Professional Documents
Culture Documents
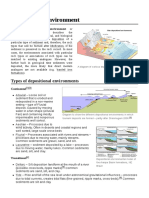
Sedimentary Environments
Uploaded by
Gelique de CastroOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sedimentary Environments
Uploaded by
Gelique de CastroCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter7
Chapter7
SedimentaryEnvironments
moorlandschool.co.uk/earth/earth_science/utah_sandstone.jpg
Sedimentaryenvironments
www.eas.purdue.edu/mesozoic/lab_03/Sedi_Environments.jpg
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
Sedimentaryenvironments
Sedimentary facies
A mass of sedimentary rock which can be defined and
distinguished from others by its geometry, lithology, sedimentary
structures,
structures paleocurrent pattern and fossils (Selley 1970).
1970)
www.thisoldearth.net/Images/transreg.gif
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
Sedimentaryenvironments
Methods of environmental diagnosis
Geometry
Lithology
Sedimentary structures
Fossils
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
moorlandschool.co.uk/earth/earth_science/utah_sandstone.jpg
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
Streams
river, creek, tributary, runnel, lick, rill, river, bayou, rivulet, streamage, wash, gill
(occasionally ghyll), gully; beck, bourne, brook, burn, nant, stream, syke, allt
(UK); kill, run, branch, fork, prong, falls, crick (USA)
3.bp.blogspot.com/_1BZgZVkngwU/TBzOqaN_L4I/AAAAAAAAAEM/bFeRtsCk9Ac/s1600/STREAM+%282%29.jpg
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
Fluvialenvironments
Stream load
www.sci.uidaho.edu/scripter/geog100/lect/11-rivers/11-09-fluvial-transport.jpg
Competence
biggest size of grain that a stream can move
Capacity
maximum amount of debris that a stream can move
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
Fluvialenvironments
Stream flow
laminar flow
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
turbulent flow
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
Fluvialenvironments
River channels
bedrock channel and alluvial channel
scioly.org/w/images/6/6a/Alluvial_stream.jpg
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
Fluvialenvironments
Knickpoint
a sharp change in channel slope, such as a waterfall or lake, resulting from
differential rates of erosion above and below the knickpoint
www.wou.edu/las/physci/taylor/eisi/photos_2006/DSC00029.JPG
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
Fluvialenvironments:Alluvialchannels
Straight
- have a low sinuosity index
- generally lack the typical features of meandering rivers, e.g. point bars
Waal River, Netherlands
www.geo.uu.nl/fg/palaeogeography/pictures/results_fluvialstyle/03_Waal.jpg
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
Fluvialenvironments:Alluvialchannels
Meandering
the most stable and efficient channel geometry, formed and maintained by
erosion of banks and deposition on point bars
Williams River, Alaska
deep, narrow channels
single sinuous channels
single,
few channel islands
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
wattsupwiththat.files.wordpress.com/2009/12/oxbow-lakes1.png
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
Fluvialenvironments:Alluvialchannels
Meander parameters
Sinuosity index
quantitative measurement of
the style of meandering
hydrotopics.files.wordpress.com/2010/10/meandergeometry1.jpg
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
Fluvialenvironments:Alluvialchannels
Helical flow pattern
- develops from the outside of the meander bend towards the inside of the bend
- erodes sediment from the outside bend and deposits point bars on the inside
bend
Huggett, 2011
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
Fluvialenvironments:Alluvialchannels
Incised meanders
occur when a meandering river on alluvium eats down into the
underlying bedrock
Goosenecks at San Juan River, USA (UT)
1.bp.blogspot.com/-0bchEgPURbc/T5TjZJ4HSAI/AAAAAAAAXmQ/t2-FgGtLDiE/s1600/100_7804.JPG
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
Fluvialenvironments:Alluvialchannels
Braided
multiple superimposed meandering channels as discharge and sediment load
vary seasonally and diurnally, e.g. semiarid and proglacial streams
Slims River, Canada
wide, shallow channels
multiple, low sinuosity
multiple
channels
numerous islands
www.geo.uu.nl/fg/palaeogeography/pictures/results_fluvialstyle/01_Slims-River.jpg
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
Fluvialenvironments
Drainage network or pattern
Arrangement of streams in a drainage, which often reflects structural
and/or lithologic control of underlying rocks
Analysis enables interpretation and identification of geologic structures
and rock types in an area
Howard, 1967
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
www.epa.gov/owow/watershed/wacademy/acad2000/stream/s28.jpg
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
Fluvialenvironments:Drainagenetwork
Dendritic
Branching of stream valleys at acute angles without systematic
arrangement
Determined by random headward erosion homogeneous
underlying material
Common on horizontally bedded sedimentary rocks or massive
igneous/metamorphic rocks
courses.missouristate.edu/emantei/creative/WeathStrem/dendri
tic.jpg
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
64.19.142.10/home.moravian.edu/users/phys/mejjg01/geology/
geology%20pages/geo_map_folder/geo_map_images/m_dendri
ticA1.jpg
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
Fluvialenvironments:Drainagenetwork
Trellis
Nearly parallel streams that flow into main trunk streams at high
angles
Subsequent in origin channels are etched out of weaker rock
Common on tilted sedimentary beds
jlmvisuals.com/photoslrwater/GL0025.jpg
64.19.142.12/home.moravian.edu/users/phys/mejjg01/geology/
geology%20pages/geo_map_folder/geo_map_images/m_trellis
1.jpg_hyuncompressed
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
Fluvialenvironments:Drainagenetwork
Rectangular
Tributary streams join trunk streams at right angles as a result of
subsequent streams adjusting to fault or joint systems
Usually formed on jointed/faulted rocks
www.aristo.com.hk/teachers_land/teacher_materials/geography
/new_design/geography/images/PhotoGallery/rectangular_drain
age.jpg
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
10
Fluvialenvironments:Drainagenetwork
Radial
Consequent streams flowing from a central area in all directions;
Streams converging into a central basin/depression form a
centripetal drainage pattern
Usually developed on high, recently formed land surfaces (e.g.,
volcanic cones or intrusive domes)
earth.jsc.nasa.gov/sseop/images/EFS/lowres/STS068/STS068
-253-7.jpg
www.proprofs.com/quizschool/upload/yuiupload/1226500853.jpg
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
Fluvialenvironments:Drainagenetwork
Annular
Streams that follow circular courses due to the erosion of
alternating weak and resistant sedimentary rocks of domes
www.proprofs.com/quizschool/upload/yuiupload/1561287329.jpg
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
11
Fluvialenvironments:Drainagenetwork
Parallel
Streams follow nearly parallel directions
Usually controlled by unidirectional regional slope or by parallel to
subparallel topographic features
resweb.llu.edu/rford/courses/ESSC500
/fluvial_slides/cuesta2.jpg
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
Fluvialenvironments
Floodplain
- the surface of low relief adjacent to a stream that becomes the stream bed
during flood
- features include meander scars, levees, and oxbow lakes
www.uwec.edu/jolhm/EH/Disrude/images/floodplain.gif
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
www.sci.uidaho.edu/scripter/geog100/lect/11-rivers/11-18-riverfloodplain.jpg
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
12
Fluvialenvironments
Alluvial fan
- low, triangular-shaped deposits built from the accumulation of sediments
deposited at the mouth of a valley (i.e., from a mountainous or upland into a
larger mainstream valley or lowland)
- size depends on (1) area of the drainage basin
basin, (2) climate
climate, (3) lithologies in
the source area, (4) tectonic activity, (5) space available for fan growth
Death Valley, USA (CA)
www.windows2universe.org/earth/geology/images/alluvial_fan_lg.jpeg
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
Fluvialenvironments
Delta
- similar morphology to an alluvial fan but deposition results from sharp
reduction in velocity as a stream enters standing water
64.19.142.12/www.pnas.org/content/104/
43/16804/F1.medium.gif
www.gly.uga.edu/railsback/1121DeltaTypes.jpeg
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
13
Fluvialenvironments
Delta lobe switching
64.19.142.12/upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/c/c2/Mississippi_Delta_Lobes.jpg
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
Fluvialenvironments
Delta
- similar morphology to an alluvial fan but deposition results from sharp
reduction in velocity as a stream enters standing water
Topset beds - horizontal layers of smaller
sediment size that form as the main channel of
the river shifts elsewhere and the larger particles
of the bed load are no longer deposited
Foreset beds - consist of the bed
load that the river is moving along
which consists of larger
sediments that roll along the main
channel
upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/f/fe/Delta_beds.png
Bottomset beds - created from the
suspended sediment that settles out
of the water as the river flows into
the body of water and loses energy
N. Ramos | Geology 11 Principles of Geology
Lecture Notes: Sedimentary Rocks
14
You might also like
- Fluids In The Earth's Crust: Their Significance In Metamorphic, Tectonic And Chemical Transport ProcessFrom EverandFluids In The Earth's Crust: Their Significance In Metamorphic, Tectonic And Chemical Transport ProcessNo ratings yet
- Sedimentary Basins & Their Sedimentation PatternDocument27 pagesSedimentary Basins & Their Sedimentation PatternRajesh Singh ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- 4-Sedimentary Rock-Texture and StructureDocument27 pages4-Sedimentary Rock-Texture and Structuredian israyaniNo ratings yet
- Sequence Stratigraphy & Depositional Environment Lecture: 2 (Unit 1)Document55 pagesSequence Stratigraphy & Depositional Environment Lecture: 2 (Unit 1)Rishabh GargNo ratings yet
- WeatheringDocument9 pagesWeatheringpaul machariaNo ratings yet
- System TractsDocument14 pagesSystem TractsTayyab FiazNo ratings yet
- Rivers Pt4 - River FeaturesDocument4 pagesRivers Pt4 - River FeaturesPrudence RwatireraNo ratings yet
- Orogeny: 1 PhysiographyDocument7 pagesOrogeny: 1 PhysiographyafjkjchhghgfbfNo ratings yet
- Continental EnvironmentDocument30 pagesContinental Environmentmoonrock1No ratings yet
- Glacial LandformsDocument5 pagesGlacial LandformsqBataye NhiBatayengeNo ratings yet
- Sedimentary RocksDocument41 pagesSedimentary RocksGelique de CastroNo ratings yet
- SEDIMENTARY STRUCTURES ReportDocument25 pagesSEDIMENTARY STRUCTURES ReportKachel Joy S. Sario100% (1)
- Geology 11 - Lecture Notes 2Document18 pagesGeology 11 - Lecture Notes 2Mars Onairis0% (1)
- Landslides Geology LectureDocument34 pagesLandslides Geology LectureRehan HakroNo ratings yet
- Igneous Activity at The Present Day: TopicDocument4 pagesIgneous Activity at The Present Day: TopicMuhammad Bilal PaulNo ratings yet
- Migmatites and Their OriginDocument3 pagesMigmatites and Their OriginDanis Khan100% (1)
- Precambrian Geology of RajasthanDocument57 pagesPrecambrian Geology of Rajasthanvn2scribd100% (1)
- Ground Water Provinces of IndiaDocument9 pagesGround Water Provinces of IndiaRatan DasNo ratings yet
- Hot Spots, Mantle Plumes, and Triple Point JunctionDocument21 pagesHot Spots, Mantle Plumes, and Triple Point JunctionAryans.GeologyNo ratings yet
- Sedimentary FaciesDocument45 pagesSedimentary Faciesugcc_sr0112No ratings yet
- Sandstone Thin Section StudyDocument7 pagesSandstone Thin Section StudyIjlal AhmadNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Earth Notes 3Document8 pagesDynamic Earth Notes 3Mike ZikoskiNo ratings yet
- Textures and Structures of Igneous RocksDocument30 pagesTextures and Structures of Igneous Rockselenageo05100% (1)
- 1.1 You Might Have Heard Us Define Structure in Rocks As Rock Geometry On A Scale MuchDocument73 pages1.1 You Might Have Heard Us Define Structure in Rocks As Rock Geometry On A Scale Muchsaptak1990No ratings yet
- Fluvial Processes and LandformsDocument25 pagesFluvial Processes and LandformsA S Verma100% (1)
- Sedimentary Rocks and The Rock CycleDocument38 pagesSedimentary Rocks and The Rock CyclemsshahenterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Sedimentary RocksDocument64 pagesChapter 5 Sedimentary RocksJabir JammyNo ratings yet
- Assignment Two Nepal HimalayaDocument5 pagesAssignment Two Nepal HimalayaNirajan Pandey0% (1)
- Physical GeologyDocument731 pagesPhysical GeologyAidan WaiteNo ratings yet
- LithostratigraphyDocument24 pagesLithostratigraphyHina Iqbal100% (1)
- Evolution of Himalaya AK JAINDocument17 pagesEvolution of Himalaya AK JAINSounak BiswasNo ratings yet
- BCCL Soumya GhoshDocument32 pagesBCCL Soumya GhoshAntahin100% (1)
- Sediments, Weathering, ErosionDocument41 pagesSediments, Weathering, Erosiondrjones5No ratings yet
- Origin of MagmaDocument7 pagesOrigin of MagmaCehn MarvidaNo ratings yet
- Master Class On StratigraphyDocument183 pagesMaster Class On StratigraphyJacques LeBlanc100% (1)
- Chapter - 16 Coast and Coral ReefsDocument50 pagesChapter - 16 Coast and Coral ReefsgopeNo ratings yet
- Example Research Proposal GeologyDocument30 pagesExample Research Proposal GeologyFazl Ullah100% (1)
- 0 Primary StructuresDocument29 pages0 Primary StructuresArslan Abbasi33% (3)
- 6 Marginal Marine Env 1Document29 pages6 Marginal Marine Env 1sandraNo ratings yet
- Brittle Shear Sense IndicatorsDocument15 pagesBrittle Shear Sense IndicatorsPurushottam Gupta100% (1)
- Classification of Igneous RocksDocument23 pagesClassification of Igneous RocksAdit8450100% (1)
- BS-II Salt Range PDFDocument88 pagesBS-II Salt Range PDFShakeeb Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- SedimentologyDocument36 pagesSedimentologymsshahenterNo ratings yet
- Sed StructureDocument25 pagesSed StructureDwi Nurul AfifahNo ratings yet
- Types of Oil TrapsDocument11 pagesTypes of Oil TrapsMunish Kohli100% (1)
- Mass WastingDocument64 pagesMass WastingEkala XuhalxNo ratings yet
- Field Trip To NainitalDocument29 pagesField Trip To NainitalPurushottam Gupta60% (5)
- Rift-Type BasinsDocument4 pagesRift-Type BasinsMaisam Abbas100% (1)
- Exogenic Processes: Weathering, Erosion & Mass WastingDocument5 pagesExogenic Processes: Weathering, Erosion & Mass WastingJohn Francis Barrios100% (1)
- Q1. How and When Were Deccan Traps Formed? The Word Deccan IsDocument11 pagesQ1. How and When Were Deccan Traps Formed? The Word Deccan IsAkriti KothialaNo ratings yet
- Paleocurrent Analysis 6 PDFDocument134 pagesPaleocurrent Analysis 6 PDFPaul LixfeNo ratings yet
- Tsunami 190907112349Document21 pagesTsunami 190907112349Nikhil RNo ratings yet
- Mineral in Thin SectionDocument30 pagesMineral in Thin SectionJorgeTrabajo100% (3)
- 178Document196 pages178VishwanathSrinivasNo ratings yet
- Granites:Origin & ClassificationDocument34 pagesGranites:Origin & ClassificationVavachi vavaNo ratings yet
- Field Report AbbotabadDocument6 pagesField Report AbbotabadSajjad MunirNo ratings yet
- Metamorphism - Introduction: Metamorphism - All Solid-State Changes in A Rock's Composition and Fabric OccurringDocument55 pagesMetamorphism - Introduction: Metamorphism - All Solid-State Changes in A Rock's Composition and Fabric OccurringAvinash Upadhyay100% (1)
- Stratigraphy of IndiaDocument48 pagesStratigraphy of Indiavenkatakrishna chalapaathi100% (12)
- Depositional EnvironmentDocument3 pagesDepositional EnvironmentGonzalo DaccoNo ratings yet
- DrainagePatternDocument12 pagesDrainagePatternVikas BhardwajNo ratings yet
- CE 198 - Reaction Paper - 19MAR2019Document1 pageCE 198 - Reaction Paper - 19MAR2019Gelique de CastroNo ratings yet
- Report - English (1) (Repaired) 2Document43 pagesReport - English (1) (Repaired) 2Gelique de CastroNo ratings yet
- Tutorial For MASTAN2: Ronald D. ZiemianDocument68 pagesTutorial For MASTAN2: Ronald D. ZiemianGelique de CastroNo ratings yet
- Public Transport Modes-Phils PDFDocument12 pagesPublic Transport Modes-Phils PDFGelique de CastroNo ratings yet
- CE 131 LE 1 TermsDocument6 pagesCE 131 LE 1 TermsGelique de CastroNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Mastan2Document68 pagesTutorial Mastan2Christian PintoNo ratings yet
- Sedimentary Environments 4Document19 pagesSedimentary Environments 4Gelique de CastroNo ratings yet
- Sedimentary RocksDocument41 pagesSedimentary RocksGelique de CastroNo ratings yet
- Sedimentary Environments 3 PDFDocument13 pagesSedimentary Environments 3 PDFGelique de CastroNo ratings yet
- Sedimentary Environments 2Document9 pagesSedimentary Environments 2Gelique de CastroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 5 Volcanism Volcanism: Igneous ProcessesDocument26 pagesChapter 5 5 Volcanism Volcanism: Igneous ProcessesGelique de CastroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Chapter 3 Minerals Minerals: MineralDocument13 pagesChapter 3 Chapter 3 Minerals Minerals: MineralGelique de Castro100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Chapter 4 Igneous Rocks Igneous Rocks: Rock CycleDocument7 pagesChapter 4 Chapter 4 Igneous Rocks Igneous Rocks: Rock CycleGelique de CastroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Chapter 2 The Planet Earth The Planet Earth: © NasaDocument26 pagesChapter 2 Chapter 2 The Planet Earth The Planet Earth: © NasaGelique de CastroNo ratings yet
- Introduction PDFDocument5 pagesIntroduction PDFGelique de CastroNo ratings yet
- Coral Reef ConservationDocument33 pagesCoral Reef ConservationPrathamesh ParabNo ratings yet
- Tampus 2012Document11 pagesTampus 2012Christian Kenneth PantonialNo ratings yet
- Rock Mechanics Assignment by Group BDocument10 pagesRock Mechanics Assignment by Group BSmruti RanjanNo ratings yet
- Review Module 24 Geotechnical Engineering 5 Part 2Document2 pagesReview Module 24 Geotechnical Engineering 5 Part 2John Andre MarianoNo ratings yet
- History of MalimonoDocument2 pagesHistory of MalimonoGlenn Vincent Malaga MakawiliNo ratings yet
- P - ERC 2018 N Level English P2 v2 Ans Key FinalDocument4 pagesP - ERC 2018 N Level English P2 v2 Ans Key FinalTan TeongShengNo ratings yet
- B2 - 5B - Vocabulary The Natural World 1Document1 pageB2 - 5B - Vocabulary The Natural World 1Jeca AlmendraNo ratings yet
- Journey To The End of The Earth - Day 2Document14 pagesJourney To The End of The Earth - Day 2anita josephNo ratings yet
- Life of ReservoirDocument53 pagesLife of ReservoirrohitsinghNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Exam Prelim - FinalDocument14 pagesEarth and Life Science Exam Prelim - Finalrichardsamrano100% (2)
- Lavenu, A. Et Al - 1995 - Neogene Ongoing Tectonics in The Southern Ecuadorian AndesDocument12 pagesLavenu, A. Et Al - 1995 - Neogene Ongoing Tectonics in The Southern Ecuadorian AndesjanlayaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Engineering ReportDocument21 pagesEarthquake Engineering ReportEsrael Corporal BalusNo ratings yet
- Facts About Phosphorus and LawnsDocument5 pagesFacts About Phosphorus and LawnsboomissyNo ratings yet
- Climate and Distance From The Ocean ActivityDocument2 pagesClimate and Distance From The Ocean ActivityDanilo Reyes100% (1)
- Quiz Factors Affecting ClimateDocument1 pageQuiz Factors Affecting Climatepauladenesse.mallariNo ratings yet
- Disaster Management: Notes For Upsc Mains Gs3Document63 pagesDisaster Management: Notes For Upsc Mains Gs3Hari ShankarNo ratings yet
- Storm Water Drainage SystemDocument18 pagesStorm Water Drainage Systemankitbalyan100% (3)
- Sdgs Why-It-Matters Goal-14Document2 pagesSdgs Why-It-Matters Goal-14api-335841488No ratings yet
- Gisement de KinsendaDocument36 pagesGisement de KinsendaYuriNo ratings yet
- Wave Snapshots LLDA 9-30-2015Document2 pagesWave Snapshots LLDA 9-30-2015Gerome RomeroNo ratings yet
- Evs MCQ BankDocument25 pagesEvs MCQ BankSahil MehtaNo ratings yet
- Batayang Sipi Blg. 1 (UNCLOS)Document2 pagesBatayang Sipi Blg. 1 (UNCLOS)John Vincent GonzalesNo ratings yet
- East Asia (China, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, Japan, Hong Kong, Taiwan, Macau)Document6 pagesEast Asia (China, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, Japan, Hong Kong, Taiwan, Macau)Tamondong BeverlyNo ratings yet
- BR 03-0613Document12 pagesBR 03-0613Al Patrick Dela CalzadaNo ratings yet
- 04 Chapter 4 - LevelingDocument110 pages04 Chapter 4 - LevelingIsmael Wael SobohNo ratings yet
- LIFESAVER Jerrycan Quick User GuideDocument2 pagesLIFESAVER Jerrycan Quick User GuideIdan AwaludinNo ratings yet
- Geography G-12 Model ExamDocument12 pagesGeography G-12 Model Examtegegn100% (1)
- CSEC BIOLOGY - Ecological StudiesDocument36 pagesCSEC BIOLOGY - Ecological StudiesNabeel Uddin86% (7)
- Glencoe Earth Science2Document76 pagesGlencoe Earth Science2Cosmina MariaNo ratings yet
- GWYEARBOOK 2018-19 - Tamil NaduDocument192 pagesGWYEARBOOK 2018-19 - Tamil NaduSuresh RNo ratings yet