Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Para Lec Tables Phasmids1
Uploaded by
Blanche AltheaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Para Lec Tables Phasmids1
Uploaded by
Blanche AltheaCopyright:
Available Formats
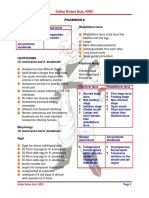
Intestinal Nematodes
Ancylostoma
Strongyloides stercoralis Ancylostoma doudenale Necator americanus Ancylostoma braziliense Ancylostoma caninum
ceylanicum
Threadworm Old World Hookworm American hookworm
Strongyloides American murderer
intestinalis New world hookworm
Anguillula stercoralis
Synonym
tiny nematode in soil
and in animal intestines
Cosmopolitan Europe, Asia; becoming Worldwide
Prevalent in tropical and worldwide but America
Geographic temperate regions restricted Australia
Distribution where sanitation is poor Middle East, North
Africa, Southern Europe
Indirect
Periods in
Direct
Development
Autoinfection
cylindroidal and stout attenuated at the
vertical curvature, anterior end
directed dorso-anteriad buccal capsule has
(bends in the same ventral and dorsal
direction as the body cutting plates
curvature) worms are strongly
pinkish or creamy in flexed dorsal ward the
Adult worm color anterior end
covered w/ tough amphidial, excretory,
cuticle and esophageal glands
has 5 glands all serve an exodigestive
Esophageal gland function
secretes ferment
campanulate bursa 7-9mm long 8mm 8mm 10mm
consisting of 3 lobes (1 bursa is long and wide
dorsal and 2 lateral) dorsal ray divides into 2
dorsal ray - 3 rays (bipartite)
(tripartite) copulatory spicules are
2 externodorsal rays- 2 long and slender and
lateral lobes contains 10 fused at the tip, forming
Male worm
rays a delicate barb
total no. of rays:13
2 spicules and cloaca;
spicules regulated by
the gubernaculum
conoidal posterior 9-11 mm long 10mm 14mm 14mm
has subterminal anal Vulva: middle or
opening somewhat anterior
Vulva: midadvertently at
Female worm the beginning of the
distal third of the body
/pavjumamilAMDG+ Page 1 5/7/2015
Intestinal Nematodes
oval or elliptical in shape resembles A. duodenale
65x40 microns but tend to be longer
colorless (not bile and somewhat
stained) elongated
2 layers (vitelline and daily egg output 9,000
hyaline membrane) eggs
Has segmented
protoplasm with 4 cannot be differentiated
blastomere with A. duodenale
Eggs
floats in saturated
solution of common salt
eggs not infective to
man
lays 25,000-30,000
eggs/day
2.2mm in length
semitransparent
filariform nematode w/
fine striated cuticle
Anterior: Slender
Posterior: short conical
end
Parasitic female Vulva: 1/3 from
posterior end
M
Uteri: single file 8-12
o
thin shelled, transparent
r
segmented ova
p
h
o
l Rhabditoid in form
o Parasitic male larger buccal chamber
g
y 0.7mm long
smaller than female
tail is curved ventrad
2 equal copulatory
Free living male
spicules
has gubernaculums
no caudal alae
1mm long
smaller than parasitic
female
typical rhabditoid free-
living nematode
double-bulbed muscular
esophageal pharynx
Free living intestine is straight
female Vulva: 2/5 from
posterior
Uteri: single column of
thin shelled, transparent
segmented ova
/pavjumamilAMDG+ Page 2 5/7/2015
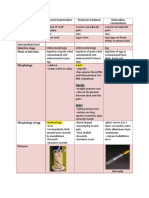
Intestinal Nematodes
225x16 microns larger than S. stercoralis
Anterior: Club shaped More attenuated
w/ post median posteriorly
constriction and a longer buccal cavity
posterior bulbus Smaller genital
esophagus primordium
conspicuous
primordium on the
Rhabditoid larva
ventral side halfway
down the midgut
buccal cavity: short
open mouth
Molt 4 times to become
free living adult
long, slender, non- larger than S. stercoralis
feeding pointed posterior end
550 microns in length infective stage to man
close mouth (urocanic acid)
long esophagus may remain viable in the
Filariform larva
tail with a notched soil for several weeks
appearance
infective to man
can swim in water
Adults are larger and Smaller and more
Size
thicker slender
Bends in the same Opposite direction to
Anterior end direction as the body body curvature
curvature
6 teeth large ventral 4 ventral semilunar Pair of large outer teeth Pair of larger outer 3 pairs of ventrad teeth
cutting teeth cutting plate Pair of small median teeth; pair of
Buccal capsule
teeth inconspicuous teeth
No of rays: 13 No of rays: 14 Broader, lateral rays, Small almost as broad as Long moderately
Dorsal ray: tripartite Dorsal ray: bipartite more curved, ray long, with short stunted slender rays
Copulatory Has 2 separate spicules, Has 2 spicules fused at supports are plump rays
bursa long and bristle like the tip forming a
delicate barb
Posterior end of Spine is present No spine
female
walking barefoot, larvae Skin penetration of Skin penetration of
can directly penetrate filariform larvae filariform larvae
Mode of Infection
exposed skin
Strongyloidiasis Ancylostomiasis Necatoriasis
Infection/Pathogen
Cochin China diarrhea Uncinariasis
esis
dermatitis: swelling, iron-deficiency anemia Classic hookworm
itching, larva currens hypothermia diseases
and mild hemorrhage at eosinophilia
the site where the skin protein malnutrition
has been penetrated stunted growth
Loffler's syndrome mental retardation
pneumonia like
symptoms
Clinical Symptoms tissue damage
sepsis
ulcers
Hyperinfection syndrom
(90% mortality rate)
/pavjumamilAMDG+ Page 3 5/7/2015
Intestinal Nematodes
1. Free living Cycle Filariform - adults - Filariform - adults -
2. Parasitic Cycle copulate - immature copulate - immature
2.1. Filariform larvae eggs (passed out with eggs (passed out with
Life Cycle 2.2. Rhabditoid feces) - mature eggs (in feces) - mature eggs (in
larvae soil) - rhabditoid larvae - soil) - rhabditoid larvae -
filariform larvae filariform larvae
Life Span 5-7 years 4-20 years
Feces stool stool
Sputum
Specimen of Choice duodenal or gastric
aspirates
Infective Stage Filariform Larvae Filariform Larvae Filariform Larvae
PAPS smears of Ovum Ovum
duodenal or gastric
aspirate - eggs,
rhabditoid larvae,
filariform larvae,
parasitic adult female
Ascitic fluid, CSF, feces,
and sputum - Filariform
Diagnostic Stage larvae
Stools and duodenal
aspirates - rhabditoid
larvae
Sputum- rhabditoid
larvae (pulmonary
infection)
Ivermectin with Benzimidazole Benzimidazole
albendazole antihelminthic such as antihelminthic such as
Treatment improved sanitation albendazole or albendazole or
practicing good hygiene mebendazole mebendazole
Pathogenicity More pathogenic less pathogenic
Hosts Man Man Dogs and cats Dogs and Cats Dogs
Habitat Large Intestine Large intestine
Immunologic tests: IHAT food of the worm: Cutaneous larva Cutaneous larva Cutaneous larva
and ELISA mucous membrane, free migrans: migrans: migrans:
Other diagnostic cells, plasma Does not produce larva produce larva migrans in produce larva migrans in
techniques: migrans in man man man
Other info
direct fecal smears
culturing fecal samples
on agar plates
/pavjumamilAMDG+ Page 4 5/7/2015
You might also like
- Week 7 Introduction To Nematodes PDFDocument5 pagesWeek 7 Introduction To Nematodes PDFewmedtechNo ratings yet
- Characteristics: Description: Ascaris Lumbricoides Trichuris Trichiura Enterobius Vermicularis Capillaria PhilippinensisDocument8 pagesCharacteristics: Description: Ascaris Lumbricoides Trichuris Trichiura Enterobius Vermicularis Capillaria PhilippinensisAlcera JemNo ratings yet
- Adult Tapeworm Is LargerDocument18 pagesAdult Tapeworm Is LargerAbby SiervoNo ratings yet
- P A R T: NematodesDocument21 pagesP A R T: NematodesGrazielle Almazan100% (2)
- Enperiment For Spotting-3Document18 pagesEnperiment For Spotting-3Debayan Bhattacharyya class:- 11-ANo ratings yet
- Veterinary Helminthology MidtermsDocument4 pagesVeterinary Helminthology Midtermshumanupgrade100% (1)
- Parasitology ReviewerDocument36 pagesParasitology ReviewerMark Justin OcampoNo ratings yet
- Goku Notes - Phasmids 2Document9 pagesGoku Notes - Phasmids 2Joulo YabutNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 18-Oct-2023Document12 pagesAdobe Scan 18-Oct-2023kavitasdewanganNo ratings yet
- NematodesDocument2 pagesNematodesRheila DuyaNo ratings yet
- 2 MosquitoDocument8 pages2 Mosquito173Swapnaneil BujarbaruahNo ratings yet
- Cestodes: Diphyllobothrium Latum, Broad or FishDocument2 pagesCestodes: Diphyllobothrium Latum, Broad or FishFrance Louie JutizNo ratings yet
- The NematodesDocument17 pagesThe NematodesCherry BucalingNo ratings yet
- FliesDocument25 pagesFliesSmpp MondhaNo ratings yet
- Phasmids 2Document6 pagesPhasmids 2Justin TayabanNo ratings yet
- 4BMT CmparaDocument4 pages4BMT Cmparajay primaNo ratings yet
- Nematodes Activity #3: AmericanusDocument7 pagesNematodes Activity #3: AmericanusVilllllNo ratings yet
- 1 Intestinal NematodesDocument2 pages1 Intestinal NematodesKaycee Gretz LorescaNo ratings yet
- Merge AbDocument17 pagesMerge AbEricsson CarabbacanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - Nematodes IDocument7 pagesLesson 8 - Nematodes IAnya IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Plus 2 PracticalDocument16 pagesPlus 2 Practicaljayantaroy783360No ratings yet
- HelminthsDocument10 pagesHelminthsMaureen Kate DuqueNo ratings yet
- Platyhelminthes - 6th Class PDFDocument23 pagesPlatyhelminthes - 6th Class PDFAbdulla Hil KafiNo ratings yet
- 107 ANIMALS PhylaDocument1 page107 ANIMALS Phylasamsung galaxyNo ratings yet
- Para Lab 2Document3 pagesPara Lab 2api-3743217100% (2)
- Cestodes: 1. Taenia Solium (Pork Tapeworm) & Taenia Saginata (Beef Tapeworm)Document18 pagesCestodes: 1. Taenia Solium (Pork Tapeworm) & Taenia Saginata (Beef Tapeworm)Genevee Ryeleen DelfinNo ratings yet
- Helminths 12Document34 pagesHelminths 12malakaiad212No ratings yet
- Parasitology PracticalsDocument106 pagesParasitology PracticalsELISHA ACHIANDONo ratings yet
- NematodaDocument30 pagesNematodaTagonna Di RaizelNo ratings yet
- Extraintestinal NematodesDocument4 pagesExtraintestinal NematodesOsannah Irish InsongNo ratings yet
- ZooLec Reviewer February 27Document6 pagesZooLec Reviewer February 27Charles GuillermoNo ratings yet
- HOOKWORMSDocument3 pagesHOOKWORMSRizzy VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology 2Document3 pagesParasitology 2Adel AlomarNo ratings yet
- M.03 THE STRONGYLIDA - Hookworms - Dr. AyochokDocument7 pagesM.03 THE STRONGYLIDA - Hookworms - Dr. AyochokJohn Louis AguilaNo ratings yet
- Merged PDF 2021 11 16T12 - 01 - 01Document15 pagesMerged PDF 2021 11 16T12 - 01 - 01Ericsson CarabbacanNo ratings yet
- Cestodes/ Tapeworms CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesCestodes/ Tapeworms CharacteristicsChinissa Ann LanonNo ratings yet
- 08 Chapter 4 Animal KingdomDocument11 pages08 Chapter 4 Animal KingdomAnusree M.SNo ratings yet
- NEMATODESDocument7 pagesNEMATODESRenz Gerard AmorNo ratings yet
- F. Buski F. Hepatica F. Gigantica C. Sinensis H. Heterophyes M. YokagawaiDocument3 pagesF. Buski F. Hepatica F. Gigantica C. Sinensis H. Heterophyes M. YokagawaiJoan Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Phylum NematodaDocument11 pagesPhylum NematodaKristine Aranna ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Workbook: Laboratory BIO32: Universiti Teknologi Mara (Uitm) Branch Sabah Campus Kota KinabaluDocument6 pagesWorkbook: Laboratory BIO32: Universiti Teknologi Mara (Uitm) Branch Sabah Campus Kota KinabaluMirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Guide QuestionDocument2 pagesParasitology Guide QuestionRoll BiNo ratings yet
- Cestodes 2020Document10 pagesCestodes 2020CDNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Notesss YehahahaDocument133 pagesIGCSE Biology Notesss YehahahaDIO yesNo ratings yet
- Parasitology-Lec 7 Lung FlukesDocument5 pagesParasitology-Lec 7 Lung Flukesapi-3743217100% (1)
- Biodiversity Part 2/2Document25 pagesBiodiversity Part 2/2Kim Say Chun / Sc.KIMNo ratings yet
- HOOKWORM TransDocument4 pagesHOOKWORM TransDavid Ryan MangawilNo ratings yet
- Week 2 (Lec-Lab) Mls 306 Clinical Parasitology Bsmls 3A: Ascaris LumbricoidesDocument4 pagesWeek 2 (Lec-Lab) Mls 306 Clinical Parasitology Bsmls 3A: Ascaris LumbricoidesHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- Nematodes For Quiz 1 RevisedDocument6 pagesNematodes For Quiz 1 RevisedAra NuesaNo ratings yet
- CESTODE1Document9 pagesCESTODE1Surminie MuksinNo ratings yet
- Comparative Anatomy - Protochordates and The Origin of CraniatesDocument16 pagesComparative Anatomy - Protochordates and The Origin of CraniatesjeannegiananNo ratings yet
- PARA NematodesDocument23 pagesPARA Nematodes12 Newton - Cayetano, Arafe Nicole A.No ratings yet
- Morphology para Lec 2Document8 pagesMorphology para Lec 2Wyenne Faye TagapanNo ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument13 pagesAnimal KingdomAanchal Pandey100% (2)
- CestodesDocument5 pagesCestodesGhina RizwanNo ratings yet
- Nematodes Cestodes, Trematodes NoteDocument3 pagesNematodes Cestodes, Trematodes NoteJanielle Medina FajardoNo ratings yet
- Trematodes: 2. MiracidiaDocument3 pagesTrematodes: 2. MiracidiaBikram ChohanNo ratings yet
- Leyte Normal University Science Unit: Lab Activity # 7 NematodaDocument11 pagesLeyte Normal University Science Unit: Lab Activity # 7 NematodaEdward Glenn AbaigarNo ratings yet
- BIONOTES2016 ChenityDocument83 pagesBIONOTES2016 ChenityMeerab Shah100% (1)
- Verification and Certification Against Non-Forum ShoppingDocument2 pagesVerification and Certification Against Non-Forum ShoppingBlanche AltheaNo ratings yet
- Ra 9262 IrrDocument12 pagesRa 9262 IrrBlanche AltheaNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of Loss TemplateDocument1 pageAffidavit of Loss TemplateBlanche AltheaNo ratings yet
- Civil LawDocument53 pagesCivil LawBlanche AltheaNo ratings yet
- Summary of The FRIA LawDocument13 pagesSummary of The FRIA LawKulit_Ako1100% (3)
- Banat V Comelec G.R. No. 179271 April 21, 2009Document4 pagesBanat V Comelec G.R. No. 179271 April 21, 2009Grace RosalesNo ratings yet
- Suggested Format of Answering For The Bar ExamsDocument4 pagesSuggested Format of Answering For The Bar ExamsBlanche AltheaNo ratings yet
- Eviste V Alameda DigestDocument2 pagesEviste V Alameda DigestBlanche AltheaNo ratings yet
- Taxation ReviewerDocument145 pagesTaxation ReviewerJingJing Romero95% (96)
- Suggested Format of Answering For The Bar ExamsDocument4 pagesSuggested Format of Answering For The Bar ExamsBlanche AltheaNo ratings yet
- BARBERS Vs COMELECDocument13 pagesBARBERS Vs COMELECAyvee BlanchNo ratings yet
- People V DoriaDocument2 pagesPeople V DoriaBlanche AltheaNo ratings yet
- Aquino Vs AureDocument14 pagesAquino Vs AureBlanche AltheaNo ratings yet
- 12 Chavez Vs CA PDFDocument7 pages12 Chavez Vs CA PDFYen YenNo ratings yet
- People Vs ValdezDocument2 pagesPeople Vs ValdezEvangelyn EgusquizaNo ratings yet
- DASR - Draft Articles On State ResponsibilityDocument18 pagesDASR - Draft Articles On State ResponsibilityMac ItaraldeNo ratings yet
- Rule 5, Governing Intra-Corp ControversyDocument6 pagesRule 5, Governing Intra-Corp ControversyBlanche AltheaNo ratings yet
- 2007 Remedial Law Bar QuestionsDocument10 pages2007 Remedial Law Bar QuestionsBlanche AltheaNo ratings yet
- DASR - Draft Articles On State ResponsibilityDocument18 pagesDASR - Draft Articles On State ResponsibilityMac ItaraldeNo ratings yet
- Ra 7438Document2 pagesRa 7438asnia07No ratings yet
- Lecture Note 3Document29 pagesLecture Note 3Blanche AltheaNo ratings yet
- Accountability of Public Officers CasesDocument35 pagesAccountability of Public Officers CasesBlanche AltheaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Bacteria: Morphology Structure FunctionDocument49 pagesAnatomy of Bacteria: Morphology Structure FunctionBlanche AltheaNo ratings yet
- DASR - Draft Articles On State ResponsibilityDocument18 pagesDASR - Draft Articles On State ResponsibilityMac ItaraldeNo ratings yet
- DASR - Draft Articles On State ResponsibilityDocument18 pagesDASR - Draft Articles On State ResponsibilityMac ItaraldeNo ratings yet
- 2007 Remedial Law Bar QuestionsDocument10 pages2007 Remedial Law Bar QuestionsBlanche AltheaNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis 4 Full TextDocument60 pagesCase Analysis 4 Full TextDaryl Noel TejanoNo ratings yet
- Para Lec Aphasmid NematodesDocument2 pagesPara Lec Aphasmid NematodesBlanche AltheaNo ratings yet
- DASR - Draft Articles On State ResponsibilityDocument18 pagesDASR - Draft Articles On State ResponsibilityMac ItaraldeNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Animalia: Phylum Summary TableDocument2 pagesKingdom Animalia: Phylum Summary TableRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Plant Pathogenic NematodesDocument34 pagesCharacteristics of Plant Pathogenic NematodesCecirly Gonzales Puig100% (4)
- Breeding Priorities and StrategiesDocument15 pagesBreeding Priorities and StrategiesDeepak MewarNo ratings yet
- 12 PDFDocument172 pages12 PDFAlfaraby100% (2)
- UNIT 1 Introduction To Food Microbiology MicrobiologyDocument20 pagesUNIT 1 Introduction To Food Microbiology MicrobiologyHarsh DwivediNo ratings yet
- 05 Animal Biology - Acoelomates & PseudocoelomatesDocument35 pages05 Animal Biology - Acoelomates & PseudocoelomatesArchy HydraNo ratings yet
- Helminths (Nematodes)Document42 pagesHelminths (Nematodes)RaunaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Nematode Study GuideDocument3 pagesChapter 15 Nematode Study GuideKristine Marie PateñoNo ratings yet
- LagawDocument3 pagesLagawMarjon Velasco Dela Cerna IINo ratings yet
- Algae and Nutrient Problems in HydroponicsDocument14 pagesAlgae and Nutrient Problems in HydroponicsHarsha_2994No ratings yet
- Intestinal NematodesDocument88 pagesIntestinal NematodesVincent Manganaan100% (1)
- 01 Februari 2021Document13 pages01 Februari 2021Nadyatul IlmaNo ratings yet
- Migs NematodesDocument61 pagesMigs NematodesJonas DatuNo ratings yet
- Phylum Nematoda (Revised) 2014 EditionDocument188 pagesPhylum Nematoda (Revised) 2014 EditionArchieDuqueNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Midterms ReviewerDocument39 pagesParasitology Midterms ReviewerMonique Eloise GualizaNo ratings yet
- Plant Pathology Course Material (CPS 2101) - 1Document110 pagesPlant Pathology Course Material (CPS 2101) - 1Yomifi AberaNo ratings yet
- Micro WormDocument3 pagesMicro WormmalditapoliticaprNo ratings yet
- Abstracts: Society of NematologistsDocument39 pagesAbstracts: Society of NematologistsFilani AyomideNo ratings yet
- EED 5 Unit 4Document17 pagesEED 5 Unit 4Lara Mariz FragataNo ratings yet
- Plant NematologyDocument463 pagesPlant Nematologydouglasman100% (2)
- Movento Insecticide - Nematode Damage Case StudyDocument2 pagesMovento Insecticide - Nematode Damage Case StudyMovento InsecticideNo ratings yet
- Sci8 Q4 Mod6Document30 pagesSci8 Q4 Mod6Alessa LamesNo ratings yet
- Resumé TEC English Cours L2Document45 pagesResumé TEC English Cours L2Ayoub DJIDJELLINo ratings yet
- Week9&10 LEC Clinical Parasitology NEMATODESDocument18 pagesWeek9&10 LEC Clinical Parasitology NEMATODESSamuel ReyesNo ratings yet
- Detection of Plant Parasitic Nematodes in The SoilDocument6 pagesDetection of Plant Parasitic Nematodes in The SoilLuisa ValdésNo ratings yet
- Rebearth Results in Pictures V22Document24 pagesRebearth Results in Pictures V22cafebuenoNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument23 pagesPhysics FormulasViral AssassinNo ratings yet
- NematodesDocument9 pagesNematodesMomo ShinNo ratings yet
- Unit 1, Diversity of Living Things, Unit Test - 1Document7 pagesUnit 1, Diversity of Living Things, Unit Test - 1hewleet100% (1)
- Parasitology Ch1 (Highlighted)Document165 pagesParasitology Ch1 (Highlighted)Bruce Bryan BautistaNo ratings yet