Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Student Sci Pro 4
Uploaded by
roh009Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Student Sci Pro 4
Uploaded by
roh009Copyright:
Available Formats
Society for Science & the Public - Page
and landfills. It was later found to migrate through the subsurface, contaminate groundwater systems, and persist for decades after initial disposal. Today, there
are approximately 202 hazardous waste sites in the U.S. containing 20 million tons of this dangerous compound. Biotic transformation of CT has been
demonstrated with cell exudates (biomolecules) of Methanosarcina thermophila, a methanogenic microorganism. These biomolecules have been found to
contain iron and zinc. In an effort to optimize and determine the most efficient and cost-effective method of CT degradation, the current research hypothesizes
that supplementing increased concentrations of iron and zinc in the growth medium of this methanogen will result in increased production of the biomolecules,
thereby resulting in higher rates of CT degradation. Pure cultures of the microorganisms were grown in the presence of 4 variables (high & low concentrations
of both iron and zinc), and the growth medium was filtered to obtain the biomolecules once the organisms were at stationary phase. CT was then added to this
filtrate, and the degradation of CT was measured using gas chromatography. Comparison (in triplicates) of the concentrations of CT in the liquid cultures, with
and without the metals over 7 time periods, indicated that the presence of high iron, low iron, high zinc, and low zinc increased the rate of degradation of CT by
49.4%, 14.1%, 231.0% and 52.2% respectively. ANOVA and t-tests indicated that the data was significant for P< 0.01. The hypothesis was, therefore,
supported. It is estimated that this process will reduce the cleanup costs of CT by almost $3 million.<br><br>
Awards won at the 2003 ISEF
Second Award of $1,500 - Microbiology - Presented by Intel Foundation
2003 - MI008
CHARACTERIZATION OF THE SECRETED ASPARTIC PROTEINASES OF CANDIDA ALBICANS USING A NOVEL COMBINATORIAL APPROACH
Jamie Elyce Rubin
Canterbury School, Fort Myers, FL, USA
Candida is a dimorphic fungus that is responsible for a wide variety of mycotic infections. The secreted aspartic proteinases (Saps) are among the organisms
putative virulence factors, and inhibition of these enzymes has been shown to have a curative effect upon candidiasis. In this study chromogenic combinatorial
libraries of octapeptides were used to investigate the extended substrate interactions of Sap1 and Sap2 of Candida albicans, the most common cause of
candidiasis in humans. This novel technique revealed a key difference between the preference of these enzymes and the preferences of human aspartic
proteinases, a characteristic that could be exploited to design effective inhibitors of Sap activity. Additionally, existing aspartic proteinase inhibitors were tested
against these enzymes to demonstrate the feasibility of targeted inhibition of Sap activity. These data were used to construct peptidomimetic inhibitors that
demonstrated marked inhibition of Sap activity and no interaction with human enzymes.
Awards won at the 2003 ISEF
Award of $500 U.S. Savings Bond - Ashtavadhani Vidwan Ambati Subbaraya Chetty (AVASC) Foundation
Second Award of $1,500 - Microbiology - Presented by Intel Foundation
Second Awards of $1,500 - U.S. Air Force
2003 - MI009
THE EFFECT OF X-RADIATION (X-RAYS) ON BACILLUS SUBTILIS
Anthony Michael Barnett
McDonaugh High School, LaPlata, Maryland USA
Research was performed to determine the effect of X-Radiation (X-Ray) exposure on observable and testable characteristics of Bacillus subtilis. With a
sufficient exposure, X-Rays are known to have a lethal affect on bacteria, and this has a potential application as a method to control pathogenic organisms
(such as Bacillus anthracis). This research was conducted to better understand how X-Rays affect Bacillus subtilis, which was selected due to its close
relationship to the anthrax bacillus. This research observed cellular functions at varying levels of low-dose, 70 kilovolts pressure (kVP), X-Rays using a dental
X-Ray machine. Easily observable (testable) characteristics were observed, before and after X-Ray exposure, including sugar metabolism (dextrose and
mannitol), cellular motility, catalase production, spore production, and colony morphology after X-Ray exposures ranging from 120 seconds up to 360 seconds.
This experiment showed that exposure to a non-lethal X-Ray dose has a significant affect on individual bacterial cell motility by direct observation (wet mount)
immediately after X-Ray exposure. It is also noted that X-Rays affect motility in subsequent generations based on testing in motility media. In addition, this
experiment noted that spores were produced by both the control (no X-Ray exposure) and by all of the cultures exposed to the various doses of X-Rays.
However, the spore count data suggests that the higher X-Ray doses appear to stimulate or accelerate spore production. Further research is needed to
determine the mechanism of the X-Ray effect on motility and to verify and explore the effect X-Rays on the spore generation process.
2003 - MI010
BACTERIAL BREAKDOWN
Hattie Bluestone Smith, Charlottesville High School
Charlottesville, Virginia (United States)
I sought to determine the effectiveness of different microorganisms (psychrophiles, mesophiles, and thermophiles) in decomposing a carbon-based compost
heap. I researched the conditions of a compost heap, the way the decomposition process works, and the three main categories of bacteria that help this
process. I found that in a compost heap the type of bacteria that is decomposing the organic matter is determined by the temperature of the heap.
Thermophiles are activated to decompose at 95 to 160 degrees F, Mesophiles are activated to decompose at 68 to 90 degrees F, and Psychrophiles are
activated to decompose at 55 to 62 degrees F. Therefore, I could isolate the work of a single type of bacteria by controlling the temperature of its compost
heap. I put a mixture of paper, wood shavings, and microbes into three compost bins. To control the temperatures of the bins, I used different amounts of
insulation. Then, to accommodate the climactic demands of a compost heap, I continuously pumped in water vapor. For three weeks I took temperature
file:///C/Users/SheilaKing/Documents/Abstracts/Society%20for%20Science%20&%20the%20Public%20-%20Microbiology.html[8/23/2015 6:38:15 PM]
Society for Science & the Public - Page
readings and made observations. After three weeks, I found that the bin with Psychrophiles at work looked similar to the original mixture, the bin with
Thermophiles at work had many parts of rich brown compost, and the bin with Mesophiles at work had some of each. I concluded that Thermophiles are the
most effective at composting a carbon-based compost heap, while Psychrophiles are the least effective.
2003 - MI011
DEVELOPMENT OF AN IMPROVED ENTEROVIRUS DETECTION PROTOCOL FOR TOMATOES: A SECOND YEAR STUDY
Hannah Mary Kaufman
Newberry High School, Newberry, Florida, United States of America
The purpose of this project was to test the effectiveness of Polyethyleneimine (PEI) on enumeration and recovery of viruses from produce and the effectiveness
of chlorine dioxide on decontamination of seeded tomatoes.<br><br>MA104 (ATCC #CRL-2378) monolayer cells were tested. Pre-filtered viruses were
procured from sewage wastewater. Rotavirus was also used. Ten tomato stem scars were inoculated with 0.1 mL of viral solution. After drying for one hour,
select tomatoes were subjected to 10 ppm chlorine dioxide treatment. An activated chlorine dioxide pouch and three tomatoes were covered with a container
and incubated for 15, 30, 60, or 120 minutes. For the aqueous treatments the pouch was activated and immersed in distilled water for one hour; tomatoes were
submerged into the solution for one minute, then briefly into a solution of 0.001% sodium thiosulfate in distilled water. The stem scars were placed in 50 mL
tubes with 20 mL Phosphate Buffered Saline and shaken for 15 minutes. Pre-Treatment with PEI and a Standard Method of cell culturing was then tested.
Three mL of .004% PEI was added to flasks for Pre-Treatment. After ten minutes, three mL of the produce/viral solution was placed into all flasks. One hour
later 10 mL of 2% medium was added. They were incubated at 370 Celsius and checked every 72 hours for cytopathic effect development. <br><br>The
hypothesis that Polyethyleneimine would enhance the susceptibility of tissue cell culture to enterovirus infection and that chlorine dioxide would effectively
decontaminate seeded tomatoes, proved to be correct.<br><br>
Awards won at the 2003 ISEF
First Award of $1,000 - Institute of Food Technologists
2003 - MI012
XYLELLA FASTIDIOSA GENETIC ANALYSES PROVIDE HOST-RANGE INSIGHTS
Mary Melissa Gardner
Spalding High School, Griffin, Georgia, United States
Preliminary data from the 2002 science fair project showed that AFLP molecular markers could be used to differentiate among host-specific Xylella fastidiosa
strains. But, without population genetic analyses of the raw molecular dataset, there was no way to determine gene flow patterns, genetic partitioning or to gain
insight into infection patterns that could be vector-specific and environment-specific. To determine if Xylella fastidiosa is geographically biased based on hostspecificity, a new research project was created to accomplish the overall goal, which is to master population genetics computer software analyses that can be
applied to many types of molecular datasets and which will facilitate continued research on Pierces disease. Data read from the ABI 377 automated sequencer
were reconstructed using a computer program that turned the dye-specific bands into a gel image that was straightened and sized. Three population genetics
programs were then used to analyze these data based on population genetics concepts and assumptions. The purpose of this study was to test the hypothesis
that population genetic analyses of host-specific Xylella fastidiosa strains will not demonstrate similarities across geography or host range to include systemic
(causing symptoms) and nonsystemic (symptomless) hosts. After evaluating the phylogeny, genetic identity and genetic distance resulting from analyses of the
molecular dataset, the original hypothesis was rejected in favor of an alternative hypothesis that population genetic analyses of host-specific Xylella fastidiosa
demonstrates similarities across geography as well as host range. The results also provided insight into nonsystematic hosts for vector acquisition of the
bacterium.<br><br>
Awards won at the 2003 ISEF
Fourth Award of $500 - Microbiology - Presented by Intel Foundation
2003 - MI013
A STUDY OF QUORUM SENSING ACITIVITY IN E. COLI (JM101) AFTER LACZ TRANSFORMATION
Caitlin Hannah Walls
South Pemiscot High School, Steele, Missouri,
Bacteria utilize a low molecular weight chemical belonging to the N-oxo-acylhomoserine Lactone (HSL) family for communication by quorum sensing. In this
project HSL production was observed in E. coli with the aid of a reporter strain modified with a LacZ reporter gene. The reporter strain produces bgalactosidase in response to exogenous HSL generated by the test organism. This production was measured quantitatively by using the lactose analog ONPG
(o-nitrophenyl-galactopyranoside) in a spectrophotometric assay. E. coli JM101 lacks both the amp and lacZ genes. A plasmid, pBLU, containing the genes for
lacZ and ampicillin was used to transform the E. coli JM101. Transformants were isolated on selective media, which contained LB/Amp/X-gal. The transformed
bacteria grew in blue colonies illustrating the uptake of the pBLU plasmid. Transformed bacteria with the reporter gene were used as the test organism.
Cultures of transformed bacteria, (-) lacZ bacteria and + lacZ bacteria were grown for 24 hours. Cell free extracts were taken every 4 hours for 4, 8, 12,16,20,
and 24-hour samples. Cell free extracts were combined with a fresh culture of transformed bacteria for 30 minutes. B-galactosidase enzyme activity was
assayed with ONPG substrate in a spectrophotometer at 420nm for 5 minutes. Optical Density of the culture was measured at 600nm. Specific activity of the
enzyme was calculated and compared to a control sample of transformer bacteria for each cell free extract sample collected over the 24-hour period. Results
indicate an increase in specific enzyme activity through the 8-hour extracts for each group tested. This corresponds to the maximum growth of the E. coli and
maximum cell density reached at 8 hours of growth.
file:///C/Users/SheilaKing/Documents/Abstracts/Society%20for%20Science%20&%20the%20Public%20-%20Microbiology.html[8/23/2015 6:38:15 PM]
You might also like
- Bmri2015 814529Document2 pagesBmri2015 814529Karen Yomara Vera ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Review Note On The Application of Metagenomics in Emerging Aquaculture Systems and Aquatic Animal Health ManagementDocument8 pagesReview Note On The Application of Metagenomics in Emerging Aquaculture Systems and Aquatic Animal Health ManagementEditor IJIRMFNo ratings yet
- Microbial Cell Disruption Methods For Efficient Release of Enzyme L AsparaginaseDocument12 pagesMicrobial Cell Disruption Methods For Efficient Release of Enzyme L AsparaginaseAdauto AlvesNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Cultural Conditions For The Production of Antifungal Chitinase by Streptomyces SporovirgulisDocument7 pagesOptimization of Cultural Conditions For The Production of Antifungal Chitinase by Streptomyces SporovirgulisDella AzzuraNo ratings yet
- Biology Methods and General Paper: B. Sc. Degree Examinations 2010Document4 pagesBiology Methods and General Paper: B. Sc. Degree Examinations 2010gggtdyfhuuoNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Bacteria From Soil ThesisDocument8 pagesIsolation of Bacteria From Soil Thesisgj3vfex5100% (2)
- Isolation and Identification of Bacteria ThesisDocument7 pagesIsolation and Identification of Bacteria Thesisafbtbegxe100% (2)
- Phylogenetically Diverse Acetaldehyde-Degrading Bacterial Community Deep Sea Water West Pacific OceanDocument11 pagesPhylogenetically Diverse Acetaldehyde-Degrading Bacterial Community Deep Sea Water West Pacific OceanAndrea EscobarNo ratings yet
- Coptisine OnDocument9 pagesCoptisine OnKRimminalNo ratings yet
- 2023 Gorman High Throughput DNA Extraction PlateDocument9 pages2023 Gorman High Throughput DNA Extraction PlateCamila GamboaNo ratings yet
- Natural Products Chemistry & ResearchDocument4 pagesNatural Products Chemistry & ResearchBella DonnaNo ratings yet
- Herrero Concepcion 2012 Flow Cytometric Physiological Alterations Herbicide MicroalgaeDocument19 pagesHerrero Concepcion 2012 Flow Cytometric Physiological Alterations Herbicide MicroalgaeBrigita de BrillarNo ratings yet
- Art 109Document6 pagesArt 109Yayan NurkasanahNo ratings yet
- DermatosisDocument8 pagesDermatosisDⒶrk OtⒶkuNo ratings yet
- 2018 Mendoza MoralesetalDocument9 pages2018 Mendoza Moralesetallucia mendozaNo ratings yet
- OcillatoriaDocument3 pagesOcillatoriaAlexis ImperioNo ratings yet
- Rife Royal Raymond - History of The Development of A Successful Treatment For Cancer and Other Virus, Bacteria and FungiDocument8 pagesRife Royal Raymond - History of The Development of A Successful Treatment For Cancer and Other Virus, Bacteria and Fungitiennos100% (2)
- Alpha Mangostin - Analisis LarvicidalDocument10 pagesAlpha Mangostin - Analisis LarvicidalDesy M WenasNo ratings yet
- Micronuclei Assessment in Buccal Cells of People Environmentally Exposed To Arsenic in Northern ChileDocument9 pagesMicronuclei Assessment in Buccal Cells of People Environmentally Exposed To Arsenic in Northern ChileRuth AlcarazNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity # 1 MICROBIOLOGYDocument4 pagesLaboratory Activity # 1 MICROBIOLOGYatvillasNo ratings yet
- Field Evaluation Against Aedes Aegypti Larvae of Aluminum-Carboxymethylcellulose-Encapsulated Spore-Toxin Complex Formulation of Bacillus Thuringien...Document8 pagesField Evaluation Against Aedes Aegypti Larvae of Aluminum-Carboxymethylcellulose-Encapsulated Spore-Toxin Complex Formulation of Bacillus Thuringien...Nguyễn Thị Hoài ThươngNo ratings yet
- SBB 2101Document234 pagesSBB 2101sharammaNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Activity of Novel Strains of Bacteriophages: An Experimental ApproachDocument12 pagesAntibacterial Activity of Novel Strains of Bacteriophages: An Experimental ApproachM. Imran QadirNo ratings yet
- Gonzles Ramrez2016Document14 pagesGonzles Ramrez2016Paula GeorgianaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Environmental MicrobiologyDocument7 pagesResearch Paper On Environmental Microbiologywwvmdfvkg100% (1)
- DocumentDocument10 pagesDocumentJayNo ratings yet
- Al Holy2006 PDFDocument12 pagesAl Holy2006 PDFCarlos LopesNo ratings yet
- Ultraviolet Disinfection With A Novel Microwave-Powered DeviceDocument9 pagesUltraviolet Disinfection With A Novel Microwave-Powered Devicebarby17_2005No ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Activity of Antibiotic Pro PDFDocument5 pagesAntimicrobial Activity of Antibiotic Pro PDFFIRDA TRYANANo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Activity of Antibiotic ProDocument5 pagesAntimicrobial Activity of Antibiotic ProFIRDA TRYANANo ratings yet
- EnumerationandidentificationofentericandpseudomonadDocument15 pagesEnumerationandidentificationofentericandpseudomonadHafsaAliNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms: Disinfectant, Soap or Probiotic Cleaning? Surface Microbiome Diversity and Biofilm Competitive ExclusionDocument19 pagesMicroorganisms: Disinfectant, Soap or Probiotic Cleaning? Surface Microbiome Diversity and Biofilm Competitive ExclusionMuhittin ÖzenNo ratings yet
- Microbiological Evaluation of Ready Ti Eat Iceberg Lettuce During Shelf Life and Effectiveness of Household Washing MethodsDocument5 pagesMicrobiological Evaluation of Ready Ti Eat Iceberg Lettuce During Shelf Life and Effectiveness of Household Washing MethodsIV�N ANDR�S RODR�GUEZ AGREDONo ratings yet
- Forensic Ecogenomics: The Application of Microbial Ecology Analyses in Forensic ContextsFrom EverandForensic Ecogenomics: The Application of Microbial Ecology Analyses in Forensic ContextsNo ratings yet
- Anti CandidaDocument8 pagesAnti CandidasivarajNo ratings yet
- Articulo Cytotoxic Activity of Ethanolic Extracts of A Selection of MacromycetesDocument9 pagesArticulo Cytotoxic Activity of Ethanolic Extracts of A Selection of MacromycetesLiseth JustinNo ratings yet
- HW 0440Document8 pagesHW 0440JaanvhiNo ratings yet
- Efficacies of Selected Disinfectants Against MycobDocument8 pagesEfficacies of Selected Disinfectants Against MycobMd. Saddam HossainNo ratings yet
- Microbial Communication Leading To The Activation of Silent Fungal Secondary Metabolite Gene ClustersDocument13 pagesMicrobial Communication Leading To The Activation of Silent Fungal Secondary Metabolite Gene ClustersLini MaliqisnayantiNo ratings yet
- Paper 11Document7 pagesPaper 11Vardhana JNo ratings yet
- 2004 Chen, HDocument6 pages2004 Chen, HMayra FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Biological Activities of The Fermentation Extract of The Endophytic Fungus Alternaria Alternata Isolated From Coffea Arabica LDocument13 pagesBiological Activities of The Fermentation Extract of The Endophytic Fungus Alternaria Alternata Isolated From Coffea Arabica LCece MarzamanNo ratings yet
- Jurnal PolyketideDocument5 pagesJurnal Polyketidewahyu dyaNo ratings yet
- Microbial Ecology Of: Activated SludgeDocument2 pagesMicrobial Ecology Of: Activated Sludgejacc0rNo ratings yet
- Lactic Acid Bacteria ThesisDocument6 pagesLactic Acid Bacteria Thesisdnr16h8x100% (2)
- Development of Detection Method For Carcinogenic Compounds Using Radish Seeds Raphanus Sativus, L Via Measuring The Alkaline Phosphatase Enzyme ActivityDocument10 pagesDevelopment of Detection Method For Carcinogenic Compounds Using Radish Seeds Raphanus Sativus, L Via Measuring The Alkaline Phosphatase Enzyme Activitympd26No ratings yet
- s41396 022 01245 4Document13 pagess41396 022 01245 4miralvaNo ratings yet
- Research Article in Vitro Effect of Cinnamomum Zeylanicum Blume EssentialDocument14 pagesResearch Article in Vitro Effect of Cinnamomum Zeylanicum Blume EssentialSiti AlifsaNo ratings yet
- Applicatio of BioinformaticsDocument4 pagesApplicatio of BioinformaticsSong AlexNo ratings yet
- (John Romeo) Integrative Phytochemistry From Ethn (BookFi) PDFDocument342 pages(John Romeo) Integrative Phytochemistry From Ethn (BookFi) PDFKima Mad100% (1)
- Comparison of The Sensitivity of Different Toxicity Test Endpoints in A Microalga Exposed To The Herbicide ParaquatDocument24 pagesComparison of The Sensitivity of Different Toxicity Test Endpoints in A Microalga Exposed To The Herbicide ParaquatMuhammad SibtainNo ratings yet
- Silver Nanoparticles Using Citrullus Colocynthis Aqueous ExtractsDocument12 pagesSilver Nanoparticles Using Citrullus Colocynthis Aqueous ExtractshameedhaaNo ratings yet
- Rowe, L. 2001Document8 pagesRowe, L. 2001Francisco FalconNo ratings yet
- Toxicity Evaluation of Biodegradable Chitosan Nanoparticles Using A Zebrafish Embryo ModelDocument16 pagesToxicity Evaluation of Biodegradable Chitosan Nanoparticles Using A Zebrafish Embryo ModelnelsrodrigNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Activity of Eugenol Against Botrytis Cinerea: Chunmei Wang, Jie Zhang, Hao Chen, Yongjian FanDocument7 pagesAntifungal Activity of Eugenol Against Botrytis Cinerea: Chunmei Wang, Jie Zhang, Hao Chen, Yongjian FanTazyinul Qoriah AlfauziahNo ratings yet
- MicrosDocument8 pagesMicrosduchess juliane mirambelNo ratings yet
- Removal of Triazine Herbicides From Freshwater Systems Using Photosynthetic MicroorganismsDocument6 pagesRemoval of Triazine Herbicides From Freshwater Systems Using Photosynthetic MicroorganismsDanaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation and Quantitative Analysis of Bioactive Compounds From Chaetocerous Calcitrans Against Human PathogensDocument13 pagesEvaluation and Quantitative Analysis of Bioactive Compounds From Chaetocerous Calcitrans Against Human PathogensIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Public Misunderstanding of GMODocument8 pagesPublic Misunderstanding of GMOcasaresdarlaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Antimicrobial Potential of Actinobacteria Strains Isolated From Mangrove Soils in The Municipality of São Caetano de Odivelas - Pará, BrazilDocument5 pagesEvaluation of The Antimicrobial Potential of Actinobacteria Strains Isolated From Mangrove Soils in The Municipality of São Caetano de Odivelas - Pará, BrazilMamta AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus Analytic Geometry Problem 1Document1 pagePre-Calculus Analytic Geometry Problem 1roh009No ratings yet
- 2017 Chapter TargetDocument8 pages2017 Chapter Targetroh009No ratings yet
- An Approach To JUMP Math Coaching Nov 2009 by Haroon Patel NotesDocument5 pagesAn Approach To JUMP Math Coaching Nov 2009 by Haroon Patel Notesroh009No ratings yet
- Students Sci ProjDocument11 pagesStudents Sci Projroh009No ratings yet
- Balancing Equations PracticeDocument1 pageBalancing Equations PracticeMax SaubermanNo ratings yet
- Students Sci Proj 2Document10 pagesStudents Sci Proj 2roh009No ratings yet
- School Merit RollDocument34 pagesSchool Merit Rollroh009No ratings yet
- Mid Module 4 RubricDocument5 pagesMid Module 4 Rubricroh009No ratings yet
- Basic Geometry Practice PDFDocument18 pagesBasic Geometry Practice PDFroh009No ratings yet
- Perfect ScoresDocument9 pagesPerfect Scoresroh009No ratings yet
- APlus NumberSense SequenceChart Rev1617Document1 pageAPlus NumberSense SequenceChart Rev1617roh009No ratings yet
- Perfect Scores: Location: United StatesDocument1 pagePerfect Scores: Location: United Statesroh009No ratings yet
- Mathcounts EtcDocument2 pagesMathcounts Etcroh009No ratings yet
- Things To Know About TrianglesDocument2 pagesThings To Know About Trianglesroh009No ratings yet
- School Honor Roll: Location: United StatesDocument1 pageSchool Honor Roll: Location: United Statesroh009No ratings yet
- Number Sense RulesDocument4 pagesNumber Sense Rulesroh009No ratings yet
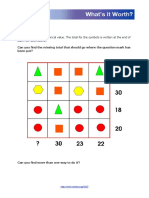
- Whatsitworthlarge PDFDocument1 pageWhatsitworthlarge PDFroh009No ratings yet
- Number SenseDocument2 pagesNumber Senseroh009No ratings yet
- Mathematics RulesDocument2 pagesMathematics Rulesroh009No ratings yet
- 532 PDFDocument3 pages532 PDFroh009No ratings yet
- Mathematics Answer SheetDocument1 pageMathematics Answer Sheetroh009No ratings yet
- Assignments Sheet Week 7Document1 pageAssignments Sheet Week 7roh009No ratings yet
- 001Document1 page001roh009No ratings yet
- Moe Ms AbstractsDocument41 pagesMoe Ms Abstractsroh009No ratings yet
- 2011 IMO Bio DocumentDocument9 pages2011 IMO Bio Documentroh009No ratings yet
- Student Sci Pro 2Document2 pagesStudent Sci Pro 2roh009No ratings yet
- Balancing Equations PracticeDocument1 pageBalancing Equations PracticeMax SaubermanNo ratings yet
- Maths Olympiad Contest Problems: Exploring Maths Through Problem SolvingDocument15 pagesMaths Olympiad Contest Problems: Exploring Maths Through Problem Solvingroh00960% (5)
- Math Olympiad Club DescriptionDocument1 pageMath Olympiad Club Descriptionroh009No ratings yet
- Astm D5231 92 2008Document4 pagesAstm D5231 92 2008Astrini WidiyantiNo ratings yet
- Soal Lus 2021 - Bahasa Inggris - Paket 1Document20 pagesSoal Lus 2021 - Bahasa Inggris - Paket 1AmbariCaesarNo ratings yet
- Is Recycling Really Worth My Time?Document8 pagesIs Recycling Really Worth My Time?ajayNo ratings yet
- Incenrator Details 12 Nov 2018Document17 pagesIncenrator Details 12 Nov 2018ptaxNo ratings yet
- Green Cleaning Policy and ProgramDocument11 pagesGreen Cleaning Policy and ProgramKyle MacdonaldNo ratings yet
- Mechanical EngineeringDocument14 pagesMechanical EngineeringEl WijaNo ratings yet
- EDITED Chapter 1 and 2Document20 pagesEDITED Chapter 1 and 2Diane BautistaNo ratings yet
- Sample RFQ For Large Power Plants PDFDocument20 pagesSample RFQ For Large Power Plants PDFvarman12100% (1)
- Qcs 2007 0115Document3 pagesQcs 2007 0115RotsapNayrbNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste Management Opportunities Challenges GujaratDocument14 pagesSolid Waste Management Opportunities Challenges GujaratRahul Kumar AwadeNo ratings yet
- Cookery SyllabusDocument6 pagesCookery SyllabusPemmasaniSrinivas0% (1)
- Environmental LawDocument21 pagesEnvironmental LawTanurag GhoshNo ratings yet
- UTLDocument77 pagesUTLrajkumar_bhoraniyaNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Lecture 5 EENVDocument51 pagesWater Treatment Lecture 5 EENVshamashergyNo ratings yet
- Generator Manual Rihand 500 MWDocument416 pagesGenerator Manual Rihand 500 MWGautamupadhyay100% (2)
- MegaDeck Heavy-Duty Composite Access MatsDocument8 pagesMegaDeck Heavy-Duty Composite Access MatsSignatureSystemsNo ratings yet
- SANTOYA DELY For Demo..contextualized DLL. WEEK 32. COT2Document8 pagesSANTOYA DELY For Demo..contextualized DLL. WEEK 32. COT2Jackie Lou ElviniaNo ratings yet
- Manual Del 2kva Liebert PDFDocument44 pagesManual Del 2kva Liebert PDFVictor GarciaNo ratings yet
- Digital BiogasTech2020Document25 pagesDigital BiogasTech2020kakangmasNo ratings yet
- Arora Textiles Pvt. Ltd.Document4 pagesArora Textiles Pvt. Ltd.Shrish TiwariNo ratings yet
- HOSPITAL ASSOCIATED Infections Overcoming Emerging Challenge by Dr.T.V.Rao MDDocument61 pagesHOSPITAL ASSOCIATED Infections Overcoming Emerging Challenge by Dr.T.V.Rao MDtummalapalli venkateswara raoNo ratings yet
- Abattoir Wastes Generation, Management and The Environment: A Case of Minna, North Central NigeriaDocument20 pagesAbattoir Wastes Generation, Management and The Environment: A Case of Minna, North Central Nigeriamulabbi brianNo ratings yet
- 1science5 Week 1Document12 pages1science5 Week 1Annie LouNo ratings yet
- Opening Closing ProcedureDocument2 pagesOpening Closing ProcedureMatteo GrazianiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document20 pagesChapter 1Vera Carpentero LamisNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Faecal Sludge Management in Nguru Town, Yobe State, Northeastern NigeriaDocument7 pagesAssessment of Faecal Sludge Management in Nguru Town, Yobe State, Northeastern NigeriaUMYU Journal of Microbiology Research (UJMR)No ratings yet
- R5G R3C: Rozzi SpaDocument1 pageR5G R3C: Rozzi SpaSzilárd SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 CSDocument35 pagesChapter 1 CSJaybee Mina100% (1)
- 2R11779 Fluitest® GOT AST - GPT ALT R2-GB-en 2018-10-18Document5 pages2R11779 Fluitest® GOT AST - GPT ALT R2-GB-en 2018-10-18RSU PURWA HUSADANo ratings yet
- Vadodara: Walk Down The City ofDocument12 pagesVadodara: Walk Down The City ofDhruv JaiswalNo ratings yet