Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Skema Fizik Kertas 2
Uploaded by
hakimCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Skema Fizik Kertas 2
Uploaded by
hakimCopyright:
Available Formats
4531/2
PHYSICS
KERTAS 2
MAJLIS PENGETUA SEKOLAH MENENGAH
(CAWANGAN PULAU PINANG)
MODUL LATIHAN BERFOKUS SPM 2016
FIZIK 2
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
UNTUK KEGUNAAN PEMERIKSA SAHAJA
Nota:
Skema pemarkahan ini
Dalam Bahasa Inggeris sahaja
Skema ini mengandungi 8 halaman bercetak
2
SECTION A
MARK
NO. MARKING SCHEME
SUB TOTAL
1(a) Voltage // Potential difference 1
(b) Zero error 1
(c) S 1
(d) Instrument S has the smallest scale division. // Scale division of
1
Instrument S is smaller than Instrument Y. 4
2(a)(i) Same 1
(a)(ii) 100
P=
0.02 1
= 5000 Pa 1
(b) Pascals principle 1
(c) Part of the applied force will be used up to compress the air
bubbles. // The pressure applied is not transmitted equally in all 1
direction throughout the fluid. 5
3(a)(i) The impulsive force acted on the egg is small. 1
(a)(ii) The egg will crack. 1
(b)(i) Zero 1
(b)(ii) 0 = m1 v1 + m2 v2
0 = (45)v1 + (60)(2) 1
v1 = 2.67 m s1 1
(b)(iii) Principle of conservation of momentum 1 6
Doping is a process of adding a certain amount of specific
4(a) 1
impurities to pure semiconductors to increase their conductivity.
(b)(i) Diode B Reverse bias 1
(b)(ii) To allow current flow in one direction only. 1
(c)(i) D3 1
(c)(ii) 1
(c)(iii) Capacitor 1
The charging and discharging process of the capacitor reduces 7
(c)(iv) 1
the ripple of the waves.
4531/2 (PP) [Lihat halaman sebelah
3
Force of gravity acting on the object // mass x acceleration due to
5(a) 1
gravity // mg (explain symbol)
(b)(i) The weight of cargo ship B is bigger than cargo ship A 1
(b)(ii) The volume of water displaced in Diagram 5.2 is higher than 1
Diagram 5.1
(c) Buoyant force 1
(d) As volume of water displaced increases, buoyant force increases. 1
(e) Archimedes Principle 1
(f) Sinks 1
Sea is denser than river 1 8
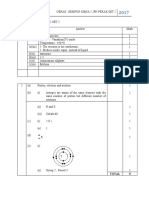
6(a) Magnetic field is the area that experiences the force of attraction 1
or force of repulsion
(b)(i) Zero//No change//Centre 1
(b)(ii) Pointer deflect / Show reading//Not pointing to zero/centre 1
(b)(iii) The greater the deflection of the pointer, the current increase 1
(b)(iv) The current increase when the relative motion of the conductor
1
and magnet increases
(b)(v) Faradays Law 1
(c)(i) Deflects in opposite direction 1
(c)(ii) Angle of deflection increases 1 8
The energy transferred from a hot object to a cold object // the
7(a) 1
energy transfer because of the difference in temperature
(b) The temperature of the forehead is higher than the temperature 1
of the pad.//Heat is transferred from the forehead to the pad until
thermal equilibrium is reached.//Cooling pad absorbs bodys heat
from forehead.
When thermal equilibrium is reached, both forehead and cooling 1
pad has same temperature.
36 15 1
(c) Q = 0.030 4.3 (36 15) 1
2.709 J with correct unit 1
-Increase the mass of the gel 1
-The heat removed increases with the mass of the gel // the heat 1
removed is directly proportional to the mass
(d) -Use a gel with higher specific heat capacity 1
-The heat removed increases with the specific heat capacity of 1
the gel // the heat removed is directly proportional to the specific
heat capacity of the gel 10
4531/2 (PP) [Lihat halaman sebelah
4
Unstable isotopes which decay and give out radioactive
8(a)(i) 1
emissions
Short half-life
(b)(i) 2
Long-time of exposure can damage cell
Gamma ray
(b)(ii) 2
High penetrating power
Liquid
(b)(iii) 2
Can flow easily in body
(c) Radioisotop Q 1
The time required by a particular radioactive substance to
(d)(i) 1
decay to half of its initial amount.
(d)(ii) To become stable 2
T = 32 / 8
=4T
(d)(iii) 1
200g 100g 50g 25g 12.5g 12
4531/2 (PP) [Lihat halaman sebelah
5
SECTION B
NO. MARK
ANSWER
SUB TOTAL
Refractive index is a measurement of the ability of a medium to slow
9 (a) 1
down speed of light that pass through it.
Angle of refraction in 9.2 > 9.1
(b)(i) Density of the glass block in 9.1 > 9.2
Refractive Index in 9.1 > 9.2 5
(b)(ii) The higher the density, the smaller the angle of refraction.
(b)(iii) The higher the refractive index, the smaller the angle of refraction.
During day time, The air at the surface of the road is hotter //
The density of air near the road is lower
The light ray propagate from more dense to less dense
When the incident angle is greater than the critical angle, total
(c) 4
internal reflection occurs
Observer can see the image of the cloud as a mirage
or Draw complete diagram with label
Characteristics material Reason
The refractive Less dense at the
index of the outer outer layer and Total internal reflection
layer and the more dense at easily to occur
inner layer the inner layer
Strength High Not easily break
(d) Easily bend // Easy to 10
Flexibility High pass through inner parts
of human body
To make it smaller // Easy
Thickness Less to pass through inner
parts of human body
Density Less / Low Lighter 20
4531/2 (PP) [Lihat halaman sebelah
6
NO. MARK
ANSWER
SUB TOTAL
The spreading of waves after passing through a gap or
10 (a) 1
obstacle
Wavelength remains unchanged
Frequency remains unchanged
(b) 4
Speed remains unchanged
Amplitude becomes smaller compared to the incident waves
Tuning fork without plastisine has higher frequency and
short wavelength
Sound will not diffracted effectively
Only student Q can hear the sound clearly
(c) Max 5
Tuning fork with plastisine has lower frequency and longer
wavelength
Sound diffracted effectively
All students can hear the sound clearly
Modification Justification
Radiowaves Able to travel for a long distance
At the top hill To get wider signal coverage
(d) Long wavelength Easier for wave to diffract when 10
passing through obstacles
Strong signal Overcome the damping effect
Add signal booster Amplify the signal 20
4531/2 (PP) [Lihat halaman sebelah
7
SECTION C
NO. MARK
MARKING SCHEME
SUB TOTAL
The ability of the material to return to their original shape and size
11(a) when the force exerted on it is removed. 1
-There are two types of force
-Attraction and repulsive force between the particles of the solid.
-When the solid is stretched, the molecules displaced away from
each other
(b) 5
-Attractive forces are acting to oppose the stretching
-When the solid is compressed, the molecules displaced closer to
each other
-Repulsive forces are acting to oppose the compression
Characteristics
Reason
material
enough space for the spring to be
Diameter is small
installed//stiffer
can support motorcylist up to 100kg//
Elastic limit is high Can withstand bigger weight
(c) 10
Spring constant is small compression of the spring
high
Natural frequency to reduce
is low bouncing//bumping,comfortable for user
D is choosen because it has a small diameter , highest elastic
limit ,highest spring constant and low natural frequency
Spring Q
(d)(i) 2
Spring constant is higher // the gradient is higher
Work difference = (FQ - F P ) x
= ( 4 - 2 ) ( 0.08 )
(d)(ii) 2
= 0.08 J 20
4531/2 (PP) [Lihat halaman sebelah
8
NO. MARK
MARKING SCHEME
SUB TOTAL
High melting point
Can withstand high temperature/heat // does not melt easily
12(a) 4
Not easily oxidized
Can last longer
Maximum current flowing through the fuse is 5 A
(b) 1
Characteristics material reason
less space needed // to carry
limited electrical current // less
Thickness of fuse wire is mass hence low heat capacity //
thin shorter time to heat up to melting
point and blow
Type of cartridge is
Can withstand higher temperature
(c) ceramic 10
Maximum rating must be slightly
Amount of rating IS 13 A
higher than normal current
For fast blow // melt faster when
Melting point is low
excessive current flow // easy to
cut the current flow
R is choosen because 10 it has thin thickness of wire, ceramic
cartridge, 13A fuse rating, low melting point
I = 12/240
(d)(i) 2
= 0.05A
1
(d)(ii) (12-10) W // 2W
Efficiency = 10/12 x 100%
(d)(iii) 2
= 83.3% 20
4531/2 (PP) [Lihat halaman sebelah
You might also like
- SPM Percubaan 2007 SBP Physics Paper 2 Marking SchemeDocument8 pagesSPM Percubaan 2007 SBP Physics Paper 2 Marking SchemeChinWynn.com100% (2)
- PAHANG-Answer Physics P1 P2 P3-Trial SPM 2009Document16 pagesPAHANG-Answer Physics P1 P2 P3-Trial SPM 2009kamalharmozaNo ratings yet
- MELAKA-answer Physics P2-Trial SPM 2009Document5 pagesMELAKA-answer Physics P2-Trial SPM 2009kamalharmozaNo ratings yet
- Exercise Bab 4 f4Document1 pageExercise Bab 4 f4Yatie Jaafar67% (3)
- Paper 2 Form 4 2020Document28 pagesPaper 2 Form 4 2020Yusfalina Mohd YusoffNo ratings yet
- Mid Year Exam Physics Paper 2 Form 4 2010Document19 pagesMid Year Exam Physics Paper 2 Form 4 2010widyahani100% (1)
- Add Maths Perfect Score Module Form 4 Marking Scheme Set 1 & Set 2Document19 pagesAdd Maths Perfect Score Module Form 4 Marking Scheme Set 1 & Set 2Yeow Pow ChooNo ratings yet
- FEB 2015 Maf151 Test 1Document3 pagesFEB 2015 Maf151 Test 1Aisyah Mohd YusreNo ratings yet
- 7 Skema Kimia K1 & K2 Trial SPM Terengganu MPP3 2019Document13 pages7 Skema Kimia K1 & K2 Trial SPM Terengganu MPP3 2019SaravananNo ratings yet
- SPM 2018 Math Additional Paper 1 Marking SchemeDocument5 pagesSPM 2018 Math Additional Paper 1 Marking Schemeallycat97No ratings yet
- Jawapan Soalan Ramalan Sains Kertas 2Document8 pagesJawapan Soalan Ramalan Sains Kertas 2syahidatul nurhanani100% (1)
- KBSM t4 Skema Kimia k2Document9 pagesKBSM t4 Skema Kimia k2kancil416670No ratings yet
- Tg4 Praktis Jawapan PDFDocument13 pagesTg4 Praktis Jawapan PDFMazni HanisahNo ratings yet
- SKEMA - SOALAN ALA FORMAT PSPM I Set 1 SK015 2020Document7 pagesSKEMA - SOALAN ALA FORMAT PSPM I Set 1 SK015 2020MOHAMAD ARMAN AZMENo ratings yet
- Skema Jawp Soalan Objektif Gerak Gempur 2Document1 pageSkema Jawp Soalan Objektif Gerak Gempur 2SK Pos TenauNo ratings yet
- Soalan Kertas 2 BiologiDocument15 pagesSoalan Kertas 2 BiologiHaslinda SheikhNo ratings yet
- Displacement Reactions of Metals in Salt SolutionsDocument4 pagesDisplacement Reactions of Metals in Salt SolutionsAini HasshimNo ratings yet
- SPM Biology 2007 k2Document22 pagesSPM Biology 2007 k2pss smk selandar67% (3)
- 2 Heat of PrecipitationDocument22 pages2 Heat of PrecipitationSyawal AnizamNo ratings yet
- MRSM-ANSWER PHYSICS-Trial SPM 2008Document20 pagesMRSM-ANSWER PHYSICS-Trial SPM 2008kamalharmoza100% (3)
- Riang Belajar KSSM Fizik TKT 5 (English Answers) PG 1-9Document9 pagesRiang Belajar KSSM Fizik TKT 5 (English Answers) PG 1-9汤思慧100% (1)
- Sample Questions and Answers For Paper 3 Section B1Document10 pagesSample Questions and Answers For Paper 3 Section B1Adsham100% (3)
- Graphing spring constant and surface area pressure relationshipDocument6 pagesGraphing spring constant and surface area pressure relationshipSeraMa JambuiNo ratings yet
- Kedah-Answer Physics P1 P2 P3-Trial SPM 2009Document16 pagesKedah-Answer Physics P1 P2 P3-Trial SPM 2009kamalharmozaNo ratings yet
- 2006 MRSM With AnswerDocument70 pages2006 MRSM With AnswerccffyNo ratings yet
- DIFFRACTION OF WAVES EXPLAINEDDocument53 pagesDIFFRACTION OF WAVES EXPLAINEDPNA100% (1)
- 6.2 Graf Laju-Masa 20200513 PDFDocument8 pages6.2 Graf Laju-Masa 20200513 PDFJiajia LauNo ratings yet
- Terangganu-Answer Physics P2-Trial SPM 2007Document15 pagesTerangganu-Answer Physics P2-Trial SPM 2007kamalharmoza100% (1)
- 03-Physic F5 2018-ElectricityDocument32 pages03-Physic F5 2018-ElectricitySreedrannNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Paper 1 2 3 SBP Trial SPM 2009Document21 pagesMarking Scheme Paper 1 2 3 SBP Trial SPM 2009Mohd Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- Skema Fizik Kertas 2 Trial PerlisDocument9 pagesSkema Fizik Kertas 2 Trial Perlisenasizuka100% (1)
- Asid, Bes Dan GaramDocument6 pagesAsid, Bes Dan GaramTENGKU AHMAD NAQIUDDIN BIN TENGKU NADZUAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Skema Fizik SPM Trial Perak 2009Document16 pagesSkema Fizik SPM Trial Perak 2009fizmie100% (2)
- Bab 07 - ElektrikDocument39 pagesBab 07 - ElektrikAl Nazuris100% (2)
- Skema Jawapan Kimia p2Document12 pagesSkema Jawapan Kimia p2HenrySeow50% (8)
- Trial Pahang Answers For Physics Paper 1 Trial 2010Document16 pagesTrial Pahang Answers For Physics Paper 1 Trial 2010lilysuhanyNo ratings yet
- W5 2020 Penang Addmath (Module 2) K1 SkemaDocument12 pagesW5 2020 Penang Addmath (Module 2) K1 SkemaJacelynNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics Project Work - Statistics and Index NumberDocument26 pagesAdditional Mathematics Project Work - Statistics and Index NumberNur Syahirah90% (10)
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument65 pagesCell Structure and FunctionIsmaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- Skema Kertas 2 KimiaDocument9 pagesSkema Kertas 2 KimiaariesNo ratings yet
- Kertas 2 PPT T4 SPM 2017Document19 pagesKertas 2 PPT T4 SPM 2017Mastura Hussin0% (1)
- (Bahagian C)Document22 pages(Bahagian C)Siti Arbaiyah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Modul Peningkatan Prestasi Tingkatan 5 Bahasa InggerisDocument11 pagesModul Peningkatan Prestasi Tingkatan 5 Bahasa InggerisYap Zi MiNo ratings yet
- SKEMA GERAK GEMPUR KIMIA 2 JPN PERAK SET 2 NewDocument8 pagesSKEMA GERAK GEMPUR KIMIA 2 JPN PERAK SET 2 NewZulkefliNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 2.SPMDocument19 pagesPhysics Paper 2.SPMRamliRem100% (1)
- Selangor-Answer Physics P2-Trial SPM 2009Document4 pagesSelangor-Answer Physics P2-Trial SPM 2009kamalharmoza100% (3)
- Mka2 Ap2 FZ t5 PHG 2016Document8 pagesMka2 Ap2 FZ t5 PHG 2016renuNo ratings yet
- Peperiksaan Percubaan SBP Fizik 2011 Marking Scheme For Physics Paper 2Document8 pagesPeperiksaan Percubaan SBP Fizik 2011 Marking Scheme For Physics Paper 2Lee Li JieNo ratings yet
- Physics principles and formulasDocument3 pagesPhysics principles and formulasahsohaNo ratings yet
- Physics Ans SBP Trial 2008 (Edu - Joshuatly.com)Document14 pagesPhysics Ans SBP Trial 2008 (Edu - Joshuatly.com)NUR AQILAH AUNI BINTI SUHAIMI MoeNo ratings yet
- SPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Physics AnswersDocument14 pagesSPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Physics AnswersChinWynn.com80% (5)
- SPM Phy Ans (Kelantan)Document15 pagesSPM Phy Ans (Kelantan)SimPor100% (1)
- 5 Skema Fizik K2 Trial SPM PPD Jasin Melaka 2019Document8 pages5 Skema Fizik K2 Trial SPM PPD Jasin Melaka 2019dalilaNo ratings yet
- Physics P1,2,3 Melaka 08 SkemaDocument13 pagesPhysics P1,2,3 Melaka 08 SkemaMohd Khairul Anuar100% (4)
- SPM Physics Trial SBP 2010 March - Marking SchemeDocument14 pagesSPM Physics Trial SBP 2010 March - Marking SchemeYudhisthiraNo ratings yet
- SEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH KEMENTERIAN PELAJARAN MALAYSIA PHYSICSDocument8 pagesSEKOLAH BERASRAMA PENUH KEMENTERIAN PELAJARAN MALAYSIA PHYSICSAudrey Joan AnthoniusNo ratings yet
- Skima T4 Fizik 18Document5 pagesSkima T4 Fizik 18murniNo ratings yet
- Selangor-Answer Physics P2-Trial SPM 2007Document7 pagesSelangor-Answer Physics P2-Trial SPM 2007kamalharmozaNo ratings yet
- Skema Trial Kelantan 2010 Physics Edit 1Document14 pagesSkema Trial Kelantan 2010 Physics Edit 1lilysuhanyNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Physics P1P2P3 SPM Kelantan 2009Document9 pagesMarking Scheme Physics P1P2P3 SPM Kelantan 2009Mohd Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- 3 Vertebrates 8.4.2019Document33 pages3 Vertebrates 8.4.2019hakimNo ratings yet
- 12 ways to travel from A to CDocument10 pages12 ways to travel from A to ChakimNo ratings yet
- MR KilmerDocument2 pagesMR KilmerhakimNo ratings yet
- 3 Vertebrates ContDocument89 pages3 Vertebrates ConthakimNo ratings yet
- Biology Cell ModuleDocument21 pagesBiology Cell ModulehakimNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes: Chapter 16: Cellular RespirationDocument24 pagesBiology Notes: Chapter 16: Cellular RespirationhakimNo ratings yet
- Should The Age of Driving Be Raised PDFDocument2 pagesShould The Age of Driving Be Raised PDFhakimNo ratings yet
- 2a Invertebrates Cont.Document44 pages2a Invertebrates Cont.hakim100% (1)
- Invertebrates: Powerpoint Lectures ForDocument58 pagesInvertebrates: Powerpoint Lectures ForhakimNo ratings yet
- Verb Conjugations: Eat in English TensesDocument1 pageVerb Conjugations: Eat in English TenseshakimNo ratings yet
- English VocabularyDocument50 pagesEnglish VocabularyhakimNo ratings yet
- BA Ba Ba Ba BA BB AA BB Aa BB AA BB Aa Ba BB Aa BB Aa BB Aa BB Aa Ba BB AA BB Aa BB AA BB Aa Ba BB Aa BB Aa BB Aa BB AaDocument3 pagesBA Ba Ba Ba BA BB AA BB Aa BB AA BB Aa Ba BB Aa BB Aa BB Aa BB Aa Ba BB AA BB Aa BB AA BB Aa Ba BB Aa BB Aa BB Aa BB AahakimNo ratings yet
- Draf DeadlineDocument1 pageDraf DeadlinehakimNo ratings yet
- Should The Age of Driving Be RaisedDocument2 pagesShould The Age of Driving Be RaisedhakimNo ratings yet
- NO Molecular Orbital Theory: Energy Diagram: Less Electronegative More ElectronegativeDocument1 pageNO Molecular Orbital Theory: Energy Diagram: Less Electronegative More Electronegativehakim100% (1)
- Limiting ReagentDocument1 pageLimiting ReagenthakimNo ratings yet
- Modul 1 Biologi Kertas 2 Soalan BHG - ADocument16 pagesModul 1 Biologi Kertas 2 Soalan BHG - ANoor Hidayah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Biological Sciences Institute Concrete Strength Mixing TechniquesDocument2 pagesBiological Sciences Institute Concrete Strength Mixing Techniqueshakim0% (1)
- ServiceRotation 080911 PDFDocument23 pagesServiceRotation 080911 PDFhakimNo ratings yet
- Dr. R.A. Siddique M.V.SC PHD Scholar National Dairy Research Institute Karnal, (Haryana) 132001 IndiaDocument20 pagesDr. R.A. Siddique M.V.SC PHD Scholar National Dairy Research Institute Karnal, (Haryana) 132001 IndiahakimNo ratings yet
- Tutorial (1) Fizik - Sem 1Document7 pagesTutorial (1) Fizik - Sem 1hakimNo ratings yet
- I Think 2018Document9 pagesI Think 2018hakimNo ratings yet
- Step 1: Obtain A Virus. The Best Way To Do This Is To Hang Around Some Sick PeopleDocument3 pagesStep 1: Obtain A Virus. The Best Way To Do This Is To Hang Around Some Sick PeoplehakimNo ratings yet
- Trial Kedah Biologi SPM 2015 k2 Skema PDFDocument13 pagesTrial Kedah Biologi SPM 2015 k2 Skema PDFhakimNo ratings yet
- Kbat Penang 2016Document2 pagesKbat Penang 2016hakimNo ratings yet
- Differentiation QuestionsDocument7 pagesDifferentiation QuestionsHsi Ning TingNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Modul Fizik Kertas 1Document1 pageJawapan Modul Fizik Kertas 1hakimNo ratings yet
- 8.isotonik SolutionDocument3 pages8.isotonik SolutionCheq ChentaNo ratings yet
- Skema Kertas 1Document6 pagesSkema Kertas 1Jacie KoeNo ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument2 pagesPHYSICSlkNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/43Document24 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/43agnesasus123No ratings yet
- Questions and Probs On RadioactivityDocument10 pagesQuestions and Probs On RadioactivityR. BALAKRISHNAN50% (2)
- Nuclear Chemistry and EnergyDocument18 pagesNuclear Chemistry and EnergyJm EscobarNo ratings yet
- Genchem 1 NOTESDocument14 pagesGenchem 1 NOTESGwend MemoracionNo ratings yet
- Using Phet Simulahons For Chemistry Inquiry: Free Research - Based Resources On The WebDocument4 pagesUsing Phet Simulahons For Chemistry Inquiry: Free Research - Based Resources On The WebLiliana GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Force LPDocument9 pagesNuclear Force LPAnonymous NXn6teNo ratings yet
- Cape Physics 2009 U2 p1Document20 pagesCape Physics 2009 U2 p1hahaNo ratings yet
- Ev Exam 3Document9 pagesEv Exam 3Rachelle Danya Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument11 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationKabir MalviyaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-V Radio Isotopes, Inorganic ChemistryDocument19 pagesUNIT-V Radio Isotopes, Inorganic ChemistrySimham VenuNo ratings yet
- PH 509 Computational Physics Lab AssignmentsDocument2 pagesPH 509 Computational Physics Lab AssignmentsSUBHASISH GUHANo ratings yet
- CoMo-170 DIN A 6 - ME MED - V3 78 - 15-06Document153 pagesCoMo-170 DIN A 6 - ME MED - V3 78 - 15-06Sohrab AbbasNo ratings yet
- Quiz Mock Exam 1 - UngradedDocument61 pagesQuiz Mock Exam 1 - Ungradedapi-635954562No ratings yet
- Transmutation and Nuclear Fission - NotesDocument6 pagesTransmutation and Nuclear Fission - Notesapi-327272079No ratings yet
- MCAT Review Physics Notes (Selected)Document38 pagesMCAT Review Physics Notes (Selected)Chris_Barber09100% (2)
- Evidence For A Young World D Russell Humphreys PDFDocument12 pagesEvidence For A Young World D Russell Humphreys PDFBogdanel MorhyNo ratings yet
- 960 SP Physics 2012Document135 pages960 SP Physics 2012Mohd SharulniZamNo ratings yet
- Cfmi Cfm56 NDTM Cfmi-Tp - nt.11 Rev 36 May 31, 2000Document392 pagesCfmi Cfm56 NDTM Cfmi-Tp - nt.11 Rev 36 May 31, 2000gm&o100% (3)
- You Will Survive DoomsdayDocument24 pagesYou Will Survive DoomsdayJan Frederik Valkenberg Castro100% (3)
- ,$ ($6DIHW/6WDQGDUGV: 6wrudjhri 5Dglrdfwlyh:DvwhDocument67 pages,$ ($6DIHW/6WDQGDUGV: 6wrudjhri 5Dglrdfwlyh:DvwhAdilNo ratings yet
- NRE 3112 Laboratory 1 Electronics - Pulse Analysis, SCA, MCADocument8 pagesNRE 3112 Laboratory 1 Electronics - Pulse Analysis, SCA, MCAOmnipotentEntityNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Reactions and Radioactivity ExplainedDocument2 pagesNuclear Reactions and Radioactivity ExplainedcristalbeamNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics QuestionsDocument11 pagesNuclear Physics Questionshamza5baigNo ratings yet
- PostDoc Position at INFN/LegnaroDocument1 pagePostDoc Position at INFN/LegnaroYoud WiishNo ratings yet
- Radiation Safety Data Sheet: Chemical Symbol: Ir Atomic Weight: 192Document2 pagesRadiation Safety Data Sheet: Chemical Symbol: Ir Atomic Weight: 192Iksan Adityo MulyoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 - Nuclear Chemistry 19.1 Nuclear Stability and Radioactive DecayDocument14 pagesChapter 19 - Nuclear Chemistry 19.1 Nuclear Stability and Radioactive Decaykaushik247No ratings yet
- Physics WaecDocument31 pagesPhysics WaecTunde IpayeNo ratings yet
- FinanceDocument5 pagesFinanceGeorge Nicole Baybayan100% (2)