Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Map of Asteroids Risks and Defence
Uploaded by
Turchin AlexeiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Map of Asteroids Risks and Defence
Uploaded by
Turchin AlexeiCopyright:
Available Formats
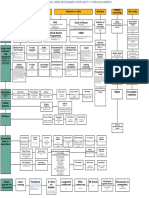
The Map of Impact Risks and Asteroid Defence
TL;DR: Observation is the best instrument in asteroid risk reduction, and large nuclear anti-asteroid defense could be more of a threat to Earth and be of negative value; but the main uncertainty is whether we live in a period of intense bombardment because of recent large comet break-up.
Higher risk of human extinction as result of impact
Type and
typical size
Stages of
defence
Tunguska
-style objects
~60 m size
Expected
frequency
Stages of prevention, time
Current
risk
Observation
Probable
deflection
methods
see in wiki
Deflection
chances
Millions dead,
economic crisis
Localised destruction, short climate
change, tsunami
Most not found
Human extinction
Human extinction
Worldwide surface
changes
Atmospheric composition changes
Most humans die on
impact or cant survive
Worldwide surface
changes
Atmospheric composition changes
Multicellular life
ends
Known object:
Comet Swift-Tuttle, 26
km size
1 in a million risk of
impact in 4479AD
Last 250 mln years???
Last one 35 mln years ago
(Popigay, 8 km body)
Last one 780 000
years ago,
another 2.1 mln.
1 in 1000 (based on
Apophis distance)
As of 2012, an estimated 20 to 30 percent of these objects
(more 100 m) have
been found.
wiki
could be different sizes,
but quicker and less predictable
-style,
~ 100 km
90 per cent found
(for next 100 years risk frame, not including
comets and dark comets)
Less than 1 in a
billion years
No such objects
known, but some
Centaurs is on this
size.
Time to Earth if it
fall from Saturn
orbit level - 5 years
Almost all found
on circular orbits
and no danger
- but not all comets found
Nukes
Impactors
Could be
deflected if warning ~10 years in
advance in
Last minute defence possible,
if defence system created in advance
Impacts with
other celestial bodies
Could be most
probable impactors
Link on Naiper
Sub-km bodies as
NEO could be invisible, and they could
be fragments of extinct comets near
Earth with dark surfaces
Centaurs large, but
remote objects between Jupiter and
Uran
Many short periodic orbit
comets has been found, but
not very long periodic
Could result in multiple
bombardment if Earth
pass through such tail,
including impacts with
several km-size dark
comet bodies or thousands tunguska-style
ojbects in hour
Unknown number.
Smaller distance of
detection or impact
without warning
Dust from comets could
affect upper atmosphere
and change its opacity
(Naiper)
Taurid meteor shower
could be part of large
comets, and also Enke
comet and Tunguska
body (Naiper)
WISE data limited
their number near
Earth ??
Impacts with Moon
and Mars could create debris showers
on Earth.
Sungrazing comets
may be connected
with superfalres
link, another link
100 body could
produce rise Suns
luminosity 1000
times for 1 sec
775 AD Sun
impact ??
link
Nothing is expected,
and chances of impact are smaller than
with Earth, as Mars
size is smaller
WISE
infrared search
Collide smaller
asteroid with
larger one
Nuclear standoff: deflection, no fracturing (10-100 times more effective than
the non-nuclear alternatives)
Nuclear surface explosion or penetration: destruction
Two stages: first crater, than nuke: HAIV
Multiple nukes in a row
Gigaton nuke on standby on orbit (Teller proposal)
Small nuke is not risky as terrestrial weapon
Could be used as a weapon! (Carl Sagan wrote about it)
NASA concluded that
it is most mature approach
Tempel comet impact deflected its orbit 10 meters
AIDA demonstrator
planned
and meteorid showers
from broken comets
(Damocloids,
Centaurs)
Difficult to observe as
they are on elliptical orbits
and most of the time behind Jupiter with no tails
Warning could be only
several years or months
(Napier)
Higher speeds (~70 km /
sec on worst case)
Size could be up to 100
km
Optical sky surveys
(Radar seems to be not effective - NASA study)
Spacecrafts
(infrared)
Comets debris
Dark
comets
1 in a million years
Once a
10 000 - 1 mln year,
depending of size
1 in 300 years
(wiki) based on
Lunar data
Civilization collapse, most humanity killed, but many survivors
Worldwide quake
Worldwide firestorm cause by
debris
Worldwide hurricane winds
Toxic gases in the air
Supervolcanic eruptions
Long volcanic winter
Half of Earth affected, climate change,
tsunami, billions
killed
Comets
Extinction level
Civilization rebuild
is possible, but extinction is
also possible
Technology stops
development for
10-50 years
Chiron
style
~30 km size
style
~10 km size
Civilization collapse
Locale effects
Localised
destruction,
Risk of accidental
nuclear war
Eros
Chicxulub
style
~1 km size
style objects
~300 m size
Could destroy
a city
Consequences
Eltanin
Apophis
Use space billiard to deflect really large
asteroid, article
Asteroid Redirection Demonstration
System (BILLIARDS) - demonstrator
Could be
deflected if warning ~30 or more
years in advance
Deflection
is difficult
Legend
The Map of Impact Risks and Asteroid Defence
This map is part of the Map of natural risks which is in its turn part of the map
Typology of global risks.
Lastmoment
destruction
Large bombs
Refuges
See refuges
map
Consequences of
large impact
see Napier
Planned
antiasteroid
programs
Hypothetic
Deflection
methods
see in wiki
Near-earth destruction is impossible
Nuclear missles
ICBM with space warheads
Gigaton bombs on Earth orbit
Could result in debris shower
The size of asteroids is roughly broken into 3 category: local effect, civilizational
collapse level and extinction level. But actual size boundary between these three
category is debatable, and depends of speed, composition, angle, location of impact and many unknowns of its consequences.
Local measures
Crater
Tsunami
Size typically
10-20 times of
the body
Could transfer energy on
large distances, but also
fading quickly
Fireball
Self-sustained Mars colony
Moon colony and near-earth space station
could be affected by debris
Deep underground refuges with high survivability
Submarines
Temporary Moon colony in tunnels
Ballistic
debris and
hot ash
Could affect all
earths surface
Earthquake
Building collapses
Focal effect on the
other side of the
Earth
Could be wordwide
EQ for very large
impact
Shockwave
Pressure changes,
wind, sound
Hot air
The vertical axis of the map shows our possible efforts in impact prevention. I
dont go into details of many projects which are excellently described in Wikipedia.
Space refuges
Specially designed shelters
Local preparedness in the impact place
and other potentially affected areas
Evacuation
EQ-preparation
Tsunami-preparation
affect no more
than 1000 km
Current
antiasteroid
programs
The horizontal axis of the map is showing more and more dangerous objects
(with some obvious caveats, as size of comets could be different, and risks from
tail debris depends of the fact if a Centarius comet has entered inner Solar system in the last 100k years and had a break-up see Napier).
Dust in the
upper atmosphere
The most important boxes are in red
Water vapor and
other gases in atmosphere
Global cooling for
years, darkness
Floods,
Acid rains nitric oxide,
CO2, toxic metals and gases
Ozone depletion
Russia
NASA
Current:
Moscow ABM
defence
Planetary Defense Coordination Office, new from 2016 coordination agency inside NASA
NEOWISE - infrared telescope on polar orbit
Scout mission - computer analysis of data from large array of telescopes
Catalina Sky Survey - search for NEO under Congress mandate from 1998
:
Asteroid Redirect Mission - planned spacecraft to asteroid, will move small boulder
NEOCAM - suggested infrared space telescope, similar to Sentinel, after 2021
ATLAS - is a proof of concept astronomical survey system for early detection of dangerous
asteroids 3 weeks for 140m, on Hawaii.
HAIV - two stage impactor
Tether with
ballast
Use
Yarkovsky
effect
Long rope attached to the
asteroid
Gravitational
tractors
Solar
sails
Laser on
asteroid
orbit creates trust
by vaporising matter
Engine of
the surface of an
asteroid
EU
Planned:
NEOshield
Sentinel: Planned
space infrared telescope on Venus orbit.
NASA
Colour
change
B612
Needs 500 mln
But only less than 2
mln a year found
Mass driver on the
surface:
throw rocks
in space
Other planned and active
missions
Near-Earth Asteroid Tracking (NEAT),
Lowell Observatory Near-Earth-Object
Search (LONEOS),
Campo Imperatore Near-Earth Object Survey (CINEOS),
Japanese Spaceguard Association,
and Asiago-DLR Asteroid Survey - more in
wiki
International research project, with budget
around 2 mln a
year
AIDA - impact
into a binary asteroid
Direct energy weapons
Solar light concentrators on the asteroid, evaporation creats trust
Nuclear explosion powered large gamma-lasers
Could be used as a weapon!
Long heating of an asteroid via space laser, wiki
Self-replicating
robots
Could build many large telescopes in
space
Large radars in space
Could replicate on asteroids and
convert them in space habitats, and
change their trajectory
Nuclear fusion during
impact
Project of Ukrainian Uzhnoe
company. 100 km s impact used
to create conditions for fusion.
No risk to use as weapons
Risk increasing factors
Natural
factors
Holocen bombardment
It may be that we are living in
a period of bombardment after a comet breakup with 100
times more background rate,
wiki
Observed rate of impacts is
higher than expected: Tunguska should fail each 3000
years, link link
Other evidences: Fires, diamonds, mass extinctions, sea
shevrons, climate changes in
last 15 000 years, zodiacal
cloud size, link.
Tsunami deposits in Australia,
craters (Mahuika)
Frequency of near misses implys to 60-200 more rate.
(Napier)
Anthropogenic
factors
Biases
Alexey Turchin, 2016, CC3.0
Anthropic shadow
We could underestimate
risks of impacts because of
observation selection effects. If large impacts could
have a higher probability,
but we could survive only
during unusually quiet periods then maybe a large
bombardment period is
long overdue. link
Oort cloud
destabilisation
Oort cloud is major
source of comets and
centaurs and could be
influenced by the close
passage of nearby stars,
hidden solar companions
or passage through the
Galactic plane. According
to some theories, this
happens periodically.
Methane
hydrates and
global warming
A medium sized
impact could lead
to runaway global
warming, if it hits
a methane hydrate
deposit or an oil
deposit;
Could affect coal
deposits also - CO2
Global warming
and water vapor
Volcanic
eruptions
Atmosphere could
be oversaturated
with water vapor
from oceanic impact
of 3km+ body, see
article.
Could trigger runaway global warming??
Large rains and
floods
In case of bad coincident impact
could lead to supervolcanic eruption.
Iron asteroids
could penetrate
deeper in crust and
create new volcanos?
A Sholtz star star passed
recently (70k years)
through an Oort clod,
but it is thought that it
will take 2 mln years for
the affected comets to
reach the inner Solar
system.
Panic on
warning
Nuclear war
trigger
Defence as
weapons
Nuclear and bio-facilities
destruction
Millennial feelings,
sects lead to civilizational collapse
Small impact
could start nuclear warning system and result in
war
Gigaton scale bombs created for asteroid destruction could be used against
Earth as a weapon and it
is more probable.
Sagan suggested to build
them only if risk is clear.
Russia wants to built
Nuclear power plants, spent
fuel facilities, bioweapons labs
and other dangerous tech could
be affected even by small impact
Natural Stevensone probe
penetrates
Earths core
Stevensone suggested the use of a
large pool of molten
iron (100k tons) to
send a probe into
the core, and Circovic shows that
this would be dangerous as it could
produce core degasation.
The impact could
also create such
hot molten iron
lake (my idea, not
proved)
Deflection of
asteroids to Earth
as weapon
Asteroid could be deflected to Earth as a
crypto-weapon
Asteroid risks in the context of
technological development
Ocean bias
Volcanic bias
We could underestimate the number
of recent impacts as
most of earth is covered by water or deserts.
It implies that Tunguska-style events
could happen more
often.
But now we have audio control system
for sonic booms.
We could underestimate the frequency of
large Verneshorts or
Kimberlit type volcanic explosions and regard their remains as
astroid impacts. Even
Tunguska could be
such explosions.
Undereatimation of historical
records
It seems not true that
there wasnt human
victims of impacts.
10 000 people died in
China in 1490
10 more cases known
link
Catastrophism
bias
There is the tendency to overestimate
the influence of impacts on the biosphere, especially
the extinction of dinosaurs.
Observation
bias
Dark and remote
objects are most
dangerous but less
observable
Defence bias
The biggest protection is the proof of
non-existence by observation, not nuclear weapons in space,
which could be dangerous themselves
Evaporation
bias ???
Smaller ice bodies
evaporate completely
in space, which bias
distribution expectations, and results in
an increasing number of larger bodies
(my idea).
Effect-size bias
Overestimation bias
The best defence
we could built works
great against smallest bodies, but the
main risk is from
larger bodies
Based on current accepted
predictions, risks of civilization killer asteroid is around 1
in million years, and so risks of
asteroids are negligible compare to other existential risks.
Our technology is constantly growing which increases our ability to detect and deflect dangerous
asteroids.
The biggest tech to deflect potentially dangerous
asteroids will be self-replicating robots (or nanotech) and AI.
They could build large infrastructure in space.
But asteroid risks are easily provable and measurable,
and also the ways of their prevention is straightforward and
clear (on first glance).
They will be created probably in next 20-100 years.
That is why they get more attention and funding than other
risks, like AI, bio tech and nanotech.
The best risk reduction would be disproving any
suggestions that we live in the epoch of intense
bombardment, as even the small probability of
such a suggestion would dominate the risk landscape.
So, the window of vulnerability to asteroid risk is
less than 100 years, and we have already lowered
the risk by observation several times.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- AI Safety LevelsDocument1 pageAI Safety LevelsTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- AI For Immortality MapDocument3 pagesAI For Immortality MapTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Resurrection of The Dead MapDocument1 pageResurrection of The Dead MapTurchin Alexei100% (1)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Map of Shelters and Refuges From Global Risks (Plan B of X-Risks Prevention)Document1 pageThe Map of Shelters and Refuges From Global Risks (Plan B of X-Risks Prevention)Turchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Map of Agents Which May Create X-RisksDocument1 pageThe Map of Agents Which May Create X-RisksTurchin Alexei100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Future SexDocument1 pageFuture SexTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Map of X-Risk-Preventing Organizations, People and Internet ResourcesDocument1 pageThe Map of X-Risk-Preventing Organizations, People and Internet ResourcesTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Map of Risks of AliensDocument1 pageThe Map of Risks of AliensTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Life Extension MapDocument1 pageLife Extension MapTurchin Alexei100% (1)
- The Map of Natural Global Catastrophic RisksDocument1 pageThe Map of Natural Global Catastrophic RisksTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Map of BiasesDocument1 pageThe Map of BiasesTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Map of Ideas of Global Warming PreventionDocument1 pageThe Map of Ideas of Global Warming PreventionTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Map of Ideas About P-ZombiesDocument1 pageThe Map of Ideas About P-ZombiesTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Map of MontenegroDocument1 pageThe Map of MontenegroTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Map of Ideas About IdentityDocument1 pageThe Map of Ideas About IdentityTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- The Map of Methods of OptimisationDocument1 pageThe Map of Methods of OptimisationTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Map of Ideas How Universe Appeared From NothingDocument1 pageThe Map of Ideas How Universe Appeared From NothingTurchin Alexei100% (1)
- Global Catastrophic Risks Connected With Nuclear Weapons and Nuclear EnergyDocument5 pagesGlobal Catastrophic Risks Connected With Nuclear Weapons and Nuclear EnergyTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- (Plan C From The Immortality Roadmap) Theory Practical StepsDocument1 page(Plan C From The Immortality Roadmap) Theory Practical StepsTurchin Alexei100% (1)
- Double Scenarios of A Global Catastrophe.Document1 pageDouble Scenarios of A Global Catastrophe.Turchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- Bio Risk MapDocument1 pageBio Risk MapTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Simulation MapDocument1 pageSimulation MapTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- The Roadmap To Personal ImmortalityDocument1 pageThe Roadmap To Personal ImmortalityTurchin Alexei100% (1)
- Russian Naive and Outsider Art MapDocument1 pageRussian Naive and Outsider Art MapTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- Doomsday Argument MapDocument1 pageDoomsday Argument MapTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- AI Failures Modes and LevelsDocument1 pageAI Failures Modes and LevelsTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- Typology of Human Extinction RisksDocument1 pageTypology of Human Extinction RisksTurchin AlexeiNo ratings yet
- Why The Big Bang Is Not An Explosion by Sten OdenwaldDocument5 pagesWhy The Big Bang Is Not An Explosion by Sten Odenwaldgcampbel0No ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Saravali - Jaimini AstrologyDocument2 pagesSaravali - Jaimini AstrologyraviamNo ratings yet
- 06 LabActivityForm BigBangBalloon PDFDocument4 pages06 LabActivityForm BigBangBalloon PDFLaurice Anne Zapanta0% (1)
- Expanding Universe School ObservatoryDocument4 pagesExpanding Universe School ObservatoryNeil Mark MortaNo ratings yet
- DSO Checklist - by Nilson BazanaDocument2 pagesDSO Checklist - by Nilson BazanapoMP3ianNo ratings yet
- Brandner W., Klahr H. (Eds.) Planet Formation (CUP, 2006) (ISBN 0521860156) (O) (320s) - PA - PDFDocument320 pagesBrandner W., Klahr H. (Eds.) Planet Formation (CUP, 2006) (ISBN 0521860156) (O) (320s) - PA - PDFIgor Di VaranoNo ratings yet
- Astronomy A Beginner S Guide To The Universe 8th Edition Chaisson Test BankDocument15 pagesAstronomy A Beginner S Guide To The Universe 8th Edition Chaisson Test Bankdubitateswanmarkm4nvo100% (21)
- The Astrology of Space PDFDocument494 pagesThe Astrology of Space PDFShashi MudgalNo ratings yet
- Gifts of The 8th HouseDocument106 pagesGifts of The 8th HouseSushimita Sharma100% (1)
- Solution Manual For An Introduction To Modern Astrophysics 2nd Edition by CarrollDocument2 pagesSolution Manual For An Introduction To Modern Astrophysics 2nd Edition by Carrolla4933324420% (9)
- Nihlen - On The Rex Degree in AstrologyDocument7 pagesNihlen - On The Rex Degree in AstrologyjungianjoeNo ratings yet
- #Adidas Sor 2018 & 2017Document25 pages#Adidas Sor 2018 & 2017Aurel KhanNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Solar System SEDocument3 pagesSolar System SEsshaxsNo ratings yet
- Hills 1988 Hyper-Velocity and Tidal Stars From Binaries Disrupted by A Massive Galactic Black HoleDocument3 pagesHills 1988 Hyper-Velocity and Tidal Stars From Binaries Disrupted by A Massive Galactic Black HoleSofía GallegoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE7-Q4 WEEk4-5 RABADONDocument14 pagesSCIENCE7-Q4 WEEk4-5 RABADONJoshua Meir DumandanNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Lecture1-Limited Face To Face ClassesDocument58 pagesPhysical Science Lecture1-Limited Face To Face ClassesGlecil Joy DalupoNo ratings yet
- EclipseDocument3 pagesEclipseLarissaAbreu100% (1)
- Kevo Birth Free Astrology Birth Chart CalculatorDocument13 pagesKevo Birth Free Astrology Birth Chart CalculatorGeorge Ka RajaNo ratings yet
- Simple Blackboard Background Bordeaux VariantDocument50 pagesSimple Blackboard Background Bordeaux VariantSilNo ratings yet
- Book - 2017 - David Bolton - The Zenith Chart - Putting You in The Center of Your HoroscopeDocument29 pagesBook - 2017 - David Bolton - The Zenith Chart - Putting You in The Center of Your Horoscopedavis mathewNo ratings yet
- Kids Puppet Theater Workshop by SlidesgoDocument43 pagesKids Puppet Theater Workshop by SlidesgoRBT1062021 Divyasree VelooNo ratings yet
- Daegu International Jazz Festival by SlidesgoDocument57 pagesDaegu International Jazz Festival by Slidesgoismail wahyudiNo ratings yet
- Ingles v2Document3 pagesIngles v2Joaquim da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Ch01 Earth in ContextDocument33 pagesCh01 Earth in ContextmimiNo ratings yet
- Soal Uas Genap X - 2012-2013 - ADocument8 pagesSoal Uas Genap X - 2012-2013 - AnurinuryaniNo ratings yet
- Eclipses in Ancient CulturesDocument8 pagesEclipses in Ancient CulturesLaura Daniela Jimenez PradaNo ratings yet
- Mapping The Stars On The Revolving SpherDocument29 pagesMapping The Stars On The Revolving SphermarcbreglianoNo ratings yet
- The Vedic Yearly Chart - New Moon in Pisces: by Steven Stuckey, USADocument4 pagesThe Vedic Yearly Chart - New Moon in Pisces: by Steven Stuckey, USARavi K NNo ratings yet
- TLE For Astronomical Science by SlidesgoDocument8 pagesTLE For Astronomical Science by Slidesgoakash kNo ratings yet
- (Gary D.E., Keller C.U. (Eds.) ) Solar and Space WeDocument425 pages(Gary D.E., Keller C.U. (Eds.) ) Solar and Space WeKarla Lopez AraujoNo ratings yet
- Under Alien Skies: A Sightseer's Guide to the UniverseFrom EverandUnder Alien Skies: A Sightseer's Guide to the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (17)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- When the Heavens Went on Sale: The Misfits and Geniuses Racing to Put Space Within ReachFrom EverandWhen the Heavens Went on Sale: The Misfits and Geniuses Racing to Put Space Within ReachRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (28)