Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cost of Capital Formulas
Uploaded by
Lealyn Martin BaculoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cost of Capital Formulas
Uploaded by
Lealyn Martin BaculoCopyright:
Available Formats
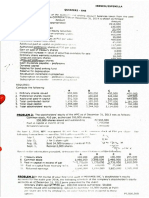
COST OF CAPITAL FORMULAS
Before-tax cost of debt
(approximation):
$ 1,000N d
2
rd =
N d + $ 1,000
2
After-tax cost of debt:
r i=r d (1T )
I+
r p=
Dp
Np
Cost of common stock
equity:
Using constantgrowth valuation
model:
Using CAPM:
rs =
D1
+g
P0
Cost of retained earnings:
r r =r s
Cost of new issues of
common stock:
r n=
Cost of preferred stock:
Weighted average cost of
capital (WACC):
Break point:
b (r mR F )
r s =RF +
D1
+g
Nn
r a= ( wi r i ) + ( w p r p ) +( ws r r n)
BP j=
AF j
wj
Definitions of Variables
AFi = amount of funds available
from financing source j at a given
cost
b = beta coefficient or a measure
of nondiversifiable
BPj = break point for financing
source j
D1 = per-share dividend expected
at the end of year 1
Dp = annual preferred stock
dividend (in dollars)
g = constant rate of growth in
dividends
I = annual interest in dollars
n = number of years to the
bonds maturity
Nd = net proceeds from the sale
of debt (bond)
Nn represent the net proceeds
from the sale of new common
stock
Np = net proceeds from the sale
of the stock
P0 = value of common stock
rr = cost of retained earnings
rs = required return on common
stock
RF = risk-free rate of return
ra= weighted average cost of
capital
rd = before-tax cost of debt
T = firms tax rate
wp = proportion of preferred
stock in capital structure
ri =after-tax cost of debt
rm = market return; return on the
market portfolio of assets
wi = proportion of long-term debt
in capital structure
ws = proportion of common stock
equity in capital structure
wi + wp + ws = 1.0
rn = cost of a new issue of
common stock
rp = cost of preferred stock
WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT
FORMULAS
Net working capital = Current assets (Payables+ Accruals)
Inventory Conversion Period + Average Collection Period
Payable Deferral Period = Cash Conversion Cycle
Inventory + Accounts receivable - Accounts payable =
Resources invested
Inventory conversion period=
Inventory
Cost of Goods Sold per day
Cost of short-term financing + Cost of long-term financing Earnings on surplus balances = Total cost of aggressive
strategy
Mathematical Development of EOQ
Order cost = O x (S Q)
Carrying cost = C x (Q 2)
Total cost = [O x (S Q)] + [C x (Q 2)]
ECQ=
S = usage in units per period
O = order cost per order
2 S Q
C
Q = order quantity in units
C = carrying cost per unit
per period
EOQ = order quantity that
minimizes the total inventory
cost.
Reorder point = Days of lead time X Daily usage
ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE
Total variable cost
of annual sales
Average investment accounts receivable=
Turnover of
accounts receivable
Turnover of accounts receivable=
Average collection period=
365
Average collection period
Accounts Receivable
Sales per day
Average investment under proposed plan - Average investment
under present plan =
Marginal investment in accounts receivable X Cost of funds tied
up in receivables =
Cost of marginal investment in A/R
Under proposed plan - Under present plan =Cost of marginal
bad debts
ACCOUNTS PAYABLE
Payablesdeferral period=
Cost of givingup cash discount=
Payables
Payables
=
Purchases per day Cost of goods sold /365
CD
365
100 CD N
CD = stated cash discount in
percentage terms
N =number of days that
payment can be delayed by
giving up the cash discount
Approximate cost of giving up cash discount =CD
Nominal annual cost of trade credit=
Effective Annual Rate=
365
N
Discount
x
100Discount
365
Days credit is
outstanding
D iscount Period
Interest
Amount borrowed
Effective Annual Ratefor a discount loan=
Simple Interest Rate per day =
Approximate Annual Rate=
Interest
Amount borrowed
Interest
Nominal Rate
DaysYear
Interest paid
Amount received/2
(Daysmonth)
( perRateday )( Amount
of loan )
Interest charge for month=
CAPITAL ASSET PRICING METHOD
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- MS01 - Introduction To Management Advisory Services - EncryptedDocument5 pagesMS01 - Introduction To Management Advisory Services - EncryptedLealyn Martin BaculoNo ratings yet
- ICARE RFBT Preweek (1) - Batch4Document15 pagesICARE RFBT Preweek (1) - Batch4john paulNo ratings yet
- CPAR Auditing TheoryDocument62 pagesCPAR Auditing TheoryKeannu Lewis Vidallo96% (46)
- Management and Legal StudyDocument43 pagesManagement and Legal StudyLealyn Martin BaculoNo ratings yet
- Income Taxes Batch 4 (Repaired)Document10 pagesIncome Taxes Batch 4 (Repaired)Lealyn Martin BaculoNo ratings yet
- E. Demand Analysis: Historical Population Year No. of Registered StallsDocument3 pagesE. Demand Analysis: Historical Population Year No. of Registered StallsLealyn Martin BaculoNo ratings yet
- Resa Afar 2016 Final PBDocument14 pagesResa Afar 2016 Final PBLealyn Martin Baculo100% (1)
- PWD Elementary Oct2022Document1 pagePWD Elementary Oct2022Lealyn Martin BaculoNo ratings yet
- PROFESSIONAL REGULATION COMMISSION EXAMINEE LISTDocument623 pagesPROFESSIONAL REGULATION COMMISSION EXAMINEE LISTLealyn Martin BaculoNo ratings yet
- MAS ReviewerDocument22 pagesMAS ReviewerBeverly HeliNo ratings yet
- Method of ResearchDocument2 pagesMethod of ResearchLealyn Martin BaculoNo ratings yet
- CPAR Auditing TheoryDocument62 pagesCPAR Auditing TheoryKeannu Lewis Vidallo96% (46)
- Resa Audit Quizzer May 2017Document89 pagesResa Audit Quizzer May 2017Lealyn Martin Baculo100% (1)
- Group1 Cis ReportDocument12 pagesGroup1 Cis ReportLealyn Martin BaculoNo ratings yet
- Letter of ConfirmationDocument1 pageLetter of ConfirmationLealyn Martin BaculoNo ratings yet
- Psa 705Document4 pagesPsa 705Lealyn Martin BaculoNo ratings yet
- Variable Costing and Segmented Reporting (Bobadilla)Document9 pagesVariable Costing and Segmented Reporting (Bobadilla)Lealyn Martin BaculoNo ratings yet
- Ias 11Document3 pagesIas 11Lealyn Martin BaculoNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument27 pagesDigestive SystemLealyn Martin BaculoNo ratings yet
- Registration Procedure of SecuritiesDocument1 pageRegistration Procedure of SecuritiesLealyn Martin BaculoNo ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument2 pagesNarrative ReportLealyn Martin BaculoNo ratings yet
- Fin ManDocument29 pagesFin ManLealyn Martin BaculoNo ratings yet
- Enron, Worldcom, TycoDocument6 pagesEnron, Worldcom, TycoLealyn Martin BaculoNo ratings yet
- Histo-biographical approach to MidsummerDocument3 pagesHisto-biographical approach to MidsummerLealyn Martin BaculoNo ratings yet
- Enron, Worldcom, TycoDocument6 pagesEnron, Worldcom, TycoLealyn Martin BaculoNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument27 pagesDigestive SystemLealyn Martin BaculoNo ratings yet
- Artificial Insemination: Inferring Diligent Darkness and Feminism in The PhilippinesDocument1 pageArtificial Insemination: Inferring Diligent Darkness and Feminism in The PhilippinesLealyn Martin BaculoNo ratings yet
- QUIZPHYSCIDocument4 pagesQUIZPHYSCILealyn Martin BaculoNo ratings yet
- System CatalogDocument2 pagesSystem CatalogLealyn Martin BaculoNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Case Analysis – Sales Force Integration Strategies at FedExDocument2 pagesCase Analysis – Sales Force Integration Strategies at FedExDheeraj singhNo ratings yet
- Case 45 Jetblue ValuationDocument12 pagesCase 45 Jetblue Valuationshawnybiha100% (1)
- Audit Market Concentration and Audit Quality of Listed Industrial Firms in NigeriaDocument13 pagesAudit Market Concentration and Audit Quality of Listed Industrial Firms in NigeriaResearch ParkNo ratings yet
- 02 - Biểu Mẫu Hoạch Định Nguồn Nhân Lực - Headcount PlanningDocument1 page02 - Biểu Mẫu Hoạch Định Nguồn Nhân Lực - Headcount PlanningHuyền Anh LêNo ratings yet
- Kantar Millward Brown 5 Principles To Drive Brand Growth PDFDocument8 pagesKantar Millward Brown 5 Principles To Drive Brand Growth PDFDang Do TriNo ratings yet
- Tate & Lyle (Financial Statement Analysis)Document28 pagesTate & Lyle (Financial Statement Analysis)Fion ShimNo ratings yet
- Pro FormaDocument8 pagesPro FormaZhiXNo ratings yet
- ELECTRONICSASSEMBLYPLANTDocument48 pagesELECTRONICSASSEMBLYPLANTTesfaye Degefa100% (1)
- Real Estate Economics: Augusto B. Agosto, Enp, Rea, RebDocument13 pagesReal Estate Economics: Augusto B. Agosto, Enp, Rea, RebAppraiser Philippines100% (4)
- Titan Case StudyDocument42 pagesTitan Case StudyManan Rawal100% (1)
- Current Scenario of Financial ServicesDocument8 pagesCurrent Scenario of Financial Servicessureshsen80% (5)
- Paper12 SolutionDocument21 pagesPaper12 Solutionpunu904632No ratings yet
- Value Chain Definition Model Analysis and ExampleDocument9 pagesValue Chain Definition Model Analysis and ExampleSR-Rain Daniel EspinozaNo ratings yet
- CHP 2 SolDocument17 pagesCHP 2 SolZakiah Abu KasimNo ratings yet
- (I) - All Questions Are Compulsory in Section A - (MCQ) (Ii) - Answer Any Six Questions - Each Carries 5 Marks in Section BDocument4 pages(I) - All Questions Are Compulsory in Section A - (MCQ) (Ii) - Answer Any Six Questions - Each Carries 5 Marks in Section BbharathNo ratings yet
- CZ ChurnopediaGuide 8.5x11 FINALDocument21 pagesCZ ChurnopediaGuide 8.5x11 FINALRevati TilokaniNo ratings yet
- Silver Jewellery ProjectDocument64 pagesSilver Jewellery Projectmadeshmb83% (6)
- Managerial Economics - 2020-22 - RevisedDocument3 pagesManagerial Economics - 2020-22 - RevisedVedant HingeNo ratings yet
- S.N. Questions Multiple Choice Questions 1Document3 pagesS.N. Questions Multiple Choice Questions 1ansh yadavNo ratings yet
- 3 Dec 2018Document54 pages3 Dec 2018siva kNo ratings yet
- Business Development Sales Manager in Colorado Springs CO Resume Rick KlopenstineDocument2 pagesBusiness Development Sales Manager in Colorado Springs CO Resume Rick KlopenstineRick KlopenstineNo ratings yet
- PR Emet 2 PDFDocument2 pagesPR Emet 2 PDFgleniaNo ratings yet
- C CCCCCCCCCCC: CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCDocument13 pagesC CCCCCCCCCCC: CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCNafees AhmedNo ratings yet
- HE DEA: Tariq Aziz Tanzeem IqbalDocument7 pagesHE DEA: Tariq Aziz Tanzeem IqbalShariq Ansari MNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment: II. WorkoutDocument5 pagesGroup Assignment: II. Workoutyohannes lemiNo ratings yet
- Competitiveness and Productivity StrategiesDocument49 pagesCompetitiveness and Productivity Strategiescybell carandangNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations: Business Studies 7115/22 May/June 2017Document12 pagesCambridge International Examinations: Business Studies 7115/22 May/June 2017emiyaNo ratings yet
- What is ADR and GDR - An overviewDocument3 pagesWhat is ADR and GDR - An overviewJonney MarkNo ratings yet
- Incremental Analysis: Relevant Costs and Decision MakingDocument43 pagesIncremental Analysis: Relevant Costs and Decision MakingRosario Diaz100% (2)
- What is B2C eCommerce? Guide to Business-to-Consumer ModelDocument8 pagesWhat is B2C eCommerce? Guide to Business-to-Consumer ModelSantosh Kumar MiriNo ratings yet