Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Steam Trap Installation Best Practices STL
Uploaded by
Rosyad Broe Caporegime0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
165 views2 pagesSteam Trap
Original Title
Steam Trap Installation Best Practices StL
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSteam Trap
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
165 views2 pagesSteam Trap Installation Best Practices STL
Uploaded by
Rosyad Broe CaporegimeSteam Trap
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
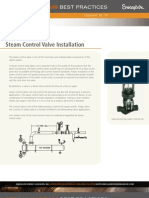
Best Practices for Steam Trap Installation
A steam trap has two major functions: to remove condensate as
quickly as it is formed, and to prevent steam discharge. There
are certain installation faults which negatively impact the ability
for traps to effectively perform these functions efficiently.
A high percentage of steam trap failures are simply due to
incorrect installation.
Proper installation should provide six years of maintenance-free
operation. 16 Best Practices for steam trap installations are
outlined on these pages:
1. The most important rule to remember for steam trap installation is GRAVITY. Condensate must flow from the process to the
steam trap by the forces of gravity. Pressure and velocity cant
be relied on to remove the condensate from the process.
2. Determine the steam leak rate of the new steam traps that
are being purchased per the following leak rate standards:
a.
b.
PTC-39
ISO 7841
All steam traps leak a quantifiable amount of steam and the
consumer should be specifying steam traps with the least
amount of steam loss to prevent unnecessary energy loss.
3. Steam traps with 1 in. or smaller connections should use tubing with tube connectors to eliminate leak points such as
threaded connections.
4. There are steam component manufacturers that have tube
connections available for steam trap installations. Ensure material pressure ratings are acceptable.
5. Never reduce diameter of the tubing/piping before the steam
trap or reduce connection size of the steam trap. Piping from
the process to the steam trap should always be equal to or larger than the process outlet connection. For example, a steam
unit heater with a 1 in. condensate outlet would require a 1 in.
or larger tubing/piping from the unit heater to a same connection size on the steam trap.
2013 Chicago Fluid System Technologies, Swagelok Company
Best Practices for Steam Trap Installation
6. Expand the tube/pipe diameter after the discharge connection of the steam trap. For example, a 1 in. (connection) steam
trap discharge tubing/piping should be increased to 1.25 in or
1.5 in.
7. Steam traps with a connection size of 1 in. or smaller should
be connected to the tubing or piping with universal mounts.
The universal mount provides the ability to connect the steam
trap to the application with two bolts, thus dramatically reducing the time for installation of a steam trap.
15. Develop and maintain installation standards for all applications.
16. Codes:
a. Material test reports on all components (steam
traps, connection devices, etc.)
b. B31.1 Piping code
8. Install a strainer as part of the installation of a steam trap.
The strainer can be accomplished by the following:
a. External strainer ahead of the steam trap
b. Steam trap with integral strainer
c. Universal mount with an integral strainer
The use of a strainer will eliminate or reduce premature failures
of steam trap due to corrosion.
9. When installing an external or internal strainer always install
a blow-off valve on the strainer. This allows the strainer to be
blown down during operation, and permits the steam trap cavity to be safely depressurized during servicing.
10. Always install the steam trap in a location that is accessible
by plant personnel.
Contact us
11. Install a visual indication of the steam trap performance on
all process applications. The visual indication can be a sight
glass or test valve.
12. Locate the steam trap below the lowest condensate discharge point of the equipment.
Email: info@swstlouisswagelok.com
Phone: 314.880.8900
Follow us
13. Never install a rise in the pipe ahead of a steam trap.
14. Check valves should be installed after the steam traps in
most applications.
2013 Chicago Fluid System Technologies, Swagelok Company
You might also like
- Pressure Vessel Costly MistakeDocument11 pagesPressure Vessel Costly MistakearjayNo ratings yet
- What Is Risk Based InspectionDocument39 pagesWhat Is Risk Based InspectionobuseNo ratings yet
- Pulsation Suppression Device Design For Reciprocating CompressorDocument9 pagesPulsation Suppression Device Design For Reciprocating CompressorAlfred LamNo ratings yet
- 10 Steps To Pump ReliabilityDocument15 pages10 Steps To Pump ReliabilityaqhammamNo ratings yet
- How To Identify The Right Scope For A Turnaround: Colin Xander Corporate Turnaround ManagerDocument12 pagesHow To Identify The Right Scope For A Turnaround: Colin Xander Corporate Turnaround ManagerEuclides PrietoNo ratings yet
- Improved Analysis of External Loads On Flanged JointsDocument1 pageImproved Analysis of External Loads On Flanged JointsTiHoRNo ratings yet
- 01 SAIP 02 - Retirement Thickness PDFDocument6 pages01 SAIP 02 - Retirement Thickness PDFAbdelrahman HosnyNo ratings yet
- Non-Dimensional Aerodynamic Design of A Centrifugal Compressor ImpellerDocument12 pagesNon-Dimensional Aerodynamic Design of A Centrifugal Compressor ImpellerSubhash PadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- Unlocking Weibull AnalysisDocument13 pagesUnlocking Weibull AnalysisVirojana TantibadaroNo ratings yet
- Living with Defects: FFS Assessment Optimizes Plant Asset IntegrityDocument16 pagesLiving with Defects: FFS Assessment Optimizes Plant Asset IntegrityNatraji100% (1)
- Piping ClassDocument2 pagesPiping ClassDylan RamasamyNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Design and Analysis of Tube Sheet Thickness by Using Uhx Code-2/comparison of Design and Analysis of Tube Sheet Thickness by Using Uhx Code-2 PDFDocument13 pagesComparison of Design and Analysis of Tube Sheet Thickness by Using Uhx Code-2/comparison of Design and Analysis of Tube Sheet Thickness by Using Uhx Code-2 PDFruponline1No ratings yet
- Calculation Methods For Thick Walled Components Under Creep Fatigue - Review and Advanced ConceptsDocument9 pagesCalculation Methods For Thick Walled Components Under Creep Fatigue - Review and Advanced ConceptsMarcus BaltesNo ratings yet
- TH10 - Pipe Loop or Expansion JointsDocument3 pagesTH10 - Pipe Loop or Expansion JointsloukatsNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Risk Management Basic ManualDocument6 pagesPipeline Risk Management Basic ManualhemnNo ratings yet
- APGA Code of Practice For Upstream PE Gathering Lines in The CSG IndustryDocument174 pagesAPGA Code of Practice For Upstream PE Gathering Lines in The CSG Industrydamian o'connorNo ratings yet
- Piping Plan Pocket PalDocument66 pagesPiping Plan Pocket PalmflorespazosNo ratings yet
- Of The Nuclear Safety Standards Commission (KTA)Document161 pagesOf The Nuclear Safety Standards Commission (KTA)pradeepajadhavNo ratings yet
- Reduce Flare System Failure with Vibration AnalysisDocument2 pagesReduce Flare System Failure with Vibration Analysissri9987No ratings yet
- Piping EngineeringDocument2 pagesPiping EngineeringSuvidya Institute of TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Spare Part Management: Classification and Decision ModelsDocument24 pagesSpare Part Management: Classification and Decision ModelsGunawan SanjayaNo ratings yet
- Process Industry Practices Vessels: PIP VEFV6100 Vessels/S&T Heat Exchangers Internals DetailsDocument4 pagesProcess Industry Practices Vessels: PIP VEFV6100 Vessels/S&T Heat Exchangers Internals Detailsmsaldivar177No ratings yet
- CRN PipingDocument12 pagesCRN PipinggoalgoalNo ratings yet
- To Rerate or Not To RerateDocument6 pagesTo Rerate or Not To ReratekblaxtonNo ratings yet
- Effect of Gap Between Pad and Vessel For Moment Loading On NozzleDocument7 pagesEffect of Gap Between Pad and Vessel For Moment Loading On NozzleRiccardo CozzaNo ratings yet
- Caesar II Enhancement ListDocument16 pagesCaesar II Enhancement Listr_surya05No ratings yet
- TR 110996Document117 pagesTR 110996Subhadip SadhukhanNo ratings yet
- Technical Notes (General Specification) FOR Valves (Gate, Globe, Check, Ball, Plug, Needle, Butterfly & Piston Valves)Document30 pagesTechnical Notes (General Specification) FOR Valves (Gate, Globe, Check, Ball, Plug, Needle, Butterfly & Piston Valves)jayakumar100% (1)
- PipingDocument4 pagesPipingramthecharm_46098467No ratings yet
- h2 E3 Test Station Version 1 Om ManualDocument90 pagesh2 E3 Test Station Version 1 Om Manualgeorge_zouridisNo ratings yet
- Upload A Document To Access Your Download: API 617 Centrifugal CompressorDocument3 pagesUpload A Document To Access Your Download: API 617 Centrifugal CompressorM Richard MenarizkiNo ratings yet
- Valves Shell Design StrengthDocument10 pagesValves Shell Design Strengthمحمد عبدالدايمNo ratings yet
- A Guide To The ANSI Z358.1-2009 StandardDocument3 pagesA Guide To The ANSI Z358.1-2009 Standardwatson123No ratings yet
- Jeida Farm Supply Corporation Catalog 2014Document10 pagesJeida Farm Supply Corporation Catalog 2014Taj Deluria100% (3)
- Application of Moment Restraining Supports in Process Plant Critical Piping-Full Paper-2019 PDFDocument5 pagesApplication of Moment Restraining Supports in Process Plant Critical Piping-Full Paper-2019 PDFPratip BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- 5-16-4 Steam Turbines: Standard SpecificationDocument3 pages5-16-4 Steam Turbines: Standard SpecificationzsmithNo ratings yet
- 10 Steps To Asset CareDocument13 pages10 Steps To Asset CareDamianNo ratings yet
- CP-208 Rev.1.0 Corrosion Management Code of Practice (Jul-12)Document33 pagesCP-208 Rev.1.0 Corrosion Management Code of Practice (Jul-12)sjs23plusNo ratings yet
- QR2 - Mechanical Maintenance Question RecordDocument2 pagesQR2 - Mechanical Maintenance Question RecordMicky PlumbNo ratings yet
- Modeling Spring Cans With FrictionDocument1 pageModeling Spring Cans With FrictionKirana SbNo ratings yet
- Print Article - How To Model A Vacuum Breaker Using PIPE-FLODocument7 pagesPrint Article - How To Model A Vacuum Breaker Using PIPE-FLORafyss RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Steam Jet Spindle Operated ThermocompressorDocument3 pagesSteam Jet Spindle Operated ThermocompressorjfejfeNo ratings yet
- KF Ball Valve M3 Series Ball ValveDocument18 pagesKF Ball Valve M3 Series Ball ValveBureau VeritasNo ratings yet
- Guide Estimates Flaring and Venting Volumes from Oil and Gas FacilitiesDocument59 pagesGuide Estimates Flaring and Venting Volumes from Oil and Gas FacilitiesSakhibNo ratings yet
- Steam Piping in Ammonia Plant at NFCLDocument28 pagesSteam Piping in Ammonia Plant at NFCLVenkatesh VakalapudiNo ratings yet
- Classification of Shell Stresses Resulting From Piping Nozzle LoadsDocument4 pagesClassification of Shell Stresses Resulting From Piping Nozzle LoadsozkanhasanNo ratings yet
- Petronas Technical Standards: Piping Classes - Refining and ChemicalsDocument63 pagesPetronas Technical Standards: Piping Classes - Refining and ChemicalsĐạt TrầnNo ratings yet
- LNG and Low Temperature Gas StorageDocument32 pagesLNG and Low Temperature Gas StoragemiladiiiNo ratings yet
- In-service Condition Monitoring of Piping SystemsDocument13 pagesIn-service Condition Monitoring of Piping Systemsamirreza_eng3411No ratings yet
- Imece2014 38164 PDFDocument9 pagesImece2014 38164 PDFYemane TesfayeNo ratings yet
- M-630 Material Data Sheets For PipingDocument85 pagesM-630 Material Data Sheets For Pipingsun2meltNo ratings yet
- ACC FAC and Cycle Chemistry SessionDocument37 pagesACC FAC and Cycle Chemistry Sessionchemicalchouhan9303No ratings yet
- IGC Doc 127-13-E Revision of Doc 127-04-EDocument35 pagesIGC Doc 127-13-E Revision of Doc 127-04-Elutfirashid87No ratings yet
- Ad CDZZZZ Pi Spe 0062 000 PDFDocument26 pagesAd CDZZZZ Pi Spe 0062 000 PDFKamal AliyevNo ratings yet
- Proceedings of the Twelfth International Cryogenic Engineering Conference Southampton, UK, 12–15 July 1988From EverandProceedings of the Twelfth International Cryogenic Engineering Conference Southampton, UK, 12–15 July 1988R. G. ScurlockNo ratings yet
- Steam System Best Practices Document No. 5 Steam Trap InstallationDocument2 pagesSteam System Best Practices Document No. 5 Steam Trap InstallationDxtr MedinaNo ratings yet
- Best Practices For Steam Control Valve InstallationDocument4 pagesBest Practices For Steam Control Valve InstallationBen MusimaneNo ratings yet
- Steam Generator Steam Generator: Quality of LifeDocument29 pagesSteam Generator Steam Generator: Quality of LifeMiguel DexsNo ratings yet
- Best Practices For Steam Control Valve InstallationDocument4 pagesBest Practices For Steam Control Valve InstallationYasmin.Shunmugam4188No ratings yet
- XB 13 InstallDocument8 pagesXB 13 InstalljbozakNo ratings yet
- NGSTECH 2008 Sample System Best Practices For Water and Hydrocarbon DP ApplicationsDocument4 pagesNGSTECH 2008 Sample System Best Practices For Water and Hydrocarbon DP ApplicationsMahesh DivakarNo ratings yet
- Piping Punch List Quality Control and Inspection Form PDFDocument1 pagePiping Punch List Quality Control and Inspection Form PDFRosyad Broe CaporegimeNo ratings yet
- Norsok R-004Document30 pagesNorsok R-004Tor MoxnesNo ratings yet
- 00 MarcusDocument10 pages00 MarcusRosyad Broe CaporegimeNo ratings yet
- Flowsheet Packing Plan Alt2 Ok WarnaDocument1 pageFlowsheet Packing Plan Alt2 Ok WarnaRosyad Broe CaporegimeNo ratings yet
- Storage Tanks: Fixed or Semi-Fixed SystemsDocument9 pagesStorage Tanks: Fixed or Semi-Fixed SystemsCarlos SalazarNo ratings yet
- Ipsmg PL DWG 002Document4 pagesIpsmg PL DWG 002Rosyad Broe CaporegimeNo ratings yet
- CFN 1000 PDFDocument12 pagesCFN 1000 PDFSudherson JagannathanNo ratings yet
- ByPass Valve Burner ModelDocument1 pageByPass Valve Burner ModelRosyad Broe CaporegimeNo ratings yet
- Hydrotest Foreman Job DescriptionDocument2 pagesHydrotest Foreman Job DescriptionRosyad Broe CaporegimeNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Motion Control Calculations, CB840, SpoolingDocument2 pagesMathcad - Motion Control Calculations, CB840, SpoolingL. A. WillisNo ratings yet
- 感應馬達安裝、保養使用說明書31057H402E (英)Document17 pages感應馬達安裝、保養使用說明書31057H402E (英)Rosyad Broe CaporegimeNo ratings yet
- Piping PDFDocument46 pagesPiping PDFGORO43100% (1)
- To STI 110114propagation Tank General Drawing - 1Document1 pageTo STI 110114propagation Tank General Drawing - 1Rosyad Broe CaporegimeNo ratings yet
- To STI 110114propagation Tank General Drawing - 1Document1 pageTo STI 110114propagation Tank General Drawing - 1Rosyad Broe CaporegimeNo ratings yet
- 04 PPP TTE API 570 Piping InspnDocument35 pages04 PPP TTE API 570 Piping InspnRosyad Broe CaporegimeNo ratings yet
- To STI 110113ammonium Sulfate Dissolving Tank Assembly - 1Document1 pageTo STI 110113ammonium Sulfate Dissolving Tank Assembly - 1Rosyad Broe CaporegimeNo ratings yet
- To STI 110117propatation Tank Foudation Plan - 1Document1 pageTo STI 110117propatation Tank Foudation Plan - 1Rosyad Broe CaporegimeNo ratings yet
- Class 150 & 300 Steel Pipe Flange Bolt Sizes & Patterns in 38 charactersDocument2 pagesClass 150 & 300 Steel Pipe Flange Bolt Sizes & Patterns in 38 characterskh88hmiNo ratings yet
- FormulaDocument37 pagesFormulaRosyad Broe CaporegimeNo ratings yet
- Autodwg PDF To DWG Converter User Guide: ContentDocument9 pagesAutodwg PDF To DWG Converter User Guide: ContentRosyad Broe CaporegimeNo ratings yet
- KS2-Design of Pressure VesselsDocument12 pagesKS2-Design of Pressure VesselsArul Kumaran KothandapaniNo ratings yet
- Piping Workbook PIDesignDocument73 pagesPiping Workbook PIDesignUrsula MoeringsNo ratings yet
- BFD General EnglDocument7 pagesBFD General EnglRosyad Broe CaporegimeNo ratings yet
- Piping PDFDocument46 pagesPiping PDFGORO43100% (1)
- Tabla de Esparragos para BridasDocument5 pagesTabla de Esparragos para BridasMaximiliano García CalderónNo ratings yet
- SMC ActuatorDocument128 pagesSMC ActuatorRosyad Broe CaporegimeNo ratings yet
- 07 - (4th Civil) (Tanks) Elevated TankDocument196 pages07 - (4th Civil) (Tanks) Elevated TankRosyad Broe CaporegimeNo ratings yet
- MP2000-104A - Installation & Web Configuration ManualDocument110 pagesMP2000-104A - Installation & Web Configuration ManualwaqkhanNo ratings yet
- Nieco Modelo 1424G PDFDocument26 pagesNieco Modelo 1424G PDFAbimael AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Standards Manual - Welding Standards M Anual - Volume 3 Welding Procedure SpecificationsDocument3 pagesEngineering Standards Manual - Welding Standards M Anual - Volume 3 Welding Procedure Specificationslaz_k50% (2)
- Slackware PKG PresentationDocument33 pagesSlackware PKG PresentationAlexandru-Marian CiotlosNo ratings yet
- IKEA Home Planner3Document9 pagesIKEA Home Planner3Cameron Michael FehringNo ratings yet
- Wika LMB Eng Ik CCB Hvac 01Document22 pagesWika LMB Eng Ik CCB Hvac 01riyadigeng19gmailcomNo ratings yet
- SAP HANA Security Introduction: Key Concepts & FeaturesDocument34 pagesSAP HANA Security Introduction: Key Concepts & FeaturesSachin Deo100% (1)
- File BerjanjiDocument23 pagesFile Berjanjihartanto harisNo ratings yet
- Block Work Masonry MethodologyDocument4 pagesBlock Work Masonry MethodologyEyutt HghghNo ratings yet
- Vertical Pumps 50hz PDFDocument36 pagesVertical Pumps 50hz PDFSameeh KaddouraNo ratings yet
- Manual VDF ABB ACS580-01 - Drives - HW - C - A5 PDFDocument218 pagesManual VDF ABB ACS580-01 - Drives - HW - C - A5 PDFMorro DelArrabalNo ratings yet
- Integration EVS AvidTM V4.3 PDFDocument113 pagesIntegration EVS AvidTM V4.3 PDFLaurentiu IacobNo ratings yet
- Comparing Local Architectural PracticesDocument2 pagesComparing Local Architectural PracticesChan LHgNo ratings yet
- Bhopal CircleDocument18 pagesBhopal CircleChristina HarmonNo ratings yet
- Shura IslandDocument7 pagesShura IslandMohamed ElbanaNo ratings yet
- LetsLearn3Gin10Days KamalVij PDFDocument397 pagesLetsLearn3Gin10Days KamalVij PDFIshraq Khurshid100% (4)
- 50 Liberty / Fan Pier: BCDC Presentation 4/2015Document17 pages50 Liberty / Fan Pier: BCDC Presentation 4/2015The Fort PointerNo ratings yet
- Schneider Electric OKKEN IntroductionDocument26 pagesSchneider Electric OKKEN IntroductionDuško TovilovićNo ratings yet
- Aggregate For Single or Multiple Bituminous Surface TreatmentsDocument3 pagesAggregate For Single or Multiple Bituminous Surface TreatmentsrajithfernandoNo ratings yet
- Flash IIP Installation Guide 8-26-14Document10 pagesFlash IIP Installation Guide 8-26-14label engineering companyNo ratings yet
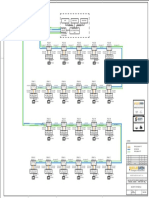
- Bsl1-Ele-032 Security System SLD .Rev 0Document1 pageBsl1-Ele-032 Security System SLD .Rev 0jdzarzalejoNo ratings yet
- Epsilon BrochureDocument8 pagesEpsilon BrochureAbdul Bijur VallarkodathNo ratings yet
- Artopex Classic Conference BrochureDocument9 pagesArtopex Classic Conference Brochuredomzrn6No ratings yet
- Carpentry and Joinery Material Prices in Addis AbabaDocument2 pagesCarpentry and Joinery Material Prices in Addis AbabaAmos KormeNo ratings yet
- 5040 Tally Passbook PrinterDocument4 pages5040 Tally Passbook PrinterReki BudimanNo ratings yet
- Register 7 - Iu Interface User Plane Protocols PDFDocument62 pagesRegister 7 - Iu Interface User Plane Protocols PDFVishal Batra100% (1)
- ClinicDocument108 pagesClinicSurendra ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Bdix Server ListDocument3 pagesBdix Server ListIftekhar Rahman RihamNo ratings yet
- 005-Sample Method Statement CivilDocument2 pages005-Sample Method Statement CivilS.C.Satish Chander100% (1)
- VLAN and Link-Aggregation Interoperability ArubaOS-switch and Cisco IOSDocument8 pagesVLAN and Link-Aggregation Interoperability ArubaOS-switch and Cisco IOSel97639No ratings yet