Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fluid Deficit
Uploaded by
VanessaMUellerOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fluid Deficit
Uploaded by
VanessaMUellerCopyright:
Available Formats
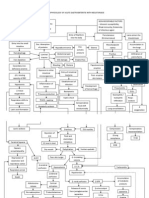
Fluid/Electrolyte Imbalance
S/S
Nursing Care
S&S: Weight, turgor, dry skin,
Fluid Deficit
Hypovolemia: Proportional loss
of extracellular fluid (ECF) and
electrolytes
Dehydration: Loss of H2O only with
Na related to N&V, diarrhea, GI
suction, sweating, fluid intake,
diuretics, adrenal insufficiency
Fluid Excess
ECF volume due to heart or renal
failure, cirrhosis, Na, excess IV
fluids, albumin, aldosterone
secretion
Syndrome of inappropriate
antidiuretic hormone (SIADH):
ADH
water retention and Na due to
disorders of CNS and lungs,
infections and malignant tumors
Hypokalemia
Potassium (K_) _3.5mEq/L; due to
vomiting, diarrhea, gastric suction,
diuretics, corticosteroids, diabetic
ketoacidosis (osmotic diuresis),
starvation; hypokalemia risk
of digoxin toxicity
Hyperkalemia
weak and cramping muscles,
thirst, oliguria, postural BP, T,
P, Hct, BUN, specific gravity
Nursing: Monitor S&S, po fluids,
isotonic/hypotonic IV fluids as
ordered, prn antiemetics or
antidiarrheals
S&S: T, P, and BP; edema,
ascites,
crackles, jugular vein distention,
HCT, BUN
Nursing: Monitor S&S; teach Na
diet, fluid restriction, and Na
content of OTC meds; diuretics and
potassium supplements if ordered
S&S: Muscle weakness, fatigue,
N&V, GI motility, reflexes,
abdominal distention,
dysrhythmias, elevated U wave
and flattened T wave on ECG
Nursing: Assess S&S, teach about
foods high in K_ (melon, apricots,
bananas, milk, meat, citrus,
grains). Give ordered po/IV K_
supplements
You might also like
- Wound Care PDFDocument100 pagesWound Care PDFVanessaMUeller100% (2)
- Nurse Brain Sheet With Shift HoursDocument2 pagesNurse Brain Sheet With Shift HoursLauren Cournoyer Foreman100% (4)
- Nurse Brain Sheet Telemetry Unit SBARDocument1 pageNurse Brain Sheet Telemetry Unit SBARvsosa624No ratings yet
- Diagnostic TestsDocument3 pagesDiagnostic Testsapi-251516913100% (1)
- Fluid Electrolyte Imbalance NvertedDocument111 pagesFluid Electrolyte Imbalance Nvertedchitrakshi khairnarNo ratings yet
- Nurse Brain Sheet Half SizeDocument1 pageNurse Brain Sheet Half Sizevsosa624No ratings yet
- Lab Values Chart GuideDocument5 pagesLab Values Chart GuideVanessaMUeller100% (3)
- Fluid Electrolyte Imbalance n132 160210135651Document100 pagesFluid Electrolyte Imbalance n132 160210135651Shahan FarooqNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte ImbalancesDocument8 pagesElectrolyte Imbalancesdonna mae junioNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes & FluidimbalancesDocument80 pagesElectrolytes & FluidimbalancesDennis Nyambane MomanyiNo ratings yet
- Newborn Assessment NORMALDocument2 pagesNewborn Assessment NORMALVanessaMUellerNo ratings yet
- Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone (Siadh) : Reported by Jo Jo AleDocument9 pagesSyndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone (Siadh) : Reported by Jo Jo Ale8hg100% (3)
- Fluid Electrolyte Balances and ImbalanceDocument157 pagesFluid Electrolyte Balances and ImbalanceManisha Shakya0% (1)
- COPD Care PLAN PDFDocument2 pagesCOPD Care PLAN PDFVanessaMUeller100% (1)
- Comprehensive Head To Toe Assessment PDFDocument22 pagesComprehensive Head To Toe Assessment PDFVanessaMUellerNo ratings yet
- RBC Disorder Guide: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument56 pagesRBC Disorder Guide: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentMunawar Adhar100% (4)
- Alcohol Withdrawal Care PlanDocument1 pageAlcohol Withdrawal Care PlanVanessaMUeller100% (1)
- Alteration in Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument118 pagesAlteration in Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceRenuga SureshNo ratings yet
- KMU Blood DisorderDocument43 pagesKMU Blood DisorderSHAFIQNo ratings yet
- CKDDocument3 pagesCKDMarc Lawrence Balderas CAra100% (1)
- Doctor's Visit Takes A Funny TurnDocument106 pagesDoctor's Visit Takes A Funny TurnaahadNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi & Penatalaksanaan Gagal Ginjal KronikDocument34 pagesPatofisiologi & Penatalaksanaan Gagal Ginjal KronikAvenaAthaliaNo ratings yet
- Equine Fluid TherapyFrom EverandEquine Fluid TherapyC. Langdon FieldingNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances Part 2Document47 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Imbalances Part 2Abinaya RanganathanNo ratings yet
- Mabes Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancesDocument15 pagesMabes Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancesMabesNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Anestesi Pada Uremic SyndromeDocument27 pagesManajemen Anestesi Pada Uremic SyndromeAdi Nugroho MelyanaNo ratings yet
- Alternative NamesDocument67 pagesAlternative NamespashaNo ratings yet
- Mia Treatment Guidelines 2007Document39 pagesMia Treatment Guidelines 2007楊將群No ratings yet
- Electrolytes Slide 21Document111 pagesElectrolytes Slide 21Elaisha Mae C. CarsulaNo ratings yet
- Prescribing Safely - Analgesia, Antimicrobials and Fluids During Cardiac Failure, Renal Failure and Hepatic Failure States by Oliver Ki Kek YeeDocument27 pagesPrescribing Safely - Analgesia, Antimicrobials and Fluids During Cardiac Failure, Renal Failure and Hepatic Failure States by Oliver Ki Kek YeeoliverkisteamNo ratings yet
- Anesthetic Concerns For The Patient With Renal and Hepatic DiseaseDocument43 pagesAnesthetic Concerns For The Patient With Renal and Hepatic Diseasekamel6No ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesChronic Renal FailureJashine DajayNo ratings yet
- Dehydratio and HyperhydrationDocument30 pagesDehydratio and Hyperhydrationparichaya wongsaNo ratings yet
- Water and Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument50 pagesWater and Electrolyte ImbalanceFarhah RahimanNo ratings yet
- Fluid and electrolyte disturbances: an overviewDocument47 pagesFluid and electrolyte disturbances: an overviewanne claire feudoNo ratings yet
- Approach To AnemiaDocument33 pagesApproach To AnemiaVaibhav KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Acute Renal FailureDocument57 pagesLecture - Acute Renal FailureJames StiltonNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure Pathophysiology, Stages, Complications & ManagementDocument18 pagesAcute Renal Failure Pathophysiology, Stages, Complications & ManagementSteven Paul DaclesNo ratings yet
- Causes, Signs, and Treatment of HyponatremiaDocument65 pagesCauses, Signs, and Treatment of HyponatremiaFaryalBalochNo ratings yet
- 2 DiureticsDocument23 pages2 DiureticsAudrey Beatrice ReyesNo ratings yet
- Sodium Imbalances Main Cation & Primary Determinant of ECF Osmolality (Na+ Is ECF) : p.325Document3 pagesSodium Imbalances Main Cation & Primary Determinant of ECF Osmolality (Na+ Is ECF) : p.325lmonesNo ratings yet
- Sodium: L.V. Rao, PHDDocument2 pagesSodium: L.V. Rao, PHDAbhilash ReddyNo ratings yet
- Systemic Effects of Diarrhea and DehydrationDocument1 pageSystemic Effects of Diarrhea and DehydrationNaseer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument20 pagesAcute Renal FailureRufus RajNo ratings yet
- Anemia Report1Document2 pagesAnemia Report1Yhan-yhan Rodriguez KhouNo ratings yet
- DR Ankit Soni DNB Trainee (Peds)Document28 pagesDR Ankit Soni DNB Trainee (Peds)Ankit SoniNo ratings yet
- Edema: Pathophysiology and Clinical ApproachDocument25 pagesEdema: Pathophysiology and Clinical ApproachPooja ShashidharanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument13 pagesFluid Electrolyte Imbalancepreet kaurNo ratings yet
- Independent Work Topic: AnemiaDocument23 pagesIndependent Work Topic: AnemiaFizzahNo ratings yet
- Co DiovanDocument2 pagesCo DiovanianecunarNo ratings yet
- Isotonic Saline (0.9%Nacl-Normal Saline) IndicationDocument3 pagesIsotonic Saline (0.9%Nacl-Normal Saline) IndicationJared AllenNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Abnormalities in The Hospitalized PatientDocument70 pagesElectrolyte Abnormalities in The Hospitalized PatientClaudiaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic tests reveal anemia and electrolyte abnormalities in acute renal failureDocument1 pageDiagnostic tests reveal anemia and electrolyte abnormalities in acute renal failureGrace DonatoNo ratings yet
- Hypoosmolar imbalance signs, causes and managementDocument2 pagesHypoosmolar imbalance signs, causes and managementAngel Joy CatalanNo ratings yet
- AnemiasDocument13 pagesAnemiasKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Gastroenteritis, Dehydration, and NecatoriasisDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Gastroenteritis, Dehydration, and NecatoriasisRalph Delos Santos100% (2)
- Differential Diagnosis ChartDocument2 pagesDifferential Diagnosis Chartaxmedfare138No ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure Causes, Progression, Complications and ManagementDocument37 pagesChronic Renal Failure Causes, Progression, Complications and ManagementsivaNo ratings yet
- Anemia Nursing Care Plan: Presented by Edi Purwanto School of Nursing University of Muhammadiyah MalangDocument26 pagesAnemia Nursing Care Plan: Presented by Edi Purwanto School of Nursing University of Muhammadiyah MalangSevina Eka ChannelNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument67 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentpashaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 CKDDocument53 pagesLecture 3 CKDPharmswipe KenyaNo ratings yet
- SodiumDocument5 pagesSodiumTepperoniNo ratings yet
- CKD PDFDocument26 pagesCKD PDFNogra CarlNo ratings yet
- Edema: Dr. Binyameen ChishtyDocument25 pagesEdema: Dr. Binyameen ChishtyFarhan MustafaNo ratings yet
- Water An Electrolyte Metabolism and Their DisordersDocument60 pagesWater An Electrolyte Metabolism and Their DisordersAbigail AdegbuluNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Withdrawal Care PlanDocument1 pageAlcohol Withdrawal Care PlanVanessaMUellerNo ratings yet
- Updated Clinical SheetDocument1 pageUpdated Clinical SheetVanessaMUellerNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment ChartDocument1 pagePhysical Assessment ChartVanessaMUellerNo ratings yet
- Fluid/Electrolyte Imbalance S/S Nursing Care Fluid DeficitDocument1 pageFluid/Electrolyte Imbalance S/S Nursing Care Fluid DeficitVanessaMUellerNo ratings yet
- Penuemonia Care PalnDocument2 pagesPenuemonia Care PalnVanessaMUellerNo ratings yet
- Name Age Room Code Dr. Isolation Activity Diet Allergy: DX: HXDocument1 pageName Age Room Code Dr. Isolation Activity Diet Allergy: DX: HXVanessaMUellerNo ratings yet
- AdmimDocument2 pagesAdmimVanessaMUellerNo ratings yet
- ManagmentDocument1 pageManagmentVanessaMUellerNo ratings yet
- Example 1 - Focus: Nausea Related To AnestheticDocument1 pageExample 1 - Focus: Nausea Related To AnestheticVanessaMUellerNo ratings yet
- Admission Database PDFDocument6 pagesAdmission Database PDFVanessaMUellerNo ratings yet
- Diseases With Dermatologic ManifestationsDocument1 pageDiseases With Dermatologic ManifestationsVanessaMUellerNo ratings yet
- (Chapter 3) : Cell BiologyDocument80 pages(Chapter 3) : Cell BiologyVanessaMUellerNo ratings yet
- AssessingWounds ProcedureDocument3 pagesAssessingWounds ProcedureVanessaMUellerNo ratings yet
- IV PushDocument3 pagesIV PushVanessaMUeller100% (1)
- Clinical AssessementDocument2 pagesClinical AssessementVanessaMUellerNo ratings yet
- Example 1 - Focus: Nausea Related To AnestheticDocument1 pageExample 1 - Focus: Nausea Related To AnestheticVanessaMUellerNo ratings yet
- Medication Guide with Side Effects and UsesDocument10 pagesMedication Guide with Side Effects and UsesVanessaMUellerNo ratings yet
- Wound Care PDFDocument100 pagesWound Care PDFVanessaMUellerNo ratings yet
- Nurse Brain Sheet Half SizeDocument1 pageNurse Brain Sheet Half SizeRobyn GrogitskyNo ratings yet
- HR Ocampo Danilo s2 E10 PDFDocument4 pagesHR Ocampo Danilo s2 E10 PDFVanessaMUellerNo ratings yet