Professional Documents
Culture Documents
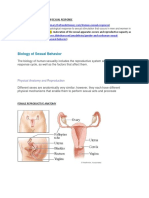
Female Reproductive System
Uploaded by
ojamil2Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Female Reproductive System
Uploaded by
ojamil2Copyright:
Available Formats
Female Reproductive System
Dr. Mubarak Bidmos
Assistant Professor (Anatomy)
College of Medicine
Qatar University
mbidmos@qu.edu.qa
22nd December 2016
Expected Learning Outcomes
Identify the organs of the female reproductive system and
describe the general function of each
Describe the functions of the vesicular follicles and corpus
luteum of the ovary.
Describe the layers of the uterine wall
Indicate the location of the different parts of the uterus and
uterine tube
Describe the basic features of the vulva
Components of the Female
Reproductive Tract
GA 3.36
Female Pelvic Viscera:
Superior View
POSTERIOR
Superior view
Uterine
tube
Sigmoid
colon
Rectum
Ovary
Uterine tube
Uterus
Urinary bladder
M&O27.11
ANTERIOR
Midsagittal section
Female Pelvic Viscera: Sagittal View
Gonads:
A. Ovaries
Reproductive tract:
B. Uterine (Fallopian) tubes
C. Uterus
D. Vagina
External genitalia (vulva):
E
F
G
E. Vestibule
D
F. Labia minora
G. Labia majora
5
The Ovary
F
M&O28.4
A. Tunica albuginea: Dense connective tissue
B. Cortex: Contains follicles at different stages of development
C.
Corpus luteum: Ruptured follicle after ovulation
D. Medulla: Highly vascularized
E. Ovarian ligament and F. Suspensory ligament
Ovarian Follicles: Review
Primordial follicle
Secondary follicle
Primary follicle
Graafian follicle
The Uterine Tubes
A
Part of the ductal system
Functions:
Reception of oocyte
Site of fertilization
Transportation of zygote
Parts:
Infundibulum with fimbriae
Ampulla
Isthmus
Intramural
M&O28.6
8
Histology of the Fallopian Tube
Simple columnar epithelium with
ciliated (A) and secretory (B) cells
Concentric smooth muscle layer
Visceral peritoneum
B
A
Scanning electron micrograph of the
surface of the uterine tube
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Infection of the ovaries and the uterine tubes
Spread of infection into the peritoneal cavity due to open
ductal system in females
10
The Uterus
C B
A
Location: Between the urinary
bladder (A) and the rectum (B)
Rectouterine pouch (C) : Site of
blood accumulation from ruptured
ectopic pregnancy
Functions: Reception,
nourishment and retention of
zygote
11
Gross Anatomy of the Uterus
Subdivisions:
Fundus (A)
Body (B)
Cervix (C)
Cancer of the cervix
Uterine wall:
Endometrium (D)
Myometrium (E)
Perimetrium
12
Ligaments of the Uterus
A. Broad ligament: Holds the uterus in place in the pelvis
B. Suspensory ligament of the ovary: Fold of peritoneum covering ovarian
blood vessels
C. Round ligament of the uterus: Prevents posterior displacement of the
uterus
13
Think Before You Reveal
A
14
The Vagina
Vagina
Extends from the cervix to vestibule
Posterior to urethra and base of
bladder and anterior to rectum
Cervix projects into vaginal canal
(birth canal)
Covered by hymen, fold of mucosa
Histology:
Stratified squamous non-keratinized
epithelium
Acidic environment: discourages bacterial
growth
M&O28.2
15
The Vagina
Vulva
Perineum
16
You might also like
- The Reproductive System - Test QuestionsDocument4 pagesThe Reproductive System - Test QuestionsflorinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Test 3 (NP Ii)Document16 pagesNursing Test 3 (NP Ii)Yuxin LiuNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesReproductive SystemanojanNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy 2008Document28 pagesEctopic Pregnancy 2008Alleya SheeneNo ratings yet
- OC Set B NEWDocument18 pagesOC Set B NEWmatrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- 23 FemaleDocument39 pages23 FemaleQaiser InayatNo ratings yet
- Embryo QuestionsDocument15 pagesEmbryo QuestionsAnon AnonNo ratings yet
- Reproduction System Terminology QuizDocument6 pagesReproduction System Terminology QuizIrams KitchenNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Female Genital TractDocument34 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Female Genital TractOsphroNo ratings yet
- OB Exam 9aDocument12 pagesOB Exam 9aJaz BenitoNo ratings yet
- 2021 Obs MidsemDocument10 pages2021 Obs MidsemADAMU wahabNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy Review QuestionsDocument5 pagesGross Anatomy Review QuestionsJames Gabriel Salarda100% (1)
- Exstrophy-Epispadias Complex: Current Management: Journal ReadingDocument64 pagesExstrophy-Epispadias Complex: Current Management: Journal ReadingAnonymous ce3S6XFdwU100% (1)
- Choose The Best AnswerDocument27 pagesChoose The Best AnswerHusseini ElghamryNo ratings yet
- 3rd Bimonthly Exam-Set BDocument7 pages3rd Bimonthly Exam-Set BSam TagardaNo ratings yet
- 2018级留学生妇产科学A卷Document8 pages2018级留学生妇产科学A卷zkcc5khhx9No ratings yet
- Section: General ObstetricsDocument15 pagesSection: General ObstetricsvarmaNo ratings yet
- CAMCA QUIZ ReviewDocument3 pagesCAMCA QUIZ ReviewShyla mayNo ratings yet
- Narayana Medical PG Coaching - Week-03 Test (28-09-2014) Anatomy (Histology & Genetics)Document5 pagesNarayana Medical PG Coaching - Week-03 Test (28-09-2014) Anatomy (Histology & Genetics)drpnnreddyNo ratings yet
- Maternity Nursing C) The Action of The Doderlein's BacillusDocument11 pagesMaternity Nursing C) The Action of The Doderlein's BacillusLeilah Khan100% (1)
- Obg Qus Set 1Document25 pagesObg Qus Set 1Imraan KhanNo ratings yet
- Breast AnatomyDocument53 pagesBreast AnatomyShriniwas RushiNo ratings yet
- Development of MidgutDocument31 pagesDevelopment of MidgutRamesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Human Embryology: 2.nd WEEK ImplantationDocument19 pagesHuman Embryology: 2.nd WEEK ImplantationArınç AykutNo ratings yet
- JSMU Semester 3 Embrology McqsDocument12 pagesJSMU Semester 3 Embrology McqsNazia WasimNo ratings yet
- A Round Ligaments: 1. Which Structure Provides The Major Support To The Uterus and Cervix?Document10 pagesA Round Ligaments: 1. Which Structure Provides The Major Support To The Uterus and Cervix?Nikhil Tyagi100% (1)
- Gynecology all in one מסודרDocument11 pagesGynecology all in one מסודרAdrianaNo ratings yet
- First Semester Question BankDocument19 pagesFirst Semester Question Banknanakwame5769No ratings yet
- Question 3Document19 pagesQuestion 3Anonymous LF9aizGhaNo ratings yet
- Ain Shams MCQDocument84 pagesAin Shams MCQAhmed M. Haroun67% (6)
- Samplex ADocument45 pagesSamplex AAizza ZarateNo ratings yet
- Gynecology & Obstetrics MCQDocument49 pagesGynecology & Obstetrics MCQOmar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Paper I MCQs AnatomyDocument31 pagesPaper I MCQs AnatomyMadhu RauniyarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 2-Final-June 2023Document9 pagesAnatomy 2-Final-June 2023Douaa lkNo ratings yet
- Pretest ScienceDocument5 pagesPretest ScienceJhonazel SandovalNo ratings yet
- Multi Choice Questions Surg IrhDocument58 pagesMulti Choice Questions Surg IrhFan Eli100% (13)
- Rani - MCQsDocument8 pagesRani - MCQsK.S. ReddyNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4 A and P 2Document8 pagesQuiz 4 A and P 2Agartha HenewaaNo ratings yet
- Gä°nekol - Englä°shDocument9 pagesGä°nekol - Englä°shesmiracelilova42No ratings yet
- Soal Obgyn Januari Paket 2 SentDocument5 pagesSoal Obgyn Januari Paket 2 SentcirererereNo ratings yet
- Section A: MCQ (80 Questions)Document16 pagesSection A: MCQ (80 Questions)Muhammed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Answer Key BOARD OB BDocument16 pagesAnswer Key BOARD OB BJonas Marvin Anaque100% (4)
- D.S.S AIIMS PREPRATION TEST SERIES - 8 ObgDocument13 pagesD.S.S AIIMS PREPRATION TEST SERIES - 8 ObgDr-Sanjay SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- EmbryologyDocument31 pagesEmbryologyBiyologebNo ratings yet
- West Visayas State University Medical CenterDocument10 pagesWest Visayas State University Medical CenterJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- QnsDocument46 pagesQnsaniridiaNo ratings yet
- Bladder CancerDocument57 pagesBladder CancerBANAWAN TRESHIA MAE D.No ratings yet
- 4 5942854446844217530Document8 pages4 5942854446844217530kassahunNo ratings yet
- Reproductive system - Ôn tậpDocument16 pagesReproductive system - Ôn tập03. Nguyễn Đặng Thiên BảoNo ratings yet
- 2ND Quarter 2023 Answer KeyDocument19 pages2ND Quarter 2023 Answer KeyKlarish Ann IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Histology Seminar 3 MCQDocument31 pagesHistology Seminar 3 MCQNeo ShiriNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing All India Instutite of Medical Sciences, Rishikesh (Uttarakhand) B.Sc. (Hons) Nursing 3 Year Batch - 2016 End Term Examination - 2019 Subject - Maternal Health NursingDocument24 pagesCollege of Nursing All India Instutite of Medical Sciences, Rishikesh (Uttarakhand) B.Sc. (Hons) Nursing 3 Year Batch - 2016 End Term Examination - 2019 Subject - Maternal Health NursingRajaNo ratings yet
- Feb 19 FCPS 2-200 MCQsDocument29 pagesFeb 19 FCPS 2-200 MCQsKahkashan HameedNo ratings yet
- 4.the Vaginal Fluid Is Strongly Acid With PH 4.5 This Is Mainly Related ToDocument16 pages4.the Vaginal Fluid Is Strongly Acid With PH 4.5 This Is Mainly Related Tohasan ahmdNo ratings yet
- Gynecologymcqs - Blog - Best Gynecologist in Mumbai - Gynaecology Doctors IndiaDocument13 pagesGynecologymcqs - Blog - Best Gynecologist in Mumbai - Gynaecology Doctors IndiaLalita Eka Pervita SariNo ratings yet
- MCQ Final obstetricsJAVAXISHVILIDocument11 pagesMCQ Final obstetricsJAVAXISHVILIMohammed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Embryology UterusDocument65 pagesAnatomy and Embryology UterusashwiniNo ratings yet
- The SAGES Manual of Hernia SurgeryFrom EverandThe SAGES Manual of Hernia SurgeryS. Scott Davis, Jr.No ratings yet
- The CervixFrom EverandThe CervixJoseph JordanNo ratings yet
- Childhood Mental Health Disorders: DR Durre Shahwar Attending Physician Child and Adolescents Psychiatry Sidra MedicineDocument40 pagesChildhood Mental Health Disorders: DR Durre Shahwar Attending Physician Child and Adolescents Psychiatry Sidra Medicineojamil2No ratings yet
- How To Survive PBL As A Medical StudentDocument7 pagesHow To Survive PBL As A Medical Studentojamil2No ratings yet
- Sat SecretsDocument1 pageSat Secretsojamil2No ratings yet
- Form.: International Financial CertificationDocument2 pagesForm.: International Financial Certificationojamil2No ratings yet
- Enzyme Reactions WorkshietDocument2 pagesEnzyme Reactions Workshietojamil2No ratings yet
- Academic Calender For 2014-2016 HARVARD. College GuideDocument6 pagesAcademic Calender For 2014-2016 HARVARD. College Guideojamil2No ratings yet
- Instruments For Examination in Obstetrics and Gynecology: Section 1Document12 pagesInstruments For Examination in Obstetrics and Gynecology: Section 1JennyDaniel100% (1)
- Vagina Pics, Hot Pussy Images, XXX Porn Photos, TDocument5 pagesVagina Pics, Hot Pussy Images, XXX Porn Photos, Tohabeeb624No ratings yet
- Science 10Document2 pagesScience 10Trisha Camille Macario100% (2)
- Susan Bratton Personalized Sex Life Bucket ListDocument11 pagesSusan Bratton Personalized Sex Life Bucket ListArturNo ratings yet
- 28-01 - The Reproductive SystemDocument18 pages28-01 - The Reproductive SystemMelinda AprilyaNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument75 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemProf Lina Ramli67% (3)
- Q2 G5 DLL Oct.31-Nov.4-2022Document33 pagesQ2 G5 DLL Oct.31-Nov.4-2022Mylene DiazNo ratings yet
- Box LunchDocument91 pagesBox LunchNicolás SpivakNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction - "Darts" Answer Sheet: Female Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesHuman Reproduction - "Darts" Answer Sheet: Female Reproductive SystemmawitterNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in ScienceDearlene NugasNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesReproductive SystemJC MangaoNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesMale Reproductive SystemShayu ShaNo ratings yet
- Obstetric FistulaDocument8 pagesObstetric FistulaHyderabad hhcNo ratings yet
- SX Education DDocument127 pagesSX Education DsarhadignNo ratings yet
- Dilators EnglDocument5 pagesDilators EnglTomy SaputraNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive Anatomy: Unit 3: Female Reproducti Ve System 1Document33 pagesFemale Reproductive Anatomy: Unit 3: Female Reproducti Ve System 1ERIC ASAMAMLEH KLEMEHNo ratings yet
- Reproductivesystems 180329094915Document28 pagesReproductivesystems 180329094915Fernadez RodisonNo ratings yet
- Cervix InformationDocument4 pagesCervix InformationEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System (Yuni)Document36 pagesFemale Reproductive System (Yuni)Ayi Abdul BasithNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument17 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemYsthanamhire TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Menstrual CycleDocument26 pagesMenstrual CycleHannah SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction QuestionsDocument9 pagesReproduction QuestionselizabethNo ratings yet
- First Summative Test Science 5Document3 pagesFirst Summative Test Science 5Gil Arriola100% (2)
- Lesson Plan in Science 5Document3 pagesLesson Plan in Science 5Analiza Atule ElliNo ratings yet
- Based From Science Writing Team Batangas ProvinceDocument93 pagesBased From Science Writing Team Batangas ProvincePrecious Roxanne BeratioNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Female Reproductive SystemDocument31 pagesAnatomy of Female Reproductive Systemhiba jawedNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive System QuestionsDocument1 pageHuman Reproductive System QuestionskaidenNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Human Sexual ResponseDocument12 pagesUnderstanding The Human Sexual ResponseMaan JosueNo ratings yet
- Project Ease Biology Module 13Document30 pagesProject Ease Biology Module 13Kebb Patrick Enar75% (4)
- The Male Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesThe Male Reproductive SystemJOEL BALAJADIANo ratings yet