Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notebook 15
Uploaded by
api-3386617480 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views2 pagesOriginal Title
notebook 15
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views2 pagesNotebook 15
Uploaded by
api-338661748Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Notebook 15
Sammy Puccini
Step 1: Turn on generator to start electricity
-Electricity goes through the line compensator
Step 2: After the line compensator, it goes through the main breaker
-Where the alternating current comes from to power the circuit.
Step 3: Press the exposure switch
-This closes the circuit to start the exposure.
Step 4: Then the circuit goes to the autotransformer
-Where kVp is adjusted
Step 5: Then it goes through the high-voltage step-up transformer
-Voltage goes up so that the x-ray tube has very high voltage to create the
potential difference between anode and cathode
Step 6: Then it travels through the four-diode rectification circuit
-This makes the current only go in one direction through the x-ray tube
- it then goes back to the autotransformer and eventually to the filament circuit
Step 7: Then through the filament circuit variable resistor
-Adjusts the current going to the filament. (mA setting)
Step 8: Next the circuit goes though the filament step-down transformer
-Steps the voltage down and therefore the current increases to cause build up of
electrons
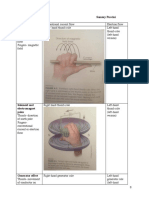
Step 9: Then to the x-ray tube
-This is where the x-rays are created.
Step 10: In the cathode of the x-ray tube the electrons go to the filament.
-The filament provides resistance to electrons to form a thermionic cloud
-When high voltage is released at exposure the cloud can be driven to the anode
target
- This is a small coil of thin thoriated tungsten wire
-At the console a large or small filament wire is chosen. Larger wire will create a
larger focal spot and smaller wire will create a smaller focal spot.
Step 11: The thermionically emitted electrons are forced in the focusing cup with its low
negative potential, this and its shape focuses the electrons in a convergence pattern.
-Focusing cup is a metal cup that filaments are embedded into
-This does not allow them to spread apart and focuses them to the target
21
Step 12: At the anode electrons are received from cathode
-X-rays are generated when electrons from the filament cross the tube and interact
with the target
-This conducts them through to connecting cables and back to high voltage
generator, provides mechanical support for target, and efficiently removes heat. Primarily
tungsten
Step 17: Current is sent to the stator (an electromagnetic induction motor), which then
causes the rotor to turn the anode.
-A rotating anode gives a larger target area
Step 13: At the target of the anode x-ray photons are created
-Focal spot is where electron beam will actually hit
-Line focus principle is sued to reduce the effect area of the focal spot
-The effective area is the area of the focal spot that is projected out of the tube
toward the object being radiographed
Step 14: In the target interactions electrons transfer kinetic energy to outer shell electrons
of target atoms, which causes them to emit infrared radiation because of vibration- heat
Step 15: The majority of the x-rays produced at the target are Bremsstrahlung x-rays.
-Incident electrons interact with the electrostatic force field of nucleus
-High-speed electrons from the filament are slowed down as they pass close to the
nuclei of the target atoms.
Step 16: The last of the electrons cause characteristic interactions
-Incident electron interacts with K-shell electron- incident electron continues in
slightly different direction
- A high-speed electron from the filament collide with an electron in the orbit of
the target atom, the electron is knocked out of its orbit, creating an open space. An
electron from an outer orbit then fills this space, when the electron drops, energy is
released as a characteristic x-ray
Step 17: Current is sent to the stator, which then causes the rotor to turn the anode
Step 18: In the envelope the x-ray beam exits through the window
Step 19: The tube housing absorbs any unwanted photons
Step 20: X-ray beam diverges and spreads out as it travels toward and through the patient
Step 21: As x-ray passes through more dense materials they will be absorbed more, and
less dense tissue (like skin) absorb less.
22
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Notebook 12Document3 pagesNotebook 12api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 10Document7 pagesNotebook 10api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 8Document2 pagesNotebook 8api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 4Document2 pagesNotebook 4api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 1Document4 pagesNotebook 1api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 3Document2 pagesNotebook 3api-338661748No ratings yet
- Test Tolerance Limits Frequency & Exceptions Performed by Explain Purpose Diagnostic Radiographic SystemsDocument5 pagesTest Tolerance Limits Frequency & Exceptions Performed by Explain Purpose Diagnostic Radiographic Systemsapi-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 7Document2 pagesNotebook 7api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 9 Sammy Puccini Artifact Causes Appearance Dirt On Optics (Lenses, Mirror, and Light Guide Not Cleaned Horizontal White LinesDocument4 pagesNotebook 9 Sammy Puccini Artifact Causes Appearance Dirt On Optics (Lenses, Mirror, and Light Guide Not Cleaned Horizontal White Linesapi-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 6Document2 pagesNotebook 6api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 2Document4 pagesNotebook 2api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 5Document2 pagesNotebook 5api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 14Document2 pagesNotebook 14api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 16Document3 pagesNotebook 16api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 11Document1 pageNotebook 11api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 12Document1 pageNotebook 12api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 10Document2 pagesNotebook 10api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 13Document1 pageNotebook 13api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 9Document1 pageNotebook 9api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 8Document1 pageNotebook 8api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 4Document2 pagesNotebook 4api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 7Document1 pageNotebook 7api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 2Document1 pageNotebook 2api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 5Document3 pagesNotebook 5api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 3Document2 pagesNotebook 3api-338661748No ratings yet
- Notebook 1Document2 pagesNotebook 1api-338661748No ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Jupiter - The Giant Planet That Destroys CometsDocument2 pagesJupiter - The Giant Planet That Destroys Cometsmaiche amarNo ratings yet
- 2 Acceleration Questions and AnswersDocument2 pages2 Acceleration Questions and Answersapi-272986951100% (2)
- Critical Thinking Chapter 9Document23 pagesCritical Thinking Chapter 9Desny LêNo ratings yet
- Basic Facts For Homebooks Stage 7Document3 pagesBasic Facts For Homebooks Stage 7api-311857762No ratings yet
- List of SDAsDocument4 pagesList of SDAsAthouba SagolsemNo ratings yet
- World MultipleDocument271 pagesWorld MultipleatrkpoleNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Thermodynamics 1Document28 pages1.1 Thermodynamics 1Lyan SantosNo ratings yet
- GulliverDocument8 pagesGulliverCris LuNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Heisenberg Groups in Analysis and GeometryDocument7 pagesAn Introduction to Heisenberg Groups in Analysis and Geometrynitrosc16703No ratings yet
- Global Financial Reporting Convergence: A Study of The Adoption of International Financial Reporting Standards by The Swedish Accountancy ProfessionDocument21 pagesGlobal Financial Reporting Convergence: A Study of The Adoption of International Financial Reporting Standards by The Swedish Accountancy Professionihda0farhatun0nisakNo ratings yet
- Ajp Microproject ReportDocument9 pagesAjp Microproject ReportRushikesh KanseNo ratings yet
- IC-V80 V80E ManualDocument64 pagesIC-V80 V80E Manualrzkyln100% (1)
- ME1001, ME1004, ME1005 - Basic Mech+Graphics+Workshop Pract.Document6 pagesME1001, ME1004, ME1005 - Basic Mech+Graphics+Workshop Pract.Mayank AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Mascot LD series hydraulic motor specsDocument6 pagesMascot LD series hydraulic motor specsM S GokulNo ratings yet
- QY25K5-I Technical Specifications (SC8DK280Q3)Document11 pagesQY25K5-I Technical Specifications (SC8DK280Q3)Everton Rai Pereira Feireira100% (1)
- A6V12050595 - Valve Actuator DIL-Switch Characteristic Overview - deDocument42 pagesA6V12050595 - Valve Actuator DIL-Switch Characteristic Overview - depolo poloNo ratings yet
- Katja Kruckeberg, Wolfgang Amann, Mike Green-Leadership and Personal Development - A Toolbox For The 21st Century Professional-Information Age Publishing (2011)Document383 pagesKatja Kruckeberg, Wolfgang Amann, Mike Green-Leadership and Personal Development - A Toolbox For The 21st Century Professional-Information Age Publishing (2011)MariaIoanaTelecan100% (1)
- 5R Invention Activity: Science LabDocument12 pages5R Invention Activity: Science LabricardoNo ratings yet
- Hardware Devices Used in Virtual Reality TechnologiesDocument6 pagesHardware Devices Used in Virtual Reality TechnologiesTheMoon LightNo ratings yet
- LADY BroshureDocument2 pagesLADY BroshureMcGabi GabrielNo ratings yet
- Writing Emails Part 1 Informal British English Teacher Ver2Document7 pagesWriting Emails Part 1 Informal British English Teacher Ver2Madalina MandiucNo ratings yet
- DLP IN ICT 9 1st MeetingDocument2 pagesDLP IN ICT 9 1st MeetingHEDDA FULONo ratings yet
- Obeid Specialized Hospital - Riyadh: Inpatient DeptsDocument4 pagesObeid Specialized Hospital - Riyadh: Inpatient DeptsLovelydePerioNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual Series 854 XTG Level GaugeDocument60 pagesInstruction Manual Series 854 XTG Level GaugeJandri JacobNo ratings yet
- IBM Release Notes - IBM SPSS Statistics 21.0 - United States PDFDocument3 pagesIBM Release Notes - IBM SPSS Statistics 21.0 - United States PDFraj sharmaNo ratings yet
- Ayurveda Signs of LifeDocument15 pagesAyurveda Signs of LifeSanjeethNo ratings yet
- Kerala University 2013 Admission ProspectusDocument50 pagesKerala University 2013 Admission ProspectusMuneer SainulabdeenNo ratings yet
- OSC - 2015 - Revised - Oct (Power Cables) PDFDocument118 pagesOSC - 2015 - Revised - Oct (Power Cables) PDFIván P. MorenoNo ratings yet
- Renal Angina Index in Pediatric Septic Patients As A Predictor of Acute Kidney Injury in Remote AreaDocument9 pagesRenal Angina Index in Pediatric Septic Patients As A Predictor of Acute Kidney Injury in Remote AreaFarhanNo ratings yet
- CBL Training ReportDocument12 pagesCBL Training ReportSwapnil Modak100% (1)