Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cornell Notes Cell Transport
Uploaded by
api-329922377Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cornell Notes Cell Transport
Uploaded by
api-329922377Copyright:
Available Formats
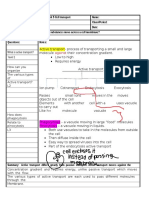
Cornell Notes Topic/Objective: Cells Name: Autumn Choate
Class/Period: 6
Date:1/23/17
Essential Question: ?
Questions: Notes:
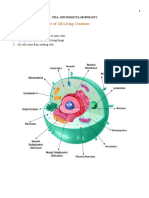
Cells:
What do you think makes
people believe viruses are *Viruses believed to be alive
living? L2 *Able to control/ invade cells
` *Made of bits of DNA and RNA
*Reproduction is only living factor
*Have evolutionary history
Who discovered *Non-living on its head
that corks looked *1600s is when microscopes began being used
like cells? L1 *Robert Hooke observed the pieces of cork, stated they looked just
like cells
*Cell Theory- A well tested description that unifies a range of
observations by multiple scientists/viewpoints
Describe the 1. All living things are composed of cells
difference between 2. Cells are all basic building units of life
polar and non 3. New cells are produced from existing cells
polar, and *Cells are different shapes and sizes, all cells contain genetics
hydrophilic and *No nucleus cells are called prokaryotic (bacteria)
hydrophobic. L3 *Cells with nucleus are called eukaryotic (Animals, plants, fungi,
protists)
Cell Membrane:
*Functions- protects and supports cell, regulates transport of
Explain the cell materials
theory using all *Lipid bilayer- a double layer sheet of phospholipids that make up
four steps, then the cell membrane. Helps provide a flexible structure that forms a
apply it to the strong barrier (cholesterol)
knowledge of if *Polar/Hydrophilic- Water loving, heads face out, like
viruses are living or *Non-polar/ Hydrophobic- Water hating, tails face inside, like
not. L4 *Fluid Mosaic Model- Cell membrane is made up of many different
parts that freely move
*Embedded protein- proteins are embedded in the lipid bilayer.
They act as channels or pumps to help move molecules across the
membrane.
*Carbohydrate chains- Act like chemical identity cards, allows
individual clls to identify one another
*Selectively Permeable- Some substances can pass through cell
membrane while others cannot
Summary: Cells are very complex beings. They are considered living because of the cell theory. The theory has
three requirements to show that something is living. They include: Cells must come from another cell, all living
organisms have cells, and cells are the basic building block of life. This is why viruses were not considered living
species. The only factor of the theory that they match was the reproductive aspect. The cell membrane is made of
a lipid bilayer, which makes the wall flexible and strong. Protein pumps and channels help molecules enter and exit
the cells depending on the size of the molecule. Molecules can be either polar (like water), or non-polar (dont like
water). Depending on the cells preference to water, it will enter the cell different ways. There are two types of
transport, active and passive. Passive transport uses diffusion and NO energy to get molecules through the
membrane. Active transport uses energy and different types of pumps/ vesicles to get molecules in.
Questions: Notes:
Passive Transport:
What is a protein
pump? L1 *Concentration- mass of a solute given in a volume of solution. Mass/volume
*Simple diffusion- molecules move from high to low concentration within the cell
*Equilibrium- concentration of the solute in the same throughout so molecules move in
and out of cells
Compare and
*Solutes in the membrane include- Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, small fats, and fat soluble
contrast simple and
vitamins (A, D, E, K)
facilitated diffusion. * Facilitated diffusion- helped along diffusion of large and charged molecules (ions)
L2 through the membrane
*Channel protein- a tunnel where large and charged molecules can enter the cell using
a gated system
* Carrier protein- a protein that holds onto molecules and then changes shape to allow
the molecules into the cell
*Osmosis- diffusion of water through the cell via special channels called aquaporins
*Vacuole- A storage bubble, controls input and output of water in organisms
* Hypotonic environment- Low solute and high water concentration
*Hypertonic environment- High solute and low water concentration
*Isotonic- equal amounts of solute in/out of the cell
*Turgid- surroundings are hypotonic (pure water), water in
*Flaccid- surroundings are isotonic, water in and out
*Plasmolysis- hypertonic surroundings, water goes out
Active Transport:
*Active transport- process of transporting small and large molecules against
concentration gradient
-Low to high energy
-Requires energy
-Uses pumps
*Ion pumps- Sodium, Potassium, Hydrogen, Chlorine
*Cotransport- Have to travel together into the cell (Na+ and sugar)
* Exocytosis- Transport using vesicles, moving out
*Endocytosis- transport using vesicles, moving out
-Phagocytosis- (cell eating) engulfs solid particles and digests
internally
-Pinocytosis- (cell drinking) engulfs liquid particles and digests
internally
-Receptor Mediated- binding of ligands to receptors trigger vesicle
formation
Summary:
You might also like
- Bio Cell Transport Cornell NotesDocument3 pagesBio Cell Transport Cornell Notesapi-335205149100% (2)
- Cornell Notes Unit 5 ActiveDocument2 pagesCornell Notes Unit 5 Activeapi-3300708430% (1)
- Webquest Conduction Convection RadiationDocument1 pageWebquest Conduction Convection Radiationapi-259781257No ratings yet
- Week 8.1++Species+&+Phylogenetic+Trees+-+preclass+slidesDocument53 pagesWeek 8.1++Species+&+Phylogenetic+Trees+-+preclass+slidesharleenNo ratings yet
- 8.2 Cell Respiration NotesDocument6 pages8.2 Cell Respiration Notescutiecat360No ratings yet
- Biology I Eoc Review BookDocument22 pagesBiology I Eoc Review Bookapi-199871042No ratings yet
- Bio 12 - Fetal Pig DissectionDocument7 pagesBio 12 - Fetal Pig Dissectionkw2533No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Respiration Choice BoardDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis Respiration Choice Boardapi-283801432No ratings yet
- 2016 BIOLOGY EOC Study Guide ANSWER KEY and Content Focus PDFDocument9 pages2016 BIOLOGY EOC Study Guide ANSWER KEY and Content Focus PDFMelisa Anne CanilangNo ratings yet
- Cells 6th GradeDocument44 pagesCells 6th Gradepauleyler100% (4)
- BioEOC PracticekeyDocument21 pagesBioEOC PracticekeyEnerya AbalosNo ratings yet
- Bio102 General Biology II SummaryDocument47 pagesBio102 General Biology II SummaryIkenna Okpala100% (1)
- Muscle Fatigue LabDocument3 pagesMuscle Fatigue LabSharmet Solarz0% (1)
- Animal CellDocument11 pagesAnimal CellDaryl De LeonNo ratings yet
- Cells WebquestDocument4 pagesCells Webquestapi-347555363No ratings yet
- Sheep Brain Observation LAB 2015Document4 pagesSheep Brain Observation LAB 2015Leo MatsuokaNo ratings yet
- The Living Cell: A Guide to Its History, Parts, Functions and TypesDocument49 pagesThe Living Cell: A Guide to Its History, Parts, Functions and TypesDaezel DeuxNo ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument18 pagesCell and Molecular BiologyHizzei CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Genetic TechnologyDocument36 pagesGenetic TechnologyAnggraeni Kusuma WardaniNo ratings yet
- Organic Molecules Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesOrganic Molecules Review WorksheetBianca BiancaNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell and Animal Cell - Docx YuvenDocument8 pagesPlant Cell and Animal Cell - Docx YuvenVikneswaran Gunahlan NeshNo ratings yet
- Venn Diagram On Osmosis and DiffusionDocument1 pageVenn Diagram On Osmosis and DiffusioncolacastellNo ratings yet
- CloningDocument6 pagesCloningkikkabuttigieg1466No ratings yet
- SAPS Photosynthesis Survival Guide Teachers NotesDocument9 pagesSAPS Photosynthesis Survival Guide Teachers NotesTechie HarryNo ratings yet
- KISS Notes Patterns in Nature 1Document37 pagesKISS Notes Patterns in Nature 1nurayozturk97No ratings yet
- Cell StructuresDocument3 pagesCell StructuresKatherine DenisNo ratings yet
- History of Dna - ScientistsDocument21 pagesHistory of Dna - Scientistsapi-244168124No ratings yet
- Biology Unit PlanDocument10 pagesBiology Unit Planapi-246097943No ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living Organisms FinalDocument13 pagesCharacteristics of Living Organisms FinalSunny x10No ratings yet
- Structure of Animal Tissue g12 BIODocument53 pagesStructure of Animal Tissue g12 BIOSimon A. Peter JohnNo ratings yet
- Ms Cell Theory TestDocument6 pagesMs Cell Theory Testapi-375761980No ratings yet
- Nerve Cell - Cell ProjectDocument23 pagesNerve Cell - Cell Projectapi-327766139No ratings yet
- Topic 9 Plant Biology IB Biology 9.2 Transport in The Phloem of Plants Nature of Science: Developments in Scientific Research Follow Improvements in Apparatus: ExperimentalDocument4 pagesTopic 9 Plant Biology IB Biology 9.2 Transport in The Phloem of Plants Nature of Science: Developments in Scientific Research Follow Improvements in Apparatus: ExperimentalMoahmed Mahmoud IB15A 363KAGYNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle & Cell DivisionDocument30 pagesThe Cell Cycle & Cell DivisionamitNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet: 1. Filling The BlanksDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis Worksheet: 1. Filling The BlanksFelix SimsungNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: Class Notes NotesDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis: Class Notes NotesDale HardingNo ratings yet
- Cell VocabularyDocument3 pagesCell Vocabularyapi-537617514No ratings yet
- Tori Daniel - DNA & RNA Notes - Student PDFDocument4 pagesTori Daniel - DNA & RNA Notes - Student PDFTori DanielNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 BOTANY - Review Questions and AnswersDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 4 BOTANY - Review Questions and AnswersPam GarciaNo ratings yet
- 6 Kingdoms of Life Lecture NotesDocument82 pages6 Kingdoms of Life Lecture NotesEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cells: Cell Membrane Cell Wall Capsule Pili Plasmid Flagella Nucleoid Region Ribosomes CytoplasmDocument3 pagesProkaryotic Cells: Cell Membrane Cell Wall Capsule Pili Plasmid Flagella Nucleoid Region Ribosomes CytoplasmErvin WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Class: 8 Science Chapter - 8 Cell - Structure and FunctionsDocument10 pagesClass: 8 Science Chapter - 8 Cell - Structure and FunctionsAmiteshwar SinghNo ratings yet
- Bio Factsheet: The Kidney: Excretion and OsmoregulationDocument4 pagesBio Factsheet: The Kidney: Excretion and OsmoregulationjesvinjesvinNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy & Phylogeny: Classification Phylogeny Cladograms QuizDocument68 pagesTaxonomy & Phylogeny: Classification Phylogeny Cladograms QuizDorothy Yen EscalañaNo ratings yet
- Cell Processes Blank ReviewDocument4 pagesCell Processes Blank ReviewDr-Qussai ZuriegatNo ratings yet
- 5.7 Cell TransportDocument6 pages5.7 Cell TransportMonica B. BautistaNo ratings yet
- Histology (Tissue Organisation) Animal Tissues: Arthur Kugonza HDocument14 pagesHistology (Tissue Organisation) Animal Tissues: Arthur Kugonza HAnonymous M7aBZl100% (1)
- Bio 100 A Virtual Labs Unit OneDocument7 pagesBio 100 A Virtual Labs Unit OneTammy SmithNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Speciation NotesDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Speciation NotesCHIENG PEI WEN MoeNo ratings yet
- Allele Frequency LabDocument1 pageAllele Frequency Labjmunozbio@yahoo.com100% (1)
- HomeostasisDocument16 pagesHomeostasisDr M K GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lec 3,4,5-Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument57 pagesLec 3,4,5-Cell and Cell OrganellesSatyam AryaNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 01 (Answer Key)Document1 pageQUIZ 01 (Answer Key)Tego Shei Harumi100% (1)
- BlankcopycornellnotesDocument3 pagesBlankcopycornellnotesapi-329922377No ratings yet
- Cornell Notes 1Document3 pagesCornell Notes 1api-330057205No ratings yet
- Cornell Notes 1Document2 pagesCornell Notes 1api-333316198100% (1)
- Blankcopycornellnotes 8Document3 pagesBlankcopycornellnotes 8api-330056815100% (1)
- Bio Cornell Notes Cell Transport 2Document3 pagesBio Cornell Notes Cell Transport 2api-335205149No ratings yet
- السيد قشطةDocument138 pagesالسيد قشطةAhmed FrahatNo ratings yet
- Student-Teacher Class Evaluation 1Document2 pagesStudent-Teacher Class Evaluation 1api-330119127No ratings yet
- Smart Goals WorksheetDocument3 pagesSmart Goals Worksheetapi-300536016No ratings yet
- Learner Profile Reflection Sheet PT ConferencesDocument3 pagesLearner Profile Reflection Sheet PT Conferencesapi-329922377No ratings yet
- Smart Goals WorksheetDocument3 pagesSmart Goals Worksheetapi-329922377No ratings yet
- Learner Profile Reflection Sheet PT ConferencesDocument2 pagesLearner Profile Reflection Sheet PT Conferencesapi-329922377No ratings yet
- Smart Goals WorksheetDocument3 pagesSmart Goals Worksheetapi-329922377No ratings yet
- BlankcopycornellnotesDocument3 pagesBlankcopycornellnotesapi-329922377No ratings yet
- BlankcopycornellnotesDocument3 pagesBlankcopycornellnotesapi-329922377No ratings yet
- Student/Teacher Evaluation Worksheet Name: - Teacher: - SubjectDocument2 pagesStudent/Teacher Evaluation Worksheet Name: - Teacher: - Subjectapi-329922377No ratings yet
- Smart Goal Unit 2Document2 pagesSmart Goal Unit 2api-329922377No ratings yet
- Biology Smart GoalDocument2 pagesBiology Smart Goalapi-307657398No ratings yet
- Progress Monitoring Unit 1 ChoateDocument1 pageProgress Monitoring Unit 1 Choateapi-329922377No ratings yet
- Developing Together. Building With Each Other.: We Create Chemistry For Advanced ConstructionDocument5 pagesDeveloping Together. Building With Each Other.: We Create Chemistry For Advanced ConstructionAlex Paye AncoNo ratings yet
- Surface Characterisation and Electrochemical Behaviour of Porous Titanium Dioxide Coated 316L Stainless Steel For Orthopaedic Applications PDFDocument6 pagesSurface Characterisation and Electrochemical Behaviour of Porous Titanium Dioxide Coated 316L Stainless Steel For Orthopaedic Applications PDFRahul MadanNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Efficacy Study of IMAGARD ID 401 IJBARDocument3 pagesAntimicrobial Efficacy Study of IMAGARD ID 401 IJBARmktginfinitilinesNo ratings yet
- Acyclovir Cream IVPT FDA 2020Document13 pagesAcyclovir Cream IVPT FDA 2020Widia TriNo ratings yet
- IV. Superpave Aggregates: Aggregate Tests and Specifications Consensus PropertiesDocument10 pagesIV. Superpave Aggregates: Aggregate Tests and Specifications Consensus PropertiesADRIAN YONANDA D DNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Oil Palm Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Composites: A ReviewDocument33 pagesMechanical Properties of Oil Palm Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Composites: A ReviewjaviergagocampusanoNo ratings yet
- GIZI PKM TAOPA STOK DAN PERGERAKAN OBAT JANUARI 2020Document20 pagesGIZI PKM TAOPA STOK DAN PERGERAKAN OBAT JANUARI 202012rahmatajangNo ratings yet
- Ethylhexylglycerin Safety ToxicologyDocument17 pagesEthylhexylglycerin Safety Toxicologybfh83730No ratings yet
- Arkifloor EHDocument2 pagesArkifloor EHChristinaNo ratings yet
- Condenser Tube: Categories of FailureDocument19 pagesCondenser Tube: Categories of FailurePaul SuicoNo ratings yet
- PDS Glasroc-F-FIRECASE ENGL 1 PDFDocument3 pagesPDS Glasroc-F-FIRECASE ENGL 1 PDFVlad TirzianNo ratings yet
- 05 0097 01 MS 5RP AFP tcm142-686106Document16 pages05 0097 01 MS 5RP AFP tcm142-686106Ssemwanga Solomon100% (8)
- Aircraft BoltDocument36 pagesAircraft BoltCokorda KesawaNo ratings yet
- DAFTAR DM FARMAKOPE INDONESIADocument7 pagesDAFTAR DM FARMAKOPE INDONESIANUNE IDHAMNo ratings yet
- NeoCryl B-736 PdsDocument2 pagesNeoCryl B-736 PdsLeandro EsvizaNo ratings yet
- Total, Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Amine Values of Fatty Amines by Alternative Indicator MethodDocument2 pagesTotal, Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Amine Values of Fatty Amines by Alternative Indicator MethodMariaJoseSalamancaDiazNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engg Lab Manual BeDocument32 pagesPower Plant Engg Lab Manual Besinan2yilmazNo ratings yet
- Suyama, Takashi L.: Electronic Theses and Dissertations UC San DiegoDocument409 pagesSuyama, Takashi L.: Electronic Theses and Dissertations UC San DiegoDiego Contreras HernándezNo ratings yet
- Structure and Bonding (Chapter 3) Exam Questions: 141 Minutes 141 MarksDocument34 pagesStructure and Bonding (Chapter 3) Exam Questions: 141 Minutes 141 Marksrejymol100% (1)
- Experiment9 A011Document35 pagesExperiment9 A011Manas GaikwadNo ratings yet
- S-3109 FinalDocument60 pagesS-3109 FinalRaúl Oscar LedesmaNo ratings yet
- The Nasrid Plasterwork at "Qubba Dar Al-Manjara L-Kubra" in Granada: Characterisation of Materials and TechniquesDocument15 pagesThe Nasrid Plasterwork at "Qubba Dar Al-Manjara L-Kubra" in Granada: Characterisation of Materials and TechniquesSiham BelhajNo ratings yet
- Module 1Q SCI 7 1Document21 pagesModule 1Q SCI 7 1PeterClomaJr.No ratings yet
- Engineering Corrosion OH-7: University of Hafr Al BatinDocument27 pagesEngineering Corrosion OH-7: University of Hafr Al BatinHussain Al-DawoodNo ratings yet
- Kerosine: Standard Specification ForDocument3 pagesKerosine: Standard Specification ForDavid CazorlaNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument37 pagesIlovepdf MergedGizelle Mae Pasiol-MacayanNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Boiler Water TreatmentDocument11 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Boiler Water TreatmentABDUL HANANNo ratings yet
- Key sheet for JEE-MAIN physics, chemistry and mathematics examDocument20 pagesKey sheet for JEE-MAIN physics, chemistry and mathematics examNavaneeth YanamadalaNo ratings yet
- Section 5.3 Representative Groups: Reading StrategyDocument2 pagesSection 5.3 Representative Groups: Reading StrategyRiley Miller67% (3)
- Jotun Penguard Express CF TDSDocument5 pagesJotun Penguard Express CF TDSnihad_mNo ratings yet