Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chap 1 (Repaired)
Uploaded by
karimCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chap 1 (Repaired)
Uploaded by
karimCopyright:
Available Formats
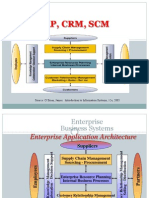
IT CHAP -1
BPM
What is
The achievement of an
organizations objectives
through improvement of
essential business process.
BPM is means to study,
identify, change, modify &
monitor business
processes.
BPM is a structure,
methodology to streamline
business process to
Why BPM
Because of huge
competition it is difficult
to survive without
improving business
processes, customer may
select alternative supplier
Need for
BPM
implementati
Create
long-term
future
Create short-term cost
effectiveness
Initiate continuous
improvement
Introduce a
knowledge of product
Re-engineer the
business
Address the cultural
barriers
Different
levels of BPM
At highest level
At second level
At third level
Operational
business
processes
BPM
principle
Create customer value
Monitor
Improvement to stay in
competition
Information technology
BPA
Proce
Challenges of
Anything that
converts input into
output
Eg: sales, purchase,
accounting, customer
care, logistics etc
BPA
Risk to job
False sense
Transaction layer
Journal
Posting
Unadjusted trial
balance
Adjustment
Adjusted trial
balance
Closing
Sales
Customer
order
Recording
Pick release
Shipping
Invoice
Receipt
Production dept.
Purchase order
Request quote
Quotation
Compare
Invoice
Receipt
Financial
resources
Operation
&Financial planning
Allocation of
monitoring
Report
Impact of IT on
BPM
Allows enterprises to
Risk of
BPA
Job- people may
Record transaction: In
journals
Safeguarding
satisfaction
Cost saving
Competitive edge
devise process centric IT
solutions
Accomplish IT enabled
business process change
Closer business
involvement
Ability to integrate people
& systems
Monitor, control & improve
become jealous
False sense of
security
Challenges
in
implementation
ofInterfaces
BPA with customer is
growing
Product, service and price
options have increased
Budgets
Automation not only
implementing technology,
It is about automating the
business process
New way of working,
monitoring & managing
Purchase
Benefits of
BPA
Customer
A/cing
Basic
Collect & store data
functions
BPM
practices
Appoint owner-
manager
Bonus to
employee
Co-operation
Radical
IT use
Training
Types of
relationship
One to one
One to
many
Many to one
Many to
Automated
Coupling
Free
Cost-savings
Compliances
Business risk of
failure of IT
Top management
Outdated
Gap analysis
Over-engineering
Not flexible
Software failure
Deficient project
Insufficient resources
Inadequatetraining
human resource
management, technology
dept, & infrastructure
Information as a
Business Asset
Major improvements
Comprises of primary &
supportive activities
Primary- inbound,
outbound logistics,
operations, sales &
services
Secondary- procurement,
ERD
Fundamental re-thinking,
and radical re-design of
existing business process
To achieve dramatic
improvement, in critical,
contemporary measures of
performance such as cost,
quality, service, & speed.
Achieve 80-90%
transformation
'Clean slate approach'
Benefits of
BPR
VCA
AI
Stand for entity relationship
diagram
Developed before database
development
To Connect 2 different entities,
Must be available,
accessible service within
organization by
continuous updating the
old database system
useful, digital,
accessible, relevant,
accurate, trustworthy,
searchable,
understandable, &
shareable
Treated as a valuable
commodity
Allow decision-makers to
better an organization's
performance
Decision-making process
can be badly hampered
without effectively
BPR success
factors wide
Organization
commitment
BPR team
composition
Business needs
analysis
Adequate IT
infrastructure
Effective change
management
Approaches
to mapping
system
Entity relationship
Data flow
Systems flow
System outline
Decision tree
Decision table
Parts of
decision-table
Condition stub
Action stub
Condition entries
Action entries
BY- CA SWAPNIL PATNI
You might also like
- CRM Systems - Selection Criteria, Process - ROI - Business CaseDocument29 pagesCRM Systems - Selection Criteria, Process - ROI - Business Caseallen1191919100% (1)
- Cost Reduction and Control Best Practices: The Best Ways for a Financial Manager to Save MoneyFrom EverandCost Reduction and Control Best Practices: The Best Ways for a Financial Manager to Save MoneyNo ratings yet
- Applications of MIS in Manufacturing SectorDocument13 pagesApplications of MIS in Manufacturing SectorPolice station100% (5)
- Customer Relationship Management: Free and Open Source CRM Software For SmesDocument12 pagesCustomer Relationship Management: Free and Open Source CRM Software For Smesfazelabegum07No ratings yet
- Oracle Trade Management (Channel Management) : Information Driven SellingDocument37 pagesOracle Trade Management (Channel Management) : Information Driven SellingChandhu VeluriNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument16 pagesNotesRosalia KatangaNo ratings yet
- Benchmarking Is An Essential Part of TQM For Continuous ImprovementDocument46 pagesBenchmarking Is An Essential Part of TQM For Continuous Improvementwaqasrashid75No ratings yet
- Changes in The Business EnvironmentDocument30 pagesChanges in The Business EnvironmentAbdulmajed Unda MimbantasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Management AccountingDocument28 pagesIntroduction To Management Accountingtj00007No ratings yet
- Oecit802a Ca2Document7 pagesOecit802a Ca2Pratham RaiNo ratings yet
- Sybaf Notes On Information Technology Semester IvDocument102 pagesSybaf Notes On Information Technology Semester Ivlaxmibpandya100% (1)
- Session On CRM in SalesDocument21 pagesSession On CRM in Salesallen1191919No ratings yet
- BPM Case Study-Dell IncDocument44 pagesBPM Case Study-Dell IncVibhore BansalNo ratings yet
- Example Assessment ReportDocument8 pagesExample Assessment ReportlaconicallyNo ratings yet
- BPO Future Forward II PDFDocument52 pagesBPO Future Forward II PDFRichard CrawfordNo ratings yet
- ErpcrmscmDocument31 pagesErpcrmscmYogesh BansalNo ratings yet
- 3-OC&JD Survey-2014 Sales Operation ManagerDocument2 pages3-OC&JD Survey-2014 Sales Operation ManagerANDYLAU1234No ratings yet
- Module 1 NotesDocument8 pagesModule 1 Notesnirmala vimalNo ratings yet
- Strategyand Commercial Excellence ProgramsDocument16 pagesStrategyand Commercial Excellence Programspulsar77No ratings yet
- Implement BPM Storyboard SampleDocument12 pagesImplement BPM Storyboard SampleRahul SasidharanNo ratings yet
- Vice President VP Director Sales Operations in Jacksonville FL Resume Michael TaskerDocument3 pagesVice President VP Director Sales Operations in Jacksonville FL Resume Michael TaskerMichaelTaskerNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document21 pagesLecture 2Vidousha GobinNo ratings yet
- Strategic Sales Management: The World of Selling Must Accommodate A Dramatically Changed World of BuyingDocument31 pagesStrategic Sales Management: The World of Selling Must Accommodate A Dramatically Changed World of Buyingnani66215487No ratings yet
- What Is Business Process Management An In-Depth BPM GuideDocument27 pagesWhat Is Business Process Management An In-Depth BPM GuideJardiel CaquiNo ratings yet
- l4 03 Measuring Purchasing PerformanceDocument150 pagesl4 03 Measuring Purchasing PerformanceMahendra Kumar Soni100% (3)
- Mis Ch3 Introscm, CRM, Erp, BPRDocument22 pagesMis Ch3 Introscm, CRM, Erp, BPRAnna StoychevaNo ratings yet
- Management Information Systems,: Learning Track 3: Primer On Business Process ManagementDocument6 pagesManagement Information Systems,: Learning Track 3: Primer On Business Process Managementmo moNo ratings yet
- L5 03 Improving Supply Chain Performance Integrative UnitDocument156 pagesL5 03 Improving Supply Chain Performance Integrative UnitRitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- A Holistic Approach To BusinessDocument5 pagesA Holistic Approach To BusinessAnuragNo ratings yet
- Business Process Reengineering: CEM 515 For: Dr. Abdulaziz Bubshait By: Hassan Al-BekhitDocument62 pagesBusiness Process Reengineering: CEM 515 For: Dr. Abdulaziz Bubshait By: Hassan Al-BekhitrishimaliNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Assignment 2Document2 pagesWeek 1 - Assignment 2CarlosNo ratings yet
- Value Chain Analysis of BPO IndustryDocument5 pagesValue Chain Analysis of BPO IndustryMark VincentNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Customer Relationship Management System: By-Atul ChaudharyDocument39 pagesPresentation On Customer Relationship Management System: By-Atul Chaudharysalmanali123No ratings yet
- Bpe - Business Processes: Streamlining For SuccessDocument20 pagesBpe - Business Processes: Streamlining For SuccessMANI 96 FFNo ratings yet
- Application of MIS in Manufacturing SectorDocument24 pagesApplication of MIS in Manufacturing SectorNamrata Thakur83% (12)
- Company SystemsDocument17 pagesCompany Systemskarthi KKA-GMNo ratings yet
- Seminar Procurement Strategy Development DubaiDocument10 pagesSeminar Procurement Strategy Development Dubaikhan4luvNo ratings yet
- Making The Case For BPM - A Benefits ChecklistDocument12 pagesMaking The Case For BPM - A Benefits ChecklistrvalentegNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document13 pagesChapter 3Joao NegreirosNo ratings yet
- Presentation ROBINROYDocument19 pagesPresentation ROBINROYAshish ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Information Technology Enabled ServicesDocument14 pagesInformation Technology Enabled ServicesPriyankar SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Bpo DomainDocument41 pagesBpo DomainPritam MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Sales Strategy and CRM: Presented By: Sudhanshu Kumar Jha Sushil Tomar Rohit Roy Animesh Triphati Pawan Priyanka BhistDocument14 pagesSales Strategy and CRM: Presented By: Sudhanshu Kumar Jha Sushil Tomar Rohit Roy Animesh Triphati Pawan Priyanka BhistSushil TomarNo ratings yet
- MIS ReportDocument14 pagesMIS ReportKhushboo JariwalaNo ratings yet
- Business Process and Its ClassificationDocument10 pagesBusiness Process and Its ClassificationJack JillNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis: Internal To The FirmDocument9 pagesSWOT Analysis: Internal To The FirmRatih AflitaNo ratings yet
- Induction Program Learning: Day 1 - Day 5: Presented By: Arnab Kumar Roy 14 May 2012Document8 pagesInduction Program Learning: Day 1 - Day 5: Presented By: Arnab Kumar Roy 14 May 2012arnab4985No ratings yet
- What Drives ERP?Document20 pagesWhat Drives ERP?sunil kumarNo ratings yet
- Bpo ReviewerDocument8 pagesBpo ReviewerKaylaMae ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information Systems Study NotesDocument24 pagesAccounting Information Systems Study NotesAlexander TrovatoNo ratings yet
- NEW Chapter 11 - CRMDocument13 pagesNEW Chapter 11 - CRMamber leeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Advanced MADocument36 pagesIntroduction To Advanced MAvivek1119No ratings yet
- A P F A C E: Utomate Rocesses OR Ompetitive DGEDocument10 pagesA P F A C E: Utomate Rocesses OR Ompetitive DGEhlgc63No ratings yet
- Efficient Processes: New Employee Orientation To QI AwarenessDocument33 pagesEfficient Processes: New Employee Orientation To QI AwarenessJessica NealNo ratings yet
- Business Process ManagementDocument10 pagesBusiness Process ManagementSneha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Business Process EngineeringDocument16 pagesBusiness Process EngineeringleesadzebondeNo ratings yet
- Trends in Management AccountingDocument2 pagesTrends in Management AccountingRishi ShibdatNo ratings yet
- MNGT 8 Chapter 3Document10 pagesMNGT 8 Chapter 3Angel MaghuyopNo ratings yet
- 15802Document3 pages15802topmu2012No ratings yet
- Solution of Linear Systems of Equations in Matlab, Freemat, Octave and Scilab by WWW - Freemat.infoDocument4 pagesSolution of Linear Systems of Equations in Matlab, Freemat, Octave and Scilab by WWW - Freemat.inforodwellheadNo ratings yet
- Verification ofDocument14 pagesVerification ofsamuel-kor-kee-hao-1919No ratings yet
- A Brief Tutorial On Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Sets and SystemsDocument10 pagesA Brief Tutorial On Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Sets and SystemstarekeeeNo ratings yet
- ME Math 8 Q1 0101 PSDocument22 pagesME Math 8 Q1 0101 PSJaypee AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Sequential Circuit Description: Unit 5Document76 pagesSequential Circuit Description: Unit 5ramjidr100% (1)
- CalibrationDocument9 pagesCalibrationLuis Gonzalez100% (1)
- Discussion Lab RefrigerantDocument3 pagesDiscussion Lab RefrigerantBroAmir100% (2)
- Five TemperamentDocument5 pagesFive TemperamentDhaivatPatelNo ratings yet
- E-WasteDocument18 pagesE-WasteNitinKotwarNo ratings yet
- 9th Computer Notes Full BookDocument14 pages9th Computer Notes Full BookKot Abdul Malik High SchoolNo ratings yet
- Forensic Dental TechniquesDocument3 pagesForensic Dental Techniqueschrisr310No ratings yet
- Botbee IntegrationDocument16 pagesBotbee IntegrationAnuj VikalNo ratings yet
- Improving MV Underground Cable Performance - Experience of TNB MalaysiaDocument4 pagesImproving MV Underground Cable Performance - Experience of TNB Malaysialbk50No ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument34 pagesReflection and Refraction of Lightseunnuga93No ratings yet
- No Man Is An Island - Friendship LoyaltyDocument4 pagesNo Man Is An Island - Friendship LoyaltyBryanNo ratings yet
- Color OverlaysDocument2 pagesColor Overlaysapi-366876366No ratings yet
- NOLS 2014 Fall Catalog PDFDocument60 pagesNOLS 2014 Fall Catalog PDFcoldflame81No ratings yet
- Doppler Weather RadarDocument35 pagesDoppler Weather RadarjosefalguerasNo ratings yet
- A Brand Building Literature ReviewDocument17 pagesA Brand Building Literature ReviewUdaya Kumar SNo ratings yet
- An Integrative Review of Relationships Between Discrimination and Asian American HealthDocument9 pagesAn Integrative Review of Relationships Between Discrimination and Asian American HealthAnonymous 9YumpUNo ratings yet
- The Entrepreneurial Spirit From Schumpeter To Steve Jobs - by Joseph BelbrunoDocument6 pagesThe Entrepreneurial Spirit From Schumpeter To Steve Jobs - by Joseph Belbrunoschopniewit100% (1)
- Decision Making Techniques: How To Make Good DecisionsDocument10 pagesDecision Making Techniques: How To Make Good DecisionsParanthaman RamanNo ratings yet
- Sample PREP-31 Standard Sample Preparation Package For Rock and Drill SamplesDocument1 pageSample PREP-31 Standard Sample Preparation Package For Rock and Drill SampleshNo ratings yet
- Effects of Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH) Education On Childhood Intestinal Parasitic Infections in Rural Dembiya, Northwest Ethiopia An Uncontrolled (2019) Zemi PDFDocument8 pagesEffects of Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH) Education On Childhood Intestinal Parasitic Infections in Rural Dembiya, Northwest Ethiopia An Uncontrolled (2019) Zemi PDFKim NichiNo ratings yet
- A Lady of Fashion: Report INVALSIDocument1 pageA Lady of Fashion: Report INVALSINicole BalboNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Physics Sixth Edition: Halliday Resnick WalkerDocument3 pagesFundamentals of Physics Sixth Edition: Halliday Resnick WalkerAhmar KhanNo ratings yet
- The Scientific Method Is An Organized Way of Figuring Something OutDocument1 pageThe Scientific Method Is An Organized Way of Figuring Something OutRick A Middleton JrNo ratings yet
- Arts & Science: Government First Grade College, AlavandiDocument5 pagesArts & Science: Government First Grade College, AlavandiAnonymous cyZVcDeNo ratings yet
- Mexico For Sale. Rafael GuerreroDocument12 pagesMexico For Sale. Rafael GuerreroGabriela Durán ValisNo ratings yet
- EI in NegotiationsDocument22 pagesEI in NegotiationspranajiNo ratings yet
- How to Lead: Wisdom from the World's Greatest CEOs, Founders, and Game ChangersFrom EverandHow to Lead: Wisdom from the World's Greatest CEOs, Founders, and Game ChangersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (95)
- Summary of Noah Kagan's Million Dollar WeekendFrom EverandSummary of Noah Kagan's Million Dollar WeekendRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Summary: The 5AM Club: Own Your Morning. Elevate Your Life. by Robin Sharma: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: The 5AM Club: Own Your Morning. Elevate Your Life. by Robin Sharma: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (22)
- The Millionaire Fastlane: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeFrom EverandThe Millionaire Fastlane: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- How to Talk to Anyone at Work: 72 Little Tricks for Big Success Communicating on the JobFrom EverandHow to Talk to Anyone at Work: 72 Little Tricks for Big Success Communicating on the JobRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (36)
- How to Win Friends and Influence People: Updated For the Next Generation of LeadersFrom EverandHow to Win Friends and Influence People: Updated For the Next Generation of LeadersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (150)
- Summary of Steven Bartlett's The Diary of a CEOFrom EverandSummary of Steven Bartlett's The Diary of a CEORating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Coaching Habit: Say Less, Ask More & Change the Way You Lead ForeverFrom EverandThe Coaching Habit: Say Less, Ask More & Change the Way You Lead ForeverRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (186)
- Leadership and Self-Deception: Getting out of the BoxFrom EverandLeadership and Self-Deception: Getting out of the BoxRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (155)
- Think Remarkable: 9 Paths to Transform Your Life and Make a DifferenceFrom EverandThink Remarkable: 9 Paths to Transform Your Life and Make a DifferenceNo ratings yet
- Optimal: How to Sustain Personal and Organizational Excellence Every DayFrom EverandOptimal: How to Sustain Personal and Organizational Excellence Every DayRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0From EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The First Minute: How to start conversations that get resultsFrom EverandThe First Minute: How to start conversations that get resultsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (57)
- How To Win Friends And Influence PeopleFrom EverandHow To Win Friends And Influence PeopleRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6513)
- Follow The Leader: A Collection Of The Best Lectures On LeadershipFrom EverandFollow The Leader: A Collection Of The Best Lectures On LeadershipRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (122)
- TED Talks: The Official TED Guide to Public SpeakingFrom EverandTED Talks: The Official TED Guide to Public SpeakingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (210)
- The 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleFrom EverandThe 7 Habits of Highly Effective PeopleRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2564)
- Summary of Leaders Eat Last: Why Some Teams Pull Together and Others Don't by Simon SinekFrom EverandSummary of Leaders Eat Last: Why Some Teams Pull Together and Others Don't by Simon SinekRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (142)
- The Catalyst: How to Change Anyone's MindFrom EverandThe Catalyst: How to Change Anyone's MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (273)
- Transformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelFrom EverandTransformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Entreleadership: 20 Years of Practical Business Wisdom from the TrenchesFrom EverandEntreleadership: 20 Years of Practical Business Wisdom from the TrenchesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (186)
- 24 Assets: Create a digital, scalable, valuable and fun business that will thrive in a fast changing worldFrom Everand24 Assets: Create a digital, scalable, valuable and fun business that will thrive in a fast changing worldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (20)
- Spark: How to Lead Yourself and Others to Greater SuccessFrom EverandSpark: How to Lead Yourself and Others to Greater SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (132)
- No Excuses!: The Power of Self-Discipline; 21 Ways to Achieve Lasting Happiness and SuccessFrom EverandNo Excuses!: The Power of Self-Discipline; 21 Ways to Achieve Lasting Happiness and SuccessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (453)
- Transformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelFrom EverandTransformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Brain Rules (Updated and Expanded): 12 Principles for Surviving and Thriving at Work, Home, and SchoolFrom EverandBrain Rules (Updated and Expanded): 12 Principles for Surviving and Thriving at Work, Home, and SchoolRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (702)
- Billion Dollar Lessons: What You Can Learn from the Most Inexcusable Business Failures of the Last Twenty-five YearsFrom EverandBillion Dollar Lessons: What You Can Learn from the Most Inexcusable Business Failures of the Last Twenty-five YearsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (52)
- Cultures of Growth: How the New Science of Mindset Can Transform Individuals, Teams, and OrganizationsFrom EverandCultures of Growth: How the New Science of Mindset Can Transform Individuals, Teams, and OrganizationsNo ratings yet