Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Advanced Four Wheel Steering System
Uploaded by
SyedAbuBakar'sAlkaffOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Advanced Four Wheel Steering System
Uploaded by
SyedAbuBakar'sAlkaffCopyright:
Available Formats
IJREAT International Journal of Research in Engineering & Advanced Technology, Volume 3, Issue 2, April-May, 2015
ISSN: 2320 8791 (Impact Factor: 2.317)
www.ijreat.org
Advanced Four Wheel Steering System
Bhupendra Pratap Singh1, Brijesh Kumar Yadav2, Lal
Bahadur Singh3, Badri Vishal4, Raj Kumar Yadav5
Mr.Ram Pratap Yadav6, Mr.Rahul Srivastav7
1,2,3,4,5
B.Tech students, Assistant professor, Lecturer, Department of Mechanical Engineering,
BIT, GIDAGorakhpur(U.P.) India
ABSTRACT
The aim of this project is to decrease the turning radius
of the vehicle using four wheels symmetric steering
system (4WS). The system being analyzed here is a
mechanical linkage between the front and the rear. The
use of a simple kinematic bar mechanism connecting the
front and rear hub making the rear wheel to turn in an
opposite direction as the front wheels are turned thereby
performing the task of reducing the turning radius of the
vehicle. In situations like low speed cornering, vehicle
parking and driving in city conditions with heavy traffic
in tight spaces, driving would be very difficult due to
vehicles larger wheelbase and track width. Hence there
is a requirement of amechanism which result in less
turning radius and it can be achieved by implementing
four wheel steering mechanism instead of regular two
wheel steering. The prototype was tested for its cornering
ability through constant radius test and was found 40%
reduction inturning radius and the vehicle was operated
at low speed of 10 kmph.
KEYWORDS: Four-Wheel Steering, 4WS,
Rear Wheels Control, Turning radius optimization.
1. INTRODUCTION
Steering is a system that is used in most type of transport
to control the movement ofthe vehicle. The steering
system allows the driver to guide the moving vehicle on
the road and turn it right or leftas desired. The vehicle is
equipped with four wheel steering system; it will be easy
for the driver to actually make the turn with ease even in
the small space that is available for him. But the main
thing is that we have two configurations in four wheel
steering systems called same phase and opposite phase.
In order to reduce the turning radius of the vehicle, we
need the opposite phase configuration of four wheel
steering system.
The main aim of this project is to reduce the turning
radius of a vehicle as much as practically possible
without crossing the practical limits of design and
assembly of the components of the steering system.
Based on these requirements, a four wheel symmetric
steering system is analyses using kinematic approach and
a conclusion is drawn regarding the geometry of the
optimum steering system and the effect of this on the
turning radius of the vehicle. This system is seen not to
cross any practical limitations of the vehicle in terms of
assembly and spacing.
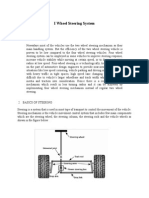
2. STEERING PRINCIPLE
According to Ackerman steering system, is a geometric
arrangement of linkages in the steering of a car or
other vehicle designed to solve the problem of wheels on
the inside and outside of a turn needing to trace
out circles of different radius. The intention of
Ackermann geometry is to avoid the need for tyres to slip
sideways when following the path around a curve. The
geometrical solution to this is for all wheels to have their
axles arranged as radii of a circle with a common centre
point. In two wheel steering as the rear wheels are fixed,
this centre point must be on a line extended from the rear
axle. Intersecting the axes of the front wheels on this line
as well requires that the inside front wheel is turned,
when steering, through a greater angle than the outside
wheel. Ackerman condition for a front wheel steering
system, the difference of the cotangents of the angles of
the front outer to the inner wheels should be equal to the
ratio of width and length of the vehicle being considered
as shown in fig. The terms represents outer wheel
angle and represents inner wheel angle. The term w
represents the wheel track and l represents wheel base.
www.ijreat.org
Published by: PIONEER RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT GROUP (www.prdg.org)
149
IJREAT International Journal of Research in Engineering & Advanced Technology, Volume 3, Issue 2, April-May, 2015
ISSN: 2320 8791 (Impact Factor: 2.317)
www.ijreat.org
Fig. Steering illustration
Fig.Oversteer
[cotocoti=w/l]
3.3 COUNTERSTEER
Counter-steering can defined as when the slip angle of
front wheels is equal to slip angle of rear wheel.
3. TURNING RADIUS
The turning radius or turning circle of a vehicle is the diameter
of the smallest circularturn that the vehicle is capable of
making.
Turning circle radius = (track/2) + (wheelbase/ sin (average
steer angle))
3.1 UNDERSTEER
When the slip angle of front wheels is greater than slip
angle of rear wheels vehicle under steers. Thus the
vehicle goes out of the circle of steering. Most vehicles
manufacturers set the vehicle profile with some
understeer.
Fig.Countersteer
4. COMPARED OF 4WS SYSTEM WITH
2WS CONVENTIONAL SYSTEM.
Car more efficient and stable on cornering.
Improved steering responsiveness and precision .
High speed straight line stability.
Notable improvement in rapid, easier, safer lane
changing maneuvers.
Smaller turning radius and tight space maneuverability at
low speed.
Relative Wheel Angles and their Control.
Risk of hitting an obstacle is greatly reduced.
Fig.Understeer
5. STEERING WHEEL CONFIGURATION
3.2 OVERSTEER
Over steer is defined when the slip angle of front wheel is
less than the slip angle of rear wheel. This makes the
vehicle move inside the circle of steer. This is a
fardangerous situation than understeer.
(i)Two Wheel Steer :
A Four Wheel Steering System is flexible enough to
work as a two wheel steer by restricting the rear wheel
movement.
(ii)Four wheel steer:
www.ijreat.org
Published by: PIONEER RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT GROUP (www.prdg.org)
150
IJREAT International Journal of Research in Engineering & Advanced Technology, Volume 3, Issue 2, April-May, 2015
ISSN: 2320 8791 (Impact Factor: 2.317)
www.ijreat.org
Front wheel directions are opposite to rear wheel
directions.This helps to take sharp turn with least turning
radius. This is done at slow speed.
(iii) Crab Steer :
At high speed lane change, both the front and rear wheels
face in same direction.
(iv) Zero turn:
Front and Rear wheels are so aligned that the vehicle
moves in acircle of zero radius.
Negative Four Wheel Steering System
In the negative four steering system
both the front and the rear wheels turn in opposite to each
other is called negative four wheel steering system.
6. FOURWHEELSTEERING TYPES
There are two types of four wheel steering
configurations.
(i)
Positive Four Wheel Steering System
(ii)
Negative Four Wheel Steering System
Positive Four Wheel Steering System
In the positive four wheel steering
both the front and the rear wheels turn in the same
direction.
Fig. Negative four wheel steering
7. TURNING CIRCLE MEASUREMENT
Turning circle measurement as per Indian Standards , the
turning circle is measured by drawing a circle on which
the outer most wheel moves when the steering wheel is
turned to the maximum lock and the vehicle moving at a
speed below 10km/h.
Case study of four wheel steering
A case study on the steered wheel angles of a vehicle is
done to find the usefulness of the symmetric four wheel
steering system in reducing the turning radius of the
vehicle compared to its counterpart i.e. the normal front
wheel steering system in which only the front wheels are
steered.
The data of the vehicle considered are as follows
Wheel Base :
Wheel Track :
Turning radius :
680mm
460mm (approx.)
1234.795mm
Fig.Positive four steering
www.ijreat.org
Published by: PIONEER RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT GROUP (www.prdg.org)
151
IJREAT International Journal of Research in Engineering & Advanced Technology, Volume 3, Issue 2, April-May, 2015
ISSN: 2320 8791 (Impact Factor: 2.317)
www.ijreat.org
Now, keeping the other angle constant and applying four
wheel symmetric steering to this vehicle and measuring
the other wheel angle for symmetric four wheel steering
geometry, we get the following as the resultant turning
radius using this system.
Fig.Steered fornt wheel angle measurment
Initially only the front wheel steering is considered to
find out the angles of the front two wheels at the given
turning radius value in the car brochure considering the
vehicle wheel base and track values.
Fig.Modified steering wheels angles 2
Now, keeping one of the angles constant and applying
four wheel symmetric steering to this vehicle and
measuring the other wheel angle for symmetric four
wheel steering geometry, we get the following as the
resultant turning radius using this system.
Out of the two observations, it is evident that the second
system gives the optimum turning radius without
exceeding the practical limitations of the vehicle which is
the turning of the inner wheel to an angle of 80.10 to one
extreme.
Fig. Optimum symmetric four wheel steering
Fig. Modified steering wheels angles 1
The optimum steering wheel angles practically suitable
for a vehicle to reduce the turning radius of the vehicle.
www.ijreat.org
Published by: PIONEER RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT GROUP (www.prdg.org)
152
IJREAT International Journal of Research in Engineering & Advanced Technology, Volume 3, Issue 2, April-May, 2015
ISSN: 2320 8791 (Impact Factor: 2.317)
www.ijreat.org
This optimum configuration gives 34% reduction of the
turning radius for this vehicle.
8. ADVANTAGE
http://www.docstoc.com/docs/73259901/Four-WheelSteering-System
[6]Control System of vehicle model with Four Wheel
Steering by P.Brabec, M.Maly,
R.Vpzenilek.
Turning radius of the vehicle can be reduced
and better parking.
Better handling in tight corners.
Improved steering response.
Stability of the vehicle increase at low speed.
Better high speed maneovers .
Better straight line stability.
Improved corning performance
9. LIMITATIONS
The effect that it produces is not felt significantly at low
speed or in commercial carsbut in heavy vehicles like
trucks and towing vans it provides significant lane
changing and low speed manoeuvrability. Its mechanism
is extensively complex. Althoughmany designs have
been brought forward so far, none has the right
combination ofsimple design, low maintenance with low
cost.
CONCLUSION
Thus, the four wheel steering system has got cornering
capability, steering response, straight linestability, lane
changing and low speed maneuverability. Even though it
is advantageous over the conventional two wheel steering
system, four wheel steering is a complex and expensive.
Currently, the cost of a vehicle with four wheel steering
is more than that of the conventional two wheel steering
ofvehicle. Four wheel steering is growing in popularity
and it is likely to come in more and more new vehicles.
As the system become more common place, the cost of
four wheel steering system will drop down.
REFERENCE
[1] H. Sakai, T. Matsuo, S. Murayama, H. Hoshino, and
R. Nagashima,Utsunomiya University, Utsunomiya,
Japan
[2]Indian Standards - 12222
[3]D.S.CHOUDHARI ,Assistant Professor, Department
of Mechanical Engineering, Atmiya Institute of
Technology andScience, Rajkot, Gujrat 4WS ISSN
2774785
[4]Institute for Dynamic System and Controls, Steering
Dynamics
[5]Unknown, Four Wheel Steering System,
www.ijreat.org
Published by: PIONEER RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT GROUP (www.prdg.org)
153
You might also like
- Chevy Differentials: How to Rebuild the 10- and 12-BoltFrom EverandChevy Differentials: How to Rebuild the 10- and 12-BoltRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Ninty Degree SteeringDocument48 pagesNinty Degree Steeringparas bhogulkarNo ratings yet
- Study of Four Wheel Steering Mechanism: JournalDocument4 pagesStudy of Four Wheel Steering Mechanism: JournalSiva HariNo ratings yet
- Project SynapsisDocument6 pagesProject Synapsisnayan RNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Four Wheel Steering System For Light Motor VehiclesDocument10 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Four Wheel Steering System For Light Motor VehiclesS18M168 SUJAN BALAJI SNo ratings yet
- Study of Steering Mechanism MechanicalDocument9 pagesStudy of Steering Mechanism MechanicalSANURASAGARNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Four Wheel Steering MechanismDocument7 pagesResearch Paper On Four Wheel Steering Mechanismnyl1hij0fup3No ratings yet
- Development of FFOUR WHEELSour WheelsDocument1 pageDevelopment of FFOUR WHEELSour WheelsRaja SekarNo ratings yet
- Study of Zero Turn Vehicle: Shirsathsachin, Jadhav Kiran, Patil Rahul, Mohite Abhilash, D.D. PatilDocument8 pagesStudy of Zero Turn Vehicle: Shirsathsachin, Jadhav Kiran, Patil Rahul, Mohite Abhilash, D.D. Patilkush alladiNo ratings yet
- Wheel Steering System PDFDocument6 pagesWheel Steering System PDFvivek ghoriNo ratings yet
- Three Mode Steering System For Light Weight Automobile VehiclesDocument4 pagesThree Mode Steering System For Light Weight Automobile VehiclesijsretNo ratings yet
- Wheel Steering SystemDocument28 pagesWheel Steering SystemKshitij SharmaNo ratings yet
- Paper On Calculation PDFDocument5 pagesPaper On Calculation PDFAnonymous Gm9VGRmVoNo ratings yet
- Steering Mechanism With Zero Turning RadiusDocument19 pagesSteering Mechanism With Zero Turning RadiusAbhay RanjanNo ratings yet
- Aen ReportDocument14 pagesAen Reportv.v.ransing22No ratings yet
- Automobile EngineeringDocument133 pagesAutomobile EngineeringAshok Singh Yadav100% (3)
- Research Paper On Four Wheel SteeringDocument7 pagesResearch Paper On Four Wheel Steeringd1fytyt1man3100% (1)
- Four WheelDocument14 pagesFour WheelMaheshNo ratings yet
- Dual Mode Four Wheel Steering System: Sanu Adolphus Sooraj AbrahamDocument7 pagesDual Mode Four Wheel Steering System: Sanu Adolphus Sooraj AbrahamVincent RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Six Wheel Three Mode Steering System PDFDocument6 pagesSix Wheel Three Mode Steering System PDFSEELAM HARSHAVARDHANREDDYNo ratings yet
- Three Mode Four Wheel Steering-1-1Document15 pagesThree Mode Four Wheel Steering-1-1sree kanthNo ratings yet
- 09db7a34f8 21 IarjetDocument4 pages09db7a34f8 21 IarjetVinit TyagiNo ratings yet
- Four Wheel Steering CarDocument6 pagesFour Wheel Steering CartrishulNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Four Wheel Steering MechanismDocument50 pagesFabrication of Four Wheel Steering MechanismMechWindNaniNo ratings yet
- TO Automotive Steering SystemDocument22 pagesTO Automotive Steering SystemJ Naveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Development of Four Wheel Steering System For A Car: K. Lohith, Dr. S. R. Shankapal, M. H. Monish GowdaDocument8 pagesDevelopment of Four Wheel Steering System For A Car: K. Lohith, Dr. S. R. Shankapal, M. H. Monish GowdaGaurav PandeyNo ratings yet
- Racetrack Raiders MNIT, JaipurDocument13 pagesRacetrack Raiders MNIT, JaipurKartikey SharmaNo ratings yet
- Design of Accurate Steering Gear MechanismDocument12 pagesDesign of Accurate Steering Gear Mechanismtarik RymNo ratings yet
- Four-Wheel Steering Mechanism - ReviewDocument4 pagesFour-Wheel Steering Mechanism - ReviewRajatNo ratings yet
- Steering GeometryDocument23 pagesSteering Geometryashukmr90No ratings yet
- MCT 311 Lesson 5Document16 pagesMCT 311 Lesson 5Moussa SaidNo ratings yet
- Design and Manufacturing of Differential Locking SystemDocument6 pagesDesign and Manufacturing of Differential Locking SystemShashank VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Design of 360 Degree Steering System: Saransh Tiwari Dr. Rajeev AryaDocument6 pagesDesign of 360 Degree Steering System: Saransh Tiwari Dr. Rajeev AryaAkarsh AdiNo ratings yet
- Design of Accurate Steering Gear MechanismDocument12 pagesDesign of Accurate Steering Gear Mechanism1DA17ME055 Harshit MDNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 AutomobileDocument11 pagesAssignment 3 Automobilepawan sharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv Steering SystemDocument20 pagesUnit-Iv Steering SystemMark MubiruNo ratings yet
- SteeringDocument27 pagesSteeringSHARATH.R.SHETTIGARNo ratings yet
- Brake Report 2015Document38 pagesBrake Report 2015Pratyush NagareNo ratings yet
- Ijme V2i6p107Document5 pagesIjme V2i6p107Atthuru ManikantaNo ratings yet
- Tribhuvan University Institute of Engineering Thapathali CampusDocument10 pagesTribhuvan University Institute of Engineering Thapathali CampusRustam Alee KhanNo ratings yet
- 4 Wheel SterringDocument8 pages4 Wheel Sterringrkh02992No ratings yet
- Zero Radius Turning and Four Wheel Steering SystemDocument27 pagesZero Radius Turning and Four Wheel Steering SystemNikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Be-Automobile Lab ManualDocument42 pagesBe-Automobile Lab ManualA.j. Jain100% (1)
- Front Wheel Steering System With Movable Hedlights Ijariie5360Document6 pagesFront Wheel Steering System With Movable Hedlights Ijariie5360Ifra KhanNo ratings yet
- Project Seminor Final ReviewDocument17 pagesProject Seminor Final ReviewDr.KVSRIT PrincipalNo ratings yet
- Usage of Tumbler Gear Mechanism in Four Wheel SteeringDocument5 pagesUsage of Tumbler Gear Mechanism in Four Wheel SteeringKitkuparbha MawrieNo ratings yet
- Chain Less BicycleDocument20 pagesChain Less BicycleSankalp HiremathNo ratings yet
- Senior Project ReportDocument6 pagesSenior Project ReportRoss Bunnell100% (1)
- Development of 360 Degree Rotating VehicleDocument4 pagesDevelopment of 360 Degree Rotating VehicleIJIRST57% (7)
- Design and Fabrication of Shaft Driven BicycleDocument46 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Shaft Driven BicycleNishanth Krishnan80% (10)
- Tri WheelDocument6 pagesTri WheelAminul HoqueNo ratings yet
- Ijmet 08 08 019Document8 pagesIjmet 08 08 019achumilemlata48No ratings yet
- Modal and Stress Analysis of Lower Wishbone Arm Along With TopologyDocument7 pagesModal and Stress Analysis of Lower Wishbone Arm Along With TopologyInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Mech 203 Term Project Automobile Differential and TransmissionDocument29 pagesMech 203 Term Project Automobile Differential and TransmissionYugi SupriatnaNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Two Modes of Steering FinalDocument38 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Two Modes of Steering FinalS18M168 SUJAN BALAJI SNo ratings yet
- 6th Semestermechanical Automobile Engineering Lab ManualDocument21 pages6th Semestermechanical Automobile Engineering Lab ManualSayan BiswasNo ratings yet
- Y4592 PDFDocument4 pagesY4592 PDFPrathamesh PatikNo ratings yet
- MI - 20033 GT46AC Schedule Maint. ProgramDocument24 pagesMI - 20033 GT46AC Schedule Maint. ProgramRafael Dutil LucianaNo ratings yet
- 1006TAG ElectropaK (PN1578 75th)Document2 pages1006TAG ElectropaK (PN1578 75th)marianusNo ratings yet
- 2021 Ferrari SF90 Stradale $849,990: CoupeDocument2 pages2021 Ferrari SF90 Stradale $849,990: CoupejjNo ratings yet
- Hyndai I20 BC3 AccessoriesDocument28 pagesHyndai I20 BC3 AccessoriesaolNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 - Engine ParametersDocument26 pagesLec 3 - Engine ParametersGODNo ratings yet
- Icu KeypadDocument84 pagesIcu Keypadcarlos maradiagaNo ratings yet
- Yamaha SHO Service Manual PDFDocument433 pagesYamaha SHO Service Manual PDFDernica Mandy100% (2)
- Engine HistoryDocument10 pagesEngine HistoryFelipe SierraNo ratings yet
- AB14EJ (AB460EJ) /AB16EJ (AB520EJ) : Compliant With CE/ANSI/CSA StandardsDocument2 pagesAB14EJ (AB460EJ) /AB16EJ (AB520EJ) : Compliant With CE/ANSI/CSA StandardsKelvin ChanNo ratings yet
- 3 MBE900 04aDocument10 pages3 MBE900 04aJorge A Salinas100% (1)
- Truck PM Inspection TemplateDocument2 pagesTruck PM Inspection TemplateTonya100% (1)
- IC Engines PPT Lecture No 1Document33 pagesIC Engines PPT Lecture No 1VishweshRaviShrimali100% (1)
- Cummins Isf2.8 Spare Parts CatalogDocument8 pagesCummins Isf2.8 Spare Parts CatalogChen Caroline100% (1)
- TBIS 15194-2019 CH 第15頁測試方法 PDFDocument143 pagesTBIS 15194-2019 CH 第15頁測試方法 PDFjogh22No ratings yet
- Camshaft1 PDFDocument3 pagesCamshaft1 PDFVladimirNo ratings yet
- Hemi Web CatalogDocument62 pagesHemi Web CatalogAdson LimaNo ratings yet
- Practical - QP - R - 2017 - AT8411 - OK - AT 8411-4.4Document3 pagesPractical - QP - R - 2017 - AT8411 - OK - AT 8411-4.4Palani VelNo ratings yet
- Peças Hangcha RW 1,0-1,8T - 2017Document360 pagesPeças Hangcha RW 1,0-1,8T - 2017Eldelson BaggetoNo ratings yet
- V8 Gas Engine For Cogeneration Plants: MAN Nutzfahrzeuge GroupDocument4 pagesV8 Gas Engine For Cogeneration Plants: MAN Nutzfahrzeuge GroupKaiser IqbalNo ratings yet
- Curso SYS FastrackDocument14 pagesCurso SYS FastrackJose Cruz candidoNo ratings yet
- 911 and Porsche World 07.2023Document132 pages911 and Porsche World 07.2023chairat yudhakarjkumthornNo ratings yet
- 01 - Introduction To Vehicles Components and Sub-Systems (Fraser)Document86 pages01 - Introduction To Vehicles Components and Sub-Systems (Fraser)Murali Krishna100% (1)
- S. No. Customer Model Part Name Working Days Weight (Ton) Drg. Weight AVG/ Day Qty Apr-21 Total Qty Total Tonage Customer WiseDocument48 pagesS. No. Customer Model Part Name Working Days Weight (Ton) Drg. Weight AVG/ Day Qty Apr-21 Total Qty Total Tonage Customer Wiseharish yadavNo ratings yet
- Ge Jenbacher - Jgs 616dsDocument4 pagesGe Jenbacher - Jgs 616dsabdulkidwai2009No ratings yet
- English Manual For The AirmaxDocument27 pagesEnglish Manual For The AirmaxUnguru BulanNo ratings yet
- 6speed Manual Trans & Diff For Subaru WRX 2005Document132 pages6speed Manual Trans & Diff For Subaru WRX 2005xfvgc8gcd8No ratings yet
- r1040 r1080 k1080 Series Industrial EnginesDocument96 pagesr1040 r1080 k1080 Series Industrial Enginessardhan.rajender84100% (1)
- BMW Bikes Collection 2010Document9 pagesBMW Bikes Collection 2010dhaannhhNo ratings yet
- MTU Series 10V1600 ESN 6601002253 PDFDocument154 pagesMTU Series 10V1600 ESN 6601002253 PDFRath Asypaden100% (1)
- ElccarsDocument4 pagesElccarsCarla LoiaconoNo ratings yet