Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Lab Result
Uploaded by
Joy Mariel Isadora Burgos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
169 views5 pagesThe nursing care plan addresses an imbalance in nutrition related to inadequate food intake. The nursing diagnosis is imbalanced nutrition less than body requirements. The nursing objective is to establish a dietary pattern to regain appropriate weight through a diet with calorie control and supplementation. The nursing intervention is to provide a nutritious diet in small, frequent meals in a pleasant environment. The expected outcome is weight gain and improved nutritional status for the client.
Original Description:
laboratory
Original Title
Ncp Lab Result
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe nursing care plan addresses an imbalance in nutrition related to inadequate food intake. The nursing diagnosis is imbalanced nutrition less than body requirements. The nursing objective is to establish a dietary pattern to regain appropriate weight through a diet with calorie control and supplementation. The nursing intervention is to provide a nutritious diet in small, frequent meals in a pleasant environment. The expected outcome is weight gain and improved nutritional status for the client.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
169 views5 pagesNCP Lab Result
Uploaded by
Joy Mariel Isadora BurgosThe nursing care plan addresses an imbalance in nutrition related to inadequate food intake. The nursing diagnosis is imbalanced nutrition less than body requirements. The nursing objective is to establish a dietary pattern to regain appropriate weight through a diet with calorie control and supplementation. The nursing intervention is to provide a nutritious diet in small, frequent meals in a pleasant environment. The expected outcome is weight gain and improved nutritional status for the client.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
X.
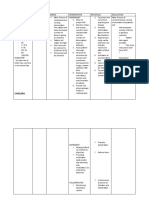
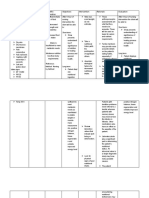
NURSING CARE PLAN
Nursing Scientific Nursing
CUES Nursing Objective Scientific Explanation Evalua
Diagnosis Explanation Intervention
Subjective: Imbalance Imbalanced -Establish dietary -To establish -Provide comparative The goa
- N/A nutrition, less nutrition: Less pattern with minimum weight baseline for effectiveness met.
than body than body calorie intake gain and daily of the therapy
requirement requirements adequate to nutritional The
Objective: related to intake of regain/maintain requirement nutritiona
inadequate nutrients appropriate -to provide diet -it will be more effective status
Height: 71 cm food intake insufficient to weight with substitution, for providing food in quite imp
Weight: 4.2 kgs meet metabolic administer enjoyable manner and in
needs. -Demonstrate nutritional diet treating malnutrition assessm
BMI: 8.3 weight gain to the with
clients expected supplementary
range food.
-this enhance
-To provide small manipulation in eating,
frequent diet with body adjustment and
consistence likely for preferred food.
approach with
pleasant
environment and
selectiveness
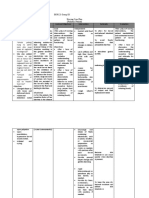
Nursing Nursing Scientific
CUES Scientific Explanation Nursing Objective Evaluat
Diagnosis Intervention Explanation
Subjective: Risk for fluid Decreased After 1 week of - Assess the -This is the After 1 w
N/A volume deficit intravascular, interstitial, nursing intervention, vital signs and indicator of nursing
related to and/or intracellular fluid. patient will not capillary refill circulatory intervention
Objective: excessive loss experience fluid and skin turgor. volume patients s
This refers
volume deficit as has a poo
of fluid to dehydration, water evidenced by: turgor, and
Poor skin turgor associated with loss alone without - Normal skin
-Monitor the dry. Goal w
Skin looks dry vomiting and/or change in sodium. turgor amount and -Dehydration met.
diarrhea. Deficient fluid volume is - Moist mucous type of fluid results in
a state or condition membrane intake(oral electrolyte
where the fluid output - Stable weight rehydration imbalance so,
exceeds the fluid intake.
solution) output the monitoring
measuring helps to identify
It happens when water
accurately and the alteration in
and electrolytes are lost
replacing it with electrolyte
as they exist in normal
fluid intake. balance.
body fluids. Common
sources of fluid loss are
the gastrointestinal
tract, polyuria, and
increased perspiration.
Risk factors for FVD are
as follows:
vomiting, diarrhea, GI
suctioning, sweating,
decreased intake,
nausea, inability to gain
access to fluids.
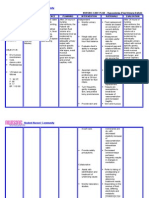
Nursing Nursing Scientific
CUES Scientific Explanation Nursing Objective Evaluat
Diagnosis Intervention Explanation
Subjective: Risk for "the state in which an Short Term: -Promoting -It helps to prevent Short Term
N/A infection related individual After 30 minutes hygienic the communicable After 30 m
to tissue is at risk to be invaded of nursing measures and disease cause by of n
Objective: by an opportunistic or intervention
destruction pathogenic
intervention, general poor hygiene.
parents we
secondary to agent (virus, fungus, parents should cleanliness
RR: 31 to know
CR: 131
colostomy bacteria, know the importance
T: 36.6 protozoa, or importance of -avoid exposure hygienic
other parasite) hygienic to cold and measures
from endogenous or measure when infection cleaning
exogenous sources" cleaning the colostomy
colostomy bag of -maintain patient.
patient. aseptic
technique and Long term:
Long term: hand washing week of n
After 1 week of practices during intervention
patient wa
nursing care
to becom
intervention will from any
be free from any and sympt
signs and having infe
symptoms of
infections.
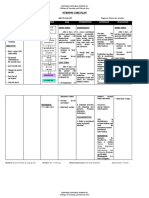
Lab Result
LABORATORY TEST RESULT NORMAL VALUE SIGNIFICANCE
Sodium 136.20 mmol/L 135-145 mmol/L -Within normal range
Potassium 3.48 mmol/L 3.5-5.1 mmol/L -Low potassium
(hypokalemia) refers to a
lower than normal potassium
level in your bloodstream.
Potassium is a chemical
(electrolyte) that is critical to
the proper functioning of
nerve and muscles cells,
particularly heart muscle
cells.
-Vomiting or diarrhea or both
can result in excessive
potassium loss from the
digestive tract.
Ionized Calcium 0.96 mmol/L 1.15-1.33 mmol/L -If you have low levels of
ionized calcium in your
blood, it can indicate:
-hypoparathyroidism,
which is an underactive
parathyroid gland
-inherited resistance to
parathyroid hormone
-malabsorption of
calcium
-a vitamin D deficiency
-osteomalacia or rickets,
which is a softening of
the bones (in many
cases due to a vitamin D
deficiency)
-a magnesium deficiency
-high phosphorus levels
-acute pancreatitis,
which is an inflammation
of the pancreas
-kidney failure
-malnutrition
You might also like
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel Banag100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanJobelyn TunayNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Labor WatchDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: Labor WatchRS BuenavistaNo ratings yet
- NCP High Risk PregnancyDocument7 pagesNCP High Risk PregnancyRica ParcasioNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.Document6 pagesIneffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.SAROL, RYAN CHRISTIAN B.No ratings yet
- NCP Deficit Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesNCP Deficit Fluid VolumeKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Regañon - Rle Case # 1Document22 pagesRegañon - Rle Case # 1Darla Janyll RegañonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudySheryl Anne GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Final PortraitDocument11 pagesCase Study Final PortraitZhy CaluzaNo ratings yet
- Silliman University: Nursing Care Plan On Preeclampsia With Severe FeaturesDocument8 pagesSilliman University: Nursing Care Plan On Preeclampsia With Severe FeaturesRyan Robert V. VentoleroNo ratings yet
- NCP MeningitisDocument2 pagesNCP MeningitisARISNo ratings yet
- San Pedro Hospitai of Davao City, Inc.: Nurses' NotesDocument7 pagesSan Pedro Hospitai of Davao City, Inc.: Nurses' NotesRosaree Mae Pantoja100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageNursing Care PlanMikki lor PuaganNo ratings yet
- Learning Feedback g2Document8 pagesLearning Feedback g2Darwin DaveNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPMcmc Ryan Ferdinand GutierrezNo ratings yet
- NCP Meningitis Sure NaniDocument2 pagesNCP Meningitis Sure NaniARISNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment FHP - Nutrition and MetabolismDocument25 pagesHealth Assessment FHP - Nutrition and MetabolismKim DajaoNo ratings yet
- RefraksiDocument85 pagesRefraksiIvonike Lim100% (1)
- Javier, Jomar A. BSN121 Group 83 Nursing Care Plan (Pediatric Patient)Document7 pagesJavier, Jomar A. BSN121 Group 83 Nursing Care Plan (Pediatric Patient)Julie AnnNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology PrintDocument4 pagesPa Tho Physiology Printaiconjucea0% (1)
- Request Letter For CHNDocument1 pageRequest Letter For CHNdusty kawiNo ratings yet
- NCP For Dehydration 1Document3 pagesNCP For Dehydration 1Khalid KhanNo ratings yet
- Reflection Video Why Mrs. X Die MATERNALDocument2 pagesReflection Video Why Mrs. X Die MATERNALQueenzee AsuncionNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPmftaganasNo ratings yet
- NCP Form Hyper ThermDocument1 pageNCP Form Hyper ThermomarskyNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired ComfortDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired ComfortGia P. de VeyraNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Oxy. Online BasedDocument5 pagesAssignment For Oxy. Online BasedNurhassem Nor AkangNo ratings yet
- A Family Nursing Care Plan OnDocument14 pagesA Family Nursing Care Plan OnMonique LeonardoNo ratings yet
- NCP DobDocument2 pagesNCP DobPaulo GeneraloNo ratings yet
- Hypovolemia (Fluid Deficit)Document2 pagesHypovolemia (Fluid Deficit)Lyn Reyes100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan DiarrheaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan DiarrheaAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesStudent Nurses' Community Nursing Care PlanMussaib MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Surgical PDFDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Surgical PDFDanielle Audrey100% (2)
- Seizure NCPDocument2 pagesSeizure NCPChristine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Drug-Study NCPDocument5 pagesDrug-Study NCPMURILLO, FRANK JOMARI C.No ratings yet
- Health EducationDocument5 pagesHealth EducationMichellin Lara VergaraNo ratings yet
- NCM 114 - NCPDocument3 pagesNCM 114 - NCPReysiela Mae ValinoNo ratings yet
- Reflective Journal 1Document4 pagesReflective Journal 1api-365605511No ratings yet
- Course Task - Traction BARTOLOME, JANIZE KHATEDocument2 pagesCourse Task - Traction BARTOLOME, JANIZE KHATEKhate BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Casepres NCPDocument6 pagesCasepres NCPdencio1992No ratings yet
- NCP Cough PneumoniaDocument2 pagesNCP Cough PneumoniaAirme Raz AlejandroNo ratings yet
- NCP PpwardDocument15 pagesNCP PpwardKarl Vincent Soso100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Imbalanced Nutrition: Less Than Body Requirements Disturbed Body Image Ineffective DenialDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan: Imbalanced Nutrition: Less Than Body Requirements Disturbed Body Image Ineffective DenialBrix ValdrizNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan. HypertensionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan. HypertensionKiara Shanelle Posadas AbrioNo ratings yet
- NCP FinalDocument4 pagesNCP FinalKathrina CraveNo ratings yet
- Cholera N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 pagesCholera N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Deficient Knowledge: Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Care Plans (NCP)Document3 pagesDeficient Knowledge: Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Care Plans (NCP)Vincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Healthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesHealthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeBenjamin CañalitaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Incarcerated Inguinal Hernia RightDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Incarcerated Inguinal Hernia RightTrisha Lapid MatulaNo ratings yet
- Nurses Notes Soapie Day 2Document3 pagesNurses Notes Soapie Day 2Sunny Al asadiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument10 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyChris CHris ChRis100% (1)
- Phenobarbital Risk For Injury EAMCDocument4 pagesPhenobarbital Risk For Injury EAMCkeitacNo ratings yet
- NCP of Endometrical CancerDocument2 pagesNCP of Endometrical CancerFrando kennethNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan2Document13 pagesNursing Care Plan2Nna ANn CastleNo ratings yet
- NCP Imbalanced NutritionDocument7 pagesNCP Imbalanced NutritionNora VarshavskiNo ratings yet
- CHA NCPDocument6 pagesCHA NCPMonty_Legaspi_5664No ratings yet
- NCP For Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument2 pagesNCP For Diabetic KetoacidosisLovely Cacapit100% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationHsintan HsuNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationKRISTINE BULACANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment: Multiple ChoiceDocument3 pagesChapter 4: Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment: Multiple ChoiceJamie100% (2)
- NCP For PostpartumDocument1 pageNCP For PostpartumMary Hope BacutaNo ratings yet
- Hemoflagellates TableDocument4 pagesHemoflagellates TableAbd Al Kareem RashedNo ratings yet
- Lived Experiences of Individuals With Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) : An Input To Infectious Disease Awareness and PreventionDocument12 pagesLived Experiences of Individuals With Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) : An Input To Infectious Disease Awareness and PreventionPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- FTT and PEMDocument38 pagesFTT and PEMdonaha87No ratings yet
- Acupuncture 123Document3 pagesAcupuncture 123Romi Brener83% (6)
- Late Pregnancy Bleeding (LPB) : Antepartum Hemorrhage (Aph) Dr. A. MutungiDocument3 pagesLate Pregnancy Bleeding (LPB) : Antepartum Hemorrhage (Aph) Dr. A. Mutungikhadzx100% (2)
- Peace Corps Vaccine Administration Schedule - TG 300 Medical Technical Guideline 300 - July 2008Document4 pagesPeace Corps Vaccine Administration Schedule - TG 300 Medical Technical Guideline 300 - July 2008Accessible Journal Media: Peace Corps Documents100% (1)
- Icra Longterms CareDocument19 pagesIcra Longterms CareFajarRachmadiNo ratings yet
- ParasitologyLec 3 Nematodes 2 PDFDocument6 pagesParasitologyLec 3 Nematodes 2 PDFDJ RelojNo ratings yet
- Toronto Notes - Cardiac SurgeryDocument32 pagesToronto Notes - Cardiac Surgerymicielij100% (1)
- Legendary NBME Rocks PicturesDocument84 pagesLegendary NBME Rocks PicturesNBMEmyselfandiNo ratings yet
- Connors and Other ADHD ScalesDocument3 pagesConnors and Other ADHD ScalesPragnya NidugondaNo ratings yet
- Baru Standar 7 S3ffkuh9brs1219brDocument191 pagesBaru Standar 7 S3ffkuh9brs1219brjumrainiNo ratings yet
- Gynecology Adnexal MassDocument2 pagesGynecology Adnexal MassgeNo ratings yet
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Workup - Laboratory Studies, Tests To Differentiate Type 1 From Type 2 DiabetesDocument3 pagesType 1 Diabetes Mellitus Workup - Laboratory Studies, Tests To Differentiate Type 1 From Type 2 DiabetesTrifosa Ika Septiana EryaniNo ratings yet
- Crohn Vs ColitisDocument5 pagesCrohn Vs Colitiswbarnes7No ratings yet
- Chioma M. Okeoma (Eds.) - Chikungunya Virus - Advances in Biology, Pathogenesis, and Treatment-Springer International Publishing (2016)Document202 pagesChioma M. Okeoma (Eds.) - Chikungunya Virus - Advances in Biology, Pathogenesis, and Treatment-Springer International Publishing (2016)sayeed_opso100% (1)
- Yale Insulin Infusion ProtocolDocument2 pagesYale Insulin Infusion ProtocolIffatNaeemNo ratings yet
- TESDA COVID-19 Test (Answer Keys)Document12 pagesTESDA COVID-19 Test (Answer Keys)ash mizushiNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia in Adults Clinical Manifestations, Definition, and CausesDocument1 pageHypoglycemia in Adults Clinical Manifestations, Definition, and CausesnovaNo ratings yet
- Toxoplasmosis in PregnancyDocument45 pagesToxoplasmosis in PregnancyTahta PambudiNo ratings yet
- AceDocument14 pagesAceJustice Ace DaprozaNo ratings yet
- AutismDocument4 pagesAutismMary WanjiruNo ratings yet
- Aortic Regurgitation PathophysiologyDocument1 pageAortic Regurgitation Pathophysiologydana100% (1)
- Rehab-Plans-and-Exercises Hip-Arthroscopy Protocol-For-Physiotherapy-Following-SurgeryDocument2 pagesRehab-Plans-and-Exercises Hip-Arthroscopy Protocol-For-Physiotherapy-Following-SurgeryMellow Moon RecordsNo ratings yet
- Female Genital Tract Cytopathology: PracticalDocument26 pagesFemale Genital Tract Cytopathology: PracticalNgotelo FunwiNo ratings yet
- Waiver For RSPC Cliniquing 2018 p2Document1 pageWaiver For RSPC Cliniquing 2018 p2Rebecca MaderalNo ratings yet
- Neuro Trauma: Nathan Mcsorley Speciality Trainee Neurosurgery 23B Ninewells HospitalDocument35 pagesNeuro Trauma: Nathan Mcsorley Speciality Trainee Neurosurgery 23B Ninewells HospitalnathanNo ratings yet
- Moisture LesionsDocument6 pagesMoisture LesionsMsPocketbook HoarderNo ratings yet