Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Energy Processing in Plants
Uploaded by
api-327567606Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Energy Processing in Plants
Uploaded by
api-327567606Copyright:
Available Formats
Energy Processing in Plants
(Text Pages 419-432)
A. Materials for Plant Processes
1. To survive, plants need food, water, and oxygen.
2. Roots absorb water, which travels inside xylem cells to all parts of the plant.
3. Most plants make their own food--a liquid called sugar, which flows to all plant
cells.
4. Plants require oxygen and carbon dioxide to make food.
B. Photosynthesis
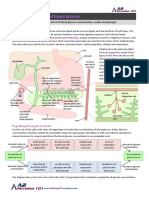
1. Photosynthesis is a series of chemical reactions that convert light energy, water,
carbon dioxide into the food-energy molecule glucose and give off oxygen.
2. Leaves are the major food-producing organs of plants.
3. The cells that make up the top and bottom layers of a leaf of leaf are flat,
irregular shaped cells called epidermal cells.
4. On the bottom epidermal layer of leaves are small openings called stomata.
5. Mesophyll cells contain the organelle where photosynthesis occurs, the
chloroplasts.
6. In the first step of photosynthesis, plants capture the energy in light.
7. Chemicals that can absorb and reflect light are called pigments.
8. The pigment chlorophyll reflects green light, absorbs other colors of light, and
uses this energy for photosynthesis.
9. During photosynthesis, water molecules are split apart, releasing oxygen into the
atmosphere.
10. Sugars are made in the second step of photosynthesis.
11. Photosynthesis is important because it produces most of the oxygen in the
atmosphere.
C. Cellular Respiration
1. Cellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that convert the energy
in food molecules into a usable form of energy called ATP.
2. During cellular respiration, food molecules are broken down into smaller
amounts, called ATP molecules.
3. Cellular respiration is important to plants because without it they could not
grow, reproduce, or repair tissue.
4. The products, or end substances, of photosynthesis are oxygen and the
energy-rich molecule glucose.
5. Most plants, some protists, and some bacteria carry on photosynthesis.
6. Cellular respiration requires the reactants glucose and oxygen, produces
carbon dioxide and water, and releases energy in the form of ATP.
7. Life on Earth depends on a balance of photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
D. Stimuli and Plant Responses
1. Stimuli are any changes in an environment that cause organisms to respond.
2. When stimulated by an insect's touch, the two sides of a Venus flytrap snap
shut immediately, trapping the insect inside.
E. Environmental Stimuli
1. Plants responses to different environmental stimuli include light, touch, and
gravity.
2. The growth of a plant toward or away from light is called tropism.
a. Leaves and stems tend to grow in the direction of light.
b. Roots generally grow away from light.
3. The response of a plant to gravity is called gravitropism.
F. Humans and Plant Responses
1. Humans make plants more productive using plant hormones.
You might also like
- Phet Contribution 4110 7478Document2 pagesPhet Contribution 4110 7478Charley Ray TaylorNo ratings yet
- Evolution Vocab ChartDocument8 pagesEvolution Vocab ChartsarfarazNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Diffusion Lab-1Document7 pagesOsmosis Diffusion Lab-1api-1658690000% (1)
- 5.1 Communities and Ecosystems: Topic 5: Ecology & EvolutionDocument20 pages5.1 Communities and Ecosystems: Topic 5: Ecology & EvolutionMorgan LockeNo ratings yet
- The Transport System IB Qq'sDocument12 pagesThe Transport System IB Qq'sJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Leaf StructureDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis: Leaf StructureMonica Sario PolicinaNo ratings yet
- Starter: - in The Back of Your Books - Think of A Job A Person Might Do - What Do They Need To Do Their Job Properly?Document22 pagesStarter: - in The Back of Your Books - Think of A Job A Person Might Do - What Do They Need To Do Their Job Properly?Kelvin RequenaNo ratings yet
- Water Cycle WebquestDocument6 pagesWater Cycle Webquestapi-330037580100% (1)
- Cell Organelles Review ActivityDocument5 pagesCell Organelles Review ActivityAngelica PantaleonNo ratings yet
- Packet Unit 1Document36 pagesPacket Unit 1Amelia Simmons0% (1)
- 2.2.5 Respiration WorksheetDocument7 pages2.2.5 Respiration WorksheeterikabeltranNo ratings yet
- Water Cycle Y5Document28 pagesWater Cycle Y5Menaga Ilangkovan100% (1)
- Unit 3 Chemical Reaction Case StudyDocument3 pagesUnit 3 Chemical Reaction Case Studyapi-3299014180% (1)
- Unit 6 & 7 Cell EnergyDocument17 pagesUnit 6 & 7 Cell EnergyRut ChristineNo ratings yet
- Copy of Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableDocument2 pagesCopy of Atomic Structure and The Periodic Tableapi-347844143No ratings yet
- The Atmosphere and Living Things Worksheet AnswersDocument18 pagesThe Atmosphere and Living Things Worksheet Answers2E (9) HON MARITA JANENo ratings yet
- 6.3 Particle ModelDocument23 pages6.3 Particle ModelFloNo ratings yet
- 7 Science NCERT Chapter 1 PDFDocument10 pages7 Science NCERT Chapter 1 PDFDebashis MallickNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Review PacketDocument17 pagesChapter 11 Review PacketLalisampt.20% (1)
- Characteristics of Life Long TestDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of Life Long TestMichelle Ramirez Co-GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Circulatory Lesson PlansDocument4 pagesCirculatory Lesson Plansapi-281424654No ratings yet
- HS Student Handout Conservation Energy NGSS (Conservation of Energy at The Skate Park)Document10 pagesHS Student Handout Conservation Energy NGSS (Conservation of Energy at The Skate Park)Alex DatsiukNo ratings yet
- Quiz, Quiz, Trade Atom and Periodic TableDocument5 pagesQuiz, Quiz, Trade Atom and Periodic TablefatraxiiNo ratings yet
- Specialised CellsDocument9 pagesSpecialised CellsJanah Pauline AbunganNo ratings yet
- 2016 BIOLOGY EOC Study Guide ANSWER KEY and Content Focus PDFDocument9 pages2016 BIOLOGY EOC Study Guide ANSWER KEY and Content Focus PDFMelisa Anne CanilangNo ratings yet
- Butterfly Life Cycle Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesButterfly Life Cycle Lesson PlanPeter GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Chem Study Guide Answer KeyDocument4 pagesChem Study Guide Answer Keyapi-240689882100% (1)
- Chemical Reactions and Enzymes 2Document26 pagesChemical Reactions and Enzymes 2api-240096234100% (1)
- Corkscrew Swamp Field Trip ReportDocument7 pagesCorkscrew Swamp Field Trip ReportKarolina Terra100% (1)
- New World International School Biology Igcse Notes Chapter - 1Document15 pagesNew World International School Biology Igcse Notes Chapter - 1Noor Samir100% (1)
- Final Exam Study Guide 7th Grade Life Science 2014Document3 pagesFinal Exam Study Guide 7th Grade Life Science 2014api-249710831No ratings yet
- Writing Balanced Chemical EquationsDocument3 pagesWriting Balanced Chemical EquationsDamian YeoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To RespirationDocument14 pagesIntroduction To RespirationAzneezal Ar-RashidNo ratings yet
- The Photosynthesis 2 Step - KEYDocument2 pagesThe Photosynthesis 2 Step - KEYinkheartkatNo ratings yet
- Chapter Resource Files Editable Classifying MatterDocument19 pagesChapter Resource Files Editable Classifying MatterRifaya Nazrin100% (1)
- Grade 10 Chemistry Final Exam Review SheetDocument3 pagesGrade 10 Chemistry Final Exam Review SheetAshleyNo ratings yet
- Process of Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesProcess of Cellular RespirationAlliah Vance O. CapuzNo ratings yet
- Bioaccumulation Lesson ScruggsDocument8 pagesBioaccumulation Lesson Scruggsapi-282053052No ratings yet
- Adi Lab 7 - Periodic TrendsDocument3 pagesAdi Lab 7 - Periodic Trendsapi-313496561No ratings yet
- Science 10 Long Range Plans 2017 RebeccaDocument4 pagesScience 10 Long Range Plans 2017 Rebeccaapi-307356982No ratings yet
- States of Matter Solid, Liquid, Gas, and Plasma. Solids LiquidsDocument6 pagesStates of Matter Solid, Liquid, Gas, and Plasma. Solids LiquidsWaleedSubhanNo ratings yet
- 9aa Environmental Variation VLE V3Document32 pages9aa Environmental Variation VLE V3syztqNo ratings yet
- Catalase Lab ActivityDocument6 pagesCatalase Lab Activitysenja fitrianaNo ratings yet
- Science Lesson Plan: REFERENCES (Exclude Class Text Include Page Numbers)Document4 pagesScience Lesson Plan: REFERENCES (Exclude Class Text Include Page Numbers)Darren AtwarooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 AnswersDocument10 pagesChapter 9 Answersosama50% (2)
- Origin and Structure of The EarthDocument5 pagesOrigin and Structure of The EarthGrace RabinaNo ratings yet
- SciFusTX Grade7 U03L04 PowerNoteDocument14 pagesSciFusTX Grade7 U03L04 PowerNoteEsther SaraviaNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical ChangesDocument7 pagesPhysical and Chemical Changesapi-609988460No ratings yet
- Animal Phylum Project ModDocument3 pagesAnimal Phylum Project ModlilyhcyNo ratings yet
- Integrated ScienceDocument6 pagesIntegrated Scienceiteachclassroom100% (2)
- 8 Isotopes-SDocument5 pages8 Isotopes-Sgracie100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Cells-1Document3 pagesLesson Plan Cells-1api-371640211No ratings yet
- Cell Unit Biology TestDocument6 pagesCell Unit Biology TestBiologyhelper Person0% (1)
- Topic 9 Plant Biology IB Biology 9.2 Transport in The Phloem of Plants Nature of Science: Developments in Scientific Research Follow Improvements in Apparatus: ExperimentalDocument4 pagesTopic 9 Plant Biology IB Biology 9.2 Transport in The Phloem of Plants Nature of Science: Developments in Scientific Research Follow Improvements in Apparatus: ExperimentalMoahmed Mahmoud IB15A 363KAGYNo ratings yet
- Practical MYP 4 Speed of SoundDocument6 pagesPractical MYP 4 Speed of SoundPrasanna PatilNo ratings yet
- Rainforest Deforestation Student WorksheetDocument9 pagesRainforest Deforestation Student WorksheetAlejandro Posada PenagosNo ratings yet
- Drug AwarnessDocument13 pagesDrug Awarnessapi-327567606No ratings yet
- 8th Grade Science ReviewDocument2 pages8th Grade Science Reviewapi-327567606No ratings yet
- 8th Grade Science ReviewDocument5 pages8th Grade Science Reviewapi-327567606No ratings yet
- The Solar SystemDocument2 pagesThe Solar Systemapi-327567606No ratings yet
- Nuclear Fission V FusionDocument8 pagesNuclear Fission V Fusionapi-327567606No ratings yet
- Vocab 13Document11 pagesVocab 13api-327567606No ratings yet
- Space Exploration Vocab 15Document11 pagesSpace Exploration Vocab 15api-327567606No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Vocab11Document11 pagesPhotosynthesis Vocab11api-327567606No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument13 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respirationapi-327567606No ratings yet
- EarthsmotionDocument2 pagesEarthsmotionapi-327567606No ratings yet
- Vocab 7Document12 pagesVocab 7api-327567606No ratings yet
- EarthsmoonDocument2 pagesEarthsmoonapi-327567606No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Chemical Bonding Vocab 10Document12 pagesUnit 3 Chemical Bonding Vocab 10api-327567606No ratings yet
- Vocab 9 Chemical ReactionsDocument11 pagesVocab 9 Chemical Reactionsapi-327567606No ratings yet
- Compounds Chemical Formulas and Covalent BondsDocument2 pagesCompounds Chemical Formulas and Covalent Bondsapi-3275676060% (1)
- Acids and BasesDocument9 pagesAcids and Basesapi-327567606No ratings yet
- Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument2 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactionsapi-327567606No ratings yet
- Science Vocab 6Document20 pagesScience Vocab 6api-327567606No ratings yet
- Introduction To Circulatory SystemDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Circulatory SystemPrisha ChhedaNo ratings yet
- Pulse Oximetry: Understanding Its Basic Principles Facilitates Appreciation of Its LimitationsDocument11 pagesPulse Oximetry: Understanding Its Basic Principles Facilitates Appreciation of Its LimitationsParadox PraveenNo ratings yet
- Physical Changes With AgingDocument53 pagesPhysical Changes With AgingRohit SejwalNo ratings yet
- Stroke: Dr. Fidha Rahmayani, M.SC, SP.S Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Lampung RS Abdul MulukDocument45 pagesStroke: Dr. Fidha Rahmayani, M.SC, SP.S Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Lampung RS Abdul Mulukdhea nadhiaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy ExamDocument4 pagesCardiovascular and Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy ExamReg LagartejaNo ratings yet
- High Acuity Exam 1 Study Guide - 2Document12 pagesHigh Acuity Exam 1 Study Guide - 2Angelica WilliamsNo ratings yet
- ACLS AHA Guidelines 2006 PosterDocument1 pageACLS AHA Guidelines 2006 PosterJeane SuyantoNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Insufficiency.Document54 pagesOxygen Insufficiency.Josephine George JojoNo ratings yet
- Early Total Care To Early Appropriate Care What.2Document8 pagesEarly Total Care To Early Appropriate Care What.2ChrisNo ratings yet
- 1st Lec On Heart Physiology by Dr. RoomiDocument13 pages1st Lec On Heart Physiology by Dr. RoomiMudassar Roomi100% (1)
- HeartDocument11 pagesHeartKei GauranoNo ratings yet
- University of Patanjali: Haridwar, UttarakhandDocument11 pagesUniversity of Patanjali: Haridwar, UttarakhandAbhimanyu RanaNo ratings yet
- Levin (1993) - Drowning and Near Drowning (Klasifikasi Tenggelam)Document16 pagesLevin (1993) - Drowning and Near Drowning (Klasifikasi Tenggelam)Filbert TandeanNo ratings yet
- G1 - Final Case Study - Anaphylaxis - BSN 3106Document43 pagesG1 - Final Case Study - Anaphylaxis - BSN 3106Dj Gwyn MandigmaNo ratings yet
- 1 6 Regulation of Blood Glucose PDFDocument3 pages1 6 Regulation of Blood Glucose PDFtiaraNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 3rd QuarterDocument7 pagesScience Reviewer 3rd QuarterLyrMa NCNo ratings yet
- Diagno With Class QuizDocument306 pagesDiagno With Class Quizrabeca johnsonNo ratings yet
- 03 Cardiopulmonary PhysiologyDocument17 pages03 Cardiopulmonary Physiologyice cream1000791100% (1)
- Manual Oximetro Choicemed EspañolDocument2 pagesManual Oximetro Choicemed Españolgcamila.102No ratings yet
- Session 11: Heart FailureDocument41 pagesSession 11: Heart FailureRayan MziriNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Pain: Methodical Manual For StudentsDocument71 pagesPhysiology of Pain: Methodical Manual For StudentsMelnic CristinaNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan For Sem 1Document17 pagesUnit Plan For Sem 1MRS CHAKRAPANI100% (10)
- Manajemen Cairan Dan Elektrolit Pada PmebedahanDocument34 pagesManajemen Cairan Dan Elektrolit Pada PmebedahanZaniaNo ratings yet
- A&P Coloring Workbook - The Urinary System PDFDocument19 pagesA&P Coloring Workbook - The Urinary System PDFYuhNo ratings yet
- Hope - 3 Grade 12: Energy Systems Quarter 1 Week 1 Module 1Document15 pagesHope - 3 Grade 12: Energy Systems Quarter 1 Week 1 Module 1Alvin Sinel Belejerdo100% (3)
- What Is A Heart AttackDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Heart AttackMaya Sari HalimNo ratings yet
- Mayasthenia Gravis NclexDocument47 pagesMayasthenia Gravis NclexKrishna SapkotaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical VentilationDocument37 pagesMechanical Ventilationmzapanta_2No ratings yet
- Edexcel IAL Biology October 2021 Unit 5 Question PaperDocument36 pagesEdexcel IAL Biology October 2021 Unit 5 Question PaperEffendi Jabid Kamal100% (1)
- Biomedical Instrumentation (BM8502)Document34 pagesBiomedical Instrumentation (BM8502)1011 BMENo ratings yet