Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Evaluation AND Control: Appropriate Measures
Uploaded by
Annabeth ChaseOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Evaluation AND Control: Appropriate Measures
Uploaded by
Annabeth ChaseCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER11
EVALUATION
CONTROL
AND
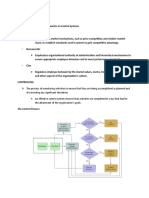
I. EVALUATION AND CONTROL
IN STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT
Evaluation and control process
ensures
that
a
company
achieving what is set out
accomplish.
is
to
5 Steps :
Determine what to measure.
Establish
standards
of
performance.
Measure actual performance.
Compare actual performance with
the standard.
Take corrective action.
II. MEASURING PERFORMANCE
Performance
end result of activity
APPROPRIATE
MEASURES
for
evaluating a corporations or a divisions
ability
to
achieve
a
profitability
objective :
Return on Investment (ROI)
Earnings per Share (EPS)
STEERING CONTROL measures
variables
that
profitability.
influence
future
Inventory Turn-over Ratio Cost of
Goods Sold is divided by the
average value of its inventories.
Customer Satisfaction
TYPES OF CONTROL
Output Controls focus on actual
performance result.
Behavior Controls how something
is to be done through policies,
rules,
standard
operating
procedures,
and
orders
from
superiors.
Input Controls focus on resources
(knowledge, skills, abilities) that
are used in performance.
ACTIVITY-BASED COSTING
accounting method for allocating
indirect and fixed cost to individual
products or product lines based on
the value-added activities going to
that product.
TRADITIONAL
ACCOUNTING
COST
useful when direct labor accounts
for most of total costs and a
company produces just a few
products
requiring
the
same
processes.
ENTERPRISE
MANAGEMENT
RISK
A
corporatewide,
integrated
process
for
managing
the
uncertainties that could negatively
or
positively
influence
the
achievement of the corporations
objective.
TRADITIONAL
MEASURES
FINANCIAL
1. Return on Investment
=Net
Income(before
taxes)
Investment
2. Earnings per Share
= Net Income / Common Stock
3. Return on Equity
= Net Income / Equity
4. Operating Cash Flow
PRIMARY
MEASURES
OF
CORPORATE PERFORMANCE
1. Stakeholder Measure
- deal with the direct and indirect
impacts of corporate activities
on stakeholders interests.
2. Shareholder Value
- the present value of the
anticipated future stream of
cash flows from business plus
the value of the company if
liquidated.
a. Economic Value Added (EVA)
measures the difference
between the pre-strategy and
post strategy values for the
business. Simply put, EVA is
the
after-tax
operating
income minus the total
annual cost of capital.
b. Market Value Added (MVA)
the difference between the
market value of a corporation
and capital contributed by
shareholders and lenders,
3. Balanced Scorecard approach
- combines financial measures
that tell the results of actions
already taken with operational
measures
4 Areas:
Financial
Customer
Internal Business Prospective
Innovation and Learning
EVALUATING TOP MANAGEMENT
AND THE BOARD OF DIRECTORS
CHAIRMAN-CEO
Feedback
Instrument
An evaluation to the CEO using a
17-item questionnaire developed
by Ram Charan, an authority on
corporate governance.
MANAGEMENT AUDIT
Very useful to Boards of Directors
in
evaluating
managements
handling of various corporate
governance.
STRATEGIC AUDIT
Type of Management Audit and is
extremely useful as a diagnostic
tool to pinpoint corporate-wide
problem areas and to highlight
organizational
strengths
and
weaknesses.
You might also like
- Controlling: Business Organization and ManagementDocument17 pagesControlling: Business Organization and ManagementKimoraLeeNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management 11Document25 pagesStrategic Management 11Mubashra BloggersNo ratings yet
- The Balanced Scorecard: Turn your data into a roadmap to successFrom EverandThe Balanced Scorecard: Turn your data into a roadmap to successRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- The Balanced Scorecard (Review and Analysis of Kaplan and Norton's Book)From EverandThe Balanced Scorecard (Review and Analysis of Kaplan and Norton's Book)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Lesson 1213 FinaleDocument89 pagesLesson 1213 FinaleMelitte BalitaNo ratings yet
- Strategic 11Document16 pagesStrategic 11Grow UpNo ratings yet
- Evaluation and ControlDocument16 pagesEvaluation and ControlSachin Sapkota125No ratings yet
- Strategy Evaluation and ControlDocument13 pagesStrategy Evaluation and ControlDr Rushen SinghNo ratings yet
- Balanced ScorecardDocument22 pagesBalanced Scorecardshreyas_1392100% (1)
- CHPT V ST EvaluationDocument58 pagesCHPT V ST EvaluationYared BitewNo ratings yet
- Designing A Performance Evaluation SystemDocument16 pagesDesigning A Performance Evaluation Systemjoint accountNo ratings yet
- GJDocument58 pagesGJKishore ChakravarthyNo ratings yet
- MOT - Managing Quality and PerformanceDocument14 pagesMOT - Managing Quality and PerformanceLeyla MalijanNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Performance ManagementDocument32 pagesSupply Chain Performance ManagementAman AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Organisational Behaviour and Effective Reward SystemsDocument27 pagesOrganisational Behaviour and Effective Reward Systemsjejoullie162No ratings yet
- Evaluating Performance and Control with Strategic Management ToolsDocument3 pagesEvaluating Performance and Control with Strategic Management ToolsOwen GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Characteristics and Approaches to Control SystemsDocument6 pagesChapter 7 Characteristics and Approaches to Control SystemsGlace AbellanaNo ratings yet
- Techniques of ControlDocument18 pagesTechniques of ControlAyush GoelNo ratings yet
- Organizational Control and ChangesDocument20 pagesOrganizational Control and ChangesGerardoAgüeroNo ratings yet
- Operational Audit Presentation ADDocument23 pagesOperational Audit Presentation ADlittleglam100% (1)
- Management Control What Is ControlDocument8 pagesManagement Control What Is ControlGrace Wamuyu KirigiNo ratings yet
- Balanced Scorecard Strategy ImplementationDocument5 pagesBalanced Scorecard Strategy ImplementationdamayNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Performance Measurement System: (With A Special Reference To Eva)Document20 pagesEnterprise Performance Measurement System: (With A Special Reference To Eva)amitprofitNo ratings yet
- Ontrolling: Source: Management - A Global Perspective by Weihrich and Koontz 11 EditionDocument23 pagesOntrolling: Source: Management - A Global Perspective by Weihrich and Koontz 11 EditionSarah ViscoNo ratings yet
- Subject Management Control SystemDocument11 pagesSubject Management Control SystemDikshit KothariNo ratings yet
- CONTROLLING PERFORMANCEDocument39 pagesCONTROLLING PERFORMANCEJosvin JoshyNo ratings yet
- Essentials of ControlDocument20 pagesEssentials of ControlthotanarasannaNo ratings yet
- 1... FMA Assignment 2Document7 pages1... FMA Assignment 2kibur amahaNo ratings yet
- Management Control System: Presented byDocument34 pagesManagement Control System: Presented bysweetyNo ratings yet
- By Sreelatha Sd. Thahaseen Venkatesh V Vinod JDocument34 pagesBy Sreelatha Sd. Thahaseen Venkatesh V Vinod JVin odNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 11 Evaluation & Control: Strategic Management & Business PolicyDocument46 pagesCHAPTER 11 Evaluation & Control: Strategic Management & Business PolicypadmavathiNo ratings yet
- ControllingDocument4 pagesControllingMohammad Kaif KabboNo ratings yet
- Balanced Scorecard GuideDocument19 pagesBalanced Scorecard GuidejhafjfNo ratings yet
- Ontrolling: Source: Management - A Global Perspective by Weihrich and Koontz 11 EditionDocument19 pagesOntrolling: Source: Management - A Global Perspective by Weihrich and Koontz 11 EditionKyle SaylonNo ratings yet
- Controlling Management With BudgetsDocument28 pagesControlling Management With Budgetscarol valenciaNo ratings yet
- 10 Chapter 10Document21 pages10 Chapter 10Ruben SucionoNo ratings yet
- Cost Audit Techniques and ProceduresDocument31 pagesCost Audit Techniques and ProceduresAkash BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Rulete Management ReportDocument58 pagesRulete Management ReportAllan MaguidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Performance AnalysisDocument13 pagesChapter 4 Performance Analysisprasad guthiNo ratings yet
- How Management Accounting Information Supports Decision MakingDocument36 pagesHow Management Accounting Information Supports Decision MakingZbRZivPQ51pEZ9PUNo ratings yet
- Controlling Is A Process of Measuring PerformanceDocument5 pagesControlling Is A Process of Measuring Performanceyukisenp4i11No ratings yet
- MBA0210 EBS 10 Performance ManagementDocument38 pagesMBA0210 EBS 10 Performance ManagementjairamhalNo ratings yet
- Performance Control Systems and Internal Controls: Topic 1 and Introduction To UnitDocument24 pagesPerformance Control Systems and Internal Controls: Topic 1 and Introduction To Unitsv03No ratings yet
- The Balanced Scorecard: A Tool To Implement StrategyDocument39 pagesThe Balanced Scorecard: A Tool To Implement StrategyAilene QuintoNo ratings yet
- Controlling 12Document27 pagesControlling 12Muhammed RashidNo ratings yet
- The Balanced Scorecard: A Tool To Implement StrategyDocument39 pagesThe Balanced Scorecard: A Tool To Implement StrategyAilene QuintoNo ratings yet
- Reformulated By: Muhammadu Sathik RajaDocument34 pagesReformulated By: Muhammadu Sathik RajaAnkitSinghNo ratings yet
- BSC and Other TechniquesDocument17 pagesBSC and Other TechniquesHARSHIT KUMAR GUPTA 1923334No ratings yet
- SM - Ch9Document33 pagesSM - Ch9Ahmed Khaled MansourNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document32 pagesChapter 10Mema SlimamNo ratings yet
- CH - 7 Strategy Evaluation and ControlDocument10 pagesCH - 7 Strategy Evaluation and ControlSneha Singh100% (1)
- Chapter 8Document8 pagesChapter 8Shem CasimiroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 THE BALANCED SCORECARDDocument5 pagesChapter 7 THE BALANCED SCORECARDDiana Mark AndrewNo ratings yet
- Latest Tools for Maximizing Financial ManagementDocument33 pagesLatest Tools for Maximizing Financial ManagementUmar SulemanNo ratings yet
- Budgeting Basics: Purposes, Types & Key ConceptsDocument6 pagesBudgeting Basics: Purposes, Types & Key ConceptsHasnat AsifNo ratings yet
- Balanced Scorecard: BY: Purvi Shah (39) (Mms Ii B)Document11 pagesBalanced Scorecard: BY: Purvi Shah (39) (Mms Ii B)purvis15100% (1)
- Controlling: Source: Management - A Global Perspective by Weihrich and Koontz 11 EditionDocument26 pagesControlling: Source: Management - A Global Perspective by Weihrich and Koontz 11 EditionMaritoni MercadoNo ratings yet
- Controlling: Strategic Control Systems Identifying Control ProblemsDocument12 pagesControlling: Strategic Control Systems Identifying Control ProblemsPaul OcampoNo ratings yet
- AF313 Lecture 2.1 Strategic Management AccountingDocument28 pagesAF313 Lecture 2.1 Strategic Management Accountings11186706No ratings yet
- BSC Framework Translates StrategyDocument6 pagesBSC Framework Translates StrategyAhmad ZydanNo ratings yet
- AUTHENTICITY AND CONGRUENCY OF GROUP ResearchDocument17 pagesAUTHENTICITY AND CONGRUENCY OF GROUP ResearchAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- Contextualizing Cebuanong Bisaya Among DapitanonsDocument17 pagesContextualizing Cebuanong Bisaya Among DapitanonsAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Teaching in Mother TongueDocument8 pagesBenefits of Teaching in Mother TongueAnnabeth Chase100% (1)
- Bus Pol HandoutsDocument3 pagesBus Pol HandoutsAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- Teaching Aids and Instructional Materials Help Teachers Facilitate LearningDocument7 pagesTeaching Aids and Instructional Materials Help Teachers Facilitate LearningAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- Organizational StructureDocument1 pageOrganizational StructureAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- Concept Paper Dynamism of Semantic Shift in English LanguageDocument5 pagesConcept Paper Dynamism of Semantic Shift in English LanguageAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- Teaching Aids and Instructional Materials Help Teachers Facilitate LearningDocument7 pagesTeaching Aids and Instructional Materials Help Teachers Facilitate LearningAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- Course Module Design I and The WorldDocument28 pagesCourse Module Design I and The WorldAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan FormatDocument4 pagesLesson Plan FormatAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- (Nayeon) Ireojido Mothaneunde Jeoreojido Mothane Geujeo Barabomyeo Baby Ba-Ba-BabyDocument2 pages(Nayeon) Ireojido Mothaneunde Jeoreojido Mothane Geujeo Barabomyeo Baby Ba-Ba-BabyAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- NarcisaDocument1 pageNarcisaAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- MCDocument3 pagesMCAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- MCDocument5 pagesMCAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Deductions From Gross Estate2013Document9 pagesChapter 4 - Deductions From Gross Estate2013incubus_yeah90% (10)
- HboDocument3 pagesHboAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- CD OutlineDocument4 pagesCD OutlineAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- Bus PolDocument2 pagesBus PolAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- Accounting TriviasDocument2 pagesAccounting TriviasAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- CD OutlineDocument1 pageCD OutlineAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- AdkjasfbjabfkDocument1 pageAdkjasfbjabfkAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- AaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaahhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhDocument1 pageAaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaahhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- WP - Dept. A WP - Dept. B WP - Dept. C Finished Goods Cost of Goods Sold XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XXDocument3 pagesWP - Dept. A WP - Dept. B WP - Dept. C Finished Goods Cost of Goods Sold XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XXAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- A Beez Iin The TrapDocument1 pageA Beez Iin The TrapAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- JZ 1741Document1 pageJZ 1741Annabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- Prayer To ST Joseph of CupertinoDocument1 pagePrayer To ST Joseph of CupertinoAnnabeth ChaseNo ratings yet
- Income TaxDocument14 pagesIncome Taxankit srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Control Your Cash and Retirement With StocksDocument60 pagesControl Your Cash and Retirement With StocksLaurent DNo ratings yet
- INS 22 Guide Overview of Personal InsuranceDocument58 pagesINS 22 Guide Overview of Personal InsuranceSABIR KHAN75% (4)
- JALANDHAR DISTRICT PROFILE: DEMOGRAPHICS, INDUSTRY, AGRICULTURE, BANKING OVERVIEWDocument5 pagesJALANDHAR DISTRICT PROFILE: DEMOGRAPHICS, INDUSTRY, AGRICULTURE, BANKING OVERVIEWsai pujitha nayakantiNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Financial Constraints, Investment Opportunity Set, and Financial Reporting Aggressiveness On Tax AggressivenessDocument16 pagesThe Effect of Financial Constraints, Investment Opportunity Set, and Financial Reporting Aggressiveness On Tax AggressivenessmuchlisNo ratings yet
- Unintended Consequences: by John MauldinDocument11 pagesUnintended Consequences: by John Mauldinrichardck61No ratings yet
- Ying Wa College Mid-Year Examination 2018 - 2019 S3 MathematicsDocument15 pagesYing Wa College Mid-Year Examination 2018 - 2019 S3 Mathematics廖陞民(LEFT-2021) LIU SING MANNo ratings yet
- Welcome To First ReviewDocument17 pagesWelcome To First Reviewkarthy143No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 and 6 Financial SystemDocument7 pagesChapter 5 and 6 Financial SystemRemar22No ratings yet
- Control Design Effectiveness Quality Review ChecklistDocument6 pagesControl Design Effectiveness Quality Review ChecklistRodney LabayNo ratings yet
- KeerthiDocument10 pagesKeerthiDvd LavanyaNo ratings yet
- PrivatizationDocument69 pagesPrivatizationgakibhaiNo ratings yet
- 10 HowToPredictForexBWDocument6 pages10 HowToPredictForexBWWihartono100% (1)
- HKSI LE Paper 11 Pass Paper Question Bank (QB)Document10 pagesHKSI LE Paper 11 Pass Paper Question Bank (QB)Tsz Ngong KoNo ratings yet
- The ROI of Optimizing Product ManagementDocument6 pagesThe ROI of Optimizing Product ManagementicrapperNo ratings yet
- FINMAN 4 - Instructional Material 1Document25 pagesFINMAN 4 - Instructional Material 1Justine NeronaNo ratings yet
- Flybe Group PLC FLYBGB Annual Report For Period End 31mar2015 English PDFDocument136 pagesFlybe Group PLC FLYBGB Annual Report For Period End 31mar2015 English PDFtheredcornerNo ratings yet
- Global interstate system and institutionsDocument4 pagesGlobal interstate system and institutionsravelyn bresNo ratings yet
- Rural DevelopmentDocument55 pagesRural DevelopmentmeenatchiNo ratings yet
- Sindh Workers Welfare Fund Act SummaryDocument4 pagesSindh Workers Welfare Fund Act SummaryAamir ShehzadNo ratings yet
- Kimly Achieves S$5.3 Million Net Profit in 1Q FY2019 On S$52.6 Million RevenueDocument3 pagesKimly Achieves S$5.3 Million Net Profit in 1Q FY2019 On S$52.6 Million RevenueWeR1 Consultants Pte LtdNo ratings yet
- Pag-IBIG Fund Public Auction Properties in Cavite, Laguna, Bulacan & Metro ManilaDocument24 pagesPag-IBIG Fund Public Auction Properties in Cavite, Laguna, Bulacan & Metro ManilaSilvino CatipanNo ratings yet
- Channel Partnership AgreementDocument3 pagesChannel Partnership AgreementNova SarmahNo ratings yet
- Loan Briefing Presentation - 10-03-07Document99 pagesLoan Briefing Presentation - 10-03-07api-381193650% (2)
- Ch16 Answer KeyDocument30 pagesCh16 Answer KeyWed Cornel0% (1)
- Court rules on deductions from spousal support arrearsDocument1 pageCourt rules on deductions from spousal support arrearsNicole CruzNo ratings yet
- Business Law - Negotiable InstrumentsDocument8 pagesBusiness Law - Negotiable InstrumentsPrincessa Lopez MasangkayNo ratings yet
- Livelihood Project For The Poor in OmanDocument6 pagesLivelihood Project For The Poor in OmanInternational Journal of Business Marketing and ManagementNo ratings yet
- Business Finance EssayDocument2 pagesBusiness Finance EssayAlex Langkwenta100% (1)