Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1374138689risk Assessment
Uploaded by
rusyadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1374138689risk Assessment
Uploaded by
rusyadCopyright:
Available Formats
Feed
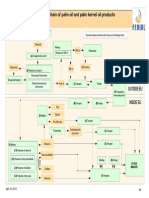
Risk analysis of the chain of biodiesel processing
8. Risk based approach
for glycerine
1. General risk: Biodiesel Processing
HAZARD
CAT.
CHANCE
SERIOUSNESS
RISK
CLASS.
Quality of water
C/B/
P
Low
High
JUSTIFICATION
Water is used in the
production of biodiesel.
LEGISLATION,
INDUSTRY STANDARDS
According to
Regulation
183/2005/EC water
used during the
manufacture of feed
shall be of suitable
quality.
CONTROL MEASURE
REMARKS
Apply suitable water of
drinking quality.
Dedicate water circuits
Cleaning agents
Low
Medium
Cleaning come into
contact with the product.
Cleaning agents used in the
production system should be
flushed. Cleaning agents used
must be evaluated and
appropriate measures taken
to bring risk to acceptable
levels.
Flying in birds
Low
Medium
Toxins from pest
control materials
Very low
High
Lubricants
Low
High
Use of lubricant should be
evaluated before use and
appropriate measures be
taken to bring risk to
acceptable levels
Insects and
rodents
Medium
Low
Building proofing, cleaning
programs and pest control
system as part of the pre
requisite programme
Not a common risk
as most
productions
facilities are
continuous process
Closed building can
prohibit this hazard
Poison bait from open
boxes could cause cross
contamination
Sector reference document on the manufacturing of safe feed materials from biodiesel processing
A pest control programme
must be applied. Appropriate
measures should be taken to
minimise risk
14
Purchasing
specifications. Risk
is low as oils are
checked before use
Feed
Risk analysis of the chain of biodiesel processing
8. Risk based approach
for glycerine
2. Reception of feedstock vegetable oil
CAT.
CHANCE
SERIOUSNESS
RISK
CLASS.
Contamination by
the previous
cargo during the
transport by truck
or barge or ocean
going vessel
Low
High
Foreign materials
Low
Low
Contamination
with undesirable
substances
- Dioxins
- Nickel
- PCB, dlPCB
HAZARD
LEGISLATION,
INDUSTRY
STANDARDS
CONTROL MEASURE
REMARKS
Transport of vegetable
oils usually takes place
in dedicated transport
vehicles
Risk must be evaluated and
appropriate measures must
be taken to bring this risk to
acceptable levels. Dedicated
transport, control of the
three previous cargos.
Visual checks
Foreign materials may
be present.
Dedicated buildings and
circuits filters, staff hygiene,
glass procedure, good
maintenance practices
High
In general, most
contaminants do not
concentrate in the
glycerine
Monitoring plan
Very Low
High
EU Regulation of
225/2012 on Dioxins
Monitoring plan
Low
High
EU Regulation
68/2013 Catalogue of
Feed Materials
Monitoring plan
Very Low
High
EU Regulation
32/2002 on
undesirable
substances on feed
materials
Monitoring plan
Low
JUSTIFICATION
Sector reference document on the manufacturing of safe feed materials from biodiesel processing
15
Contamination with
undesirable substance
normal cases CHANCE
is LOW if
manufacturer
purchases a raw
material of lower
quality the risk
elevates to medium
Nickel in most cases
not used in biodiesel
production
Feed
Risk analysis of the chain of biodiesel processing
- PAH
Low
High
Pesticide residues
above the minimal
risk levels (MRL),
i.e. residues of
herbicides,
insecticides,
fungicides or
rodenticides
above the MRL.
Low
Medium
Regular monitoring of
pesticide residues on
crude oil shows that
residue levels remain
within legal limits.
Regulation 396/2005
sets limits for
residues of
pesticides. This
regulation allows
using a transfer
factor for authorised
pesticides into
processed products,
providing food safety
is assured.
Monitoring plan
Most pesticides are not
water soluble and will
not move to the
glycerine water phase
Pesticides
residues as listed
in EU Directive
2002/32 for
undesirable
substances in
feeding stuff
Very low
High
Some of the banned
pesticides may be
present in the
environment. The chance
of finding them in crude
soybean oil, however, is
very low. The use of
endosulfan is allowed on
soybeans. Monitoring
data show that its
residue in crude oil
remains within the legal
limit.
Directive 2002/32/EC
sets limits for a
number of pesticides
residues in feeding
stuff.
Monitoring plan
Most pesticides are not
water soluble and will
not move to the
glycerine water phase
Low
Medium
Microbiological
contamination
Monitoring plan
Sector reference document on the manufacturing of safe feed materials from biodiesel processing
Monitoring plan
16
Feed
Risk analysis of the chain of biodiesel processing
8. Risk based approach
for glycerine
3. Storage of the incoming material
LEGISLATION,
INDUSTRY
STANDARDS
CAT.
CHANC
E
SERIOUSNES
S
RISK
CLASS.
Contamination by
cleaning agents
Low
Medium
This risk classification applies to
terminals that store both
chemicals and vegetable oils.
They may abstain from using
cleaning agents that are
suitable for use in the food
industry. For tank terminals in
the EU that apply HACCP and
that keep the storage of
vegetable oils and chemicals
separated, the chance of using
the wrong cleaning agents is
very low.
Cleaning agents used must
be evaluated and
appropriate measures taken
to bring risk to acceptable
levels.
Thermal heating
fluids from failing
equipment
Low
High
Toxic thermal heating fluids
may still be used. However, due
to the relatively low heating
temperatures applied during
storage, the chance of leakage
of thermal heating fluids into
the product is low.
Documentation on nett
losses and analyse
accordingly, if necessary.
Cross
contamination
Low
Medium
Sources of risk include
equipment malfunction and
operator accident. Extremely
low frequency of occurrence.
Preventative measures to
reduce impact include
automated safety mechanisms,
spill containment, site security,
restricted site access.
Storage procedure in place
HAZARD
JUSTIFICATION
Sector reference document on the manufacturing of safe feed materials from biodiesel processing
CONTROL MEASURE
17
REMARKS
The use of water and
steam heating is
recommended.
Thermal heating fluids
are not commonly used
Feed
Risk analysis of the chain of biodiesel processing
8. Risk based approach
for glycerine
HAZARD
Processing aids
(alkali solution,
acids)
4. Stage 1 of 3 Trans esterification (Reaction stage)
CAT.
CHANCE
SERIOUSNESS
RISK
CLASS
Low
Medium
JUSTIFICATION
LEGISLATION,
INDUSTRY
STANDARDS
Processing aids come into
contact with the product.
CONTROL MEASURE
REMARKS
Processing aids that directly
come into contact with the
oil must be evaluated and
appropriate measures taken
to bring risk to acceptable
levels.
Online process monitoring,
correct labelling of the
chemical containers
Contamination
caused during
addition of
Catalyst
(Methanol)
Low
Medium
Undesirable substances in
the Methanol
Apply methanol of suitable
quality
Described in the contract
specification
Online process monitoring,
correct labelling of the
chemical containers
Sector reference document on the manufacturing of safe feed materials from biodiesel processing
18
In very small scale
operations, the
handling of dangerous
chemicals may pose a
greater risk to the
operator if these
chemicals are manually
transferred and
employed in a batch
process versus an
automated system.
Feed
Risk analysis of the chain of biodiesel processing
8. Risk based approach
for glycerine
5. Stage 2 of 3 Trans esterification (Separation stage)
CAT.
CHANCE
SERIOUSNESS
RISK
CLASS.
Methyl ester
remaining in
glycerine
Low
High
Methanol in
glycerine
Medium
High
HAZARD
JUSTIFICATION
Separation of biodiesel
from coproducts - stage 1
LEGISLATION, INDUSTRY
STANDARDS AND/OR
CONTRACT TERMS
Legalisation 68/2003
mentions: May contain
up to 4% of Matter
Organic Non Glycerol
(MONG comprising of
Fatty ACID Methyl
Esters, Fatty Acid Ethyl
Esters, Free Fatty Acids
and Glycerides
Legislation 68/2013
mentions: May contain up to
0,5 % methanol
Sector reference document on the manufacturing of safe feed materials from biodiesel processing
19
CONTROL MEASURE
Monitoring plan and
process follow up
CCP: analysis methanol or
control by process
parameters
REMARKS
Feed
Risk analysis of the chain of biodiesel processing
8. Risk based approach
for glycerine
HAZARD
Processing aids
(alkali solution,
acids)
Pesticide residues
above the MRL,
i.e. residues of
herbicides,
insecticides,
fungicides or
rodenticides
above the MRL.
Delivery of Fatty
Matter
6. Stage 3 of 3 - Acidulation and FFA separation
CAT.
CHANCE
SERIOUSNESS
RISK
CLASS.
Low
High
JUSTIFICATION
Processing aids come into
contact with the product.
Risk of overdoses
Low
Low
Medium
High
Regular monitoring of
pesticide residues shows
that residue levels
remain within legal limits.
Pesticides do not
concentrate in the
glycerine
LEGISLATION,
INDUSTRY
STANDARDS
Regulation 68/2013
set limits for
maximum contents
of chemical
impurities resulting
from manufacturing
process or from
processing aids
CONTROL MEASURE
REMARKS
Processing aids that directly
come into contact with the oil
must be must be evaluated
and appropriate measures
taken to bring risk to
acceptable levels.
Online process monitoring
(consumption rates)
Regulation 396/2005
sets limits for
residues of
pesticides.
Sector reference document on the manufacturing of safe feed materials from biodiesel processing
If fatty matter is delivered as
a by product, label fatty
matter as nonfeed/nonfood
in order to assure this is not
used in feed sector
20
Fatty acids with
methyl esters (also
called fatty matter)
collected after
methanol recovery at
a biodiesel
production, are
prohibited for feed
purposes, since
liphophile additives,
used in biodiesel
production,
concentrate in fatty
acids.
Feed
Risk analysis of the chain of biodiesel processing
8. Risk based approach
for glycerine
7. Storage
LEGISLATION,
INDUSTRY
STANDARDS
AND/OR
CONTRACT TERMS
CAT.
CHANCE
SERIOUSNESS
RISK
CLASS.
Contamination
due to lack of
segregation
Low
High
Contamination by
cleaning agents
Low
Medium
This risk classification applies to
terminals that store both
chemicals and vegetable oils.
They may abstain from using
cleaning agents that are
suitable for use in the food
industry. For tank terminals in
the EU that apply HACCP and
that keep the storage of
vegetable oils and chemicals
separated, the chance of using
the wrong cleaning agents is
very low.
Cleaning agents used must
be evaluated and
appropriate measures
taken to bring risk to
acceptable levels
Thermal heating
fluids from failing
equipment
Low
High
Toxic thermal heating fluids
may still be used. However, due
to the relatively low heating
temperatures applied during
storage, the chance of leakage
of thermal heating fluids into
the product is low.
If thermal heating fluids
have been used, the
storage company must
provide for documentation
on nett losses and analyse
accordingly, if necessary.
Cross
contamination
Medium
Medium
HAZARD
JUSTIFICATION
CONTROL MEASURE
REMARKS
Storage procedures in
place to reduce the risk of
cross contamination
Dedicated tanks
Sector reference document on the manufacturing of safe feed materials from biodiesel processing
Dedicated circuits and
storage tanks. Storage
procedure in place
21
The use of water and
steam heating is
recommended.
Thermal heating fluids
are not commonly used
Feed
Risk analysis of the chain of biodiesel processing
8. Risk based approach
for glycerine
8. Transport of glycerine
LEGISLATION,
INDUSTRY
STANDARDS
AND/OR CONTRACT
TERMS
CAT.
CHANCE
SERIOUSNESS
RISK
CLASS.
Contamination by
previous cargo
P/C/B
Low
Medium
- Tank cars, rail
tanks and barges
Low
High
Contamination by
cleaning agents
Low
High
Tank cars
Low
Little
Foreign bodies
Low
High
A quality plan should require
the loading of tank cars with
glycerine under a roof.
Pest
Medium
Medium
PRP program for pest control
HAZARD
JUSTIFICATION
CONTROL MEASURE
REMARKS
Control of the three previous
cargoes
Transport of glycerine
based on customer
requirements
EC Regulation No.
183/2005 setting
rules in the
transport of feed
materials
Check previous cargoes via
IDTF database
Transport suitable for feed
materials as described in the
European Code for the
industrial manufacturing for
safe feed materials
Stainless steel tanks are
used which are heated
with cooling water from
the motor through a
system of double walls
(and not coils).
Sector reference document on the manufacturing of safe feed materials from biodiesel processing
22
Check on pest activity
You might also like
- HACCP Planrefinedpalm, Plamkerneloil 2010Document16 pagesHACCP Planrefinedpalm, Plamkerneloil 2010JyShe_laNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Palm OilDocument22 pagesRisk Assessment Palm Oilanniq141100% (1)
- HACCP Plan-Refined Palm-Palm Kernel OilDocument5 pagesHACCP Plan-Refined Palm-Palm Kernel OilSYju Elias100% (3)
- Flowchart-Production Chain of CNO (FEDIOL)Document17 pagesFlowchart-Production Chain of CNO (FEDIOL)Lim Chee SiangNo ratings yet
- Compressed Air BcasfoodgradecodeDocument11 pagesCompressed Air BcasfoodgradecodeSujit NairNo ratings yet
- Aijn Hygiene CodeDocument53 pagesAijn Hygiene CodeAnilZapateNo ratings yet
- Pesticides Manufacturing PDFDocument4 pagesPesticides Manufacturing PDFwakasensei99No ratings yet
- Foodchem PresentationDocument21 pagesFoodchem PresentationFarhanaNo ratings yet
- HACCPDocument64 pagesHACCPvalsvalsaraj50% (2)
- Food Safety Management: A Practical Guide for the Food IndustryFrom EverandFood Safety Management: A Practical Guide for the Food IndustryHuub L. M. LelieveldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (12)
- Pestisides Formulation PDFDocument4 pagesPestisides Formulation PDFwakasensei990% (1)
- ff5 - Haccp Frying (2004)Document22 pagesff5 - Haccp Frying (2004)Banuraspati100% (1)
- Safety Data Sheet: Product Name: MOBILITH SHC 220Document9 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Product Name: MOBILITH SHC 220patelchiragisNo ratings yet
- RC Maleic AnhydrideDocument5 pagesRC Maleic AnhydrideTuan Phan NguyenNo ratings yet
- AccessC PeptideCalibratorDocument5 pagesAccessC PeptideCalibratorDiego CostantiniNo ratings yet
- En BeDocument17 pagesEn Beمحمد مقلدNo ratings yet
- CAC Fruit and VegitableDocument31 pagesCAC Fruit and VegitableSunil GirdharNo ratings yet
- Cleaning and disinfection of food factories: a practical guideFrom EverandCleaning and disinfection of food factories: a practical guideNo ratings yet
- Processing Contaminants in Edible Oils: MCPD and Glycidyl EstersFrom EverandProcessing Contaminants in Edible Oils: MCPD and Glycidyl EstersNo ratings yet
- Microbiological Standard Values and Stability of FlavoringsDocument5 pagesMicrobiological Standard Values and Stability of Flavoringslisi_aresNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Product Name: MOBILGREASE 33Document10 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Product Name: MOBILGREASE 33Anibal RiosNo ratings yet
- Hygiene and Sanitary Conditions in A Meat Processing Plant PDFDocument30 pagesHygiene and Sanitary Conditions in A Meat Processing Plant PDFsureshNo ratings yet
- HEB EspecificacionesDocument7 pagesHEB EspecificacionesAna María SnzNo ratings yet
- AIJN Hygiene CodeDocument53 pagesAIJN Hygiene CodeLayflo100% (1)
- XXXVI/3. Absorber Pads Based On Cellulosic Fibres For Food PackagingDocument4 pagesXXXVI/3. Absorber Pads Based On Cellulosic Fibres For Food Packaging刘佳奇No ratings yet
- Example HACCP StudyDocument9 pagesExample HACCP Studycassilda_carvalho@hotmail.comNo ratings yet
- Pesticides Use and ManagementDocument16 pagesPesticides Use and ManagementBudi SiswantoNo ratings yet
- Vegoil PPAHDocument3 pagesVegoil PPAHChinedu NwufoNo ratings yet
- QCVN02 32 1 - 09082019BNN (E)Document7 pagesQCVN02 32 1 - 09082019BNN (E)Thanh Tâm TrầnNo ratings yet
- SDB 2684 Ie enDocument13 pagesSDB 2684 Ie en2121 2323No ratings yet
- Faculty Science and Techonlogy: Matriculation No: Identity Card No.: Telephone No.: E-Mail: Learning CentreDocument21 pagesFaculty Science and Techonlogy: Matriculation No: Identity Card No.: Telephone No.: E-Mail: Learning CentreNatasha YusofNo ratings yet
- Axion Liq LimónDocument7 pagesAxion Liq Limónyenni viviana67% (3)
- Rymax Themis ISO VG 220 CLP en GB LUB006912 SDS 201607 PDFDocument8 pagesRymax Themis ISO VG 220 CLP en GB LUB006912 SDS 201607 PDFAnuj ShahNo ratings yet
- BIOGAS PresentationDocument33 pagesBIOGAS PresentationAndreas Abraham91% (11)
- Parker FoodDocument28 pagesParker FoodMahiKapoorNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Metraclin - Simsd01Document5 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Metraclin - Simsd01deppit pedNo ratings yet
- Haccp Potatoes PDFDocument22 pagesHaccp Potatoes PDFRoberto Carlos Marin Perez50% (2)
- Section2 CODDocument14 pagesSection2 CODfabian_granoblesNo ratings yet
- Lactuca LT 3000: Safety Data SheetDocument12 pagesLactuca LT 3000: Safety Data SheetsheldonNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Section 1: Identification of The Substance/Mixture and of The Company/UndertakingDocument10 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Section 1: Identification of The Substance/Mixture and of The Company/UndertakingGEINER ANDRES OSSA GALVISNo ratings yet
- Development of Haccp Protocols For The Production of Soy MilkDocument18 pagesDevelopment of Haccp Protocols For The Production of Soy MilkTyooNoersatyoNo ratings yet
- Cxs 152e CodexDocument3 pagesCxs 152e CodexGisela Prima PaskhalienNo ratings yet
- Mimas Grovrent - SDS - ENDocument18 pagesMimas Grovrent - SDS - ENlopezionNo ratings yet
- Agrochemicals Accepted by The BBPADocument13 pagesAgrochemicals Accepted by The BBPAanon_623653380No ratings yet
- Control of Chemicals in Gots GoodsDocument4 pagesControl of Chemicals in Gots GoodsTHYAGUNo ratings yet
- MSDS 609680Document8 pagesMSDS 609680Manish GoyalNo ratings yet
- Lurgi BiodieselDocument8 pagesLurgi BiodieselManish KumarNo ratings yet
- SDS - High Temp Premium 2Document9 pagesSDS - High Temp Premium 2Georgina SuleNo ratings yet
- Msds For TretinionDocument10 pagesMsds For TretinionYen Ling NgNo ratings yet
- HACCP GUIDELINE - Canning Corned BeefDocument22 pagesHACCP GUIDELINE - Canning Corned BeefChen Li100% (4)
- Dallethrin Spec Eval March 04Document23 pagesDallethrin Spec Eval March 04yeotekarprasadNo ratings yet
- Conqor 303 ADocument6 pagesConqor 303 AjelaapeNo ratings yet
- Sds Gwax Eur EnglishDocument11 pagesSds Gwax Eur Englishperret.yap.weilunNo ratings yet
- HACCP of Fried FoodsDocument7 pagesHACCP of Fried FoodsChrisa KargiotouNo ratings yet
- (CRC Industries LTD) Ados Food Grade Silicone Sealant Translucent H3590 24-11-2015Document6 pages(CRC Industries LTD) Ados Food Grade Silicone Sealant Translucent H3590 24-11-2015Syarif HidayatullahNo ratings yet
- Engen Transformer Oil PDFDocument5 pagesEngen Transformer Oil PDFUrsula JohnsonNo ratings yet
- MSDS 480680 - 2Document11 pagesMSDS 480680 - 2Carlos SantosNo ratings yet
- Mobilfluid 350 MSDS 012808Document8 pagesMobilfluid 350 MSDS 012808lupilla RoNo ratings yet
- Chlorine Spectroquant 100602 Method 2000Document20 pagesChlorine Spectroquant 100602 Method 2000rafaeldelperu1982No ratings yet
- SRB-Hydraulic 46ES Oil MSDSDocument4 pagesSRB-Hydraulic 46ES Oil MSDSBen WigginsNo ratings yet
- Gleason's Flat Earth Map PDFDocument1 pageGleason's Flat Earth Map PDFrusyad100% (6)
- Superol Kpo Tds 2012Document1 pageSuperol Kpo Tds 2012rusyadNo ratings yet
- Boiling PointDocument3 pagesBoiling PointrusyadNo ratings yet
- Na OHDocument2 pagesNa OHrusyadNo ratings yet
- Carbon AktivDocument4 pagesCarbon AktivrusyadNo ratings yet
- Glycerine Ecogreen SpecDocument1 pageGlycerine Ecogreen SpecrusyadNo ratings yet
- Vacuum TheoryDocument79 pagesVacuum TheoryrusyadNo ratings yet
- 7) Hydro TestDocument3 pages7) Hydro TestPramod AthiyarathuNo ratings yet
- APN 9.02.01 Biodiesel Glycerol RefiningDocument2 pagesAPN 9.02.01 Biodiesel Glycerol RefiningrusyadNo ratings yet
- Award Report TemplateDocument3 pagesAward Report Templatechriscivil12No ratings yet
- Ispmach 4000V/B/C/Z Family: FeaturesDocument100 pagesIspmach 4000V/B/C/Z Family: Featuresjose morenoNo ratings yet
- Autocad R12 Autocad R13 Autocad R14 Autocad 2000 Autocad 2000I Autocad 2002 Autocad 2004Document12 pagesAutocad R12 Autocad R13 Autocad R14 Autocad 2000 Autocad 2000I Autocad 2002 Autocad 2004veteranul13No ratings yet
- Draft Tech Proposal NTB UtmDocument20 pagesDraft Tech Proposal NTB Utmdudi hidayatNo ratings yet
- HRSG Design and Operation On Unit Reliability and Remaining LifeDocument74 pagesHRSG Design and Operation On Unit Reliability and Remaining LifeNisal PereraNo ratings yet
- HT Service-ManualDocument31 pagesHT Service-ManualMonete FlorinNo ratings yet
- ANSI-IEEE, NEMA and UL Requirements For SwitchgearDocument4 pagesANSI-IEEE, NEMA and UL Requirements For Switchgearefmartin21No ratings yet
- The Effectiveness of Acceptance and Commitment-BasDocument18 pagesThe Effectiveness of Acceptance and Commitment-BasRaphaele ColferaiNo ratings yet
- Brazing Solutions For Car Body Production+ (EN)Document2 pagesBrazing Solutions For Car Body Production+ (EN)komklaveNo ratings yet
- CMM 25-11-466529430584234180428Document288 pagesCMM 25-11-466529430584234180428Radmanovic Uros MrmyNo ratings yet
- Urea ProjectDocument17 pagesUrea ProjectAbdo Shaaban100% (2)
- Crichton, Michael - NextDocument351 pagesCrichton, Michael - NextrtarakNo ratings yet
- RoundingDocument65 pagesRoundingSourav Kumar100% (1)
- White Paper - SuperUserDocument16 pagesWhite Paper - SuperUsermdsauberNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter EIM 4Document6 pages1st Quarter EIM 4Victor RosalesNo ratings yet
- Rules For Building and Classing Marine Vessels 2022 - Part 5C, Specific Vessel Types (Chapters 1-6)Document1,087 pagesRules For Building and Classing Marine Vessels 2022 - Part 5C, Specific Vessel Types (Chapters 1-6)Muhammad Rifqi ZulfahmiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Eighteen: Creating Competitive AdvantageDocument34 pagesChapter Eighteen: Creating Competitive AdvantageSana MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Isuzu REDTech 4J Lit SheetDocument2 pagesIsuzu REDTech 4J Lit SheetVăn Tuấn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Ann (02) 23 08 2018Document73 pagesAnn (02) 23 08 2018Paul RajNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Business Management Vol I PDFDocument284 pagesThe Basics of Business Management Vol I PDFKnjaz Milos100% (1)
- Letter Calling For State Department of Oil and Gas To Investigate Gas LeakDocument4 pagesLetter Calling For State Department of Oil and Gas To Investigate Gas LeakLos Angeles Daily NewsNo ratings yet
- NTE931 Integrated Circuit 3-Terminal Positive Voltage Regulator 5V, 3ADocument2 pagesNTE931 Integrated Circuit 3-Terminal Positive Voltage Regulator 5V, 3AWilfredo MolinaNo ratings yet
- BC-2800 - Service Manual V1.1 PDFDocument109 pagesBC-2800 - Service Manual V1.1 PDFMarcelo Ferreira CorgosinhoNo ratings yet
- Heidenhain MotorsDocument44 pagesHeidenhain MotorsmarhiNo ratings yet
- Urethyn HG 0 - Pi - (Gb-En)Document2 pagesUrethyn HG 0 - Pi - (Gb-En)CriVe OffeNo ratings yet
- IA-NT-PWR-2.4-Reference GuideDocument110 pagesIA-NT-PWR-2.4-Reference GuideSamuel LeiteNo ratings yet
- Litografia Soft LithographyDocument33 pagesLitografia Soft Lithographyrfm147No ratings yet
- CV FaisalDocument3 pagesCV FaisalAnonymous UNekZM6No ratings yet
- Dispersant Manual WebDocument108 pagesDispersant Manual Webcamilinrodriguezzzz100% (1)