Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reduction of Harmonics in HVDC Transmission System Using High Pulse Converter
Uploaded by
imranOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reduction of Harmonics in HVDC Transmission System Using High Pulse Converter
Uploaded by
imranCopyright:
Available Formats
ISSN (Print) : 2320 9798
ISSN (Online): 2320 9801
International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering
Vol. 1, Issue 4, June 2013
Reduction of Harmonics in HVDC
Transmission System using High Pulse
Converter
R. Kiranmayi
Associate Professor, Dept. of EEE, JNTUH CEH, A.P., India
ABSTRACT: HVDC is capable of transmitting power over long distances economically and connects two
asynchronous AC systems. HVDC transmission can be made more feasible by eliminating problems faced in it such as
cost of converting stations and harmonics. This paper presents high pulse converters like 12, 24, 48 in the HVDC
transmission system to reduce harmonics in the DC link.
KEYWORDS: HVDC, high pulse converters, harmonics, .
I. INTRODUCTION
During the last 20 years, HVDC has become the dominating technology for long distance transmission of bulk
power. For long distance power transmission, the DC transmission system is proved to be very efficient and economic
rather than AC transmission system. Rapid development in the field of power electronic devices with turn off capability
like insulated gate bipolar transistors (IGBT) and gate turn-off thyristors (GTO), makes the voltage sourced converters
(VSC) more and more attractive for high voltage direct current transmission (HVDC). This new innovative technology
provides substantial technical and economical advantages for different applications compared to conventional HVDC
transmission systems based on thyristor technology. Since thyristor-based switches (i.e., solid-state rectifiers) were
incorporated into them, hundreds of HVDC sea cables have been laid, and have worked with high reliability, usually
better than 96% of the time. This paper proposes high pulse converters to reduce the harmonic content in the HVDC
Transmission.
II. HARMONIC REDUCTION IN HVDC TRANSMISSION
The actual level of harmonics generated by an AC/DC converter is a function of the duration over which a
particular phase is required to provide unidirectional current to the load. Hence, the higher the Pulse number of the
converter, which means the more switching between phases within a cycle, the lower the harmonic distortion in both
the AC line current and the DC terminal voltage. The Harmonics generated in the link can be minimized by
(A) USING DC SMOOTHING REACTORS
The smoothing reactor provides high impedance to the flow of the harmonic currents, reduce their magnitude
and thus smoothens the DC current.
(B) USING DC & AC HARMONIC FILTERS
The filter has a zero impedance at the tuned frequency thus absorbing the harmonic of interest.
(C) BY INCREASING THE PULSE NUMBER
The higher the pulse number of the converter, which means the more switching between phases within a cycle,
the lower the harmonic distortion in both the AC line current and the DC terminal voltage.
The basic building block used for HVDC conversion is the three-phase, full-bridge referred to as a 6-pulse or Graetz
bridge. The term 6-pulse is due to the characteristic harmonic ripple in the dc output voltage, which is at multiples of 6
times the fundamental frequency. Each 6-pulse bridge is comprised of 6 controlled switching elements or thyristor
valves. Each valve is comprised of a number of series-connected thyristors to achieve the desired dc voltage rating.
The figure 1 shows the voltages of each half wave bridge of this topology, VDpos and VDneg, the total instantaneous dc
voltage VD, and the anode-to-cathode voltage VAK in one of the bridge thyristors. The maximum value of VAK is
03VMAX which is the same as of the half-wave converter and the inter phase transformer converter. The double star
converter presents a maximum anode-to-cathode voltage of 2 times VMAX.
Copyright to IJIRCCE
www.ijircce.com
1063
ISSN (Print) : 2320 9798
ISSN (Online): 2320 9801
International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering
Vol. 1, Issue 4, June 2013
Fig.1 Six-pulse converter (Graetz Bridge)
An ideal input wave would like to be completely sinusoidal. The waveform of the converters however contains many
harmonics. Analysis of the input show that the lowest harmonics is not the 6th. Even number harmonics, such as the 6th
cannot exist in any waveform that is symmetrical in its positive and negative half cycles. The predominant harmonics
are 5th and the 7th. The amplitude variation with respect to harmonics is shown in figure 2.
h = np 1
h = harmonic numbers of the spectrum
n = 1, 2, 3, . . .
p = 6 for a 6-pulse converter
Therefore,
h = 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 25, . .
.
Fig. 2 Amplitude Vs harmonic number
These input harmonics are much more difficult to filter than output harmonics. Although a low pass filter might be
used, it becomes difficult to design a filter that attenuates the harmonics, while still passing the fundamental line
frequency. The better method is to use a notch filter rather than a low-pass filter. Yet, even notch filters when used in
converter applications are sometime difficult to implement. The filter relies on resonating components such as
inductors and capacitors to perform its function. In a facility wide installation, there are many unknowns that affect the
proper tuning of these filters.
Table. 1 Harmonic reduction with the increase in Pulse number
Copyright to IJIRCCE
www.ijircce.com
1064
ISSN (Print) : 2320 9798
ISSN (Online): 2320 9801
International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering
Vol. 1, Issue 4, June 2013
III. SIMULAION AND RESULTS
(A) Simulink model of Thyristor based 6 Pulse Converter in HVDC Transmission:
The firing pulses for the thyristors is obtained from synchronized six pulse generator. Simulink model of basic
six pulse converter followed by corresponding voltage and current waveforms is shown as below:
Fig. 3 Thyristor based 6 pulse converter
Fig. 4 Thyristor based 6 pulse converter output voltage
(B) Simulink model of Thyristor based 12 Pulse Converter in HVDC Transmission:
Fig, 5 Thyristor based 12 pulse converter
Copyright to IJIRCCE
www.ijircce.com
1065
ISSN (Print) : 2320 9798
ISSN (Online): 2320 9801
International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering
Vol. 1, Issue 4, June 2013
Fig. 6 Thyristor based 12 pulse converter output voltage
(C) Simulink model of Thyristor based 24 Pulse Converter in HVDC Transmission:
Fig. 7 Thyristor based 24pulse converter
Fig. 8 Thyristor based 24 pulse converter output voltage
Copyright to IJIRCCE
www.ijircce.com
1066
ISSN (Print) : 2320 9798
ISSN (Online): 2320 9801
International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering
Vol. 1, Issue 4, June 2013
(D) Simulink model of Thyristor based 48 Pulse Converter in HVDC Transmission:
Fig. 9 Thyristor based 48 pulse converter
Fig. 10 Thyristor based 48 pulse converter output voltage
IV.CONCLUSION
Thus by reducing harmonic and ripple content DC transmission can be made more reliable. Since harmonic
content affects every element in transmission it has to be reduced to minimum level using efficient techniques.
According to IEEE 519 standards, the voltage THD% of the converter output must be below 1.5% for a HVDC line of
voltage capacity161.001KV and above. In order to obtain the voltage THD% below the specified value a fourty-eight
pulse converter is implemented. By comparing the simulation results obtained for six, twelve, twenty four and fourty
eight pulse converters, it can be concluded that by increasing pulses in converter harmonic content in HVDC
transmission can be reduced to maximum extent.
REFERENCES
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
N. Arvindan and P. Pushpakarthick, '24-Pulse rectifier realization by 3-phase to four 3-phase transformation using conventional transformers",
IEEE Conference,vS.S.N. College of Engineering, Anna University (Chennai), Tamilnadu.
Fco. Javier Chivite-Zabalza, and Andrew J. Forsyth, "A Passive 36-Pulse ACDC Converter With Inherent Load Balancing Using Combined
Harmonic Voltage And Current Injection" IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 22, NO. 3, MAY 2007.
Angelo J. J. Rezek; * Jose P. G.de Abreu"Power factor improvement of line-commutated graetz converters by increasing their number of
pulses: modeling and experimental results" IEEE Conference 2012.
Arief Hernadi, Taufik "Modeling and Simulation of 6-Pulse and 12-Pulse Rectifiers under Balanced and Unbalanced Conditions with Impacts
to Input Current Harmonics" Second Asia International Conference on Modelling & Simulation, 2008.
HVDC transmission systems by K.R. Padiyar, New Age International.
Basic Understanding of Harmonics in Electrical Systems by Stephen David Hearn.
Copyright to IJIRCCE
www.ijircce.com
1067
You might also like
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Improvement of Power Factor and Harmonic Reduction With VSC For HVDC SystemDocument7 pagesImprovement of Power Factor and Harmonic Reduction With VSC For HVDC SystemGiwrgos GewrgiadisNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- The Impacts of Harmonics Reduction On THD Analysis in HVDC Transmission System Using Three-Phase Multi-Pulse and Higher Level ConvertersDocument6 pagesThe Impacts of Harmonics Reduction On THD Analysis in HVDC Transmission System Using Three-Phase Multi-Pulse and Higher Level ConvertersAshwani GargNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 31 2 Level, 48 PulseDocument6 pages31 2 Level, 48 PulseSumit MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Cascaded H-Bridge Multilevel Inverter Using OHSW PWM For The Elimination of HarmonicsDocument14 pagesSimulation of Cascaded H-Bridge Multilevel Inverter Using OHSW PWM For The Elimination of HarmonicsBib SaNo ratings yet
- Project 3 - 2xDocument37 pagesProject 3 - 2xSamala NagarajuNo ratings yet
- High-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversFrom EverandHigh-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversNo ratings yet
- 24 Pulse Ac DC Converters For Improved PDocument6 pages24 Pulse Ac DC Converters For Improved Pdebasisbasu KHARAGPURMETALSNo ratings yet
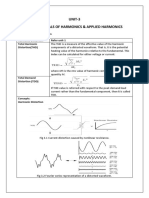
- UNIT-3 Fundamentals of Harmonics & Applied HarmonicsDocument14 pagesUNIT-3 Fundamentals of Harmonics & Applied Harmonicslvb123No ratings yet
- Analysis of Harmonic Mitigation Using Hybrid Passive FilterDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Harmonic Mitigation Using Hybrid Passive FilterDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Matlab Simulink of Three Phase Six-PulseDocument6 pagesMatlab Simulink of Three Phase Six-PulseMohammed SelmanNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 - Harmonics & FiltersDocument10 pagesUnit-5 - Harmonics & Filtersravikumar_ranganNo ratings yet
- 15ipst054 PDFDocument7 pages15ipst054 PDFGuiNo ratings yet
- DC Transformers 77Document15 pagesDC Transformers 77Keshavamurthy MurthyNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv: Fundamentals of Harmonics: Fig.1: Current Distortion Caused by Nonlinear ResistanceDocument12 pagesUnit Iv: Fundamentals of Harmonics: Fig.1: Current Distortion Caused by Nonlinear Resistancelvb123No ratings yet
- Naresh DC Re Injection FinalDocument6 pagesNaresh DC Re Injection FinalRamu ThommandruNo ratings yet
- Two-Stage H-Bridge Transformer Coupled DC-DC Converter With Zero Voltage SwitchingDocument8 pagesTwo-Stage H-Bridge Transformer Coupled DC-DC Converter With Zero Voltage SwitchingRakeshconclaveNo ratings yet
- 1) A Three-Phase Soft-Switched High-Power-Density DC-DC ConverterDocument11 pages1) A Three-Phase Soft-Switched High-Power-Density DC-DC Converteralberfilba2No ratings yet
- Ijert Ijert: Immunity of AC-DC Harmonics in VSC HVDC Transmission For Multi-Level ConvertersDocument6 pagesIjert Ijert: Immunity of AC-DC Harmonics in VSC HVDC Transmission For Multi-Level ConvertersR.SRIKANTHNo ratings yet
- A Very High Frequency DC-DC Converter Based On A Class Pfi Resonant InverterDocument10 pagesA Very High Frequency DC-DC Converter Based On A Class Pfi Resonant InvertererdemsecenNo ratings yet
- Digital Simulation of DC Links and AC MachinesDocument8 pagesDigital Simulation of DC Links and AC MachinesNarges FallahNo ratings yet
- Ijset 2014 201Document7 pagesIjset 2014 201Innovative Research PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Ehvac To HvacDocument5 pagesEhvac To HvacInsaf MohamedNo ratings yet
- Coupling Capacitor Voltage Transformers As Harmonics Distortion Monitoring Devices in Transmission SystemsDocument6 pagesCoupling Capacitor Voltage Transformers As Harmonics Distortion Monitoring Devices in Transmission SystemsgdgdinNo ratings yet
- A High-Efficiency 6.78-Mhz Full Active Rectifier With Adaptive Time Delay Control For Wireless Power TransmissionDocument10 pagesA High-Efficiency 6.78-Mhz Full Active Rectifier With Adaptive Time Delay Control For Wireless Power Transmissionfelix_007_villedaNo ratings yet
- HVDC (High Voltage Direct Current) Transmission System: A Review PaperDocument10 pagesHVDC (High Voltage Direct Current) Transmission System: A Review Paperalif coinNo ratings yet
- Mac Int J.Power ElectronicsDocument14 pagesMac Int J.Power Electronicssandeepbabu28No ratings yet
- Report On HVDCDocument20 pagesReport On HVDCMk Enterprise JamuriaNo ratings yet
- Multilevel Optimal Predictive Dynamic Voltage RestorerDocument14 pagesMultilevel Optimal Predictive Dynamic Voltage RestorerChikha SaidNo ratings yet
- Input and Output: Power Electronic Direct Current Alternating Current Voltage PowerDocument4 pagesInput and Output: Power Electronic Direct Current Alternating Current Voltage PowerMohamed AbubackerNo ratings yet
- Likhith IJSETR15961-1167Document4 pagesLikhith IJSETR15961-1167Likhithmohan VNo ratings yet
- Resonant DC Link InverterDocument9 pagesResonant DC Link InverterSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- 9-Level Trinary DC Source Inverter Using Embedded ControllerDocument6 pages9-Level Trinary DC Source Inverter Using Embedded ControllerIOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalNo ratings yet
- A Novel Single Phase Cascaded H-Bridge Inverter With Reduced Power Electronics SwitchesDocument8 pagesA Novel Single Phase Cascaded H-Bridge Inverter With Reduced Power Electronics SwitchesHemanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Multicarrier - Based PWM Control Strategies For Five - Level CMLIDocument7 pagesMulticarrier - Based PWM Control Strategies For Five - Level CMLIDharani DeviNo ratings yet
- Final 1Document78 pagesFinal 1Steve JantzenNo ratings yet
- A Modified Harmonics Reduction Technique For A Three-Phase Controlled ConverterDocument8 pagesA Modified Harmonics Reduction Technique For A Three-Phase Controlled Convertereladle7No ratings yet
- Research Paper Improvement of Power System Stability by Simultaneous AC-DC Power TransmissionDocument6 pagesResearch Paper Improvement of Power System Stability by Simultaneous AC-DC Power Transmissionmaazsiddiqui.ee7193No ratings yet
- Different PWM Modulation Techniques Indexes Performance Evaluation, 1993.Document7 pagesDifferent PWM Modulation Techniques Indexes Performance Evaluation, 1993.Ali H. NumanNo ratings yet
- 125 130 PDFDocument6 pages125 130 PDFJubin JainNo ratings yet
- Review of Inverter and Multilevel Inverter: Features, Techniques, Topology and Latest DevelopmentsDocument12 pagesReview of Inverter and Multilevel Inverter: Features, Techniques, Topology and Latest DevelopmentsIkram RidhoNo ratings yet
- C 3 PDFDocument7 pagesC 3 PDFAmanda HayesNo ratings yet
- Sixty Pulse AC-DC Controlled Multipulse Converter For Total Harmonic ReductionDocument4 pagesSixty Pulse AC-DC Controlled Multipulse Converter For Total Harmonic ReductionerpublicationNo ratings yet
- WireDocument74 pagesWireShaik MajeedNo ratings yet
- Switching Regulator Fundamentals: Application ReportDocument28 pagesSwitching Regulator Fundamentals: Application Reportbookreader1968No ratings yet
- Multi Pulse Converter Based HVDCDocument13 pagesMulti Pulse Converter Based HVDCNetra Ray100% (1)
- Electromagnetic Interference Issues of Power Electronics Systems With Wide Band Gap Semiconductor DevicesDocument6 pagesElectromagnetic Interference Issues of Power Electronics Systems With Wide Band Gap Semiconductor DevicesDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- IJETR022139Document4 pagesIJETR022139erpublicationNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation of Asymmetricalcascaded Hbridge Multilevel InverterDocument10 pagesPerformance Evaluation of Asymmetricalcascaded Hbridge Multilevel InverterKrishna KamalNo ratings yet
- V01I031119Document7 pagesV01I031119IJARTETNo ratings yet
- Zigzag Connected Autotransformer-Based 24-Pulse AC-DC ConverterDocument12 pagesZigzag Connected Autotransformer-Based 24-Pulse AC-DC ConverterMiguel OchoaNo ratings yet
- Performance of A Current-Fed Soft Switched Full-Bridge Boost Double Stage Converter Using ZVS PWMDocument8 pagesPerformance of A Current-Fed Soft Switched Full-Bridge Boost Double Stage Converter Using ZVS PWMiajerNo ratings yet
- HVDC Proven TechnologyDocument48 pagesHVDC Proven TechnologyMano Paul100% (1)
- International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER)Document7 pagesInternational Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER)International Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)No ratings yet
- A New Single-Phase Single-Stage Three-LevelDocument12 pagesA New Single-Phase Single-Stage Three-LevelGururaj BandaNo ratings yet
- Line Harmonics On Systems Using Reduced DC-link CapacitorsDocument6 pagesLine Harmonics On Systems Using Reduced DC-link CapacitorsDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 04 Surveys Cattell PDFDocument16 pages04 Surveys Cattell PDFBrenda MaggNo ratings yet
- AY 2015-16cvbbnjDocument245 pagesAY 2015-16cvbbnjSyed Abdul AzizNo ratings yet
- 545 ELP-ES-2011 - Catálogo de DisipadoresDocument24 pages545 ELP-ES-2011 - Catálogo de DisipadoresrichkidNo ratings yet
- Hazard-Identification Dec 2015Document22 pagesHazard-Identification Dec 2015Dumitru EninNo ratings yet
- Debug 1214Document2 pagesDebug 1214Faizah Ayulia NawitaNo ratings yet
- ABB LMU 574 - mcd80Document12 pagesABB LMU 574 - mcd80gadware2011bplNo ratings yet
- US Hex Bolt SizesDocument2 pagesUS Hex Bolt SizesYana Jarang OlNo ratings yet
- LG Wd1873rds Manual de UsuarioDocument76 pagesLG Wd1873rds Manual de UsuarioJosè Otoniel Osorio BarreraNo ratings yet
- TSA Surface Preparation and ApplicationDocument7 pagesTSA Surface Preparation and ApplicationMythri Metallizing Pvt Ltd Projects100% (1)
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1MikeyNo ratings yet
- USS ProtocolDocument77 pagesUSS Protocolreza2131No ratings yet
- Aurora: AE MC-120 SeriesDocument2 pagesAurora: AE MC-120 SeriestasoNo ratings yet
- Antena 700 2m - TongyuDocument2 pagesAntena 700 2m - TongyuLenin Alejandro Ramirez HuaypatinNo ratings yet
- AE Yanmar 6GL UTDocument151 pagesAE Yanmar 6GL UTMehdi Es-SafiNo ratings yet
- EN 61000 3-2 GuideDocument19 pagesEN 61000 3-2 Guideyunus emre KılınçNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic CompatibilityDocument12 pagesElectromagnetic Compatibilityoadipphone7031No ratings yet
- Mole Reactions and Stoichiometry MultipleDocument25 pagesMole Reactions and Stoichiometry MultiplelinaNo ratings yet
- EST 2011B v1.0 Configuration 10/28/2018 7:43 AMDocument2 pagesEST 2011B v1.0 Configuration 10/28/2018 7:43 AMbagusNo ratings yet
- Factors That Affect The Quality of CommunicationDocument9 pagesFactors That Affect The Quality of CommunicationWilliam Paras Inte100% (3)
- Maintenence SchedulingDocument4 pagesMaintenence SchedulingCarloVanZyl0% (1)
- Pakistani Radio MarketDocument72 pagesPakistani Radio MarketNajeeb Anwar100% (1)
- Insulin, Recombinant HumanDocument2 pagesInsulin, Recombinant HumanMuhammad AkramNo ratings yet
- Vem BrochureDocument8 pagesVem BrochureVamshi Krishnam Raju NadimpalliNo ratings yet
- 02 - Student Lesson 2 Pile Driving SystemDocument91 pages02 - Student Lesson 2 Pile Driving SystemdannyzuanNo ratings yet
- DUNAN Fan Coil UnitDocument14 pagesDUNAN Fan Coil UnitDjordjeNo ratings yet
- On The Gaussian Error Function (1935) : Robert J. KolkerDocument4 pagesOn The Gaussian Error Function (1935) : Robert J. KolkerSanthosh KulandaiyanNo ratings yet
- Stelzer Catalog PDFDocument12 pagesStelzer Catalog PDFlhphong021191No ratings yet
- RAB PE20Tx1set Amo, 60HP (1) Cetakan 50kg (400 Balok 16 Can) + Ice Storage 50TDocument3 pagesRAB PE20Tx1set Amo, 60HP (1) Cetakan 50kg (400 Balok 16 Can) + Ice Storage 50THidayat SyamsiNo ratings yet
- Various Allowances Referred To 7th CPCDocument73 pagesVarious Allowances Referred To 7th CPCGiri KumarNo ratings yet
- Instrument Panel - Standard: 1988 Toyota CelicaDocument26 pagesInstrument Panel - Standard: 1988 Toyota CelicaToua Yaj100% (1)
- Programming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonFrom EverandProgramming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Journeyman Electrician Exam Study Guide: Proven Methods for Successfully Passing the Journeyman Electrician Exam with ConfidenceFrom EverandThe Journeyman Electrician Exam Study Guide: Proven Methods for Successfully Passing the Journeyman Electrician Exam with ConfidenceNo ratings yet
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (543)
- Electrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tFrom EverandElectrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (27)
- Retro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsFrom EverandRetro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsNo ratings yet
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (331)
- Multiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...From EverandMultiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...No ratings yet
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeFrom EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Digital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosFrom EverandDigital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersFrom Everand2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Power System Control and ProtectionFrom EverandPower System Control and ProtectionB. Don RussellRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- INCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesFrom EverandINCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Guide to the IET Wiring Regulations: IET Wiring Regulations (BS 7671:2008 incorporating Amendment No 1:2011)From EverandGuide to the IET Wiring Regulations: IET Wiring Regulations (BS 7671:2008 incorporating Amendment No 1:2011)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Build Your Own Electronics WorkshopFrom EverandBuild Your Own Electronics WorkshopRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Hacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsFrom EverandHacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionFrom EverandTeach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (15)
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsFrom EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Digital Transformation: Survive and Thrive in an Era of Mass ExtinctionFrom EverandDigital Transformation: Survive and Thrive in an Era of Mass ExtinctionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Empires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the WorldFrom EverandEmpires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (87)