Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Preboard EST 2ndbatch April2015 SetB
Uploaded by
George Ezar N. QuiriadoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Preboard EST 2ndbatch April2015 SetB
Uploaded by
George Ezar N. QuiriadoCopyright:
Available Formats
Republic of the Philippines
Professional Regulation Commission
Board of Electronics Engineering
ECE Licensure Examination Pre-Board Exam
1:00 pm 6:00 pm
Page 1 of 15
ELECTRONICS SYSTEMS AND TECHNOLOGIES
SET B
INSTRUCTION: Select the correct answer for each of the following questions. Mark
only one answer for each item by shading the box corresponding to the letter of
your choice on the answer sheet provided.
STRICTLY NO ERASURES ALLOWED. Use pencil no. 2 only.
NOTE:
Whenever you come across a caret (^) sign, it means exponentiation.
Ex. x^2 means x2; (x+y)^(x-z) means
(x+y) raised to the (x-z). Pi=3.1416
1. What is the frequency difference (in MHz) between the aural and visual carriers in
System B/G?
A. 5.5 MHz *
B. 6.5 MHz
C. 7.5 MHz
D. 8.5 MHz
2. Pulse modulation consists essentially of sampling analog information signals and
then converting those samples into discrete pulses and transporting the pulses from
a source to a destination over a physical transmission medium. One of the four
predominant methods of pulse modulation is pulse amplitude modulation (PAM). With
PAM, the amplitude of a constant width, constant-position pulse is varied according
to the amplitude of the sample of the analog signal. Which is not a disadvantage of
PAM compared to other pulse modulation techniques?
A. The bandwidth needed for transmission of PAM signal is very very large compared
to its maximum frequency content.
B. The amplitude of PAM pulses varies according to modulating signal. Therefore
interference of noise is maximum for the PAM signal and this noise cannot be
removed very easily.
C. Since amplitude of PAM signal varies, this also varies the peak power required by
the transmitter with modulating signal.
D. PAM becomes inefficient for signals with very high frequencies.*
3. Identify the output produced from the system shown below.
A. TDM
B. FDM
C. PAM
D. PCM*
4. A television transmitter actually transmits two signals at once. They are
A.
B.
C.
D.
An amplitude-modulated video signal and frequency-modulated audio signal*
Two amplitude-modulated signals: video and audio
An amplitude-modulated audio signal and frequency-modulated video signal
Two frequency-modulated signals: video and audio
5. One kilowatt is supplied to a rhombic antenna which results in a field strength of
20 V/m at the receiving station. In order to produce the same field strength at
the receiving station, a half-wave antenna, properly oriented and located near the
rhombic, must be supplied with 16.6 kW. What is the gain of the rhombic?
A. 12.2 dB *
B. 21.2 dB
C. 15.2 dB
D.25.1 dB
6. In an asynchronous data system
A. Both sender and receiver are exactly synchronized to the same clock frequency.
B. Each computer word is preceded by a start bit and followed by a stop bit to frame
the word.*
C. The receiver derives its clock signal from the received data stream.
D. All the above.
7. The square-law relationship of the FETs input versus output
A. Allows for greater sensitivity in an FM receiver
B. Provides improved noise performance
C. Reduces shot noise
D. Minimizes cross-modulation*
8. What electrical length of standard RG-8/U coaxial cable would be required to obtain
a 45 phase shift at 300 MHz?
Republic of the Philippines
Professional Regulation Commission
Board of Electronics Engineering
ECE Licensure Examination Pre-Board Exam
1:00 pm 6:00 pm
Page 2 of 15
ELECTRONICS SYSTEMS AND TECHNOLOGIES
A. 0.0825 m*
SET B
B. 0.165 m
C. 0.0413 m
D. 0.125 m
9. An analog signal is band-limited to 4 kHz, sampled at the Nyquist rate and the
samples are quantized into 4 levels. The quantized levels are assumed to be
independent and equally probable. If we transmit two quantized samples per second,
the information rate is
A. 1 bit/sec
B. 2 bits/sec
C. 3 bits/sec
D. 4 bits/sec*
10. It is a form of store-and-forward network. Data, including source and destination
identification codes, are transmitted into the network and stored in a switch. Each
switch within the network has message storage capabilities. The network transfers
the data from switch to switch when it is convenient to do so. Consequently, data
are not transferred in real time; there can be a delay at each switch. With this
switching cannot occur, blocking cannot occur.
A. circuit switching
B. message switching*
C. packet switching D. code switching
11. What is the impedance seen at the input when transmission line is shorted?
A. infinity
B. jZocot(l)
C.0
D. jZotan(l) *
12. Network topology describes the layout or appearance of a networkthat is, how the
computers, cables, and other components within a data communications network are
interconnected, both physically and logically. What network topology is considered a
multipoint data communications circuit that makes it relatively simple to control
data flow between and among the computers because this configuration allows all
stations to receive every transmission over the network? With this topology, all the
remote stations are physically or logically connected to a single transmission line.
The two ends of the transmission line never touch to form a complete loop. It is the
simplest and most common method of interconnecting computers.
A. bus*
B. mesh
C. star
D. ring
13. Standing-wave ratio (SWR) is a mathematical expression of the non-uniformity of an
electromagnetic field (EM field) on a transmission line such as coaxial cable.
Usually, SWR is defined as the ratio of the maximum radio-frequency (RF) voltage to
the minimum RF voltage along the line. This is also known as the voltage standingwave ratio (VSWR). The SWR can also be defined as the ratio of the maximum
RF current to the minimum RF current on the line (current standing-wave ratio or
ISWR). What is the ideal value of SWR?
A. zero
B. infinite
C. one*
D. equal to reflection coefficient
14. Reflection coefficient is a parameter that describes how much of an electromagnetic
wave is reflected by an impedance discontinuity in the transmission medium. It is
the ratio of the complex amplitude of the reflected wave to that of the incident
wave. In particular, at a discontinuity in a transmission line, it is
the complex ratio of the electric field strength of the reflected wave to that of
the incident wave. This is typically represented with a . Which of the following is
false about reflection coefficient?
A. A reflection coefficient of zero means that the characteristic impedances of two
transmission lines connected together are equal. Therefore, power transfer is
maximum.
B. The worst value for reflection coefficient is 1.
C. Reflection coefficient can be improved by using quarter wavelength impedance
transformer.
D. When the characteristic impedance of the transmission line is not matched with
the impedance of the antenna to which it is connected, the reflection coefficient
becomes infinite.*
15. Dual-tone multifrequency (DTMF) is a simple two-of-eight encoding scheme where each
digit is represented by the linear addition of two frequencies. It is a more
efficient means of dialing than dial pulsing for transferring telephone numbers from
a subscribers location to the central office switching machine. Its main advantage
is speed and control. It was originally called Touch-Tone. Suppose you press 9,
this will be equivalent to what pair of frequencies?
A. 852 Hz and 1336 Hz
C. 941 Hz and 1477 Hz
B. 852 Hz and 1477 Hz*
D. 941 Hz and 1336 Hz
16. It is a pulse of a direct-sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) code, such as a Pseudorandom Noise (PN) code sequence used in direct-sequence code division multiple
access (CDMA) channel access techniques
Republic of the Philippines
Professional Regulation Commission
Board of Electronics Engineering
ECE Licensure Examination Pre-Board Exam
ELECTRONICS SYSTEMS AND TECHNOLOGIES
1:00 pm 6:00 pm
Page 3 of 15
SET B
A. flake
B. bit
C. nibble
D. chip *
is a redundancy error detection scheme that uses parity to determine if a
transmission error has occurred within a message and is therefore sometimes called
message parity. With this redundancy scheme, each bit position has a parity bit.
A. LRC*
B. VRC
C. checksum
D. CRC
18. Three common switching techniques are used with public data networks: circuit
switching, message switching, and packet switching. Packet switching involves
dividing data messages into small bundles of information and transmitting them
through communications networks to their intended destinations using computercontrolled switches. Why is it faster to send packets of a fixed size compared to
packets of variable size?
A. Only packets of a fixed size are compatible for parallel transmission. Packets of
variable size are compatible to series transmission only.
B. The processing required to store and forward packets of different lengths is
greater than that required for packets of a fixed length.*
C. Packets of variable size need start and stop bits while packets of fixed size
dont.
D. None of these. Both packets of variable size and packets of fixed size require
equal transmission time.
19. When a transmission line is terminated in either a short or an open circuit, there
is an impedance inversion every quarter-wavelength. For a loss-less line, the
impedance varies from infinity to zero. However, in a more practical situation where
power losses occur, the amplitude of the reflected wave is always less than that of
the incident wave except at the termination. Therefore, the impedance varies from
some maximum to some minimum value or vice versa, depending on whether the line is
terminated in a short or an open. Which of the following statements is false
regarding transmission line?
A. A quarter-wavelength, short circuited transmission line has maximum impedance.
B. A half-wavelength, open circuited transmission line has maximum impedance.
C. A transmission line less than one quarter-wavelength long and short circuited
will appear capacitive.*
D. A transmission line more than one half-wavelength long and open circuited will
appear inductive.
20. The input to an FM receiver has a S/N of 2.8. What is the frequency deviation caused
by the noise if the modulating frequency is 1.5 kHz and the permitted deviation is 4
kHz?
A. 547.8 Hz*
B. 635.1 Hz
C. 983.5 Hz
D. 298.2 Hz
21. A PLL is set up such that its VCO free-runs at 10 MHz. The VCO does not change
frequency until it is within 50 kHz of 10 MHz. After that condition, the VCO follows
the input to 200 kHz of 10 MHz before the VCO starts to free-run again. Determine
the lock range.
A. 100 kHz
B. 200 kHz
C. 150 kHz
D. 400 kHz*
22. Infrared travels through an optical fiber cable by what is known as total internal
reflection. This happens when light or any electromagnetic wave travels from one
medium to another with different refractive indices. It is also required that the
incident angle be less than the critical angle for total internal refraction to
occur. What is meant by critical angle?
A. Critical angle is the angle at which light is refracted.
B. Critical angle is the angle at which light becomes invisible.
C. Critical angle is the angle at which light has gone from the refractive mode to
the reflective mode.*
D. Critical angle is the angle at which light has crossed the boundary layers from
one index to another.
23. An earth mat for a communication tower consists of
17. It
A. one or two radials extending from base of tower at a depth of about 5 cm below
ground
B. a large number of radials extending from base of tower at a depth of about 3 m
C. a large number of radials extending from base of tower at a depth of about 30 cm *
D. none of the above
24. For an optical fiber 10 km long with a pulse-spreading constant of 5 ns/km,
determine
the
maximum
digital
transmission
rates
for
Nonreturn-to-zero
transmissions.
Republic of the Philippines
Professional Regulation Commission
Board of Electronics Engineering
ECE Licensure Examination Pre-Board Exam
1:00 pm 6:00 pm
Page 4 of 15
ELECTRONICS SYSTEMS AND TECHNOLOGIES
A. 20 Mbps
B. 10 Mbps*
SET B
C. 5 Mbps
D. 50 Mbps
25. Which one of the following is non-resonant antenna?
A. Folded dipole
B. Broad side array
C. End fire array
D. Rhombic antenna*
26. Microstrip is a flat conductor separated by an insulating dielectric from a large
conducting ground plane. The microstrip is usually onequarter or one-half wavelength
long. As the distance between copper trace and the ground plane increases, the value
of the characteristic impedance of your stripline
A. increases*
C. decreases
B. remains constant
D. Zo is temperature dependent
27. German astronomer Johannes Kepler discovered the laws that govern satellite motion.
Keplers laws can be applied to any two bodies in space that interact through
gravitation. The larger of the two bodies is called the primary and the smaller is
called the secondary or satellite. Keplers second law is known as the Law of Areas.
It states that for equal intervals of time, a satellite will sweep out equal areas
in the orbital plane, focused at the barycenter (the center of mass of the primary).
What conclusion can be drawn from Keplers second law?
A. The velocity of a satellite will be greatest at the point of closest approach to
earth and least at the farthest point.*
B. The velocity of a satellite will be least at the point of closest approach to
earth and greatest at the farthest point.
C. The velocity of a satellite does not change regardless of its position relative
to the earth.
D. Forget it. Keplers second law has nothing to do with the velocity of the
satellite.
28. Why do CSMA/CD packets have a minimum size limit?
A. If a packet is too short, nodes at either end of a cable could get on, send a
packet, and get off before the packets travel far enough to collide. The
collision would not be detected.*
B. If a packet is too short, nodes at either end of a cable could not get on as
collision can easily happen.
C. If a packet is too short, nodes at either end of a cable could get on, send a
packet, and get off before the packets travel far enough to collide. The
collision would be detected but cannot be avoided.
D. None of these. CSMA/CD packets dont have a minimum size limit.
29. A point-to-point communication system consists of a transmitter operating at 400 MHz
with an RF output of 90 W. It is fed to a 6 dBi antenna through a 150 ft coaxial
cable which has attenuation through a 150 ft coaxial cable which has an attenuation
of 1.7 dB per 100 ft. The receiving stations, located several miles away, has an
antenna system consisting of 9 dB gain antenna, with a 100 ft coaxial cable with an
attenuation of 1.5 dB per 100 ft. if the path
loss between the transmitter and
receiving stations is 124 dB, determine the signal level in dBm at the receiver.
A. 184.49 dBm
B. -55.41 dBm
C. -63.51 dBm
*
D. -60.57 dBm
30. In electroacoustics, what do you call the equation show to measure reverberation
time?
A. Sabine Equation
B. Stephens & Bates Equation
C. Norris Eyring Equation *
D. Bose Equation
31. A loudspeaker produces an SPL of 85dB-SPL at 1 meter distance and input electrical
power of 1 W. How loud is the SPL at distance of 20 meters if this speaker is driven
to 10 W of electrical power?
A. 59 dB-SPL
B. 69 dB-SPL *
C. 79 dB-SPL
D. 69 dB-SPL
32. The receiving installation whose G/T was found to be 20.6 dB is used as a ground
terminal to receive a signal from a satellite at a distance of 38,000 km. The
satellite has a transmitter power of 50 watts and an antenna gain of 30 dBi. Assume
losses between the satellite transmitter and its antenna is negligible. The
frequency is 12 GHz. Calculate the carrier to noise at the receiver, for bandwidth
of 1 MHz.
A. 31.32 dB*
B. 6.70 dB
C. 32.31 dB
D. 7.60 dB
Republic of the Philippines
Professional Regulation Commission
Board of Electronics Engineering
ECE Licensure Examination Pre-Board Exam
1:00 pm 6:00 pm
Page 5 of 15
ELECTRONICS SYSTEMS AND TECHNOLOGIES
SET B
33. There
are two devices commonly used to detect light energy in fiber-optic
communications receivers: PIN diodes and APDs. The most important characteristics of
light detectors are stated below. Identify the false statement.
A. Responsivity. It is the measure of the conversion efficiency of a photodetector.
It is the ratio of the output current of a photodiode to the input optical power
and has the unit of amperes per watt. It is generally given for a particular
wavelength or frequency.
B. Dark current. The leakage current that flows through a photodiode with no light
input. Thermally generated carriers in the diode cause dark current.
C. Transit time. The time it takes a light-induced carrier to travel across the
depletion region of a semiconductor. This parameter determines the maximum bit
rate possible with a particular photodiode.
D. Light sensitivity. The maximum optical power a light detector can receive and
still produce a usable electrical output signal. Light sensitivity is generally
given for a particular wavelength in either dBm or dB. *
34. Suppose there is an obstacle midway between the transmitter and receiver over a
distance of 45km. The frequency used in the transmission is 11GHz. If the obstacle
is placed 10 km closer to the transmitter, what is the change of your Fresnel zone?
A.
B.
C.
D.
decrease
increase
decrease
increase
of
of
of
of
29.72%
29.72%
16.85%
16.85%
from
from
from
from
the
the
the
the
original
original
original
original
value
value
value *
value
35. For 10 bit PCM system, the signal to quantization noise ratio is 62 dB. If the
number of bits is increased by 2, then the signal to quantization noise ratio will
A. increased by 6 dB
B. increased by 12 dB *
C. decreased by 6 dB
D. decreased by 12 dB
36. What is the main difference with Pre-emphasis and De-emphasis in FM Broadcasting?
A. Pre-emphasis is increasing the relative strength of low-frequency components
before being fed into the modulator of an FM transmitter while de-emphasis is
decreasing the relative strength of low-frequency components of the output signal
of an FM detector in an FM receiver.
B. Pre-emphasis is decreasing the relative strength of low-frequency components
before being fed into the modulator of an FM transmitter while de-emphasis is
increasing the relative strength of low-frequency components of the output signal
of an FM detector in an FM receiver.
C. Pre-emphasis is decreasing the relative strength of high-frequency components
before being fed into the modulator of an FM transmitter while de-emphasis is
increasing the relative strength of high-frequency components at the output
signal of an FM detector in an FM receiver.
D. Pre-emphasis is increasing the relative strength of high-frequency components
before being fed into the modulator of an FM transmitter while de-emphasis is
decreasing the relative strength of high-frequency components at the output
signal of an FM detector in an FM receiver.*
37. The resistance of any wire conductor, whether it is a resistor or capacitor lead or
the wire in an inductor, is primarily determined by the ohmic resistance of the wire
itself. However, other factors influence it. The most significant one is skin
effect, the tendency of electrons flowing in a conductor to flow near and on the
outer surface. As the skin effect increases, what happens to the resistance of the
wire?
A. increases*
B. no change
C. decreases
D. no effect
38. Single
Sideband was mathematically recognized and understood as early as 1914;
however, not until 1923 was the first patent granted ad a successful communication
link established between England and United States. One common designation assigned
by International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is C3F designation. Describe this
configuration.
A. AM Independent Sideband (ISB). It is a form if amplitude modulation in which a
single carrier frequency is independently modulated by two modulating signals. In
essence, ISB is a form of double sideband transmission in which the transmitter
consists of two independent single-sideband suppressed carrier modulators.
Republic of the Philippines
Professional Regulation Commission
Board of Electronics Engineering
ECE Licensure Examination Pre-Board Exam
1:00 pm 6:00 pm
Page 6 of 15
ELECTRONICS SYSTEMS AND TECHNOLOGIES
SET B
B. AM Vestigial Sideband. It is a form of amplitude modulation in which the carrier
and once complete sideband are transmitted, but only part of the second sideband
is transmitted. The carrier is transmitted at full power. Consequently, the lower
frequencies can appreciate the benefit of 100% modulation, whereas the higher
frequencies cannot achieve more than the effect of 50% modulation. *
C. AM Single-Sideband Suppressed Carrier. It is a form of amplitude modulation in
which the carrier is totally suppressed and one of the sidebands is removed.
Therefore, it requires half as much bandwidth as conventional AM and considerably
less transmitted power.
D. AM Single-Sideband Reduced Carrier. It is a form amplitude modulation in which
one sideband is totally removed and the carrier voltage is reduced to
approximately 10% of its unmodulated amplitude. To produce a reduced carrier
component, the carrier is totally suppressed during modulation and then
reinserted at reduced amplitude.
39. It is a more advanced upgrade to the GSM standard that requires additional hardware
and software of existing base stations. It allows for nine different (autonomously
and rapidly selectable) air interface formats. It is known as multiple modulation
and coding scheme (MCS), with varying degrees of error control protection. What is
this that was developed from the desire of GSM and IS-136 operators to have a common
technology path to eventual 3G high speed data access?
A. LTE
B. EDGE*
C. 2.5G
D. GPRS
40. It provides independence to the application processes by addressing any code or
syntax conversion necessary to present the data to the network in a common
communications format. It specifies how end-user should format the data. This layer
provides
for
translation
between
local
representations
of
data
and
the
representation of data that will be used for transfer between end users. The results
of encryption, data compression, and virtual terminals are examples of the
translation service.
A. Session Layer
B. Presentation Layer*
C. Transport Layer
D. Physical layer
41. For a binary FSK modulator with space, rest, and mark frequencies of 60, 70, and 80
MHz, respectively and an input bit rate of 20 Mbps, determine the output baud and
the minimum required bandwidth.
A. BW=60 MHz, baud rate= 20 Mbaud *
B. BW=80 MHz, baud rate= 20 Mbaud
C. BW=70 MHz, baud rate= 20 Mbaud
D. BW=60 MHz, baud rate= 30 Mbaud
42. The half wave dipole is formed from a conducting element which is wire or metal tube
which is an electrical half wavelength long. It is typically fed in the centre where
the impedance falls to its lowest. In this way, the antenna consists of the feeder
connected to two quarter wavelength elements in line with each other. The voltage
and current levels vary along the length of the radiating section of the antenna.
This occurs because standing waves are set up along the length of the radiating
element. At the feedpoint of this antenna, the current is
A. maximum*
B. minimum
C. remains constant D. zero current
43. A feedback oscillator is an amplifier with a feedback loop (i.e. path for energy to
propagate
generates
where it
statement
from the output back to the input. Once started, a feedback oscillator
an ac output signal of which a small portion if fed back to the input,
is amplified. Among the following statements, which of the following
is not a requirement for a feedback oscillator to work?
A. Amplification. An oscillator circuit must include atleast one active device and
be capable of voltage amplification. In fact, at times, it may be required to
provide infinite gain.
B. Positive Feedback. An oscillator must have a complete path for a portion of the
output signal to be returned to the input. The feedback must be degenerative. If
the phase is incorrect of the amplitude is insufficient, the oscillation will
saturate. *
C. Frequency-determining components. An oscillator must have frequency-determining
components such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, or crystals to allow
frequency of operation to be set or changed.
D. Power source. An oscillator must have a source of electrical energy, such as dc
power supply.
Republic of the Philippines
Professional Regulation Commission
Board of Electronics Engineering
ECE Licensure Examination Pre-Board Exam
ELECTRONICS SYSTEMS AND TECHNOLOGIES
1:00 pm 6:00 pm
Page 7 of 15
SET B
44. Open
systems interconnection (OSI) is the name for a set of standards for
communicating among computers. The primary purpose of OSI standards is to serve as a
structural guideline for exchanging information between computers, workstations, and
networks. In the OSI layer, what is the purpose of session layer?
A. The layer is responsible for network availability (i.e., data storage and
processor capacity). This protocol provides the logical connection entities at
the application layer. These applications include file transfer protocols and
sending e-mail. The responsibilities include network log-on and log-off
procedures and user authentication. *
B. It is responsible for providing error-free communications across the physical
link connecting primary and secondary stations (nodes) within a network
(sometimes referred to as hop-to-hop delivery). It packages data from the
physical layer into groups called blocks, frames, or packets and provides a means
to activate, maintain, and deactivate the data communications link between nodes.
C. It provides details that enable data to be routed between devices in an
environment using multiple networks, subnetworks, or both. Components that
operate at this layer include routers and their software. It determines which
network configuration is most appropriate for the function provided by the
network and addresses and routes data within networks by establishing,
maintaining, and terminating connections between them.
D. It provides independence to the application processes by addressing any code or
syntax conversion necessary to present the data to the network in a common
communications format. This specifies how end-user applications should format the
data. This layer provides for translation between local representations of data
and the representation of data that will be used for transfer between end users.
45. A line of length less than /4 length and open circuited at far end behaves as
A. an inductance
B. a capacitance *
C. series resonant D. parallel resonant
46. In a channel voice coder, the outputs of sixteen 20 Hz low pass filters are sampled,
multiplexed and A/D converted. If sampling is at 40 samples/second and 3 bits/sample
represents each voltage sample, the bit rate is about
A. 1.9 k bits/sec *
B. 0.95 k bits/sec
C. 3.8 k bits/sec
D. 7.6 k bits/sec
47. Bandwidth utilization is the wise use of available bandwidth to achieve specific
goals. Efficiency can be achieved by multiplexing; privacy and antijamming can be
achieved by spreading. Spread spectrum achieves its goals through two principles:
the bandwidth allocated to each station needs to be, by far, larger than what is
needed. This allows redundancy. Second, expanding the original bandwidth B to the
bandwidth Bss must be done by a process that is independent of the original signal.
In other words, the spreading process occurs after the signal is created by the
source. By this concept, what is the difference of Frequency hopping spread spectrum
and Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum?
A.
The direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) technique uses M different carrier
frequencies that are modulated by the source signal. At one moment, the signal
modulates one carrier frequency; at the next moment, the signal modulates another
carrier frequency while frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) technique
expands the bandwidth of a signal by replacing each data bit with n bits using a
spreading code. In other words, each bit is assigned a code of n bits, called
chips.
B.
The frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) technique uses M different carrier
frequencies that are modulated by the source signal. At one moment, the signal
modulates one carrier frequency; at the next moment, the signal modulates another
carrier frequency while direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) technique expands
the bandwidth of a signal by replacing each data bit with n bits using a
spreading code. In other words, each bit is assigned a code of n bits, called
chips. *
C.
The frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) technique uses M different carrier
frequencies that are modulated by the source signal. At one moment, the signal
modulates one carrier frequency; at the next moment, the signal modulates another
carrier frequency while direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) technique, a low
bit pseudorandom code is added to a high-bit rate information signal to generate
a low bit rate pseudorandom signal closely resembling noise that contains both
the original data signal and the pseudo random code must be known.
D.
The direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) technique uses M different carrier
frequencies that are modulated by the source signal. At one moment, the signal
Republic of the Philippines
Professional Regulation Commission
Board of Electronics Engineering
ECE Licensure Examination Pre-Board Exam
1:00 pm 6:00 pm
Page 8 of 15
ELECTRONICS SYSTEMS AND TECHNOLOGIES
SET B
modulates one carrier frequency; at the next moment, the signal modulates another
carrier frequency while frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS, a low bit
pseudorandom code is added to a high-bit rate information signal to generate a
low bit rate pseudorandom signal closely resembling noise that contains both the
original data signal and the pseudo random code must be known.
48. Open
systems interconnection (OSI) is the name for a set of standards for
communicating among computers. The primary purpose of OSI standards is to serve as a
structural guideline for exchanging information between computers, workstations, and
networks. In the OSI layer, what is the purpose of network layer?
A. It is responsible for providing error-free communications across the physical
link connecting primary and secondary stations (nodes) within a network
(sometimes referred to as hop-to-hop delivery). It packages data from the
physical layer into groups called blocks, frames, or packets and provides a means
to activate, maintain, and deactivate the data communications link between nodes.
B. The layer is responsible for network availability (i.e., data storage and
processor capacity). This protocol provides the logical connection entities at
the application layer. These applications include file transfer protocols and
sending e-mail. The responsibilities include network log-on and log-off
procedures and user authentication.
C. It provides details that enable data to be routed between devices in an
environment using multiple networks, subnetworks, or both. Components that
operate at this layer include routers and their software. It determines which
network configuration is most appropriate for the function provided by the
network and addresses and routes data within networks by establishing,
maintaining, and terminating connections between them. *
D. It provides independence to the application processes by addressing any code or
syntax conversion necessary to present the data to the network in a common
communications format. This specifies how end-user applications should format the
data. This layer provides for translation between local representations of data
and the representation of data that will be used for transfer between end users.
49. It is found that in a telephone system 60 subscribers initiate calls during a 30
minute interval and the total duration of all the calls is 100 minutes. The load is
A. 2 Erlang
B. 3 Erlang
C. 3.333 Erlang *
50. A
transmission line terminated with a load resistance that
transmission lines characteristic impedance has a VSWR of:
A. -1
B. 0
C. +1 *
D. 0.333 Erlang
is
equal
to
the
D. infinity
51. It is found that a ship to ship communication suffers from fading. This can be
avoided by using
A. space diversity
C. broad band antenna
B. frequency diversity *
D. directional antenna
52. A telephone line has a bandwidth of 3.2 kHz and a signal to noise ratio of 35 dB. A
signal is transmitted down this line using a four level. What is the maximum
theoretical date rate?
A. 4.6kbps
B. 12.8 kbps *
C. 37.2 kbps
D.18. 6kbps
53. A
device has two resistances 300 Ω and 200 Ω respectively. The noise
voltages due to these two resistance calculated separately are 5.38 V and 4.38 V
respectively. When both of them are used together, the noise voltage will be
A. 9.76 V
B. 1 V
C. 23.56 V
D. 6.94 V *
54. Consider a video signal that has a resolution of 640 by 480 pixels; with a 30 Hz
frame rate and progressive scan. The luminance is sampled using 8 bits per sample.
The two chroma channels also use 8 bits per sample, but the color resolution is one
fourth that used for luminance. Find the approximate bit rate of this signal,
neglecting synchronization, error correction, and compression.
A. 27.65 Mbps
B. 110.6 Mbps*
C. 55.3 Mbps
D. 221.2 Mbps
55. In angle modulation, the amount of carrier deviation is proportional to the rate of
change of the modulating signal. What is the main difference of FM and PM modulated
carrier?
A. Both FM and PM appear to be frequency modulated by a cosine of the modulating
signal.
Republic of the Philippines
Professional Regulation Commission
Board of Electronics Engineering
ECE Licensure Examination Pre-Board Exam
1:00 pm 6:00 pm
Page 9 of 15
ELECTRONICS SYSTEMS AND TECHNOLOGIES
SET B
B. Both FM and PM appear to be frequency modulated
signal
C. PM carrier appears to be frequency-modulated by
signal while FM appears to be frequency-modulated
signal *
D. FM carrier appears to be frequency-modulated by
signal while PM appears to be frequency-modulated
signal
by a sine of the modulating
the cosine of the modulating
by the sine of the modulating
the cosine of the modulating
by the sine of the modulating
56. The antenna diameter of a radar system is doubled. The maximum range will
A. be doubled *
B. be halved
C. become four times
D. decrease to one fourth
57. A radio station works at 800 kHz and uses AM. If this is a public broadcast system,
it should transmit using
A.
B.
C.
D.
parabolic reflector to transmit all round
turnstile antenna for the required land
half wave long horizontal wave
a vertical antenna less than quarter for practical reasons *
58. One of receiver parameters in a communication system is the selectivity. It is a
parameter that is used to measure the ability of the receiver to accept a given band
of frequencies and reject all others. There are several ways to describe the
selectivity of the receiver. One common way is to simply give the bandwidth at two
level attenuations, -3dB and -60 dB. Thus the ratio of the two bandwidths is called
the shape factor. In the receiver part of your communication system, what is the
main difference between an overly selective and underselective receiver?
A. If a receiver is overly selective only part of the bandwidth of the AM signal is
amplified, causing some of the sideband information to be lost and distortion
results while underselective receiver is
more than one radio station on
different frequencies may be picked up by the receiver at the same time. *
B. If a receiver is underselective only part of the bandwidth of the AM signal is
amplified, causing some of the sideband information to be lost and distortion
results while overly selective receiver is
more than one radio station on
different frequencies may be picked up by the receiver at the same time.
C. If a receiver is overly selective, the volume control is tuned up to maximum, the
desired station is very weak while underselective receiver received too much
noise and then picked up and amplified by the receiver.
D. If a receiver is underselective, the volume control is tuned up to maximum, the
desired station is very weak while overly selective receiver received too much
noise and then picked up and amplified by the receiver.
59. A satellite-dish owner has a 3 meter dish designed for C-band (4GHz) operation. The
owner wants to use the same dish with a new feedhorn, for Ku- band (12GHz)
satellites. What effect will the change in frequency have on the gain and beamwidth
of the antenna?
A. Gain decreases by 9.54 dB, beamwidth decreases three times of its former value.
B. Gain increases by 9.54 dB, beamwidth decreases three times of its former value.
C. Gain decreases by 9.54 dB, beamwidth decreases 1/3 of its former value.
D. Gain increases by 9.54 dB, beamwidth decreases 1/3 of its former value. *
60. What is an auto configuration protocol used on IP networks where computers that are
connected to IP networks must be configured before they can communicate with other
computers on the network.
A. Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP)
B. Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP)
C. Inverse Address Resolution Protocol (IARP)
D. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)*
61. The VLF, LF and MF antennas are
A. horizontally polarized
C. non linearly polarized
B. vertically polarized *
D. either (a) or (b)
62. The antenna that is radiating electromagnetic energy appears to the generator as an
ideally resistive electrical load so that the applied power is consumed as radiated
energy. In addition to the resistive component, an antenna can have a reactive
component. The resistive component is equivalent to a resistor which, if used to
Republic of the Philippines
Professional Regulation Commission
Board of Electronics Engineering
ECE Licensure Examination Pre-Board Exam
1:00 pm 6:00 pm
Page 10 of 15
ELECTRONICS SYSTEMS AND TECHNOLOGIES
SET B
replace the antenna, would dissipate power equal to the radiated power of the
antenna. This is known as
A. antenna coupler
C. radiation resistance*
B. loading coil
D. dummy load
63. A transmission line is a metallic conductor system used to transfer electrical
energy from one point to another using electrical current flow. It is a two or more
electrical conductors separated by a nonconductive insulator (dielectric), such as
pair of wires or system of wire pairs. When Zo is not equal to ZL, some of incident
power is absorbed by the load and some is reflected to the source. This is called
unmatched or mismatched lines. A non-lossy transmission line terminated with an open
circuit will have:
A. An in-phase reflected current that is equal in magnitude to the incident current
B. An opposite-phase reflected current that is equal in magnitude to the incident
current *
C. An in-phase reflected current that is smaller n magnitude than the incident
current
D. An opposite-phase reflected current that is smaller in magnitude than the
incident current
64. Convert the 12 bit sample 100110100100 into an 8 bit compressed code?
A. 11011010 *
B. 10111010
C. 11110001
D. 10101111
65. The bandwidth of a video signal is 4.5 MHz. This signal is to be transmitted using
PCM with the number of quantization levels Q = 1024. The sampling rate should be 20%
higher than the Nyquist rate. Calculate the system bit rate
A. 54Mbps
B. 108 Mbps *
C. 90 Mbps
D. 45 Mbps
66. In _______ encoding, the duration of the bit is divided into two halves. The voltage
remains at one level during the first half and moves to the other level in the
second half. The transition at the middle of the bit provides synchronization.
A. Manchester
B. Differential Manchester
C. NRZ-L
D. Both A and B *
67. A radar transmitter has a power of 10 kW and operates at a frequency of 9.5 GHz. Its
signal reflects from a target 15 km away with a radar cross section of 10.2 square
meter. The gain of the antenna is 20 dBi. Calculate the received signal power.
A. 10.1 fW*
B. 23.1 fW
C. 3.41 fW
D.9.8 fW
68. Quantization is the process of converting an infinite number of possibilities to a
finite number of conditions. Analog signals contain an infinite number of amplitude
possibilities. Thus, converting an analog signal to a PCM code with a limited number
of combinations requires quantization. In essence, quantization is the process of
rounding off the amplitudes of flat-top samples to a manageable number of levels.
The decimal value added to or subtracted from the original value is considered an
error and is called quantization error. Which of the following decreases
quantization error?
A. Decrease the number of levels
C. Increase the sampling pulse
B. Decrease the sampling pulse
D. Decrease the step size*
69. Bit rate refers to the rate of change of a digital information signal, which is
usually binary. Baud, like bit rate, is also a rate of change; however, baud refers
to the rate of change of a signal on the transmission medium after encoding and
modulation have occurred. Hence, baud is a unit of transmission rate, modulation
rate, or symbol rate. If the transmitter sends 500 symbols per second, each of which
contains 3 bits, determine the bit rate, baud and the modulation used.
A. 1500 bps, 500 baud, FSK
C. 1500 bps, 1500 baud, BPSK
B. 1500 bps, 500 baud, 8-PSK*
D. 1500 bps, 1500 baud, 8-QAM
70. A type of blocking coding scheme designed to be used in combination with NRZ-I.
Problem with synchronization in NZR-I can be minimized by changing the bit stream,
prior to encoding with NRZ-I, so that it does not have long stream of 0s.
A. 4B/5B *
B. 8B/10B
C. 5B/4B
D. 10B/8B
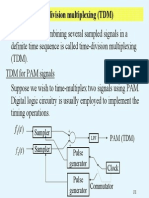
multiplexing (TDM) is a digital process that allows several
connections to share the high bandwidth of a link. TDM is a digital multiplexing
technique for combining several low-rate channels into one high-rate one. We can
divide TDM into two different schemes: synchronous or statistical. Differentiate the
two types of TDM?
71. Time-division
Republic of the Philippines
Professional Regulation Commission
Board of Electronics Engineering
ECE Licensure Examination Pre-Board Exam
1:00 pm 6:00 pm
Page 11 of 15
ELECTRONICS SYSTEMS AND TECHNOLOGIES
SET B
In synchronous TDM, each input connection has an allotment in the output even if
it is not sending data while in statistical TDM, slots are dynamically allocated
to improve bandwidth efficiency. *
B. In statistical TDM, each input connection has an allotment in the output even if
it is not sending data while in synchronous TDM, slots are dynamically allocated
to improve bandwidth efficiency.
C. A statistical TDM has a finite number of high-speed data input lines with one
high-speed multiplexed data output line, and each input line has its own digital
encoder and buffer while synchronous TDM often contains an abundance of time
slots within each frame that contain no information.
D.
A synchronous TDM has a finite number of high-speed data input lines with one
high-speed multiplexed data output line, and each input line has its own digital
encoder and buffer while statistical TDM often contains an abundance of time
slots within each frame that contain no information.
A.
72. Suppose
you are given a task by your boss to analyze a specific microwave
communication system. An FM LOS microwave link operates at 6.15 GHz. The required
receiver IF bandwidth is 20 MHz The transmitter output power is 30 dBm. The receiver
front ends first active stage is a mixer with a noise figure of 9 dB. The path
length is 21 mi; the antennas at each end have a 35-dB gain and the transmission
line losses at each end are 3 dB. IF the improvement threshold is used as the
unfaded reference, what is the reliability of the radio link?
A. 98.995%
B. 98.595%
C. 99.982% *
D. 98.929%
73. Crosstalk can be defined as any disturbance created in a communications channel by
signals in other communications channels. It is a potential problem whenever two
metallic conductors carrying different signals are located in close proximity to
each other. Using the concept of crosstalk, what is the difference between nonlinear
crosstalk and transmittance crosstalk?
A. Nonlinear crosstalk is a direct result of nonlinear amplification (hence the
name) in analog communications systems. Nonlinear amplification produces
harmonics and cross products (sum and difference frequencies) while transmittance
crosstalk is most prevalent when filters do not adequately reject undesired
products from other channels. Because this type of interference is caused by
inadequate control of the transfer characteristics or transmittance of networks.*
B. Nonlinear crosstalk is most prevalent when filters do not adequately reject
undesired products from other channels. Because this type of interference is
caused by inadequate control of the transfer characteristics or transmittance of
networks while transmittance crosstalk is a direct result of nonlinear
amplification (hence the name) in analog communications systems. Nonlinear
amplification produces harmonics and cross products (sum and difference
frequencies).
C. Nonlinear crosstalk is due to the effects of near-field mutual induction between
cables from physically isolated circuits. To reduce nonlinear crosstalk due to
mutual induction, wires are twisted together (hence the name twisted pair) while
Transmittance Crosstalk is a direct result of nonlinear amplification (hence the
name) in analog communications systems. Nonlinear amplification produces
harmonics and cross products (sum and difference frequencies)
D. Nonlinear crosstalk is a direct result of nonlinear amplification (hence the
name) in analog communications systems. Nonlinear amplification produces
harmonics and cross products (sum and difference frequencies)while Transmittance
Crosstalk is due to the effects of near-field mutual induction between cables
from physically isolated circuits. To reduce nonlinear crosstalk due to mutual
induction, wires are twisted together (hence the name twisted pair)
74. In amplitude modulation, the information signal varies the amplitude of the carrier
sine wave. The instantaneous value of the carrier amplitude changes in accordance
with the amplitude and frequency variations of the modulating signal. Which is not
true about amplitude modulation?
A. The repetition rate of the envelope of the AM wave is equal to the frequency of
the modulating signal.
B. AM wave has its maximum value at the positive peak of the modulating signal and
minimum value at the negative peak.
C. The output of the modulator is the carrier signal when the modulating signal is
not present.
Republic of the Philippines
Professional Regulation Commission
Board of Electronics Engineering
ECE Licensure Examination Pre-Board Exam
1:00 pm 6:00 pm
Page 12 of 15
ELECTRONICS SYSTEMS AND TECHNOLOGIES
SET B
D. When the modulating signal amplitude is greater than the carrier signal
amplitude, crossover distortion occurs which is a result of overmodulation.*
75. For the given parameters, determine the energy per bit-to noise power density ratio
C = 10-12 W, fb = 60 kbps, N = 1.2 x 10-14 W, B = 120 kHz
A. 26.4 dB
B. 15.3 dB
C. 22.2 dB*
D. 33.7 dB
76. Delta
modulation uses a single-bit PCM code to achieve digital transmission of
analog signals. Rather than transmit a coded representation of the sample, only a
single bit is transmitted, which simply indicates whether that sample is larger or
smaller than the previous sample. If the slope of the analog signal is greater than
the delta modulator can maintain, slope overload results. Which of the following is
not a way to reduce slope overload?
A. Increasing the step size while using the same sampling frequency will reduce the
slope overload.
B. Increasing the sampling frequency for the same step size will reduce slope
overload.
C. Adaptive delta modulation can be used to reduce slope overload.
D. A limiter is used to remove the excess voltage produced by slope overload.*
77. What
is the line encoding used in a Standard Ethernet Implementation {10Base5,
10Base2, 10Base-T & 10Base-F}?
A. MLT-3
B. NRZ-I
C. Manchester*
D. 4D-PAM
78. Companding is the process of compressing and then expanding. With companded systems,
the higher-amplitude analog signals are compressed (amplified less than the loweramplitude signals) prior to transmission and then expanded (amplified more than the
lower-amplitude signals) in the receiver. The following describes the effect of
companding except
A. Companding is a means of improving the dynamic range of a communications system.
B. Companding decreases quantization error without the need to increase the number
of levels required for quantization.
C. Companding improves synchronization by using clock recovery.*
D. Companding improves the signal-to-quantization noise ratio.
79. In this encoding method, the duration of the bit is divided into two halves. The
voltage remains at one level during the first half and moves to the other level in
the second half. The transition at the middle of the bit provides synchronization.
A. B8ZS
B. Manchester
*
C. AMI
D. pseudotenary
80. Fading can be minimized by using what is called a diversity system. A diversity
system uses multiple transmitters, receivers, or antennas to mitigate the problems
caused by multipath signals. What type of diversity system uses two receiver
antennas spaced as far apart as possible to receive the signals? This diversity
system is used mainly at base stations rather than in portable or handheld units.
The basic idea is that antennas at slightly different locations will receive
different variations of the signals, with one being better than the other.
A. Frequency diversity
C. Spatial diversity*
B. Polarization diversity
D. Receiver diversity
81. It is the OSI layer responsible for network availability (i.e., data storage and
processor capacity). Its protocols provide the logical connection entities at the
application layer. These applications include file transfer protocols and sending email. Its responsibilities include network log-on and log-off procedures and user
authentication. It determines the type of dialogue available (i.e., simplex, half
duplex, or full duplex). Its characteristics include virtual connections between
applications entities, synchronization of data flow for recovery purposes, creation
of dialogue units and activity units, connection parameter negotiation, and
partitioning services into functional groups.
A. Application layer
C. Session layer*
B. Transport layer
D. Presentation layer
82. Phase-shift keying (PSK) is another form of angle-modulated, constant-amplitude
digital modulation. PSK is an M-ary digital modulation scheme similar to
conventional phase modulation except with PSK the input is a binary digital signal
and there are a limited number of output phases possible. The input binary
information is encoded into groups of bits before modulating the carrier. Its
Republic of the Philippines
Professional Regulation Commission
Board of Electronics Engineering
ECE Licensure Examination Pre-Board Exam
1:00 pm 6:00 pm
Page 13 of 15
ELECTRONICS SYSTEMS AND TECHNOLOGIES
SET B
variations include BPSK, QPSK, 8-PSK, 16-PSK among others. Which is the major
advantage of QPSK in terms of bandwidth and noise immunities?
A. The bandwidth required for QPSK is half than PSK with similar noise immunities*
B. The bandwidth required for QPSK is twice than PSK with similar noise immunities
C. The bandwidth required for QPSK is one -third than PSK with different noise
immunities
D. The bandwidth required for QPSK is double than PSK with either same or different
noise immunities depending on the transmission rate
83. The bandwidth of a video signal is 4.5 MHz. This signal is to be transmitted using
PCM with the number of quantization levels Q = 1024. The sampling rate should be 20%
higher than the Nyquist rate. Calculate the system bit rate.
A. 9.216 Gbps
B. 11.0592 Gbps
C. 90 Mbps
D. 108 Mbps*
84. A line of sight radio link is to be built in Baguio, operating at a frequency of
6GHz has a separation of 40km between antennas. An obstacle, 10 m high, in the path
is located 10km form the transmitting antenna. By how much must the beam clear the
obstacle?
A. 19.3 m
B. 11.6 m
C. 21.6 m*
D. 29.3 m
85. An optic fiber is made of glass with a refractive index of 1.55 and is clad with
another glass with a refractive index of 1.51. Launching takes place from air. What
numerical aperture does the fiber have?
A. 0.132
B. 0.352*
C. 0.032
D. 0.475
86. The ratio of the modulating signal amplitude to the carrier signal amplitude is
called the modulation index, the ideal value of which is 1. When modulation index is
greater than 1 which means that the modulating signal amplitude is greater than the
carrier signal amplitude, overmodulation occurs. Which is not a result of
overmodulation?
A. The bandwidth of the resulting signal is greater because of the harmonics created
due to overmodulation.
B. Some part of the signal is clipped, thus information becomes unintelligible.
C. Overmodulation causes the local oscillator to drift from its center frequency.*
D. Distortion caused by overmodulation produces adjacent channel interference.
87. A sensitive and selective receiver can be made using only amplifiers, selective
filters, and a demodulator. This is called a tuned radio frequency or TRF receiver.
Early radios used this design. However, such a receiver does not usually deliver the
kind of performance expected in modern communications applications. One type of
receiver that can provide that performance is the superheterodyne receiver.
Superheterodyne receivers convert all incoming signals to a lower frequency, known
as the intermediate frequency (IF), at which a single set of amplifiers and filters
is used to provide a fixed level of sensitivity and selectivity. Which is not an
advantage of superheterodyne over the TRF design?
A. Superheterodyne has superior gain since it uses AGC which automatically adjusts
the gain depending on the level of the received signal.
B. It is more stable because it has lesser number of amplifiers to be tuned to the
same center frequency.
C. The receiver is more selective because it only needs to accept signals with
frequencies equal to the Intermediate Frequency.
D. The local oscillator is less likely to drift for a superheterodyne receiver than
for the TRF design.*
88. A 1 mW video signal having a bandwidth of 100 MHz is transmitted to a receiver
through cable that has 40 dB loss. If the effective one-side noise spectral density
at the receiver is 10-20 Watt/Hz, then the signal-to-noise ratio at the receiver is
A. 50 dB*
B. 30 dB
C. 40 dB
D. 60 dB
89. Determine the Hamming distance for the codewords (10101, 11001)
A. one
B. two*
C. three
D. four
90. Which
of the following statements best describe the purpose for the use of an
antenna coupler?
A. It allows the transmitter to be operated at more than one carrier frequency at
the same time.
B. It allows the transmitter to be connected to several antennas at the same time.
Republic of the Philippines
Professional Regulation Commission
Board of Electronics Engineering
ECE Licensure Examination Pre-Board Exam
ELECTRONICS SYSTEMS AND TECHNOLOGIES
1:00 pm 6:00 pm
Page 14 of 15
SET B
C. It is used to filter out the carrier frequency from the transmitters AM output
signal.
D. It is used to match the output impedance of the transmitter with the input
impedance of the antenna to ensure maximum power transfer.*
91. Pulse dialing is a signaling technology in telecommunications in which a direct
current local loop circuit is interrupted according to a defined coding system for
each signal transmitted, usually a digit. How long does it take to dial the number
784-3745 using pulse dialing with .5s inter digit time?
A. 6.8 s*
B. 4.3 s
C. 9.2 s
D. 7.0 s
92. In fiber optics terminology, the word mode simply means path. If there is only one
path for light rays to take down a cable, it is called single mode. If there is more
than one path, it is called multimode. Which of the following refers to a
characteristic of a multimode fiber optic?
A. Cladding thickness is greater than the radius of the core and the diameter of the
core must be much greater than the wavelength of the light to be carried.*
B. Cladding thickness is less than the radius of the core and diameter of the core
must be greater than the wavelength of the light to be carried.
C. Cladding thickness is greater than the radius of the core and the diameter of the
core must be lesser than the wavelength of the light to be carried.
D. Cladding thickness is less than the radius of the core and the diameter of the
core must be lesser than the wavelength of the light to be carried.
93. Any circuit that will convert a frequency variation in the carrier back to a
proportional voltage variation can be used to demodulate or detect FM signals.
Circuits used to recover the original modulating signal from an FM transmission are
called demodulators, detectors, or discriminators. An FM receiver rarely works
satisfactorily without an RF amplifier because
A. FM receivers typically work with smaller input signal levels due to their noise
characteristics*
B. FM receivers have a narrower bandwidth.
C. FM receivers do not have very much gain in their IF amplifier stages.
D. FM receivers need RF amplifier stages to be able to decode stereo signals.
94. A half wave dipole with a gain of 2.14 dBi is fed, by means of lossless, matched
line by a 25 watts transmitter. What is the electric field strength of the signal
measured 15 km from the antenna in free space in the direction of maximum radiation?
A. 2.34 mV/m*
B. 5.23 mV/m
C. 4.56 mV/m
D. 45.26 mV/m
95. Image frequency is any frequency other than the selected radio frequency carrier
that, if allowed to enter a receiver and mix with local oscillator will produce a
cross-product frequency that is equal to intermediate frequency. Thus, it is
desirable that the receiver should be able to reject image frequencies as it mixes
with the desired signal. FM is less likely to encounter problems with image
frequencies than AM. Why are image frequencies somewhat less of a problem in FM
receivers than they are in SSB or AM receivers?
A. Single sideband systems use less bandwidth than FM. Narrowband signals are more
likely to be affected by image frequencies.
B. If it receives two signals with the same frequency, it only demodulates the
signal with the higher power. This is known as capture effect.*
C. FM mixer stages are square-law devices. Second harmonic is eliminated which is
the main source of image frequency.
D. FM receivers do not use the superheterodyne design. The superheterodyne design is
more likely to create image frequency.
96. Whether digital signals are being transmitted by baseband methods or broadband
methods, before the data is put on the medium, it is usually encoded in some way to
make it compatible with the medium or to facilitate some desired operation connected
with the transmission. One of the encoding techniques is the Return to Zero or RZ.
In return to zero (RZ) encoding, the voltage level assigned to a binary 1 level
returns to zero during the bit period. Which of the following is not a common RZ
code?
A. RZ-unipolar
B. RZ-bipolar
C. RZ-M*
D. RZ-AMI
97. How a light ray reacts when it meets the interface of two transmissive materials
that have different indexes of refraction can be explained with Snells law. The
angle of incidence is the angle at which the propagating ray strikes the interface
with respect to the normal, and the angle of refraction is the angle formed between
the propagating ray and the normal after the ray has entered the second medium.
Republic of the Philippines
Professional Regulation Commission
Board of Electronics Engineering
ECE Licensure Examination Pre-Board Exam
1:00 pm 6:00 pm
Page 15 of 15
ELECTRONICS SYSTEMS AND TECHNOLOGIES
SET B
Which of the following will not happen when light travels from one medium to another
medium with a different refractive index?
A. If the first medium has a lower index of refraction than the second, light will
be refracted towards the normal line.
B. If the first medium has a lower index of refraction than the second and the angle
of incidence is equal to the critical angle, light will travel along the
boundary.*
C. If the first medium has a higher index of refraction than the second, light will
be refracted away from the normal line.
D. If the first medium has a higher index of refraction than the second, it is
possible that light will be reflected.
98. An earth station for use with a geostationary satellite has a dish antenna which
sees a sky temperature of 25 K. It is connected to the receiver with a feedline
having 1 dB loss. The receiver equivalent noise temperature is 15 K. Calculate the
noise temperature for the system.
A. 95 K*
B. 80 K
C. 45 K
D. 115 K
99. The antenna is the interface between the transmission line and space. Antennas are
passive devices; the power radiated cannot be greater than the power entering from
the transmitter. In other words, antenna cannot amplify signals. However, some
antennas can receive higher signal levels than others because of higher gain. What,
then, is meant by antenna gain?
A. The final amplifier gain minus the transmission line losses (including any
phasing lines present)
B. The ratio of the amount of power produced by the antenna compared to the output
power of the transmitter
C. The ratio of the signal in the backward direction
D. The numeric ratio relating the radiated signal strength of an antenna to that of
another antenna*
100. Suppose you had an FM signal with a carrier of 10 MHz and a deviation of 10 kHz.
Which of the following best explain how you could use it to get an FM signal
MHz with a deviation of 20 kHz.
A. First, put the signal through a frequency doubler to get a 20-MHz carrier
10-kHz deviation. Then mix that signal with a 150-MHz carrier to generate
MHz carrier with 20-kHz deviation.
B. First, put the signal through a frequency doubler to get a 20-MHz carrier
20-kHz deviation. Then mix that signal with an 80-MHz carrier to generate
MHz carrier with 20-kHz deviation.*
C. First, put the signal through a frequency doubler to get a 20-MHz carrier
10-kHz deviation. Then mix that signal with an 80-MHz carrier to generate
MHz carrier with 20-kHz deviation.
D. First, put the signal through a frequency doubler to get a 20-MHz carrier
20-kHz deviation. Then mix that signal with a 150-MHz carrier to generate
MHz carrier with 20-kHz deviation.
----------------------------NOTHING FOLLOWS----------------------------
at 100
with a
a 100with a
a 100with a
a 100with a
a 100-
You might also like
- Iecep Compilation EsatDocument10 pagesIecep Compilation Esatjanno2101No ratings yet
- Iecep EsatDocument29 pagesIecep EsatIvy Cee100% (1)
- Preboard EST 2ndbatch April2015 SetBDocument15 pagesPreboard EST 2ndbatch April2015 SetBLopez Shian ErvinNo ratings yet
- Electronics Engineering FundamentalsDocument77 pagesElectronics Engineering FundamentalsLeonard Jobet Villaflor PantonNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation FundamentalsDocument80 pagesInstrumentation FundamentalsRonnie TorresNo ratings yet
- Excel TranslineDocument145 pagesExcel TranslineHazel Grace Del MonteNo ratings yet
- EPR 364 Lecture 3: Electrical Measurements with Multirange Ammeters and VoltmetersDocument38 pagesEPR 364 Lecture 3: Electrical Measurements with Multirange Ammeters and Voltmetersahmed gamalNo ratings yet
- Excel Review Center Refresher Course EST: Give Your Best Shot !Document4 pagesExcel Review Center Refresher Course EST: Give Your Best Shot !Nida Bagoyboy NatichoNo ratings yet
- Answer:: Y Abc + A + B + CDocument10 pagesAnswer:: Y Abc + A + B + CKarumon UtsumiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Noise in Communication SystemsDocument19 pagesUnderstanding Noise in Communication SystemsRomeo Ganelo100% (1)
- Pinoybix WADocument28 pagesPinoybix WAKenNo ratings yet
- PTEE6201 - CIRCUIT THEORY: KEY CONCEPTSDocument19 pagesPTEE6201 - CIRCUIT THEORY: KEY CONCEPTSSiva KumarNo ratings yet
- MCQ in Modulation Part 1 ECE Board ExamDocument13 pagesMCQ in Modulation Part 1 ECE Board ExamXyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 BisaresDocument6 pagesLecture 5 BisaresTopher Palma0% (1)
- Draft of October 2015 Electronics Engineering Board Exam Questions and ConceptsDocument5 pagesDraft of October 2015 Electronics Engineering Board Exam Questions and ConceptsAyel Cejas Costiniano100% (1)
- IECEP ELEX Key TermsDocument6 pagesIECEP ELEX Key TermsAnonymous 7efeHnCNo ratings yet
- Electronic Systems and TechnologiesDocument5 pagesElectronic Systems and TechnologiesShiekaMikaelaEdaugalBesoNo ratings yet
- Final Preboard Oct2017 EsatsetaDocument7 pagesFinal Preboard Oct2017 Esatsetajj012586100% (1)
- Microwave Communications - Mcqs (1-300)Document43 pagesMicrowave Communications - Mcqs (1-300)Abdul Hameed100% (1)
- Iecep Elecs 2Document10 pagesIecep Elecs 2Rick SarmientoNo ratings yet
- (EDGE) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS in COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING by Yu and CamachoDocument88 pages(EDGE) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS in COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING by Yu and CamachocathyNo ratings yet
- PINOYBIX NoiseDocument50 pagesPINOYBIX NoiseNida Bagoyboy NatichoNo ratings yet
- ESAT ProblemsDocument164 pagesESAT ProblemsSherwin JhonNo ratings yet
- Powerline Pre Board Ree Sept 2010Document15 pagesPowerline Pre Board Ree Sept 2010Junnar Jay AbañoNo ratings yet
- Questions On Signals and AmplifiersDocument30 pagesQuestions On Signals and Amplifierskibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- Electronics MCQDocument4 pagesElectronics MCQHary KrizNo ratings yet
- MCQ in Wire and Wireless Communications System ECE BoardDocument20 pagesMCQ in Wire and Wireless Communications System ECE BoardIan John MontalboNo ratings yet
- Group Study - Antennas - QuestionnaireDocument7 pagesGroup Study - Antennas - QuestionnaireSheehan Kayne De CardoNo ratings yet
- ELEX Evaluation 6Document4 pagesELEX Evaluation 6Achilles AldaveNo ratings yet
- MCQ in Communications Engineering by Lomboy & VillanuevaDocument114 pagesMCQ in Communications Engineering by Lomboy & VillanuevaSheehan Kayne De CardoNo ratings yet
- Excel Geas 2 Coaching PDFDocument8 pagesExcel Geas 2 Coaching PDFTeena Marie SantosNo ratings yet
- Ece Board Exam AwarenessDocument3 pagesEce Board Exam AwarenessDarwin TacubanzaNo ratings yet
- TECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE OF THE PHILIPPINES – MANILA TRANSMISSION MEDIA AND ANTENNA SYSTEMS FINAL EXAM REVIEWDocument10 pagesTECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE OF THE PHILIPPINES – MANILA TRANSMISSION MEDIA AND ANTENNA SYSTEMS FINAL EXAM REVIEWKerwin TejucoNo ratings yet
- Frenzel Exam Sheet (Key To Correction)Document22 pagesFrenzel Exam Sheet (Key To Correction)Patrick James De LeonNo ratings yet
- Electronics Engineering Laws and PRC FunctionsDocument6 pagesElectronics Engineering Laws and PRC FunctionsあいうえおかきくけこNo ratings yet
- Iecep GeasDocument9 pagesIecep GeaswengNo ratings yet
- INDIABIXDocument7 pagesINDIABIXJanicz BalderamaNo ratings yet
- Sand NotesDocument226 pagesSand NotesHGFLJJ0% (1)
- REVIEWER in Electronic Communications System by Wayne TomasiDocument112 pagesREVIEWER in Electronic Communications System by Wayne TomasiSheehan Kayne De CardoNo ratings yet
- Est Reviewer Final and OriginalDocument437 pagesEst Reviewer Final and Originalvon kervy onrade0% (1)
- Road To EngineerDocument73 pagesRoad To EngineerDwight Eizen CristobalNo ratings yet
- EST For CorrectionDocument2 pagesEST For CorrectionCaurelou PitocNo ratings yet
- Electronics Engineering CommunicationsDocument15 pagesElectronics Engineering CommunicationsArn TupasNo ratings yet
- Est Question For Iecep 2012Document4 pagesEst Question For Iecep 2012Ericson Blue Sta MariaNo ratings yet
- ECS QuestionsDocument130 pagesECS Questionsjjmmnn1001100% (1)
- MCQ in Communications by Alejamdro H. Ballado, Jr.Document51 pagesMCQ in Communications by Alejamdro H. Ballado, Jr.Ismaela CatipayNo ratings yet
- EST Sample Problems 01Document4 pagesEST Sample Problems 01Genesis PinedaNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication BasicsDocument18 pagesTelecommunication Basicsd_aroyNo ratings yet
- Model-Dpcm100: Differential Pulse Code Modulation/Demodulation TrainerDocument15 pagesModel-Dpcm100: Differential Pulse Code Modulation/Demodulation TrainerVăn Tấn ĐìnhNo ratings yet
- Wired Digital Comms Protocols & ModulationDocument9 pagesWired Digital Comms Protocols & ModulationKenan BaltaciNo ratings yet
- All CommunicationsDocument7 pagesAll CommunicationsJhasper ManagyoNo ratings yet
- (A) What Is The Need of Modulating A Signal? Will It Be A Right Approach To Send The Information As The Signal Itself?Document44 pages(A) What Is The Need of Modulating A Signal? Will It Be A Right Approach To Send The Information As The Signal Itself?shubhamNo ratings yet
- Iecep EsatDocument29 pagesIecep EsatChaeyoung YooNo ratings yet
- Short Questions of Digital Communication: Unit 1: Pulse ModulationDocument7 pagesShort Questions of Digital Communication: Unit 1: Pulse ModulationSakib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Standard - Notes - TSN Unit III 2Document19 pagesStandard - Notes - TSN Unit III 2Priyabrata GhoraiNo ratings yet
- Line Coding Techniques 2023Document31 pagesLine Coding Techniques 2023Gerald KapinguraNo ratings yet
- ESATtrueDocument1,111 pagesESATtruevon kervy onradeNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Baseband ModulationDocument65 pagesSampling and Baseband ModulationAbdul Qawi AnsariNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 6 Telecommunications and Advanced Communications: Characteristic Impedance Topics 6 - Return LossDocument35 pagesChapter - 6 Telecommunications and Advanced Communications: Characteristic Impedance Topics 6 - Return LossLokendra Khati100% (1)
- High-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversFrom EverandHigh-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversNo ratings yet
- PdeDocument2 pagesPdeGeorge Ezar N. QuiriadoNo ratings yet
- Electronics Engineering Questions - DifficultDocument5 pagesElectronics Engineering Questions - DifficultGeorge Ezar N. QuiriadoNo ratings yet
- How To Answer The Toughest Interview QuestionsDocument42 pagesHow To Answer The Toughest Interview QuestionsGeorge Ezar N. QuiriadoNo ratings yet
- ELECTRONICS SYSTEMS QUESTIONSDocument3 pagesELECTRONICS SYSTEMS QUESTIONSgiophilipNo ratings yet
- Electronics Systems and Technologies Questions - EasyDocument3 pagesElectronics Systems and Technologies Questions - EasygiophilipNo ratings yet
- Electronics Engineering Average Questions SolvedDocument4 pagesElectronics Engineering Average Questions SolvedGeorge Ezar N. QuiriadoNo ratings yet
- Electronics Engineering Questions - DifficultDocument5 pagesElectronics Engineering Questions - DifficultGeorge Ezar N. QuiriadoNo ratings yet
- Electronics Engineering Average Questions SolvedDocument4 pagesElectronics Engineering Average Questions SolvedGeorge Ezar N. QuiriadoNo ratings yet
- Professional Regulations Commission Board of Electronics EngineeringDocument8 pagesProfessional Regulations Commission Board of Electronics EngineeringGeorge Ezar N. QuiriadoNo ratings yet
- Electronics Systems and Technologies Questions - AverageDocument3 pagesElectronics Systems and Technologies Questions - AveragegiophilipNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line 101Document6 pagesTransmission Line 101George Ezar N. QuiriadoNo ratings yet
- Professional Regulations Commission Board of Electronics EngineeringDocument8 pagesProfessional Regulations Commission Board of Electronics EngineeringGeorge Ezar N. QuiriadoNo ratings yet
- Electronics Engineering Questions - EasyDocument4 pagesElectronics Engineering Questions - EasygiophilipNo ratings yet
- Tos - Est FinalDocument2 pagesTos - Est FinalGeorge Ezar N. QuiriadoNo ratings yet
- Computer History 1Document88 pagesComputer History 1George Ezar N. QuiriadoNo ratings yet
- TOS - MathDocument4 pagesTOS - MathGeorge Ezar N. QuiriadoNo ratings yet
- EstDocument4 pagesEstGeorge Ezar N. QuiriadoNo ratings yet
- Taylor Series and Numerical MethodsDocument14 pagesTaylor Series and Numerical MethodsGeorge Ezar N. QuiriadoNo ratings yet
- EstDocument4 pagesEstGeorge Ezar N. QuiriadoNo ratings yet
- BIT The BeezDocument17 pagesBIT The BeezGeorge Ezar N. QuiriadoNo ratings yet
- Measuring ErrorsDocument20 pagesMeasuring ErrorsDiego Gómez Páez100% (1)
- CDMADocument24 pagesCDMAGeorge Ezar N. QuiriadoNo ratings yet
- Measuring ErrorsDocument20 pagesMeasuring ErrorsDiego Gómez Páez100% (1)
- Licensure SyllabiDocument7 pagesLicensure SyllabiKento FujimoriNo ratings yet
- B) B) P (A) and P (B) - Ans. P (A) P (B)Document1 pageB) B) P (A) and P (B) - Ans. P (A) P (B)George Ezar N. QuiriadoNo ratings yet
- How To Answer The Toughest Interview QuestionsDocument42 pagesHow To Answer The Toughest Interview QuestionsGeorge Ezar N. QuiriadoNo ratings yet
- MagneticDocument14 pagesMagneticNurulazmi Bin Abd RahmanNo ratings yet
- Source of Erros in Numerical MethodsDocument28 pagesSource of Erros in Numerical MethodsGeorge Ezar N. QuiriadoNo ratings yet
- BSCDocument1 pageBSCAbdirihmanNo ratings yet
- AM transmitter power and modulation index questionsDocument212 pagesAM transmitter power and modulation index questionsjigar16789100% (1)
- Digital Modulation Lesson SupplementDocument10 pagesDigital Modulation Lesson SupplementCaurelou PitocNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Coding and Modulation Experiment WithDocument11 pagesAdaptive Coding and Modulation Experiment WithSpace EngineerNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Mimo Wimax Using STBCDocument30 pagesSimulation of Mimo Wimax Using STBCSarang DamleNo ratings yet
- Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM) Techniques and Line Coding MethodsDocument40 pagesTime-Division Multiplexing (TDM) Techniques and Line Coding Methodsmuhaned190No ratings yet
- ATM - Asynchronous Transfer ModeDocument38 pagesATM - Asynchronous Transfer ModeRaviNo ratings yet
- Digital Modulation Solved Problems Data Rate Limits: N S N SDocument3 pagesDigital Modulation Solved Problems Data Rate Limits: N S N Sgazzie rayNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital ConversionDocument37 pagesAnalog To Digital ConversionSharanya VaidyanathNo ratings yet
- Lora-Based Smart Agriculture System ThesisDocument101 pagesLora-Based Smart Agriculture System ThesisFrancis Ian CalubagNo ratings yet
- ModulationsDocument8 pagesModulationsTofiqe AdamNo ratings yet
- VSAT Presentation 3Document54 pagesVSAT Presentation 3Waqar Asmat100% (1)
- Implementation and Performance Evaluation of OFDM System in Diverse Transmission Channel Using SimulinkDocument7 pagesImplementation and Performance Evaluation of OFDM System in Diverse Transmission Channel Using SimulinkAbdallah ToolmakerNo ratings yet
- GB LC70 - 60le740 - 741Document80 pagesGB LC70 - 60le740 - 741Joel WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument8 pagesProblem SetADSRNo ratings yet
- Information CapacityDocument22 pagesInformation CapacityEDRICK PARASNo ratings yet
- Adtec en 91 ManualDocument67 pagesAdtec en 91 ManualTony PerezNo ratings yet
- Callisto Terminal Commands GuideDocument8 pagesCallisto Terminal Commands Guidenicolás_lorréNo ratings yet
- 08-Asynchronous and Synchronous Serial CommunicationDocument113 pages08-Asynchronous and Synchronous Serial CommunicationTarq AbdullahNo ratings yet
- VI 101 Weighing Indicator: U U Ss Ee RR M M Aa NN Uu Aa LLDocument11 pagesVI 101 Weighing Indicator: U U Ss Ee RR M M Aa NN Uu Aa LLRicardo CorredorNo ratings yet
- DENT 3563: Telecommunication EngineeringDocument38 pagesDENT 3563: Telecommunication EngineeringSanji KarunaNo ratings yet
- SAE J1939 TrainingDocument80 pagesSAE J1939 Trainingjocker100% (1)
- Pulse Modulation Consists Essentially of Sampling Analog Information Signals and Then ConvertingDocument40 pagesPulse Modulation Consists Essentially of Sampling Analog Information Signals and Then ConvertingDaniel LoNo ratings yet
- Agilent Bluetooth EdrDocument24 pagesAgilent Bluetooth EdrOleg AleksieievNo ratings yet
- Seastar3510LR User ManualDocument51 pagesSeastar3510LR User ManualGersonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Wireless Coding and ModulationDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Wireless Coding and ModulationTuấn Đạt Lê XuânNo ratings yet
- Sample QuestionsDocument108 pagesSample QuestionsAaje Baaje67% (3)
- Configure Lab Equipment for UBWA CourseDocument139 pagesConfigure Lab Equipment for UBWA Courserogeriomachado_rsNo ratings yet
- What Is OFDMDocument39 pagesWhat Is OFDMRenu PareekNo ratings yet
- T6 TRVDocument68 pagesT6 TRVSUNYAOZONGNo ratings yet