Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Los Tiempos Gramaticales en Ingles
Uploaded by
Ana Belén Torres RuizCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Los Tiempos Gramaticales en Ingles
Uploaded by
Ana Belén Torres RuizCopyright:
Available Formats
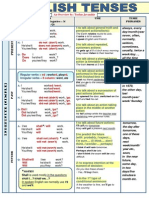
TENSES
FORMS
(Affirmative - A/Negative - N
Question - Q)
A: I
work.
works.
work.
PRESENT
He/she/it
You/we/they
N: I
do not (dont) work.
He/she/it
does not (doesnt) work_.
You/we/they do not (dont) work.
Q: Do
Does
Do
I
work?
he/she/it
work_?
you/we/they work?
USE
TIME
PHRASES
1-to talk about general truth and
permanent actions(facts):
always, every
day/month/year
The Earth rotates round its axis.
never, often,
It rains a lot in autumn.
I speak English and French.
normally,
seldom,
2-to talk about repeated,
sometimes,
customary actions:
He gets up at 8 oclock every morning. usually, twice a
They never listen to their teacher.
week/day,
all the time
3-to talk about a planned future
action (a timetable or schedule )
The train leaves at 3 tomorrow.
PAST
A: I
worked /went.
worked/went.
worked/went .
He/she/it
You/we/they
N: I
did not (didnt) work_/go.
He/she/it
did not (didnt) work_/go.
You/we/they did not (didnt) work_/go.
Q: Did I
Did he/she/it
Did you/we/they
work_/go?
work_/go?
work_/go?
I met my friend yesterday.
Did you go to the seaside last
summer?
2-to talk about a succession of
past actions (stories):
He opened the door, switched on the
light and fed his cat.
A: I/we
He/she/it
You/they
N: I/we
He/she/it
You/they
Q: Shall/will
Will
Will
shall*
*/ will
will
will
work.
work.
work.
shall not (shant) * work
will not (wont)
work.
will not (wont) work.
will not (wont) work.
I/we
he/she/it
you/they
work?
work?
work?
*NOTE!!!
Shall is used mostly in the questions
shall I?/shall we?
In spoken English we normally use Ill
and well.
yesterday, 2
minutes/hours/
days/years
ago,
in 1970,
the other day,
last
month/year/
week/ Sunday
3- to talk about an action taking
place in the middle of another
action:
He fell asleep while the teacher was
explaining new grammar rules.
1-to talk about future actions:
FUTURE
INDEFINITE (SIMPLE)
Regular verbs + ed : worked, played,
Irregular verbs II column: went, ate
1-to talk about actions
performed in the past
(with finished time expressions):
Ill call you tomorrow.
Mary will get a present next month.
2-to predict the future
(with probably, I expect...,
I'm sure..., (I) think..., don't
think, I wonder..., perhaps)
I think it will rain tomorrow.
Perhaps she'll be late.
I don't think the exam will be very
difficult.
3- to express intention at the
moment of decision:
Do you like these shoes?
- Yes, I'll buy them.
4-in the 1st type of
conditional sentences
If the weather is fine, well go to
the country.
tomorrow,
the day after
tomorrow,
one of these
days,
next
week/month/
year etc.,
soon,
in the near
future,
some day,
in two
days/five
minutes/a
month etc.
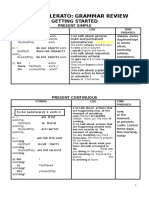
TENSES
FORMS
(Affirmative - A/Negative - N
Question - Q)
to be (am/is/are) + verb + -ing
PRESENT
A: I
He/she/is
You/we/they
N: I
am not (Im not) working.
is not (isnt)
working.
He/she/it
You/we/they/ are not (arent) working.
Q: Am
I
he/she/we
you/we/they
Is
Are
working?
working?
working?
to be(was/were) + verb + -ing
PAST
A: I
He/she/it
You/we/they
was
was
were
working.
working.
working.
N: I
was not (wasnt) working.
He/she/it
was not (wasnt) working.
You/we/they were not (werent) working.
Q: Was
I
he/she/it
you/we/they
Was
Were
working?
working?
working?
shall/will + be + verb +-ing
A: I/we
He/she/it
You/they
N: I/we
FUTURE
CONTINUOUS (progressive)
am (Im) working.
is (hes) working.
are (were) working.
shall*
*/will be working.
will
be working.
will
be working.
shall not (shant) *be working.
will not (wont)
be working.
He/she/it will not (wont)
You/they will not (wont)
Q: Shall/will
Will
Will
be working.
be working.
I/we
be working?
he/she/it be working?
you/they be working?
*NOTE!!!
Shall is used mostly in the questions shall
I?/shall we?
In spoken English we normally use Ill and
well.
USE
1-to talk about actions that are
happening now, at the moment of
speaking:
Look! The boys are playing football. Hurry
up! The train is coming.
2- to talk about actions that are
happening around now, but not
exactly at the moment of speaking:
We are studying very hard these days.
We have to prepare for our exams.
3-to speak about what you have
already arranged to do:
-What are you doing on Saturday?
-I am meeting my friend at the station.
She is arriving at 8 pm.
1-to talk about a temporary action
taking place at a given moment in the
past:
What were you doing at 6 oclock
yesterday?
2-two or more actions happening at
the same time in the past:
She was cooking dinner and her kids
were watching TV.
3- action interrupted by another
shorter action in the past:
I was working on computer when the
telephone rang.
4- background information in a story:
The sun was shining and the birds
were singing
1- to talk about an action at a
particular moment in the future.
The action will start before that
moment but it will not have
finished at that moment:
I will be playing tennis at 10am
tomorrow.
This time on Sunday I'll be bathing in
the sea.
When you arrive, he will be waiting for
you.
TIME
PHRASES
now,
at the
moment,
at present;
Look!,
Listen!
these days,
this
morning,
today
at 6 oclock
yesterday,
from 3 to 6
On Monday,
when Mum
came, while
at 5 oclock
tomorrow,
this time on
Sunday,
when I
come
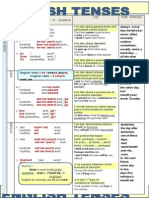
TENSES
FORMS
(Affirmative - A/Negative - N
Question - Q)
USE
TIME
PHRASES
-is always connected with the
have/has +participle II
- regular verbs +ed
worked, asked
-irregular verbs-III column gone, eaten
PRESENT
A: I/we/you/they have
He/she/it
has
worked/gone.
worked/gone.
N: I/we/you/they have not (havent) worked/gone.
He/she/it
has not (hasnt)
worked/gone.
Q: Have
Has
I/we/you/they
he/she/it
worked/gone?
worked/gone?
already, ever,
just, never,
not yet, so
far, till now,
up to now , of
late, lately,
recently; with
for and
since; with
This is the
2-questions in the Present Perfect
first time
never start with when:
this morning/
When did you see this film?
evening,
3-with this morning/evening, today
today, this
this week, this year (when the time
periods are not finished at the time week, this
year
of speaking):
present and the only thing which
matters here is the result: the time
when the action took place is of no
importance:
I have lost my keys. I cant open the
door.
1-to talk about a completed action
connected with the present:
I have seen this film and I can
discuss it with you now.
PAST
had +participle II
- regular verbs +ed :
worked, asked
-irregular verbs-III column: gone, eaten
A: I/you/we/they had
He/she/it
had
worked/gone.
worked/gone.
N: I/we/you/we/they had not (hadnt) worked/gone.
He/she it
had not (hadnt) worked/gone.
Q: Had
Had
I/you/we/they
he/she/it
worked/gone?
worked/gone?
shall/will + have +participle II
shall*
*/will have worked/gone.
will
have worked/gone.
will
have worked/gone.
A: I/we
FUTURE
perfect
Have you called you mother today?
He/she/it
You/they
N: I/we
shall not (shant) * have worked/gone.
will not (wont)
He/she/it will not (wont)
You/they will not (wont)
Q: Shall/will
Will
Will
I/we
he/she/it
you/they
have worked/gone.
have worked/gone?
have worked/gone?
have worked/gone?
1-denotes an action completed
before a certain moment in the
past; it is not used to denote a
succession of actions (Past
Simple):
She has already finished her work
when he came.
But: When I wrote the letter, I
posted it.(Past Simple
succession of actions)
By the time the police arrived ,he had
already disappeared.
2-with the
conjunctions(hardly/scarcely/
nearly/barely + when)
I had hardly done it when they
came.
No sooner had they arrived than it
started to rain.
when I
entered, by 5
oclock
yesterday,
(with the
same
adverbs as
Present
Perfect but in
the past
context); no
soonerthan
1-denotes an action completed
before a definite moment in the
future:
She will have finished this work by
2 oclock tomorrow.
The film will have already started
by the time we come .Hurry up!
by this time
tomorrow, by
2 oclock
tomorrow,
when you
come back
*NOTE!!!
Shall is used mostly in the
questions shall I?/shall we?
In spoken English we normally use
Ill and well.
TENSES
FORMS
(Affirmative - A/Negative - N
Question - Q)
have/has + been + verb + -ing
PRESENT
A: I we/you/they have been working.
He/she/it
has been working.
N: I/we/you/they have not (havent) been working.
He/she/it
has not (hasnt)
been working.
Q: Have
Has
I/we/you/they
he/she/it
been working?
been working?
USE
TIME
PHRASES
1-to say how long things have been
continuing up to now:
Ive been learning English for six
years.
Its been raining all day.
for, since;
How
long?
2-to say how we have been filling
our time (up to now)
-Your hands are dirty.
-Ive been painting the walls.
NOTE!!! We dont use Present
Perfect Cont. with be, know ,
have and other non-progressive
verbs:
PAST
had + been + verb + -ing
A: I /we/you/they
He/she/it
had been working.
had been working.
N: I/we/you/they
He/she/it
had not (hadnt) been working.
had not (hadnt) been working.
Q: Had
Had
I/we/you/they been working?
he/she/it
been working?
shall/will + have + been+ verb + -ing
A: I/we
He/she/it
You/they
N: I/we
FUTURE
Perfect continuous
How long have you had your
car? (Present Perfect)
shall/will * have been working.
will
have been working.
will
have been working.
shall not (shant)*
*
will not (wont)
have been working.
He/she/it will not (wont) have been working.
You/they will not (wont) have been working.
Q: Shall/will
Will
Will
I/we
he/she/it
you/they
have been working?
have been working?
have been working?
*NOTE!!!
Shall is used mostly in the questions
shall I?/shall we?
In spoken English we normally use Ill
and well.
1-denotes an action which began
before a definite moment in the
past, continued up to that moment
and was still going on at the
moment:
We could not go out because it had
been raining for two hours.
2-denotes an action which was no
longer going on at a definite
moment in the past, but which had
been in progress not long before:
The babys face was red and wet. He
had been crying.
since, for
1-denotes an action which will begin
before a definite moment in the
future, will continue up to the
moment and will be going on at that
moment:
You will have been waiting for more
than two hours when her plane finally
arrives.
In the fall I will have been studying
here for 2 years.
He will be tired when he arrives. He
will have been travelling for 24
hours.
for
You might also like
- English TensesDocument4 pagesEnglish TensesNicoleta Rotaru100% (2)
- Prepositions in English RulesDocument8 pagesPrepositions in English Rulesnilvemangesh100% (1)
- Grammar BookDocument119 pagesGrammar BookBetsabe Tejada100% (3)
- English Grammar Pre Form One CourseDocument54 pagesEnglish Grammar Pre Form One CourseInvo Makyao100% (3)
- 16 TensesDocument1 page16 TensesSyafiq Alan NaufaNo ratings yet
- Simple Present QuestionsDocument2 pagesSimple Present QuestionsPontevedro English CentreNo ratings yet
- Opposites and prefixes suffixesDocument26 pagesOpposites and prefixes suffixeskoolketan16No ratings yet
- English tenses at a glance: a complex testDocument4 pagesEnglish tenses at a glance: a complex testjohnkehoe211630No ratings yet
- English Past Perfect and Present Perfect 1Document6 pagesEnglish Past Perfect and Present Perfect 1Osama Hayder100% (1)
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument8 pagesGerunds and Infinitiveskumaar1980100% (1)
- English Tense SystemDocument25 pagesEnglish Tense SystemMOhammad ZOhaib100% (10)
- + Gerund: Will, Going ToDocument7 pages+ Gerund: Will, Going ToTeresa De Jesús Juárez GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Regular Verbs ListDocument7 pagesRegular Verbs ListYolandaNo ratings yet
- English Grammar SecretsDocument72 pagesEnglish Grammar SecretsEskender Ahmed87% (15)
- Use Examples: Modals in English Grammar 1. CanDocument5 pagesUse Examples: Modals in English Grammar 1. Canangelito peraNo ratings yet
- Grammar o Comparative Adjectives: Look Like Tobe LikeDocument8 pagesGrammar o Comparative Adjectives: Look Like Tobe LikeLuis Nguyen HaNo ratings yet
- 100 Golden Grammar RulesDocument29 pages100 Golden Grammar RulesTimcsa82100% (2)
- Learn Prepositions "On," "At," and "InDocument3 pagesLearn Prepositions "On," "At," and "IneylulozgeNo ratings yet
- Gang Swarm Flight Troupe Troop Collection Team Flock Bunch/combDocument2 pagesGang Swarm Flight Troupe Troop Collection Team Flock Bunch/combnur_ainzatiNo ratings yet
- O o o O: English TensesDocument6 pagesO o o O: English Tensesamaro.sandra3996No ratings yet
- Tenses FormulaDocument1 pageTenses Formularrusmita75% (4)
- Complete English Tenses PDF Chart DownloadDocument3 pagesComplete English Tenses PDF Chart DownloadSumit Thakur79% (58)
- Presentation On TensesDocument10 pagesPresentation On TensesKarthick Raj100% (2)
- Present Perfect Continuous TenseDocument14 pagesPresent Perfect Continuous Tenseshuga3100% (2)
- Namma Kalvi General English Grammar Study MaterialDocument9 pagesNamma Kalvi General English Grammar Study MaterialdeviNo ratings yet
- The Present Perfect With Ever' and Never'Document9 pagesThe Present Perfect With Ever' and Never'Yaina Ivanova100% (1)
- English TensesDocument3 pagesEnglish TensesIbrahim Elmogy50% (10)
- Gerund & InfinitiveDocument26 pagesGerund & InfinitiveAnnisa nur fadilla0% (1)
- Verb To Be: Person State Permanent Temporary Quality State JobDocument4 pagesVerb To Be: Person State Permanent Temporary Quality State JobViviana MuñozNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH TENSES TIMELINE CHART & ActivitiesDocument15 pagesENGLISH TENSES TIMELINE CHART & ActivitiesLola Mento100% (1)
- English Grammar Topics List PDF Free Download PDF HunterDocument4 pagesEnglish Grammar Topics List PDF Free Download PDF HunterRamin ShamsNo ratings yet
- BasicsentenceDocument61 pagesBasicsentenceOkan EmanetNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Mod 3Document8 pagesEnglish Grammar Mod 3chetanmadhupNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Revision - Questions, Auxiliary Verbs, Compound AdjectivesDocument2 pagesLesson Plan - Revision - Questions, Auxiliary Verbs, Compound AdjectivesSorin FluturNo ratings yet
- BBC Forming QuestionsDocument4 pagesBBC Forming QuestionsfakelookNo ratings yet
- 16 TensesDocument18 pages16 TensesAnonymous eCws3ENo ratings yet
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument39 pagesSubject Verb Agreementapi-3742089100% (1)
- English Grammar TensesDocument35 pagesEnglish Grammar Tensespolisetti_sudhakarNo ratings yet
- Using unless, as long as, and provided to express conditionsDocument8 pagesUsing unless, as long as, and provided to express conditionsOmar Ruben Garcia AragonNo ratings yet
- 100 Golden Grammar RulesDocument12 pages100 Golden Grammar RulesShy Do88% (8)
- Infinitive and The GerundDocument8 pagesInfinitive and The GerundSergoSanikidze100% (2)
- 4,000 Useful Adverbs In English: Types, Comparison and Formation of AdverbsFrom Everand4,000 Useful Adverbs In English: Types, Comparison and Formation of AdverbsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Words That Act as Multiple Parts of Speech (PART 1): Types of WordsFrom EverandWords That Act as Multiple Parts of Speech (PART 1): Types of WordsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- How to Use the Word “Make” In English: A Comprehensive Guide to the Word “Make”From EverandHow to Use the Word “Make” In English: A Comprehensive Guide to the Word “Make”No ratings yet
- TENSES FORMS USE TIME PHRASESDocument4 pagesTENSES FORMS USE TIME PHRASESshashik1007730100% (1)
- English TensesDocument4 pagesEnglish TensesToofanNo ratings yet
- Work, Play, Went, Ate: Regular Verbs Irregular VerbsDocument4 pagesWork, Play, Went, Ate: Regular Verbs Irregular VerbsGosia MrówkaNo ratings yet
- Mixed Tenses PDFDocument4 pagesMixed Tenses PDFJoe Benegas50% (2)
- Grammar Theory 2nd BachDocument26 pagesGrammar Theory 2nd Bachjrb7590No ratings yet
- All Tenses ChartDocument4 pagesAll Tenses ChartKaren Andrade100% (2)
- Grammar Theory 1st BachDocument23 pagesGrammar Theory 1st Bachjrb7590No ratings yet
- Forms (Affirmative - A/Negative - N Question - Q) USE Time PhrasesDocument4 pagesForms (Affirmative - A/Negative - N Question - Q) USE Time PhrasesSyairah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect & Cont H2 - 9Document5 pagesPresent Perfect & Cont H2 - 9Stefan Andrei Lupu100% (1)
- C2 The Perfect Aspect. The Continuous Aspect.: PRESENT PERFECT SIMPLE (Have / Has + Past Participle)Document4 pagesC2 The Perfect Aspect. The Continuous Aspect.: PRESENT PERFECT SIMPLE (Have / Has + Past Participle)Patricia GonzalezNo ratings yet
- TENSES Ingles 3rd ESODocument4 pagesTENSES Ingles 3rd ESOM. Eulalia Montero GarcíaNo ratings yet
- OmniaDocument20 pagesOmniaOmnia ElgendyNo ratings yet
- Flash ShortcutDocument15 pagesFlash Shortcutelasu850% (1)
- Mahishasura PartDocument2 pagesMahishasura Partelasu85No ratings yet
- Smoothly Animate A Caricature Using Motion TweensDocument54 pagesSmoothly Animate A Caricature Using Motion Tweenselasu85No ratings yet
- GemFire ArchitectureDocument72 pagesGemFire Architectureelasu85No ratings yet
- WWW - Tmv.edu - in PDF Distance Education BCA Books BCA III SEM BCA-324 Communication SkillsDocument116 pagesWWW - Tmv.edu - in PDF Distance Education BCA Books BCA III SEM BCA-324 Communication Skillsilakkikarthi100% (2)
- Introduction To Electronics and Breadboarding Circuits-Fair Use BuildingDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Electronics and Breadboarding Circuits-Fair Use Buildingelasu85No ratings yet
- Professional SkillDocument334 pagesProfessional SkillSubodh RoyNo ratings yet
- English Grammar TensesDocument38 pagesEnglish Grammar Tensesapi-283719185No ratings yet
- Ch01 PPT SlidesDocument20 pagesCh01 PPT Slideselasu85No ratings yet
- Essential English Tenses GuideDocument5 pagesEssential English Tenses Guideelasu85100% (1)
- Technical Communication in a Global ProjectDocument20 pagesTechnical Communication in a Global Projectmithu11100% (1)
- English Grammar TensesDocument38 pagesEnglish Grammar Tensesapi-283719185No ratings yet
- South AsiaDocument2 pagesSouth Asiaelasu85No ratings yet
- Essential English Tenses GuideDocument5 pagesEssential English Tenses Guideelasu85100% (1)
- TNPSC Aptitude Tamil For HANDWRITINGDocument20 pagesTNPSC Aptitude Tamil For HANDWRITINGelasu85No ratings yet
- South West Pacific: Supermarine Spitfire VIII in The Markings ofDocument2 pagesSouth West Pacific: Supermarine Spitfire VIII in The Markings ofelasu85No ratings yet
- Introduction To Basic ElectronicswDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Basic Electronicswapi-317835274No ratings yet
- South West Pacific: Supermarine Spitfire VIII in The Markings ofDocument2 pagesSouth West Pacific: Supermarine Spitfire VIII in The Markings ofelasu85No ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Planckian locus in CIE chromaticity diagramDocument2 pagesPlanckian locus in CIE chromaticity diagramelasu85No ratings yet
- South AsiaDocument2 pagesSouth Asiaelasu85No ratings yet
- Ombat SupportDocument1 pageOmbat Supportelasu85No ratings yet
- Italian Cobelligerent Air ForceDocument1 pageItalian Cobelligerent Air Forceelasu85No ratings yet
- Late PhotoDocument2 pagesLate Photoelasu85No ratings yet
- NormandyDocument2 pagesNormandyelasu85No ratings yet
- September 1944 To May 1945Document2 pagesSeptember 1944 To May 1945elasu85No ratings yet
- Early Photo-Reconnaissance Spitfires: HauptmannDocument1 pageEarly Photo-Reconnaissance Spitfires: Hauptmannelasu85No ratings yet
- Pitfire Spotters: United States Navy Royal NavyDocument1 pagePitfire Spotters: United States Navy Royal Navyelasu85No ratings yet
- Supermarine Spitfire Second World War Battle of Britain J.E. "Johnnie" JohnsonDocument1 pageSupermarine Spitfire Second World War Battle of Britain J.E. "Johnnie" Johnsonelasu85No ratings yet