Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrical System Analysis
Uploaded by
Avery DuckworthCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrical System Analysis
Uploaded by
Avery DuckworthCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrical System Analysis
Service Amperages & Voltage to the Panels:
Transformer 120/208V, 3 Phase, 4 Wire, 1200A
List of Operating Voltages:
Panel MP Main Distribution Panel: 120/208V, 3 Phase, 4 Wire, 400A, Main Breaker
Panel S Sub-Panel from Panel MP: 120/208V, 3 Phase, 4 Wire, 200A
Electrical Control Systems:
The following panel schedules list the circuits that they supply:
Electrical System Analysis
Electrical System Analysis
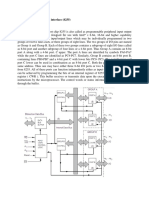
Electricity Distribution Diagram:
The diagram above displays the distribution of power throughout the building.
The transformer feeds the riser pole, and power is sent to the meter which then feeds
power to panel MP which is the main distribution panel. Panel MP feeds power to sub
panel S. Both panels feed power to circuits. In the event of a power outage, an ATS is
connected to a generator and both panel MP and P. If the switch is activated, the
generator will provide temporary power in lieu of the utility service.
Building Equipment Needs:
The following equipment items rely on the electrical system in order to operate properly:
Roof Top Units, Exhaust Fans, Unit Heaters, Destratification Fans, Overhead Doors,
Folding Doors, Cord Reels, Telecomm System, Door Access Controls, Video Intercom
System, and the Equipment Rack
Types and Locations of Conduit:
Metal Conduit & Tubing Types
Rigid Steel Conduit: ANSI C80.1.
1. Fittings: threaded only.
IMC: ANSI C80.6.
1. Fittings: threaded only.
Plastic-Coated Steel Conduit and Fittings:
NEMA RN 1.
Legend
EMT: Electrical metallic tubing.
ENT: Electrical nonmetallic tubing.
FMC: Flexible metal conduit.
IMC: Intermediate metal conduit.
LFMC: Liquidtight flexible metal conduit.
LFNC: Liquidtight flexible nonmetallic conduit.
RMC: Rigid metal conduit.
Plastic-Coated IMC and Fittings: NEMA RN 1.
RNC: Rigid nonmetallic conduit.
Electrical System Analysis
EMT and Fittings: ANSI C80.3.
1. Fittings: Steel Set-screw type.
FMC: Zinc-coated steel.
LFMC: Flexible steel conduit with PVC jacket.
Fittings: NEMA FB 1; compatible with conduit/tubing materials.
Nonmetallic Conduit & Tubing Types
ENT: NEMA TC 13.
RNC: NEMA TC 2, Schedule 40 or 80 PVC.
ENT and RNC Fittings: NEMA TC 3; match to conduit or conduit/tubing type and
material.
LFNC: UL 1660.
Locations
Outdoors:
Exposed: Rigid steel or IMC.
Concealed: Rigid steel or IMC.
Underground, Single Run: RNC.
Underground, Grouped: RNC.
Connection to Vibrating Equipment (Including Transformers and Hydraulic,
Pneumatic, Electric Solenoid, or Motor-Driven Equipment): LFMC.
Indoors:
Exposed: EMT.
Concealed: EMT.
Connection to Vibrating Equipment (Including Transformers and Hydraulic,
Pneumatic, Electric Solenoid, or Motor-Driven Equipment): FMC; except in wet
or damp locations, use LFMC.
Damp or Wet Locations: Rigid steel conduit.
Emergency Power System:
The emergency power system features a natural gas powered packaged engine
generator. An automatic transfer switch (ATS) is installed so when electrical power fails
via the utility source, the backup generator can provide temporary electrical power.
Power failures are detected immediately and the transition from utility power to
generator power is seamless. The ATS detects a power failure and initiates procedures
to start the backup generators engine.
Electrical System Analysis
Electrical System Schedule Impacts:
The electrical system is a key system to the building and has multiple schedule impacts.
The electrical system supplies conduit to HVAC equipment such as roof top units,
exhaust fans, and plumbing equipment such as unit heaters, and a water heater. In
addition to these equipment items, the overhead and folding doors are powered by the
electrical system as well. In order for these items to be connected to the system, all the
conduit and wire must be in place for connections to take place. Coordination with the
utility pole relocation must take place as well. Panels and conduit can be installed, but
electrical utility lines must be installed in order for the main distribution panel to connect
to the main power source. In regards to interior finishes, it is important that all in-ceiling
and in-wall wire is pulled and terminated so inspection can take place and drywall and
ACT can be installed. As interior finishes are completed, electrical trim out work occurs
as well such as installing receptacle covers. The electrical contractors are one of the
last trades to leave the jobsite. The installation of the electrical system is key all across
the project, so careful thought and coordination is required to ensure that the project
schedule is on track.
You might also like
- Structural AnalysisDocument10 pagesStructural AnalysisAvery DuckworthNo ratings yet
- HVAC System AnalysisDocument9 pagesHVAC System AnalysisAvery DuckworthNo ratings yet
- Site Utilization Plan NarrativeDocument1 pageSite Utilization Plan NarrativeAvery DuckworthNo ratings yet
- Plumbing System AnalysisDocument3 pagesPlumbing System AnalysisAvery DuckworthNo ratings yet
- Estimate Npfs2 QTODocument157 pagesEstimate Npfs2 QTOAvery DuckworthNo ratings yet
- Estimate Npfs2 QTODocument157 pagesEstimate Npfs2 QTOAvery DuckworthNo ratings yet
- Estimate Npfs2 PricingDocument52 pagesEstimate Npfs2 PricingAvery DuckworthNo ratings yet
- Estimate Npfs2 PricingDocument52 pagesEstimate Npfs2 PricingAvery DuckworthNo ratings yet
- Project Timeline of Events: Northport Fire Station No. 2Document1 pageProject Timeline of Events: Northport Fire Station No. 2Avery DuckworthNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Programmable Peripheral Interface (8255) Architecture of 8255Document15 pagesProgrammable Peripheral Interface (8255) Architecture of 8255shivaniNo ratings yet
- Simranjeet's ResumeDocument1 pageSimranjeet's ResumeGurjeet kaur RanaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Crimes in IndiaDocument11 pagesCyber Crimes in Indiaanoos04100% (1)
- Diesel Generator Set QSK60 Series Engine: 1760kVA - 2500kVA 50 HZ 1825kW - 2250kW 60 HZDocument4 pagesDiesel Generator Set QSK60 Series Engine: 1760kVA - 2500kVA 50 HZ 1825kW - 2250kW 60 HZ3efooNo ratings yet
- Bim Contract IssuesDocument9 pagesBim Contract IssuesEl ZharNo ratings yet
- Careers Puzzle GuideDocument2 pagesCareers Puzzle Guidepepac41425% (12)
- MRP User GuideDocument691 pagesMRP User GuideZubair KhanNo ratings yet
- User - S Manual of Haiwell Cloud BoxDocument28 pagesUser - S Manual of Haiwell Cloud BoxMOHAMMED AKILNo ratings yet
- ArtiDiag900 BT Sell SheetDocument1 pageArtiDiag900 BT Sell SheetFrancisco MoraNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficient Scheduling of Server With Multi-Sleep Modes For Cloud Data CenterDocument20 pagesEnergy Efficient Scheduling of Server With Multi-Sleep Modes For Cloud Data CenterAnil Kumar GodishalaNo ratings yet
- E AadharDocument1 pageE AadharPranita RathodNo ratings yet
- Meter Comparison Table: Powerlogic Power Monitoring and Control SystemsDocument11 pagesMeter Comparison Table: Powerlogic Power Monitoring and Control SystemsRomi AntonNo ratings yet
- LC-75N8000U User ManualDocument91 pagesLC-75N8000U User ManualtrillianhNo ratings yet
- HP iLO4 Command Line Interface (CLI) Guide and Cheatsheet With Examples - GoLinuxHubDocument15 pagesHP iLO4 Command Line Interface (CLI) Guide and Cheatsheet With Examples - GoLinuxHubAHMED LAAGUIDNo ratings yet
- Phase 1 Diagnostic Review Report PDFDocument175 pagesPhase 1 Diagnostic Review Report PDFWarzer AramNo ratings yet
- ZOOMLION QY25V Truck Crane Technical SpecificationsDocument15 pagesZOOMLION QY25V Truck Crane Technical SpecificationsLi ZhangNo ratings yet
- Project Report: Social Media Marketing As A Tool For Business DevelopmentDocument46 pagesProject Report: Social Media Marketing As A Tool For Business Developmentayushi gargNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 ControllingDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 7 ControllingsyahswiftNo ratings yet
- Digital Signatures Ensure Message AuthenticityDocument9 pagesDigital Signatures Ensure Message AuthenticityAshenafi Abebe DawudNo ratings yet
- Understanding Routing What Is Routing?Document17 pagesUnderstanding Routing What Is Routing?Sanjay Kumar MahanaNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument9 pagesSyllabusNerdNo ratings yet
- Catalog of RBS Honda ListDocument35 pagesCatalog of RBS Honda Listcbaautoparts197No ratings yet
- Jungheinrich Spare Parts List Tool Et v4!37!498!07!2023Document43 pagesJungheinrich Spare Parts List Tool Et v4!37!498!07!2023codysmith231084jsm99% (98)
- Edit and query features offlineDocument4 pagesEdit and query features offlinenagendra reddy panyamNo ratings yet
- Road Map To ISO 14001 2004Document1 pageRoad Map To ISO 14001 2004Budi WibowoNo ratings yet
- Public Health Engineering Department, Haryana Public Health Engineering Division No.2, Panipat Notice Inviting TenderDocument17 pagesPublic Health Engineering Department, Haryana Public Health Engineering Division No.2, Panipat Notice Inviting Tenderpmcmbharat264No ratings yet
- Proguard SFDocument1 pageProguard SFahmedyahea181No ratings yet
- 6 Data StructuresDocument59 pages6 Data StructuresAbraNo ratings yet
- Se Você É Usuário de Programa de Leitura de TelaDocument6 pagesSe Você É Usuário de Programa de Leitura de TelaEverton MaiaNo ratings yet
- Rollback HUAWEI ALE-L21 from Android 6.0 to 5.0Document5 pagesRollback HUAWEI ALE-L21 from Android 6.0 to 5.0Anca Ioana StanciuNo ratings yet