Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Explanation of Lenz's Law: Case-I
Uploaded by
MCHOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Explanation of Lenz's Law: Case-I
Uploaded by
MCHCopyright:
Available Formats
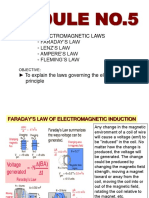
Explanation of Lenz's Law
For understanding Lenz's law, consider two cases :
CASE-I When a magnet is moving towards the coil.
When the north pole of the magnet is approaching towards the coil,
the magnetic flux linking to the coil increases.
According to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, when there
is change in flux, an emf and hence current is induced in the coil
and this current will create its own magnetic field.
Now according to Lenz's law, this magnetic field created will oppose
its own or we can say opposes the increase in flux through the coil
and this is possible only if approaching coil side attains north
polarity, as we know similar poles repel each other.
Once we know the magnetic polarity of the coil side, we can easily
determine the direction of the induced current by applying right
hand rule.
In this case, the current flows in anticlockwise direction.
CASE-II When a magnet is moving away from the coil
When the north pole of the magnet is moving away from the coil,
the magnetic flux linking to the coil decreases.
According to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, an emf and
hence current is induced in the coil and this current will create its
own magnetic field.
Now according to Lenz's law, this magnetic field created will oppose
its own or we can say opposes the decrease in flux through the coil
and this is possible only if approaching coil side attains south
polarity, as we know dissimilar poles attract each other.
Once we know the magnetic polarity of the coil side, we can easily
determine the direction of the induced current by applying right
hand rule.
In this case, the current flows in clockwise direction.
You might also like
- Practice Sheet Calculating DensityDocument2 pagesPractice Sheet Calculating Densityapi-2856984310% (2)
- Linear Expanison Worksheet (Key)Document3 pagesLinear Expanison Worksheet (Key)MCH100% (7)
- Lenz Law For DCDocument5 pagesLenz Law For DCGenette AringoNo ratings yet
- Lenz Law...Document6 pagesLenz Law...MuhammadAsyrafNo ratings yet
- Lenz LawDocument4 pagesLenz LawWilliam Simms0% (1)
- Electromagnetic Induction ExplainedDocument3 pagesElectromagnetic Induction ExplainedAli HamzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Magnetic Induction, Inductance, Ac and LC CircuitsDocument13 pagesChapter 7 Magnetic Induction, Inductance, Ac and LC CircuitsShara TayonaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument21 pagesElectromagnetic InductionParth GuptaNo ratings yet
- Written Report: (Magnetism)Document34 pagesWritten Report: (Magnetism)Jasmine DataNo ratings yet
- Submitted By:-Name: - Mandeep Dhiman ROLL NO.: - 24 SECTION: - B4802 Course: - B.Tech (Me) - MbaDocument7 pagesSubmitted By:-Name: - Mandeep Dhiman ROLL NO.: - 24 SECTION: - B4802 Course: - B.Tech (Me) - Mbashailesh singhNo ratings yet
- Fundacom SRPDocument45 pagesFundacom SRPSaurabhPrasadNo ratings yet
- Padhle 10th - Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument30 pagesPadhle 10th - Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentBitan DasNo ratings yet
- ATPL Inst 2.1 PDFDocument8 pagesATPL Inst 2.1 PDFKoustubh VadalkarNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - DC MachDocument8 pagesModule 5 - DC MachNoel BactonNo ratings yet
- FaradayDocument14 pagesFaradayVarad KakodkarNo ratings yet
- Electromagnatic InductionDocument2 pagesElectromagnatic InductionSouvik ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Induced EmfDocument5 pagesInduced Emftajju_121No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument13 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Currentdrphysics256No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument21 pagesElectromagnetic InductionEs ENo ratings yet
- Some Basic Principle of MagnetismDocument2 pagesSome Basic Principle of MagnetismAce Matthew100% (1)
- 11.2.1 Lenzs Law Part 1Document7 pages11.2.1 Lenzs Law Part 1FishBowl GangNo ratings yet
- Identifying Poles Of An Electromagnet:: Emf = −Dnϕ DtDocument3 pagesIdentifying Poles Of An Electromagnet:: Emf = −Dnϕ DtIntiser RahmanNo ratings yet
- Electromgnetic InductionDocument5 pagesElectromgnetic InductionGhanshyam SinghNo ratings yet
- Basic Electricity 4Document6 pagesBasic Electricity 4anuradhaNo ratings yet
- DOWLATH Soln MAGNETISMDocument26 pagesDOWLATH Soln MAGNETISMRuqayya ImranNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction LecturesDocument9 pagesElectromagnetic Induction LecturesDoyen DanielNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction: Experiment 1Document13 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: Experiment 1midhunesh41No ratings yet
- Notes For Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument9 pagesNotes For Magnetic Effects of Electric Currenttanishq.sonar03No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument13 pagesElectromagnetic InductionRanjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - Class 10Document6 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric Current - Class 10rachna chhabraNo ratings yet
- ElectroMagnetic InductionDocument8 pagesElectroMagnetic InductionRobin Singh100% (1)
- Magnetic Effects of Ec-Part1Document6 pagesMagnetic Effects of Ec-Part1Prisoner FFNo ratings yet
- Phy Topic 2 F4Document12 pagesPhy Topic 2 F4Kandrossy GlassNo ratings yet
- Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic InductionDocument16 pagesFaraday's Law of Electromagnetic InductionPawan TiwariNo ratings yet
- Phy - Magnetic Effects of Current WsDocument11 pagesPhy - Magnetic Effects of Current Wsburramokshitha88No ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of CurrentDocument7 pagesMagnetic Effect of CurrentgoyalnahveNo ratings yet
- 4th General Physics 2 (Week 1-2)Document38 pages4th General Physics 2 (Week 1-2)Darious PenillaNo ratings yet
- Fleming Left Hand RuleDocument4 pagesFleming Left Hand RuleFatyn AlawiNo ratings yet
- EMO Project Perposal 062 055 079Document4 pagesEMO Project Perposal 062 055 079Nassr KhanNo ratings yet
- Elect Roma Gneti SM: How Electric Current Produce A Magnetic FieldDocument8 pagesElect Roma Gneti SM: How Electric Current Produce A Magnetic FieldIsmail MzavaNo ratings yet
- Theories of MagnetismDocument6 pagesTheories of MagnetismAnonymous xZCFQbQ4No ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument7 pagesPHYSICSMohamed Mounir MYP3No ratings yet
- Lecture3 - Magnetism and Electromagnetism PDFDocument8 pagesLecture3 - Magnetism and Electromagnetism PDFOcwich FrancisNo ratings yet
- WJRTy 96 L 5 U2 WL Tns IqomDocument27 pagesWJRTy 96 L 5 U2 WL Tns IqomVenu GopalNo ratings yet
- Physics - Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocument7 pagesPhysics - Magnetism and ElectromagnetismNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Faraday's & Lenz LawDocument14 pagesFaraday's & Lenz LawPnDeNo ratings yet
- Physics 12 Lens 2Document14 pagesPhysics 12 Lens 2Roshan SafeekaNo ratings yet
- Attachment PHPDocument7 pagesAttachment PHPKunal Bagade.No ratings yet
- Class 10 Magnetic EffectDocument8 pagesClass 10 Magnetic EffectVirendra BansalNo ratings yet
- Dow 00068Document150 pagesDow 00068Kunal Bagade.No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument13 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentkunalNo ratings yet
- Law of Electromagnetic InductionDocument3 pagesLaw of Electromagnetic InductionnonofogoitsemodimoNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Induction and Faradays Law in General Physics 2Document43 pagesMagnetic Induction and Faradays Law in General Physics 2Heidi QuiranteNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Radiation and The Near FieldDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic Radiation and The Near FieldFrederick David TombeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5.1 Faraday's Law and Lenz's LawDocument17 pagesChapter 5.1 Faraday's Law and Lenz's LawsNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-07-17 at 11.14.36 PMDocument14 pagesScreenshot 2022-07-17 at 11.14.36 PMdoe45781No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductonDocument12 pagesElectromagnetic InductonAishwarya TripathiNo ratings yet
- Analogue Electronics 1: Magnetism + ElectromagnetismDocument21 pagesAnalogue Electronics 1: Magnetism + ElectromagnetismUmZy08No ratings yet
- A Single Wire That Has Current Passing ThroughDocument3 pagesA Single Wire That Has Current Passing Throughrajkumar karjeeNo ratings yet
- 7.magnetic Effect of Electric Current - Doc (VII)Document25 pages7.magnetic Effect of Electric Current - Doc (VII)Haerfing AuwNo ratings yet
- Maxwell's Sea of Molecular VorticesDocument7 pagesMaxwell's Sea of Molecular Vorticescrystal01heartNo ratings yet
- Maxima or Minima Quadratic EquationDocument1 pageMaxima or Minima Quadratic EquationMCHNo ratings yet
- CS1 1 1Document1 pageCS1 1 1MCHNo ratings yet
- JC1 SeatworkDocument1 pageJC1 SeatworkMCHNo ratings yet
- CS3 - Inversely ProportionalDocument2 pagesCS3 - Inversely ProportionalMCHNo ratings yet
- Recall Topic TrigonometryDocument1 pageRecall Topic TrigonometryMCHNo ratings yet
- B A B A: Solve The Simultaneous EquationDocument2 pagesB A B A: Solve The Simultaneous EquationMCHNo ratings yet
- cs3 PDFDocument3 pagescs3 PDFMCHNo ratings yet
- AS Physics Topic Wise Questions: ForcesDocument17 pagesAS Physics Topic Wise Questions: ForcesAryan KingerNo ratings yet
- Alternating CurrentDocument10 pagesAlternating CurrentMCHNo ratings yet
- 9702 p1 Current Electricity AllDocument35 pages9702 p1 Current Electricity AllMCHNo ratings yet
- 9702 p1 Kinematics AllDocument28 pages9702 p1 Kinematics Allshimoni rathoreNo ratings yet
- 0610 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesDocument7 pages0610 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesMCHNo ratings yet
- .Document15 pages.kwon jiyongNo ratings yet
- Topic: Date: Duration: SubjectDocument3 pagesTopic: Date: Duration: SubjectMCHNo ratings yet
- Boyles' Law: Use Boyles' Law To Answer The Following QuestionsDocument3 pagesBoyles' Law: Use Boyles' Law To Answer The Following QuestionsMCHNo ratings yet
- Area of The Shaded Part TestDocument2 pagesArea of The Shaded Part TestMCHNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Harapan Bangsa CambridgeDocument4 pagesSekolah Harapan Bangsa CambridgeMCHNo ratings yet
- 5 - Snells Law Worksheet PDFDocument4 pages5 - Snells Law Worksheet PDFMCHNo ratings yet
- 0653 Y17 SM 2Document2 pages0653 Y17 SM 2MCHNo ratings yet
- Temp NotrDocument15 pagesTemp NotrMCHNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 4.1 & 4.2 (A) Multiple Choice Questions (5 Marks) 12Document2 pagesWORKSHEET 4.1 & 4.2 (A) Multiple Choice Questions (5 Marks) 12MCH100% (1)
- 0610 s14 QP 11Document20 pages0610 s14 QP 11hosni_syrNo ratings yet
- 0610 Y16 SM 6Document4 pages0610 Y16 SM 6DevalNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion MS PDFDocument2 pagesCircular Motion MS PDFMCHNo ratings yet
- Ch:2 Quadratics: - Nature of RootsDocument2 pagesCh:2 Quadratics: - Nature of RootsMCHNo ratings yet
- 0610 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2015 SeriesDocument10 pages0610 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2015 SeriesMCHNo ratings yet
- RulesDocument2 pagesRulesMCHNo ratings yet
- Scientific NotationDocument2 pagesScientific NotationMCHNo ratings yet