Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acute Bronchitis SHORT TEXT
Uploaded by
KatieJMCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acute Bronchitis SHORT TEXT
Uploaded by
KatieJMCopyright:
Available Formats
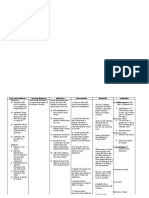
Acute bronchitis
In bronchitis, areas of the bronchial wall become inflamed and swollen, and mucus
increases. As a result, the air passageway is narrowed. Bacteria and viruses are usually
present. Symptoms lasting up to 90 days are usually classified as acute bronchitis.
Infectious bronchitis can be caused by infection or exposure to irritants. However, acute
bronchitis occurs most often during the winter and is most often caused by viruses.
Smokers and people who have chronic lung diseases may have repeated attacks of acute
bronchitis because mucus is less able to drain from their airways. Malnutrition may
increase the risk of upper respiratory tract infections and subsequent acute bronchitis,
especially in children and older people.
Acute bronchitis
In bronchitis, areas of the bronchial wall become inflamed and swollen, and mucus
increases. As a result, the air passageway is narrowed. Bacteria and viruses are usually
present. Symptoms lasting up to 90 days are usually classified as acute bronchitis.
Infectious bronchitis can be caused by infection or exposure to irritants. However, acute
bronchitis occurs most often during the winter and is most often caused by viruses.
Smokers and people who have chronic lung diseases may have repeated attacks of acute
bronchitis because mucus is less able to drain from their airways. Malnutrition may
increase the risk of upper respiratory tract infections and subsequent acute bronchitis,
especially in children and older people.
Acute bronchitis
In bronchitis, areas of the bronchial wall become inflamed and swollen, and mucus
increases. As a result, the air passageway is narrowed. Bacteria and viruses are usually
present. Symptoms lasting up to 90 days are usually classified as acute bronchitis.
Infectious bronchitis can be caused by infection or exposure to irritants. However, acute
bronchitis occurs most often during the winter and is most often caused by viruses.
Smokers and people who have chronic lung diseases may have repeated attacks of acute
bronchitis because mucus is less able to drain from their airways. Malnutrition may
increase the risk of upper respiratory tract infections and subsequent acute bronchitis,
especially in children and older people.
Acute bronchitis
In bronchitis, areas of the bronchial wall become inflamed and swollen, and mucus
increases. As a result, the air passageway is narrowed. Bacteria and viruses are usually
present. Symptoms lasting up to 90 days are usually classified as acute bronchitis.
Infectious bronchitis can be caused by infection or exposure to irritants. However, acute
bronchitis occurs most often during the winter and is most often caused by viruses.
Smokers and people who have chronic lung diseases may have repeated attacks of acute
bronchitis because mucus is less able to drain from their airways. Malnutrition may
increase the risk of upper respiratory tract infections and subsequent acute bronchitis,
especially in children and older people.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Case Study: A Patient With Type 2 Diabetes Working With An Advanced Practice Pharmacist To Address Interacting ComorbiditiesDocument8 pagesCase Study: A Patient With Type 2 Diabetes Working With An Advanced Practice Pharmacist To Address Interacting ComorbiditiessamanNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Manual Digital Therapy MachineDocument37 pagesManual Digital Therapy MachineEduardo Soares100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Sound Finf in 280722Document13 pagesSound Finf in 280722jongsu kimNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Aaa Gastrectomy NCP FinalDocument13 pagesAaa Gastrectomy NCP Finallexzaf100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- POCQI-Slides For Lead Facilitator Ver-3Document62 pagesPOCQI-Slides For Lead Facilitator Ver-3muna WarohNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- DLL - Health 10 - Week 1 - 2Document17 pagesDLL - Health 10 - Week 1 - 2Alfredo Apa-ap100% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Arcon Engineering and Services ProfileDocument30 pagesArcon Engineering and Services ProfilearconsteelNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Nifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyDocument4 pagesNifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyJomer GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- 2018 Jordanian Conference BookletDocument51 pages2018 Jordanian Conference BookletAurelian Corneliu MoraruNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Cor PulmonaleDocument21 pagesCor Pulmonalemaibejose100% (1)
- Nursing PresentationDocument63 pagesNursing PresentationDeekayNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- People As ResourceDocument9 pagesPeople As ResourceArup Dey100% (1)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Capstone Essay-2Document10 pagesCapstone Essay-2api-460858215No ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Exams GR 11Document16 pagesExams GR 11Methushellah AdolfoNo ratings yet
- City Health Office 2 PDFDocument2 pagesCity Health Office 2 PDFSeth CastilloNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Burning Mouth SyndromeDocument28 pagesBurning Mouth SyndromeMelissa KanggrianiNo ratings yet
- STROBE Case-Control Study PDFDocument3 pagesSTROBE Case-Control Study PDFLuis Gabriel Parra LaraNo ratings yet
- MG Hse Bulletin 01 2020 The Take 5 For SafetyDocument1 pageMG Hse Bulletin 01 2020 The Take 5 For SafetyvivekNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Infection Control Measures in Dental Clinics in Kingdom of Saudi ArabiaDocument4 pagesInfection Control Measures in Dental Clinics in Kingdom of Saudi Arabiaاحمد القحطانيNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Iron SucroseDocument14 pagesIron SucroseTejaswi J DamerlaNo ratings yet
- HR Report For Handing OverDocument19 pagesHR Report For Handing OverSimon DzokotoNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- GMC Handwara Recruitment 2023Document4 pagesGMC Handwara Recruitment 2023Ummar WaniNo ratings yet
- Childhood Glaucoma: by Kelli OrdakowskiDocument16 pagesChildhood Glaucoma: by Kelli OrdakowskikmordakowskiNo ratings yet
- 2 Dr. Cruz v. CADocument2 pages2 Dr. Cruz v. CAMigs GayaresNo ratings yet
- Stuart Stress Adaptation ModelDocument10 pagesStuart Stress Adaptation ModelRoscelie KhoNo ratings yet
- Laws Affecting Nursing PracticeDocument52 pagesLaws Affecting Nursing Practiceapi-3731845100% (3)
- OSHA Slide Chapter 1Document56 pagesOSHA Slide Chapter 1Jia Yee Ten100% (1)
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare Pregnancy GuidelinesDocument173 pagesMinistry of Health and Family Welfare Pregnancy GuidelinesKhushi GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Personal Development 11 Q1 LAS Week4Document8 pagesPersonal Development 11 Q1 LAS Week4Ruben100% (1)
- 05 - A Study To Evaluate The Effectiveness ofDocument21 pages05 - A Study To Evaluate The Effectiveness ofMuheto100% (1)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)