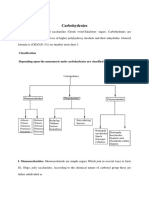
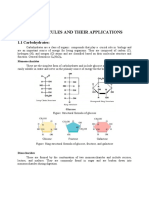
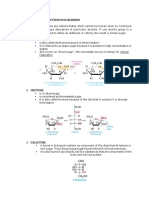
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Glossary
Uploaded by
api-345121761Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Glossary
Uploaded by
api-345121761Copyright:
Available Formats
Diet: the kinds of food that a person, animal, or community habitually eats.
Calorie: the energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water through 1 C,
used to measure food.
Macronutrient:a substance required in relatively large amounts by living organisms, in
particular (Protein, Fats, Carbs, etc.).
Micronutrient: a chemical element or substance required in trace amounts for the
normal growth and development of living organisms.
Daily Value: a guide to the nutrients in one serving of food.
Minerals: certain substances necessary for the maintenance of life and good health.
Nutrients: a substance that provides nourishment essential for growth and the
maintenance of life.
Cholesterol: a steroid alcohol that is present in animal cells and body fluids, regulates
membrane fluidity, and functions as a precursor molecule in various metabolic pathways
and as a constituent of LDL may cause atherosclerosis.
Fiber: dietary material containing substances such as cellulose, lignin, and pectin,
which are resistant to the action of digestive enzymes.
Added Sugar: Added sugars are sugars and syrups that are added to foods or
beverages when they are processed or prepared.
Metabolism: the chemical processes that occur within a living organism in order to
maintain life.
Malnutrition: lack of proper nutrition, caused by not having enough to eat, not eating
enough of the right things, or being unable to use the food that one does eat.
Obesity: the condition of being grossly fat or overweight.
Protein: large molecules composed of one or more long chains of amino acids and are
an essential part of all living organisms, especially as structural components of body
tissues such as muscle, hair, collagen, etc., and as enzymes and antibodies.
Carbohydrates: any of a large group of organic compounds occurring in foods and
living tissues and including sugars, starch, and cellulose.
Saturated Fat:a type of fat containing a high proportion of fatty acid molecules without
double bonds, considered to be less healthy in the diet than unsaturated fat.
Unsaturated Fat: a type of fat containing a high proportion of fatty acid molecules with
at least one double bond, considered to be healthier in the diet than saturated fat.
Trans Fat: An unhealthy substance, also known as trans fatty acid, made through the
chemical process of hydrogenation of oils.
Organic: Relating to or derived from living matter. Fats are organic compounds that are
made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
Whole Grain: Made with or containing whole unprocessed grain.
Fructose: a hexose sugar found especially in honey and fruit.
Folic Acid: a vitamin of the B complex, found especially in leafy green vegetables, liver,
and kidney.
Body Mass Index: a weight-to-height ratio, calculated by dividing one's weight in
kilograms by the square of one's height in meters and used as an indicator of obesity
and underweight.
Pasteurization: a process that kills microbes (mainly bacteria) in food and drink, such
as milk, juice, canned food, and others.
Vitamin A: any of several fat-soluble vitamins (as retinol) found especially in animal
products (as egg yolk, milk, or fish-liver oils) or a mixture of them whose lack in the
animal body causes epithelial tissues to become keratinous (as in the eye with resulting
visual defects)
Vitamin C: a group of water-soluble vitamins that are found especially in yeast, seed
germs, eggs, liver and flesh, and vegetables and that have varied metabolic functions
and include coenzymes and growth factors
Vitamin D: any or all of several fat-soluble vitamins chemically related to steroids,
essential for normal bone and tooth structure, and found especially in fish-liver oils, egg
yolk, and milk or produced by activation (as by ultraviolet irradiation) of sterols.
Calcium: Calcium is the most plentiful mineral found in the human body. The teeth and
bones contain the most calcium.
Basal Metabolic Rate: is the amount of energy expended while at rest in a neutrally
temperate environment, in the postabsorptive state
Omega 3 & 6 Fatty Acids: Essential fatty acids needed that the body does not
produce.
www.dictionary.com
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Lesson Plan Grade 8 - BiomuleculesDocument7 pagesLesson Plan Grade 8 - BiomuleculesRoxanne Reglos67% (3)
- Food ScienceDocument288 pagesFood Scienceمسٹر بلوچNo ratings yet
- The Primal Blueprint With Mark Sisson Slides May13Document19 pagesThe Primal Blueprint With Mark Sisson Slides May13Nimit JindalNo ratings yet
- Practice Quiz Nutrition Answer KeyDocument4 pagesPractice Quiz Nutrition Answer KeyMelbourneSinisinNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Exam Multiple ChoiceDocument8 pagesNutrition Exam Multiple ChoiceSofia Spears Elma100% (6)
- Biomolecule ActivityDocument2 pagesBiomolecule Activitymarife gupaalNo ratings yet
- Applied Spectroscopy ReviewsDocument47 pagesApplied Spectroscopy ReviewsNicholas GravesNo ratings yet
- Revised Chemistry Syllabus - SrinivasDocument9 pagesRevised Chemistry Syllabus - SrinivasMegha Rajesh0% (1)
- Nutrition Intervention - What's AvailableDocument39 pagesNutrition Intervention - What's AvailablesitihawamtNo ratings yet
- FST556 - Dietary Fibre ObeDocument37 pagesFST556 - Dietary Fibre Obeinshirahizham100% (1)
- Konjac FoodsDocument45 pagesKonjac Foodskang_eebNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument12 pagesCarbohydratesDynamic & CannyNo ratings yet
- 100ml Sugar Cane JusDocument5 pages100ml Sugar Cane JusHasna RofikawatiNo ratings yet
- Module 1 NotesDocument31 pagesModule 1 NotesManoj BNo ratings yet
- Biochem Transes 1st TermDocument18 pagesBiochem Transes 1st TermFaye Hashly AfunggolNo ratings yet
- Trans Lecture Intro To BiochemDocument3 pagesTrans Lecture Intro To Biochemlovely coleenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.3 - Rehydration and DehydrationDocument33 pagesChapter 2.3 - Rehydration and DehydrationSyahirah Fazial100% (3)
- Experiment 6 - CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesExperiment 6 - CarbohydratesShaira Dawn PlancoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry 2Document65 pagesClinical Chemistry 2Jennifer BaluarteNo ratings yet
- Test For CarbohydratesDocument15 pagesTest For CarbohydratesKevin SangNo ratings yet
- Biologically Importants of Carbohydrates Students Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesBiologically Importants of Carbohydrates Students Lecture NotesKRISTINE CHAD NAVALES CANTALEJONo ratings yet
- Rosenfelder 2013 - Nutritive Value of Wheat and Wheat By-Products in Pig NutritionDocument19 pagesRosenfelder 2013 - Nutritive Value of Wheat and Wheat By-Products in Pig NutritionMario DavilaNo ratings yet
- Ponemang SuprasegmentalDocument59 pagesPonemang SuprasegmentalLemz LemzNo ratings yet
- Macronutrients PPT 1416heDocument47 pagesMacronutrients PPT 1416heMA. DOMINIQUE CLORESNo ratings yet
- Nutri-Quiz Bee 2019: Ama Computer College-LipaDocument31 pagesNutri-Quiz Bee 2019: Ama Computer College-LipaJP RoxasNo ratings yet
- Diet and Dental Caries - ReenaDocument118 pagesDiet and Dental Caries - ReenaReenaChauhanNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Module 1Document178 pagesGen Bio Module 1Ritney Jean AgpalasinNo ratings yet
- Biological Macromolecules: Learning Activity Sheet in Physical ScienceDocument9 pagesBiological Macromolecules: Learning Activity Sheet in Physical ScienceVitamae BrazalNo ratings yet
- 18btc101j Biochem-Unit 1Document134 pages18btc101j Biochem-Unit 1nikteshgNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Biology Genetic Modification & MicroorganismDocument7 pagesUnit 6 Biology Genetic Modification & MicroorganismWendyNo ratings yet