ratings yet
- Extra Problem Phys 1 CH 5Document2 pagesExtra Problem Phys 1 CH 5Uyên Lương PhươngNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document4 pagesCH 10Mohammed Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- I-Taalem Task - Chapter 6Document3 pagesI-Taalem Task - Chapter 6ruzaimi98No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - Phy210Document1 pageTutorial 1 - Phy210Mimi SaffrinNo ratings yet
- All ImpDocument48 pagesAll Impdevrarimanish72No ratings yet
- Phy210 Tutorial 1&2Document4 pagesPhy210 Tutorial 1&2Alees Rahaizan100% (1)
- FHSC1014 Mechanics Tutorial 8Document3 pagesFHSC1014 Mechanics Tutorial 8许敬霖No ratings yet
- Geas Coaching 1Document3 pagesGeas Coaching 1Aaron Joseph SolanoNo ratings yet
- 10308634Document10 pages10308634dsfsdfsdfNo ratings yet
- Gravity and Rotational MotionDocument14 pagesGravity and Rotational MotionReagan KoNo ratings yet
- Sheet Exercise 2 - Circular Motion - S - L-1 1668503345455Document5 pagesSheet Exercise 2 - Circular Motion - S - L-1 1668503345455Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- 14 Rolling and Energy-ProblemsDocument5 pages14 Rolling and Energy-ProblemsMichael Kevin YangNo ratings yet
- Physics PaperDocument17 pagesPhysics PaperharshanauocNo ratings yet
- PHY11 CO2 Reviewer 1Document3 pagesPHY11 CO2 Reviewer 1Tetsuya OkazakiNo ratings yet
- Rotatinal Motion Practice QuestionsDocument2 pagesRotatinal Motion Practice QuestionsJaival KansagaraNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument15 pagesCircular Motionpraveen alwisNo ratings yet
- Mga Sagot Ni Ashe Montage (Gen. Physics)Document4 pagesMga Sagot Ni Ashe Montage (Gen. Physics)John Michael Cañero MaonNo ratings yet
- Mga Sagot Ni Ashe Montage Gen Physics1Document4 pagesMga Sagot Ni Ashe Montage Gen Physics1Valencia AngieNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument25 pagesQuestionsSkye JabaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Problems 1,, Straightforward, IntermediateDocument22 pagesChapter 10 Problems 1,, Straightforward, IntermediatevenkatNo ratings yet
- Rotation Review Questions AnswersDocument2 pagesRotation Review Questions AnswersPffflyers KurnawanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 6Document6 pagesAssignment 6CapsanneNo ratings yet
- Calculus Physics 1 Preexam 3Document3 pagesCalculus Physics 1 Preexam 3TylerNo ratings yet
- CircularMotion PCDocument18 pagesCircularMotion PCAaryan KeshanNo ratings yet
- Rotational Dynamics: 1.1 Short Answer QuestionsDocument2 pagesRotational Dynamics: 1.1 Short Answer QuestionsKishor ParajuliNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam 2 PDFDocument8 pagesPractice Exam 2 PDFDavid WeitzelNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument29 pagesCircular MotionRamlloyd SuelloNo ratings yet
- HW (Rotary Motion)Document4 pagesHW (Rotary Motion)naikin_1031No ratings yet
- Physics Chap 7Document14 pagesPhysics Chap 7Shivali PatelNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word Chapter 8Document13 pagesMicrosoft Word Chapter 8Shashank Shekhar100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Mechanics of Rigid BodiesDocument8 pagesChapter 3 - Mechanics of Rigid BodiesPhúc Lộc NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Mid Exam FisdasDocument13 pagesMid Exam FisdasipaclosefriendsNo ratings yet
- Old-Exam-Questions-Ch-11-091 - Dr. Naqvi (Phys101.016-018) : R I J A I NMDocument4 pagesOld-Exam-Questions-Ch-11-091 - Dr. Naqvi (Phys101.016-018) : R I J A I NMddasiodwjadmwaNo ratings yet
- 106 C 12 InclassDocument5 pages106 C 12 InclassSarvesh KanaujiaNo ratings yet
- Question 41Document7 pagesQuestion 41Skye JabaNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- DOM Model QuestionDocument2 pagesDOM Model QuestionSenthilkumar SubbiahNo ratings yet
- TCR7 Rotation Extended APNDocument2 pagesTCR7 Rotation Extended APNBeverly Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Rotational Motion ProblemsDocument19 pagesRotational Motion ProblemsShahd MuhamedNo ratings yet
- AP PhysicsDocument27 pagesAP PhysicsJoao Figueiredo100% (1)
- 3 CircularMotion PCDocument21 pages3 CircularMotion PCsureshserious7226No ratings yet
- Phys Exam 3 ReviewDocument4 pagesPhys Exam 3 Reviewsydneyrawls7No ratings yet
- Centripetal Acceleration WorksheetDocument4 pagesCentripetal Acceleration WorksheetKevin KroytNo ratings yet
- R (4.0 CM + (2.5 CM/S) I + (5.0 CM/S) T J: - (A) Find The Magnitude and Direction of The Dot's AverageDocument4 pagesR (4.0 CM + (2.5 CM/S) I + (5.0 CM/S) T J: - (A) Find The Magnitude and Direction of The Dot's AverageOlojo Oluwasegun EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument4 pagesCircular MotionJohn Philip D. NapalNo ratings yet
- XI Physics Important ProblemsDocument2 pagesXI Physics Important ProblemsganeshblogsNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 4Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 4MansonNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Week 14Document6 pagesTutorial Week 14Chin Tiong LeeNo ratings yet
- 06 Rotation of Rigid BodiesDocument3 pages06 Rotation of Rigid BodiesJerico LlovidoNo ratings yet
- Mock Test: Advanced English Material For The Gifted 2020Document13 pagesMock Test: Advanced English Material For The Gifted 2020Mai Linh ThânNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction To VLSI Design Lecture 1: Motivation of The CourseDocument2 pagesModule 1: Introduction To VLSI Design Lecture 1: Motivation of The CourseGunjan JhaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Outline: College Physics, 7 EditionDocument25 pagesLecture Outline: College Physics, 7 EditionRaman Aylur SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Amatillah - SakinahDocument12 pagesPresentation of Amatillah - SakinahFareed Ahmed MemonNo ratings yet
- NSTP ReportDocument8 pagesNSTP ReportMary Grace MendeNo ratings yet
- Is Euclidean Zoning The New Pig in The Parlor?: The Coming of Age of Form-Based Zoning (Damon Orobona)Document19 pagesIs Euclidean Zoning The New Pig in The Parlor?: The Coming of Age of Form-Based Zoning (Damon Orobona)Damon Orobona100% (1)
- Sentence Cont. ExerciseDocument6 pagesSentence Cont. ExerciseKim Thy Trần PhạmNo ratings yet
- Ontologies For Location Based Services Quality Enhancement: The Case of Emergency ServicesDocument8 pagesOntologies For Location Based Services Quality Enhancement: The Case of Emergency Serviceskhairul_fajar_3No ratings yet
- Newton's Three Law of MotionDocument6 pagesNewton's Three Law of MotionRey Bello MalicayNo ratings yet
- Matter Week 6Document4 pagesMatter Week 6api-316479601No ratings yet
- Qualifications Recruitment Promotions Scheme - University AcademicsDocument10 pagesQualifications Recruitment Promotions Scheme - University Academicsuteachers_slNo ratings yet
- Eecs 314 Homework SolutionsDocument6 pagesEecs 314 Homework Solutionsppuylstif100% (1)
- Geometric Tracking Control of A Quadrotor UAV On SEDocument6 pagesGeometric Tracking Control of A Quadrotor UAV On SEnaderjsaNo ratings yet
- Rebecca Wilman 17325509 Educ4020 Assessment 3Document6 pagesRebecca Wilman 17325509 Educ4020 Assessment 3api-314401095No ratings yet
- Academics: Qualification Institute Board/University Year %/CGPADocument1 pageAcademics: Qualification Institute Board/University Year %/CGPARajesh KandhwayNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Oyo & Ginger Grp-9 PDFDocument31 pagesComparative Analysis of Oyo & Ginger Grp-9 PDFadityakr2410100% (1)
- Balberan, Julliene Paula Gozon, Aleha Ann Macabalang, Mary Jomelane Manzano, JakeDocument9 pagesBalberan, Julliene Paula Gozon, Aleha Ann Macabalang, Mary Jomelane Manzano, JakeJake ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document4 pagesModule 2Amethyst LeeNo ratings yet
- Filmmaking 101Document4 pagesFilmmaking 101maheshNo ratings yet
- Eng 105 S 17 Review RubricDocument1 pageEng 105 S 17 Review Rubricapi-352956220No ratings yet
- Double Helix Revisited PDFDocument3 pagesDouble Helix Revisited PDFPaulo Teng An SumodjoNo ratings yet
- Better Typing and Dictating PracticesDocument7 pagesBetter Typing and Dictating PracticesDiyansh JainNo ratings yet
- GVP CmdsDocument3 pagesGVP CmdsShashank MistryNo ratings yet