Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Index PDF
Uploaded by
JAGADEESHOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Index PDF
Uploaded by
JAGADEESHCopyright:
Available Formats
Botany
6 - 8 chapters
4 Marks Questions
1. List the changes observed in angiosperm
flower subsequent to pollination and fertilization.
A: Flower is the reproductive shoot which possesses androecium and gynoecium to produce male and female gametes respectively.
Depending on the type of plant species self
or cross pollination takes place to transfer
the pollen with male gametes to the stigma.
The pollination is followed by pollen tube
entry into the ovule and embryosac and fertilization of the male gamete with the egg cell
in the embryosac. The changes that occur in
a flower after fertilization are :
The calyx and corolla wither and fall off
(Sometimes the calyx may be persistant)
Ex: Tridax, Brinjal
The stamens fall off.
The style and stigma fall off.
The ovary transforms into a fruit.
The ovules transform into seeds.
Zygote and endosperm are formed in the seed.
2. List three strategies that a bisexual chasmogamous flower can evolve to prevent self
pollination (Autogamy).
A: Bisexual chasmogamous flowers prevent
self pollination by the following out breeding
devices:
a) Dichogamy: Maturation of androecium
and gynoecium at different times in a
flower is called Dichogamy. If the pollen is
released before the stigma becomes
receptive it is called Protandry. Ex:
Sunflower. If the stigma becomes receptive before the release of pollen it is called
Protogyny. Ex: Datura.
b) Herkogamy: If the anthers and stigma are
placed at different positions so that the
pollen cannot come in stigma of the same
flower it is called Herkogamy.
Ex: Gloriosa and Hibiscus.
c) Heterostyly: The styles of the flowers of
the same species are in different heights.
Ex: Primula.
d) Self-sterility: The germination of self-pollen
on the stigma is prevented. Ex: Abutilon.
3. Discuss the various types of pollen tube entry
into ovule with the help of diagrams.
A: Pollen grains germinate on the stigma of the
2 Marks Questions
1. What is meant by heterospory? Mention the
two types of spores developed in an
angiospermic plant.
A: Production of two types of spores by a plant
is called heterospory. Microspores and
megaspores.
2. Which of the following are monoecious and
dioecious organisms?
a) Date palm
b) Coconut
c) Chara
d) Marchantia
A: Date palm - dioecious
Coconut - monoecious
Chara - monoecious
Marchantia - dioecious
3. What do the following parts of a flower develop into after fertilization?
a) ovary b) stamens c) ovules d) calyx
A: Ovary - fruit
Stamens - fall off
Ovules - seeds
Calyx - falls off ( In plants like Solanum it is
persistent after fertilization)
4. Define vivipary with an example.
Q: Explain the scope and significance of Numerical taxonomy.
(2 Marks)
A: Numerical taxonomy can be used to evaluate differences
and similarities between taxonomic groups using mathematics and computers. As this method uses numbers
and codes it is easy and quick process and can be used
for hundreds of characters at a time.
What is triple fusion..?
flower and produce pollen tube which carries
male gametes towards the ovule and
embryosac. The pollen tube is formed by the
intine of the ovule and emerges through the
pores in the exine and grows down into the
style. Later it enters the ovule by any of the
following methods:
Porogamy: The pollen tube enters the ovule
through the micropyle.
Mesogamy: The pollen tube enters the ovule
through the integuments.
Chalazogamy: The pollen tube enters the
ovule through the chalaza.
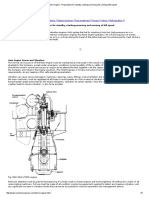
Chalaza
Pollen Tube
Integument
Micropyle
Pollen Tube
Porogamy
Chalazogamy
Mesogamy
Three modes of entry of pollen tube into the ovule
4. What is triple fusion? Where and how does it
take place? Name the nuclei involved in
triple fusion.
A: During fertilization in angiosperms one male
gamete fuses with the egg cell to form a
diploid zygote. The second male gamete
fuses with the diploid secondary nucleus
present in the central cell. This fusion of
three haploid nuclei (one male gamete and
two nuclei in the secondary nucleus) inside
the embryosac is called triple fusion. Triple
fusion takes place inside the embryosac.
The nuclei involved in triple fusion are one
male nucleus and two polar nuclei which has
formed a diploid secondary nucleus.
5. Describe the essential floral parts of plants
belonging to Liliaceae.
A: Androecium and gynoecium are the essential floral parts. In Liliaceae the androecium
and gynoecium show the following features:
A: Vivipary is the germination of the seeds
while still attached to the mother plant.
Ex: Rhizophora (mangrove).
5. Name the component cells of the egg apparatus in an embryosac.
A: One egg cell. Two synergids.
6. Name the common functions that cotyledons
and nucellus perform.
A: Both cotyledons and nucellus contain abundant food materials. The cotyledons provide
food and energy to the germinating seed.
The nucellus provides food for the growing
embryo.
7. Name the parts of pistil which develop into
fruit and seeds.
A: Ovary develops into fruit. Ovule develops
into seed.
8. Which are the three cells found in a pollen
grain when it is shed at the three celled
stage?
A: One vegetative cell and Two male gametes.
9. What is self-incompatibility?
A: The inability of pollen to germinate on the
stigma of the same flower is called self
incompatibility or self-sterility. Ex: Abutilon
8 Marks Question
Writer :
Dr. P. Uma Amareswari
Senior Lecturer in Botany
Androecium: Six stamens in two whorls of
three each, free or epiphyllous (attached to
tepals), anthers are dithecous, basifixed,
introrse and show longitudinal dehiscence.
Gynoecium: Tricarpellary, syncarpous,
ovary superior, trilocular with ovules on axile
placentation. Style is terminal, stigma trifid or
capitate.
6. Describe
the
essential
organs
of
Solanaceae.
A: Androecium and gynoecium are the essential organs in the flowers of Solanaceae.
Androecium: There are five stamens alternating with petals in epipetalous condition.
The filaments are long. The anthers are
dithecous, basifixed and introrse.
Gynoecium: Bicarpellary, syncarpous
gynoecium with bilocular (unilocular in chillie)
superior ovary with many ovules on swollen
axile placenta. The carpels are arranged
obliquely at 45. Terminal style and stigma
capitate.
7. Give economic importance of plants belonging to Fabaceae.
A: Economic importance of Fabaceae: The
plants are a good source of proteins (pulses). Ex: Cajanus, Cicer
Pods of beans are used as vegetables.
Ex: Phaseolus
Edible oil is obtained from soya bean and
groundnut. Ex: Arachis
Timber is produced by rose wood.
Ex: Dalbergia
Blue dye from Indigofera and yellow dye
from Butea are obtained.
Derris is used in medicine. Crotalaria,
Phaseolus are used as fodder. Sesbania and
Tephrosia are used as green manure.
10. Name the parts of an angiosperm flower in
which development of male and female
gametophyte take place.
A: Male gametophyte - pollen grain.
Female gametophyte (embryosac) - nucellus of the ovule.
11. What is meant by scutellum? In which type
of seeds it is present?
A: The cotyledon of a monocot embryo is
called scutellum. It is present in monocot
seeds Ex: Grasses.
12. Define with examples endospermic and
non-endospermic seeds.
A: Endospermic seeds castor and
coconut. Non endospermic seeds groundnut, beans and peas.
Q: With a neat labeled diagram describe the
parts of a mature angiosperm embryosac.
Mention the role of synergids.
A: Embryosac or female gametophyte in
many angiosperms is formed from a single functional megaspore.
This kind of development is called monosporic development.
The single megaspore divides by three
nuclear (mitotic) divisions to produce 8
nuclei which become 7 celled later.
A typical angiosperm embryosac is thus 8
nucleated and 7 celled.
The eight nuclei organize into three
regions: Egg apparatus, Antipodals and
Central cell.
The egg apparatus is present at the
micropylar end and contains one egg cell
(female gamete) and two synergids with
filiform apparatus.
Three antipodal cells are present at the
chalazal end. These are the vegetative
cells of the embryosac and degenerate
before or after fertilization.
The large central cell has two polar nuclei.
Role of synergids:
The synergids guide the movement of
pollen tube into them. They also direct the
movement of one male gamete towards the
egg cell for fertilization.
Chalaza
Nucellus
Integuments
Antipodal cells
Central cell
Embryosac
Secondary
nucleus
Egg (Oosphere)
Synergids
Vascular strand
Funiculus
Micropyle
13. What is Omega Taxonomy?
A: The taxonomy which uses information from
other sources like embryology, cytology,
palynology, phyto chemistry, serology etc.
along with morphological features is known
as Omega Taxonomy.
14. What is natural system of plant classification? Name the scientists who followed it.
A: The system of classification that considers
all possible morphological characters and
their natural relationships is called natural
system of classification. Bentham and
Hooker followed this system.
15. Give the technical description of anthers of
Allium cepa.
A: Anthers of Allium cepa are dithecous, basifixed, introrse and show longitudinal dehiscence.
16. What is geocarpy? Name the plant which
exhibits this phenomenon.
A: Production of fruit inside the soil is called
geocarpy. Arachis hypogea (groundnut).
17. Name the type of pollination mechanism
found in members of Fabaceae.
A: Piston mechanism.
You might also like
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Total Production of 'C'..?: Quantitative AptitudeDocument1 pageThe Total Production of 'C'..?: Quantitative AptitudeJAGADEESHNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- What Is The Difference Between The Carnot Cycle and The Rankine Cycle - QuoraDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between The Carnot Cycle and The Rankine Cycle - QuoraJAGADEESHNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Police Constables Prelims Model Paper: No. of Questions: 200 Marks: 200 Time: 3 HrsDocument1 pagePolice Constables Prelims Model Paper: No. of Questions: 200 Marks: 200 Time: 3 HrsJAGADEESHNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Big SST OverviewDocument15 pagesBig SST OverviewJAGADEESHNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Most Polluted City Is... : WriterDocument1 pageThe Most Polluted City Is... : WriterJAGADEESHNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- 001BGR Energy Systems LimitedDocument1 page001BGR Energy Systems LimitedJAGADEESHNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- 001rotary Gear Pumps, Reciprocating Pumps, Chemical Dosing Pumps Industry ApplicationsDocument2 pages001rotary Gear Pumps, Reciprocating Pumps, Chemical Dosing Pumps Industry ApplicationsJAGADEESHNo ratings yet
- 01condensate Polisher Systems - Degremont Technologies - Worldwide Water and Wastewater Treatment SpecialistsDocument2 pages01condensate Polisher Systems - Degremont Technologies - Worldwide Water and Wastewater Treatment SpecialistsJAGADEESHNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Plain Bearing - WikipediaDocument10 pagesPlain Bearing - WikipediaJAGADEESHNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Bearing Sensor Stock InventoryDocument5 pagesBearing Sensor Stock InventoryJAGADEESHNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Diesel Engines: Home Boilers Feed Systems Steam Turbines Fuel Treatment Pumps Valves RefrigerationDocument5 pagesDiesel Engines: Home Boilers Feed Systems Steam Turbines Fuel Treatment Pumps Valves RefrigerationJAGADEESHNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Generator: How It Makes Electricity Reactor Turbine Generator Cooling Fuel Containment LinksDocument2 pagesGenerator: How It Makes Electricity Reactor Turbine Generator Cooling Fuel Containment LinksJAGADEESHNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- III.1 Dino IntroductionDocument10 pagesIII.1 Dino IntroductionCesar Alarcon ZapataNo ratings yet
- SyllogismsDocument4 pagesSyllogismssajaydas6No ratings yet
- SPHENODONDocument3 pagesSPHENODONDhurjati Pathak100% (1)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Woods Ho!e Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, MassachusettsDocument18 pagesWoods Ho!e Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, MassachusettsRizky Aulia DewiNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Soal Bahasa Inggris Kelas 8 3.2 (WIIL) DAN 3.3 (MUST) : Excuse MeDocument9 pagesSoal Bahasa Inggris Kelas 8 3.2 (WIIL) DAN 3.3 (MUST) : Excuse MesirivaNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Ecology 2nd Midterm NotesDocument3 pagesEcology 2nd Midterm NotesLloyd Bijuli-SinghNo ratings yet
- Dichotomous Key ExerciseDocument64 pagesDichotomous Key ExerciseAnne Sharmaine OchoaNo ratings yet
- Bio 102 Handout Muscular SysDocument3 pagesBio 102 Handout Muscular Sysgjsup100% (1)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Skin & Sense of TouchingDocument42 pagesSkin & Sense of TouchingMario IstrefiNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Physiology Safety RulesDocument1 pagePhysiology Safety Ruleshengki wijayaNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument4 pagesCell MembraneNoraNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Animalia Deep FlowchartDocument2 pagesKingdom Animalia Deep Flowchartmeerab uroojNo ratings yet
- Captivity Effects On Wide-Ranging CarnivoresDocument2 pagesCaptivity Effects On Wide-Ranging CarnivoresMiguel LessaNo ratings yet
- DNAMethodsforHLATyping WorkbookDocument81 pagesDNAMethodsforHLATyping WorkbookithilaminNo ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument10 pagesAnimal KingdomsuryababaNo ratings yet
- ICMR JRF 2015 Previous - Model Question Paper - EasybiologyclassDocument10 pagesICMR JRF 2015 Previous - Model Question Paper - EasybiologyclassSharad GajuryalNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Pacheco Et Al Phyllotis Pearsoni TH 2014Document28 pagesPacheco Et Al Phyllotis Pearsoni TH 2014Dennisse RuelasNo ratings yet
- Burit Earl - Itl Worksheet-2Document5 pagesBurit Earl - Itl Worksheet-2api-433196599No ratings yet
- Literature Review: Periodontal AnatomyDocument68 pagesLiterature Review: Periodontal AnatomyRoshna NarayanNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom by Rakshita SinghDocument82 pagesAnimal Kingdom by Rakshita Singhshakuntalagayakwad5No ratings yet
- Arthropods: Surviving The Frost: Charmayne Roanna L. GalangDocument2 pagesArthropods: Surviving The Frost: Charmayne Roanna L. GalangBabes-Rose GalangNo ratings yet
- Class Amphibia MammaliaDocument7 pagesClass Amphibia MammaliaKristella DraheimNo ratings yet
- Soal Pat Genap Kelas Viii Bahasa Inggris Tapel 2020-2021 Foskam - 2Document4 pagesSoal Pat Genap Kelas Viii Bahasa Inggris Tapel 2020-2021 Foskam - 2nazar azkhafNo ratings yet
- Sofolympiadtrainer: Animal WorldDocument3 pagesSofolympiadtrainer: Animal WorldmanasmanojNo ratings yet
- UPCPMT Sample Paper-9 - (CPMT - Paper-1 - 2007)Document16 pagesUPCPMT Sample Paper-9 - (CPMT - Paper-1 - 2007)Firdosh KhanNo ratings yet
- Report Text About Panda (1)Document2 pagesReport Text About Panda (1)hanumsaavNo ratings yet
- Test KL 8 3 Mujori I 1 Grupi BDocument2 pagesTest KL 8 3 Mujori I 1 Grupi BDiamanta SericaNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Blg1502 Exam Prep Doc - Part 1&2Document18 pagesBlg1502 Exam Prep Doc - Part 1&2Pasipanodya MuzendaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Bugs Week 2Document2 pagesLesson Plan Bugs Week 2api-314832142No ratings yet
- Answer Appendix PDFDocument47 pagesAnswer Appendix PDFSantosh Sharma100% (1)