Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PSA Course File - 2016
Uploaded by
Mohammad Tahir Khan NiaziCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PSA Course File - 2016
Uploaded by
Mohammad Tahir Khan NiaziCopyright:
Available Formats
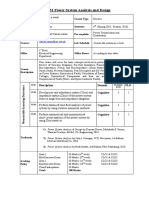
EE451 Power System Analysis & Design
Lecture
Schedule
See Timetable
Semester
7th (Session 2013)
Credit Hours
Three + One
Prerequisites
Power Engineering
Specialization
Instructor(s)
Dr. Faizan Dastgeer
faizan.uetian@gmail.com
Office
Room No. 21
Office Hours
Full time faculty member
Teaching/Lab
Assistant(s)
None
Lab Schedule
See Timetable
This introductory course will cover the basic concepts involved in power system
analysis: Per-Unit Quantities; Bus-Admittance (Ybus) and Bus-Impedance (Zbus)
Course
Description
Matrices, Faults on Power Systems; Symmetrical Faults, Calculation of
Symmetrical-Fault Currents and Voltages, Symmetrical Components and their use
in Unsymmetrical Faults, Unsymmetrical Faults (Short- and Open-Conductor
Faults); and modelling of synchronous machine.
Expected
Outcomes
Textbooks
Upon completion of this course, students will learn
Per unit system
About Ybus and Zbus matrices
The Synchronous Machine and Transformer
Symmetrical Fault Analysis
Symmetrical Components Technique
Unsymmetrical fault analysis
REQUIRED:
Duncan Glover, Mulukutla S. Sarma, Thomas Overbye, Power System
Analysis & Design, 5th Ed., CL-Engineering, 2012
John J. Grainger, W.D. Stevenson, Power System Analysis, McGraw-Hill
Book Co., 1994.
Optional
Grading
Policy
Hadi Saadat, Power System Analysis, 3rd Edition, PSA Publishing, 2010.
Quizzes:
Midterm:
Final:
30%
30%
40%
EE451 Power System Analysis & Design
Lecture Plan
Week
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Topics
Introduction History of power systems, HVDC, transmission line
voltages, Energy generation by fuel type, Computers in power system
engineering etc.
Phasors, Instantaneous power for resistive, inductive and capacitive load.
Real and Reactive power. Balanced Three phase circuits.
Power in balanced three phase circuits. Balanced three phase generators
and motors. Advantages of three phase vs. Single Phase.
Transformers The ideal Transformer. Practical Transformer behavior
Saturation, Inrush Current, Non-sinusoidal exciting current, Surge
Phenomena. The per-unit system.
1st Quiz
Chapter 1
(Glover)
Chapter 2
(Glover)
Chapter 2
(Glover)
Chapter 3
(Glover)
Three Phase transformer connections and phase shift. Per-unit equivalent
circuits. Three winding transformers. Auto-transformers.
Chapter 3
(Glover)
Equivalent Admittance Models, Formation of Bus-Admittance Matrix
(Ybus). Modifications of Ybus and other related topics.
The Bus Impedance Matrice, Thevenins Theorem and Zbus. Modification
of an Existing Zbus, Direct Determination of Zbus.
Series RL circuit transients, Three phase short circuits
Chapter 7
(tentative)
Textbook
Ref.
MID TERM EXAMINATION
The Synchronous Machine Three Phase generation, Synchronous
Reactance and Equivalent Circuits, Real and Reactive power control,
Loading capability diagram.
10
Circuit Breaker and Fuse selection.
11
Symmetrical Components. Sequence networks of impedance loads, series
impedances, Three phase lines.
12
Sequence networks of rotating machines, Three Phase Transformers.
Power in sequence networks. Unsymmetrical Series Impedances.
(Grainger)
Chapter 8
(Grainger)
Chapter 7
(Glover)
Chapter 3
(Grainger)
Chapter 7
(Glover)
Chapter 8
(Glover)
Chapter 8
(Glover)
Chapter 11
(Grainger)
13
2nd Quiz
Unsymmetrical Faults System Representation. Single Line to Ground
Fault. Line-to-Line fault.
14
Double Line to ground Fault. Sequence Bus Impedance Matrices.
15
Open Conductor Faults. Adding and Removing Multiple lines.
(tentative)
Chapter 9
(Glover)
Chapter 9
(Glover)
Chapter 12
Chapter 14
(Grainger)
Final Term Examination
You might also like
- Eee-Vi-power System Analysis and Stability (10ee61) - NotesDocument119 pagesEee-Vi-power System Analysis and Stability (10ee61) - NotesNurul Islam Faruk0% (1)
- Symmetrical Components: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionFrom EverandSymmetrical Components: The Commonwealth and International Library: Applied Electricity and Electronics DivisionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- PSA Notes Unit 3Document45 pagesPSA Notes Unit 3Sandeep AyyagariNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis (ELE3154) : Dr. R.C. MalaDocument12 pagesPower System Analysis (ELE3154) : Dr. R.C. Malapurple thanosNo ratings yet
- Eee-Vi-power System Analysis and Stability (10ee61) - NotesDocument119 pagesEee-Vi-power System Analysis and Stability (10ee61) - Notessrinu24750% (2)
- Eee-Vi-Power System Analysis and Stability (10ee61) - Notes PDFDocument119 pagesEee-Vi-Power System Analysis and Stability (10ee61) - Notes PDFLatisha CarterNo ratings yet
- Optimal Power Systems - Lecture 1 AnnotatedDocument32 pagesOptimal Power Systems - Lecture 1 AnnotatedAhmad AbunassarNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis and Stability Intro Compiled NotesDocument70 pagesPower System Analysis and Stability Intro Compiled NotesAbhishek ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Course Title: Elements of Power System Credit Units: 03 Course CodeDocument4 pagesCourse Title: Elements of Power System Credit Units: 03 Course CodeDs TomNo ratings yet
- IJIRMF201902032Document13 pagesIJIRMF201902032Jill Danica GundranNo ratings yet
- PSA NotesDocument67 pagesPSA NotesPriyankaNo ratings yet
- Course Outline - Power System Analysis - Summer2009-10Document4 pagesCourse Outline - Power System Analysis - Summer2009-10smfuad7526No ratings yet
- EEE F312 Power Systems 2014-15Document3 pagesEEE F312 Power Systems 2014-15Harsha DuttaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Evaluation Between Theoretical Models For Three-Phase Induction Motor Under Voltage UnbalanceDocument6 pagesComparative Evaluation Between Theoretical Models For Three-Phase Induction Motor Under Voltage UnbalanceDante HollandaNo ratings yet
- EE 451 Power System Analysis and Design: Usman - Aslam@uet - Edu.pkDocument2 pagesEE 451 Power System Analysis and Design: Usman - Aslam@uet - Edu.pkMujtaba FarrukhNo ratings yet
- Be - Eee 2011-12Document84 pagesBe - Eee 2011-12nishantsinglas339No ratings yet
- UEE509 General InformationDocument7 pagesUEE509 General InformationAditya AdityaNo ratings yet
- EE 453-Power System Protection and Stability-Mashood NasirDocument4 pagesEE 453-Power System Protection and Stability-Mashood NasirgNo ratings yet
- EE432 Course SyllabusDocument3 pagesEE432 Course SyllabusHabes Nora100% (1)
- Course Outline DocumentDocument2 pagesCourse Outline Documentcicepa3157No ratings yet
- Transformer Internal Faults Simulation: Advances in Electrical and Computer Engineering June 2008Document7 pagesTransformer Internal Faults Simulation: Advances in Electrical and Computer Engineering June 2008Ali AldesogeNo ratings yet
- EE2351Document27 pagesEE2351Anonymous TJRX7C100% (1)
- Power (2) EPM320 L01 13Document15 pagesPower (2) EPM320 L01 13ahmedinaNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis Lecture NotesDocument134 pagesPower System Analysis Lecture NotesHyma GelliNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis 2 MarksDocument35 pagesPower System Analysis 2 MarksSyama ShankarNo ratings yet
- Effects of Unsymmetrical Power Transmission System On The Voltage Balance and Power Flow Capacity of The LinesDocument4 pagesEffects of Unsymmetrical Power Transmission System On The Voltage Balance and Power Flow Capacity of The LinesVaishali MoreNo ratings yet
- Errors in Fault Analysis of Power Distribution Systems Using Sequence Components ApproachDocument6 pagesErrors in Fault Analysis of Power Distribution Systems Using Sequence Components ApproachAbcdNo ratings yet
- Al Hinai2009Document5 pagesAl Hinai2009Lê Trung DũngNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Unbalanced Networks On Synchronous and Asynchronous Machine Transient StabilityDocument9 pagesThe Effects of Unbalanced Networks On Synchronous and Asynchronous Machine Transient StabilitykfaliNo ratings yet
- 9609 PDFDocument13 pages9609 PDFnaghamNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit Currents.Document11 pagesShort Circuit Currents.Shiju Kp.No ratings yet
- EE1352 Monograph UnitIDocument23 pagesEE1352 Monograph UnitIafzalbaigsa100% (2)
- Power System Fault Analysis Using Fault Reporting Data: What Is A Fault?Document5 pagesPower System Fault Analysis Using Fault Reporting Data: What Is A Fault?Sagar AndeNo ratings yet
- Fault Analysis of Power SystemDocument2 pagesFault Analysis of Power SystemHitesh MathurNo ratings yet
- Prerequisites Automation Control EngineeringDocument3 pagesPrerequisites Automation Control EngineeringFombu MuluhNo ratings yet
- P Matlab y Estab TransitDocument4 pagesP Matlab y Estab TransitrdelgranadoNo ratings yet
- EE258 2024 CoursePlan - SubjectedToDUGCapprovalDocument3 pagesEE258 2024 CoursePlan - SubjectedToDUGCapprovalSumukha ShettyNo ratings yet
- M.tech Syllabus Jamia University DelhiDocument1 pageM.tech Syllabus Jamia University Delhidheerajdb99No ratings yet
- Mathematical Calculation and MATLAB Programming of Symmetrical and Asymmetrical Faults in Power SystemDocument4 pagesMathematical Calculation and MATLAB Programming of Symmetrical and Asymmetrical Faults in Power SystemLalbahadur MajhiNo ratings yet
- EE2351 PSA Answers PDFDocument58 pagesEE2351 PSA Answers PDFkrishnandrkNo ratings yet
- Per Unit SystemDocument5 pagesPer Unit SystemJeremy DeleonNo ratings yet
- 7 Sem. B.Tech. EEE: Power System - IiiDocument6 pages7 Sem. B.Tech. EEE: Power System - IiiDIBYANSU RANJAN SAHUNo ratings yet
- Symmetric-Faults-1-1 PresentationDocument22 pagesSymmetric-Faults-1-1 Presentationfilip.porebski69No ratings yet
- Ee8501 QB 2 MarkDocument15 pagesEe8501 QB 2 MarkGLARIDAAMALANo ratings yet
- Electrical Fault Calculation - Positive Negative Zero Sequence ImpedanceDocument8 pagesElectrical Fault Calculation - Positive Negative Zero Sequence ImpedanceMehrdad Nirui100% (1)
- 3 PH Transformer and Generator ModelsDocument11 pages3 PH Transformer and Generator ModelsMansa ManuNo ratings yet
- Deparment of Electrical Engineering: Mirpur University of Science and Technology (Must), MirpurDocument16 pagesDeparment of Electrical Engineering: Mirpur University of Science and Technology (Must), MirpurShehriyar RanaNo ratings yet
- TheoryDocument7 pagesTheoryJosé Pedro MarquesNo ratings yet
- Power Systems-III Ditital NotesDocument102 pagesPower Systems-III Ditital NotesSimranNo ratings yet
- Ee2351 Question BankDocument59 pagesEe2351 Question Banksaran_0666100% (1)
- Advance Electrical Machine LabDocument2 pagesAdvance Electrical Machine LabKhan YousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Unsymmetrical Fault Analysis of 5-Bus Power System Using Powerworld SimulatorDocument12 pagesUnsymmetrical Fault Analysis of 5-Bus Power System Using Powerworld SimulatorcuntNo ratings yet
- Ee 1352 Power System Analysis Question and AnswersDocument7 pagesEe 1352 Power System Analysis Question and AnswersSandhosh RajaNo ratings yet
- Symmetrical and UnsymmetricalDocument8 pagesSymmetrical and Unsymmetricalwillquicksilver04No ratings yet
- Review Paper On Three Phase Fault AnalysisDocument6 pagesReview Paper On Three Phase Fault AnalysisPritesh Singh50% (2)
- Week 4Document18 pagesWeek 4Syed Faras HaiderNo ratings yet
- Power System AnalysisDocument1 pagePower System Analysismuhammad waseemNo ratings yet
- EE423 Fault Analysis NotesDocument26 pagesEE423 Fault Analysis NotesadnanNo ratings yet
- Revista de La Uni On Matem Atica Argentina Volumen 49, N Umero 1, 2008, P Aginas 1-14Document14 pagesRevista de La Uni On Matem Atica Argentina Volumen 49, N Umero 1, 2008, P Aginas 1-14premNo ratings yet
- Command Guidance: Command To Line-Of-Sight (CLOS)Document3 pagesCommand Guidance: Command To Line-Of-Sight (CLOS)Mohammad Tahir Khan Niazi100% (1)
- Cruise MissileDocument106 pagesCruise MissileMohammad Tahir Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- Etymology: Smog Is A Type of AirDocument10 pagesEtymology: Smog Is A Type of AirMohammad Tahir Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- Sir Syed SC Ed School of Excellence Taxila CanttDocument4 pagesSir Syed SC Ed School of Excellence Taxila CanttMohammad Tahir Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Robot, A New Era of InnovationDocument60 pagesAgricultural Robot, A New Era of InnovationMohammad Tahir Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- 19836nb PDFDocument2 pages19836nb PDFMohammad Tahir Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- Ybus LectureDocument8 pagesYbus LectureMohammad Tahir Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines and DrivesDocument123 pagesElectrical Machines and Drivesanon-427532100% (14)
- Power System Analysis: Complex Power, Reactive Compensation, Three PhaseDocument35 pagesPower System Analysis: Complex Power, Reactive Compensation, Three PhaseMohammad Tahir Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 1 PsaDocument21 pagesLecture - 1 PsaMohammad Tahir Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- Agribot: An Agriculture Robot: Vol. 4, Issue 1, January 2015Document3 pagesAgribot: An Agriculture Robot: Vol. 4, Issue 1, January 2015Mohammad Tahir Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- Plant Watering Automation Project DescriptionDocument4 pagesPlant Watering Automation Project DescriptionMohammad Tahir Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- Opt Encoder 62CDocument2 pagesOpt Encoder 62CPeter BirdNo ratings yet
- Interactive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Document19 pagesInteractive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768FeDe Aavina Glez100% (1)
- BYD Bus AmericaDocument213 pagesBYD Bus Americaunyuunyu00100% (1)
- Zener Diode As Voltage RegulatorDocument2 pagesZener Diode As Voltage RegulatorRATONNo ratings yet
- Boat WiringDocument4 pagesBoat WiringRenganathanPadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- Manual For DX-HF-PRO-2-PLUS-T Broadband Portable AntennaDocument2 pagesManual For DX-HF-PRO-2-PLUS-T Broadband Portable AntennaquirxiNo ratings yet
- Harmony XALD XALD03Document3 pagesHarmony XALD XALD03Hansen LaMessiah SaputraNo ratings yet
- Lot (1) - RFQ-Drawing - Bayt As-Sultan H.CDocument20 pagesLot (1) - RFQ-Drawing - Bayt As-Sultan H.CMOHAMMED. HAKAMINo ratings yet
- Acti 9 Catalogue 2012 KSADocument298 pagesActi 9 Catalogue 2012 KSAJabir QuadriNo ratings yet
- Darlington: Silicon NPN Triple Diffused Planar TransistorDocument1 pageDarlington: Silicon NPN Triple Diffused Planar TransistorsilvertronicNo ratings yet
- Manejo Service ToolDocument35 pagesManejo Service ToolClementeNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Static Relays (Switchgear and Protection)Document54 pagesUnit-4 Static Relays (Switchgear and Protection)sujithNo ratings yet
- Angle Modulation PDFDocument129 pagesAngle Modulation PDFSudhanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Chap2 - Transceiver Architectures IDocument30 pagesChap2 - Transceiver Architectures ILong Lê VănNo ratings yet
- Basics of Semiconductor Materials - With NotesDocument57 pagesBasics of Semiconductor Materials - With Notesgourishetty_raveesh100% (1)
- Consumer Electronics Servicing Learning Module 130610203451 Phpapp02Document145 pagesConsumer Electronics Servicing Learning Module 130610203451 Phpapp02Maureen Pusing80% (10)
- Unit - 3 MCQ'sDocument7 pagesUnit - 3 MCQ'srishavr2001No ratings yet
- Solar Renewable EneggyDocument12 pagesSolar Renewable EneggysamyektapolNo ratings yet
- MEE Micro ProjectDocument15 pagesMEE Micro ProjectSanchit BamaneNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument38 pagesUntitledMuhdisa HamdiNo ratings yet
- ZMUX 30 English PDFDocument18 pagesZMUX 30 English PDFUsman AhmadNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Test in Science 5Document8 pages3rd Quarter Test in Science 5Sonny Matias83% (29)
- Operation Manual Transmitter O2 M300Document64 pagesOperation Manual Transmitter O2 M300tayakee_jernNo ratings yet
- TX 500/S TX 1000/S "PLUS SERIES": FM Broadcasting ExciterDocument4 pagesTX 500/S TX 1000/S "PLUS SERIES": FM Broadcasting Exciterguestisor100% (1)
- Jam DigitalDocument4 pagesJam Digitaledi_ragileNo ratings yet
- Gew Project ON: (Electronic Voting Machine)Document26 pagesGew Project ON: (Electronic Voting Machine)Pritish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet 6ED1052-1CC08-0BA0: DisplayDocument2 pagesData Sheet 6ED1052-1CC08-0BA0: DisplayraghuNo ratings yet
- EPX-series Manual Ver 0.9 PDFDocument136 pagesEPX-series Manual Ver 0.9 PDFNguyen TriNo ratings yet
- 34 21 01-1 PDFDocument42 pages34 21 01-1 PDFJames FranklinNo ratings yet
- 7 SegmentDocument7 pages7 SegmentMohammed AlnajjarNo ratings yet