Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Road To The Revolution Unit Test
Uploaded by
api-315723574Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Road To The Revolution Unit Test
Uploaded by
api-315723574Copyright:
Available Formats
Name: ______________________________
Date: ________________________
The Road to the Revolution Test
trace the events that shaped the revolutionary movement in America (GPS) (4SS_F2008-40) 40a - define interdependence and the slogan "no taxation
without representation"40b - analyze the causes and effects of the French and Indian War, British Imperial Policy that led to the 1765 Stamp Act, the
Boston Massacre, the activities of the Sons of Liberty, and the Boston Tea Party. describe key individuals in the American Revolution (GPS) (4SS_F2008-43)
43a - determine the significance of King George III, George Washington, Benjamin Franklin, Thomas Jefferson, Benedict Arnold, Patrick Henry,
John Adams, Lafayette, Paul Revere, Minutemen, Thomas Paine, Lord Cornwallis, Samuel Adams. describe how physical systems affect human systems in
regard to the American Revolution (GPS) (4SS_F2008-44) 44a - explain how each force (American and British) attempted to use the physical geography of
each battle site to its benefit. name positive character traits of key historic figures and government leaders (honesty, patriotism, courage, trustworthiness)
associated with the American Revolution (GPS) (4SS_F2008-45). use the basic economic concepts of trade, opportunity cost, specialization, voluntary
exchange, productivity and price incentives to illustrate historical events specific to the American Revolution (GPS) (4SS_F2008-46) 46a - explain how
price incentives affect people's behavior and choices such as colonial decisions about what crops to grow and products to produce. 46b - describe how
specialization improves standards of living such as how specific economies in the three colonial regions developed. 46c - explain how voluntary exchange
helps both buyers and sellers such as colonial trade in North America
1. What was one major cause of the French and Indian War?
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
2. What did the British government do to help pay the costs of the French and Indian War?
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
3. Many colonists said that Parliament should
not tax them because they had no representation.
What does the word representation mean in the
sentence above?
A.
a plan for spending money
B.
money that governments collect from
citizens
C.
a voice in one's government
D.
a lawmaking body
4. How did many colonists protest the taxes
placed on British goods?
A.
They left the colonies.
B.
They fought with British soldiers.
C.
They refused to buy British goods.
D.
They refused to make British goods.
7. Why were the battles at Lexington and
Concord important?
A.
They marked the end of the French and
Indian War.
B.
They forced Parliament to repeal all new
tax laws.
C.
They marked the beginning of the
American Revolution.
5. How did Committees of Correspondence help
the colonists fight British rule?
A.
They spread information quickly.
B.
They housed British soldiers.
C.
They voted to declare independence.
D.
They stole British goods.
6. When did the British realize that fighting the
colonists would not be easy?
A.
after the battles at Lexington and
Concord
B.
after the Battle of Bunker Hill
C.
after the Boston Tea Party
D.
after Congress approved the Declaration
of Independence
D.
They were the first battles led by George
Washington.
8. What happened on July 4, 1776, that makes it
such an important date in American history?
A.
The colonists won the American
Revolution.
B.
The 13 colonies formed their first united
government.
C.
Congress voted to accept the
Declaration of Independence.
D.
The colonists formed the first
Committee of Correspondence.
9. What was the first plan of government for the United States called?
A.
the Albany Plan
B.
the Articles of Confederation
C.
the Declaration of Independence
D.
the Olive Branch Petition
10. What is one effect that the Articles of Confederation had on the new nation?
A.
Congress was given the power to control trade.
B.
Congress was able to collect taxes.
C.
The power of the states was limited.
D.
The states were held together as a nation during the Revolutionary War.
11. ______________was the commander in chief of the Continental Army
A. Samuel Adams
B. John Dickinson
C. Thomas Jefferson
D. Richard Henry Lee
E. George Washington
12. ______________was the head of the committee for the Articles of Confederation
A. Samuel Adams
B. John Dickinson
C. Thomas Jefferson
D. Richard Henry Lee
E. George Washington
13. ______________organized the first Committee of Correspondence in Boston and was thought by
many people to have planned the Boston Tea Party
A. Samuel Adams
B. John Dickinson
C. Thomas Jefferson
D. Richard Henry Lee
E. George Washington
14. ______________was the main author of the Declaration of Independence
A. Samuel Adams
B. John Dickinson
C. Thomas Jefferson
D. Richard Henry Lee
E. George Washington
15. __________called for a resolution in the Second Continental Congress for independence from Britain
A. Samuel Adams
B. John Dickinson
C. Thomas Jefferson
D. Richard Henry Lee
E. George Washington
16. What was the Proclamation of 1763, and how did colonists react to it? _________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
17. In what ways did colonists protest British imperial policies? _________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Answer Key for Chapter 8 Assessment
1. Varies- France and Britain both claimed the same lands in North America.
2. Varies- It passed new tax laws for the colonies.
3. C
4. C
5. A
6. B
7. C
8. C
9. B
10. D
11. E
12. B
13. A
14. C
15. D
16. It was a British announcement that set aside lands west of the Appalachian Mountains for
Native Americans. Many colonists were angry about the proclamation, and many ignored
it by continuing to settle on those lands.
17. They boycotted British goods. They wove their own cloth instead of buying British cloth.
They chased British tax collectors out of their towns. They formed Committees of
Correspondence. They organized protests. They sent petitions to Parliament. They formed
militias.
You might also like
- Old CSEC Geography MCQ Answers PDFDocument2 pagesOld CSEC Geography MCQ Answers PDFTrevor G. SamarooNo ratings yet
- Separating Mixtures TechniquesDocument2 pagesSeparating Mixtures TechniquesHenry TuganoNo ratings yet
- Measuring devices worksheetDocument5 pagesMeasuring devices worksheetSubhash Chandra SahuNo ratings yet
- World War 1 BitesizeDocument11 pagesWorld War 1 BitesizeDaniel Yannik Awuah-darkoNo ratings yet
- Solubility Lab ReportDocument3 pagesSolubility Lab ReportJampathippong SorraveeNo ratings yet
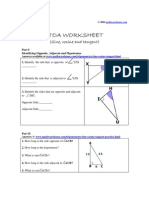
- SOHCAHTOA Worksheet LessonDocument4 pagesSOHCAHTOA Worksheet LessonJ Pomales100% (1)
- CSEC Chemistry Section A QuizDocument2 pagesCSEC Chemistry Section A QuizViCtOrIa M.No ratings yet
- Usman Public School System: Pressure WorksheetDocument2 pagesUsman Public School System: Pressure Worksheetmarium khanNo ratings yet
- Prelim 2 p3 2011 (For Sharing)Document14 pagesPrelim 2 p3 2011 (For Sharing)Yee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- Anglyn Pob SbaDocument32 pagesAnglyn Pob SbaAnglyn CharlesNo ratings yet
- Energy changes in reactionsDocument2 pagesEnergy changes in reactionsSamandarbek Numonov100% (1)
- CSEC Technical Drawing June 2013 P032Document6 pagesCSEC Technical Drawing June 2013 P032Britney valladaresNo ratings yet
- American Revolution: Taxation, Independence, and the First Successful Colonial Revolt (1775-1783Document2 pagesAmerican Revolution: Taxation, Independence, and the First Successful Colonial Revolt (1775-1783Freedel LogieNo ratings yet
- Geog Specimen MCDocument28 pagesGeog Specimen MCBranson Kaution Peters II100% (1)
- Electrical Resistance in Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument10 pagesElectrical Resistance in Series and Parallel CircuitsRaja AleeyaNo ratings yet
- Csec 2004Document10 pagesCsec 2004Cherise Exøgenesis RobertsNo ratings yet
- Collective Agreement Between The Chief Personnel Officer and The National Union of Government and Federated Workers, 2011 - 2013 - 0Document44 pagesCollective Agreement Between The Chief Personnel Officer and The National Union of Government and Federated Workers, 2011 - 2013 - 0claire63% (32)
- Csec Chemistry Notes 7Document2 pagesCsec Chemistry Notes 7debestieNo ratings yet
- CXC Physics 1994 - Paper1Document10 pagesCXC Physics 1994 - Paper1Jotham OmoregieNo ratings yet
- Causes of WWI LessonDocument8 pagesCauses of WWI LessonAnnieNo ratings yet
- Practice Test (CH 10 - Projectile Motion - Kepler Laws)Document7 pagesPractice Test (CH 10 - Projectile Motion - Kepler Laws)Totoy D'sNo ratings yet
- Comparing Photosynthesis and Aerobic Respiration in Plants and AnimalsDocument8 pagesComparing Photosynthesis and Aerobic Respiration in Plants and AnimalsJoy BoehmerNo ratings yet
- Social Studies Worksheet 2015 June 2015Document2 pagesSocial Studies Worksheet 2015 June 2015Clair VickerieNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS - FORM FOUR - Topic 1 - WAVES - MSOMI BORA PDFDocument54 pagesPHYSICS - FORM FOUR - Topic 1 - WAVES - MSOMI BORA PDFstarbornkidsNo ratings yet
- Marketing (Pob)Document7 pagesMarketing (Pob)Joshua BrownNo ratings yet
- CXC CSEC Chemistry MCQ AnswersDocument3 pagesCXC CSEC Chemistry MCQ AnswersVir Boodhoo 2 FaithNo ratings yet
- IGCSE 2.0 - Thermal Physics - Test 2018Document9 pagesIGCSE 2.0 - Thermal Physics - Test 2018Brandeice BarrettNo ratings yet
- Csec Agricultural Science Syllabus With Specimen PapersDocument138 pagesCsec Agricultural Science Syllabus With Specimen Papersapi-508592459No ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document28 pagesChapter 10api-32740845100% (1)
- Biology Past PapersDocument20 pagesBiology Past Papersdemetri lanezNo ratings yet
- FT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (General Phy)Document10 pagesFT 12 Gr10 P2 Qs (General Phy)farogh hamidNo ratings yet
- Review Chemical Reactions Test Chap 7Document2 pagesReview Chemical Reactions Test Chap 7townsenr94No ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry June 2013 P1 PDFDocument9 pagesCSEC Chemistry June 2013 P1 PDFJeff LamboNo ratings yet
- UCE Revision Physics Paper 1 and 2: Student's BookDocument220 pagesUCE Revision Physics Paper 1 and 2: Student's BookMwijuka GilbertNo ratings yet
- Oi2I2Oio TP: 2016054 Caribbean ExaminationsDocument11 pagesOi2I2Oio TP: 2016054 Caribbean ExaminationsLaimen ReveskiNo ratings yet
- Notes - Unit 1of Matter and Measurment - Answer Key PacketDocument25 pagesNotes - Unit 1of Matter and Measurment - Answer Key PacketLizeth PautaNo ratings yet
- Cracking AlkanesDocument2 pagesCracking Alkaneskadek_windyNo ratings yet
- Chem Topic 4 QuestionsDocument19 pagesChem Topic 4 QuestionsOscarHigson-SpenceNo ratings yet
- Moments Centre of Mass QP PDFDocument14 pagesMoments Centre of Mass QP PDFshradhaNo ratings yet
- H2 Jun Holiday Assignment 2013 AnswersDocument12 pagesH2 Jun Holiday Assignment 2013 AnswersKaitlyn HoNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics June 2010 P032Document11 pagesCSEC Physics June 2010 P032aidan kamrajNo ratings yet
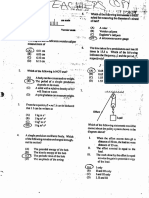
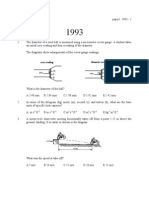
- 1993 - Paper1 PHYSICSDocument11 pages1993 - Paper1 PHYSICSNalini Rooplal100% (1)
- G. Cape Chem Sample Mult-ChoiceDocument9 pagesG. Cape Chem Sample Mult-ChoiceGervent GayleNo ratings yet
- 2023msce P IDocument12 pages2023msce P Imtende mwale100% (1)
- CSEC Chemistry January 2009 P032Document7 pagesCSEC Chemistry January 2009 P032AshleyNo ratings yet
- CSECDocument8 pagesCSECAnonymous FIwVj1mNo ratings yet
- Bio June 2011 p1Document13 pagesBio June 2011 p1lalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry CSEC June 2015 P1Document9 pagesChemistry CSEC June 2015 P1Toni-Krys HardyNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Physics Notes for Electricity Topic 2Document7 pagesAQA GCSE Physics Notes for Electricity Topic 2solzorNo ratings yet
- CXC Jan 2000 p2Document7 pagesCXC Jan 2000 p2omar_oj_40% (1)
- Physics of The AtomDocument38 pagesPhysics of The AtomLicia AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Atomic - Structure of The Periodic Table WorksheetDocument1 pageAtomic - Structure of The Periodic Table WorksheetEdison Alfonso SturgessNo ratings yet
- Reading Practice Set 2: Questions 1-11 Are Based On The Following Passage and Supplementary MaterialDocument8 pagesReading Practice Set 2: Questions 1-11 Are Based On The Following Passage and Supplementary MaterialTrần Minh Trang Đặng100% (1)
- Csec Chemistry lectures (module 1-principle of chemistryDocument46 pagesCsec Chemistry lectures (module 1-principle of chemistryUnknown100% (1)
- Worksheet 4Document4 pagesWorksheet 4JabarrioMykaelHolligan0% (2)
- Csec Chemistry Chapter 6 - MolesDocument16 pagesCsec Chemistry Chapter 6 - Moleschelsea AlexandriaNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics June 2000 P1Document14 pagesCSEC Physics June 2000 P1Saif Khan50% (2)
- WASSCE WAEC Social Studies Syllabus PDFDocument10 pagesWASSCE WAEC Social Studies Syllabus PDFdaasebre ababiomNo ratings yet
- 2014 May CSEC Physics Paper2 PDFDocument15 pages2014 May CSEC Physics Paper2 PDFCXC Dl1100% (1)
- Jamaica Driver's Education Handbook: A Comprehensive Driver Training GuideFrom EverandJamaica Driver's Education Handbook: A Comprehensive Driver Training GuideNo ratings yet
- Medt7487 Portfolio Matrix AfoxDocument17 pagesMedt7487 Portfolio Matrix Afoxapi-315723574No ratings yet
- Assignment6 Medt7490 FoxDocument10 pagesAssignment6 Medt7490 Foxapi-315723574No ratings yet
- 7461 Student Instruction Project AmfDocument25 pages7461 Student Instruction Project Amfapi-315723574No ratings yet
- Medt7478 Deweylessonassessment AfoxDocument2 pagesMedt7478 Deweylessonassessment Afoxapi-315723574No ratings yet
- Medt6465 Instructional Order Justification AfoxDocument2 pagesMedt6465 Instructional Order Justification Afoxapi-315723574No ratings yet
- Assignment5 Edrs6301 Final AfoxDocument3 pagesAssignment5 Edrs6301 Final Afoxapi-315723574No ratings yet
- Assignment5 Medt7490 FoxDocument10 pagesAssignment5 Medt7490 Foxapi-315723574No ratings yet
- 7461 Instructionaldesignmodels AmfDocument9 pages7461 Instructionaldesignmodels Amfapi-315723574No ratings yet
- Medt7478 Deweylessonhandout AfoxDocument2 pagesMedt7478 Deweylessonhandout Afoxapi-315723574No ratings yet
- Medt6465 Instructional Order List AfoxDocument12 pagesMedt6465 Instructional Order List Afoxapi-315723574No ratings yet
- Assignment4 Medt7490 FoxDocument3 pagesAssignment4 Medt7490 Foxapi-315723574No ratings yet
- Revolutionary Journal ProjectDocument3 pagesRevolutionary Journal Projectapi-315723574No ratings yet
- Facilitiesfloorplan Medt6461 AfoxDocument5 pagesFacilitiesfloorplan Medt6461 Afoxapi-315723574No ratings yet
- Budget Medt6461 AfoxDocument2 pagesBudget Medt6461 Afoxapi-315723574No ratings yet
- Boston Massacre AssignmentDocument9 pagesBoston Massacre AssignmentJohn Brendel100% (1)
- Road To Revolution TestDocument4 pagesRoad To Revolution Testapi-315723574No ratings yet
- Curr6575k12overview AfoxDocument5 pagesCurr6575k12overview Afoxapi-315723574No ratings yet
- Amanda Todd's Story of Cyberbullying and SuicideDocument6 pagesAmanda Todd's Story of Cyberbullying and SuicideAndreia Pereira da SilvaNo ratings yet
- What Makes A LanguageDocument26 pagesWhat Makes A Languageმიშა ლაბაძეNo ratings yet
- Dr. Paul Cameron - Psychiatric Professions Falsely Claim Gays No More Apt To MolestDocument13 pagesDr. Paul Cameron - Psychiatric Professions Falsely Claim Gays No More Apt To MolestRuben MicleaNo ratings yet
- Meghan Markle Pismo KongresuDocument2 pagesMeghan Markle Pismo KongresuTportal.hrNo ratings yet
- Action Research: (English) S.Y. 2015 - 2016Document5 pagesAction Research: (English) S.Y. 2015 - 2016Fred Ryan Canoy DeañoNo ratings yet
- ABC Cooperative land agreementDocument3 pagesABC Cooperative land agreementBetsy Maria ZalsosNo ratings yet
- Acquire Original Certificate of Title in 11 StepsDocument3 pagesAcquire Original Certificate of Title in 11 Stepsmsparalegal100% (1)
- Review of Related Literature 2Document3 pagesReview of Related Literature 2Erick Anopol Del Monte100% (2)
- Role of Local GovtDocument39 pagesRole of Local GovtRara AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Gender and Development (Gad)Document4 pagesGender and Development (Gad)Romar TaroyNo ratings yet
- ABEL, Marco. Violent Affect - Literature, Cinema and Critique After RepresentationDocument313 pagesABEL, Marco. Violent Affect - Literature, Cinema and Critique After RepresentationMatheus AhNo ratings yet
- ELITE INFLUENCE ON REGIME DURABILITY IN SYRIA AND LEBANON Kenan KadicDocument110 pagesELITE INFLUENCE ON REGIME DURABILITY IN SYRIA AND LEBANON Kenan KadicPedro Navarro SeguraNo ratings yet
- Free Legal Form: Vehicle Deed of SaleDocument2 pagesFree Legal Form: Vehicle Deed of SaleArchie Joseph LlanaNo ratings yet
- SukumarDocument215 pagesSukumarRoonah KayNo ratings yet
- Political Law Review Case ListDocument5 pagesPolitical Law Review Case ListZaira Gem GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Treasury Letter To Congress 100115Document2 pagesTreasury Letter To Congress 100115Brett LoGiuratoNo ratings yet
- Impact of Globalisation Social and Cultural Values in IndiaDocument37 pagesImpact of Globalisation Social and Cultural Values in IndiaRavikiranNo ratings yet
- Velasco Vs Republic, G.R. No. L-14214, May 25, 1960Document2 pagesVelasco Vs Republic, G.R. No. L-14214, May 25, 1960Aldrin Tang50% (2)
- Lesson Plan Law and Criminal Justice For EFLDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Law and Criminal Justice For EFLAnicaNo ratings yet
- Gamboa v. Chan G.R. No. 193636 July 24, 2012 Justice Sereno FactsDocument3 pagesGamboa v. Chan G.R. No. 193636 July 24, 2012 Justice Sereno FactsBill MarNo ratings yet
- PP v Fabian Anuar Mail High Court Ruling on Anti-Corruption ChargesDocument7 pagesPP v Fabian Anuar Mail High Court Ruling on Anti-Corruption ChargesAlias IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Keynes - 4 SectorDocument16 pagesModule 4 Keynes - 4 SectorPrashastiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document21 pagesChapter 02NotesfreeBookNo ratings yet
- Upsc Cse Mains Past 10 Years Topic Wise Questions PolityDocument6 pagesUpsc Cse Mains Past 10 Years Topic Wise Questions PolityhguytNo ratings yet
- Kuzio Disinformation Soviet Origins of Contemporary Russian UkrainophobiaDocument39 pagesKuzio Disinformation Soviet Origins of Contemporary Russian UkrainophobiaOleh KostiukNo ratings yet
- HistoryDocument2 pagesHistoryKalliste HeartNo ratings yet
- Electoral and Their Political ConsequencesDocument352 pagesElectoral and Their Political ConsequencesLorenzoNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Political ScienceDocument17 pagesFundamental of Political ScienceUsman Riaz33% (3)
- Commercial Revolution ExplainedDocument4 pagesCommercial Revolution ExplainedFrancis De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Rutherford and The JewsDocument23 pagesRutherford and The JewsChas AllenNo ratings yet