Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ParticlesSM PDF
Uploaded by
Enrique Escalante EchagüeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ParticlesSM PDF
Uploaded by
Enrique Escalante EchagüeCopyright:
Available Formats
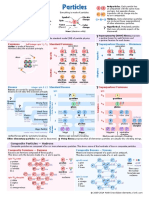
Spin.
Spin is a quantum property of
particles. Bosons have integer spin.
Fermions have half-integer spin.
Particles u u
Antiparticles. Each particle has
an antiparticle with the same mass
and spin, but opposite charge.
A particle with non-zero spin has Everything is made of particles. A particle with no charge may be
e e+
left- or right-handed chirality. its own antiparticle.
Symbol Electric
Electric Charge. Each particle has charge + = Mixtures. Some elementary particles
positive, negative, or zero electric charge. Spin are mixtures (linear superpositions)
1
2 u
Color Charge. A quark has one of three of other elementary particles.
Name up Color
color charges called red, green, or blue.
An anti-quark has an anti-color.
(Flavor) ___ MeV charge
? Hypothetical. Postulated particles
that many physicists expect will be
A gluon has a color and an anti-color. Mass (electron volts) discovered.
Elementary Particles
This shows all the elementary particles in the standard model (SM) of particle physics plus the hypothetical graviton.
Fermions half-integer spin 12 32 Fermions
Matter is made of fermions. generation
Fermions obey the exclusion principle. spin I II III
u c t
Quarks
1 up charm top
2 1.73.1 MeV 1.11.4 GeV 171175 GeV
Atom e
nucleus - - -
d s b
u d u u proton
d d uud down strange bottom
d u u d neutron 4.1-5.7 MeV 80130 MeV 4.14.4 GeV
u d udd
electron e
Leptons
e
1 electron muon tau
2 511 keV 106 MeV 1.8 GeV
e
electron muon tau
neutrino neutrino neutrino
<1 eV? <1 eV? <1 eV?
Bosons integer spin 0 1 2 Bosons
Forces are carried by gauge bosons.
Bosons do not obey the exclusion principle. spin
Gravitational
force
2 ? G
Gravitational
force
? masses attract graviton
massless
Quantum
Gauge Bosons
Strong force Strong
Force Carriers
Gravity 1 g
?
Color force force
Planck
scale quarks/gluons attract gluon
1019 GeV Grand massless
Unification Weak force Weak
Wi Weak
GUT scale
1 Isospin W Z force
Flavor change
1016 GeV Electro- radioactivity W W Z
weak massless 80 GeV 91 GeV
Weak
EW scale Electromagnetic B Electromagnetic
102 GeV 1 Hyper-
force
force charge
charges attract/repel, B photon
light massless massless
Bosons
Scalar
0
Higgs field(s) 0 H H H Higgs field
creates mass, breaks symmetry Higgs Higgs
124-127 GeV
Unified forces split by symmetry breaking. Electroweak symmetry breaking
Other elementary particles may yet be discovered.
?
Supersymmetry (SUSY) proposes that every elementary particle has a superpartner.
String theory proposes that all elementary particles are actually tiny vibrating strings.
Composite Particles Hadrons
Composite particles are composed of two or more elementary particles. This shows some of the hundreds of known composite particles.
Composite Fermions Baryons Composite Bosons Mesons
Baryons are fermions composed of three quarks. Mesons are bosons composed of a quark and an antiquark.
This shows only the baryons made of u, d, and s quarks. This shows only the mesons made of u, d, and s quarks.
spin 12 octet p+ uud n0 udd p+ = u u
d spin 0 nonet K0 K+ 0 = u u
p proton ds us
proton uud pion pion uu
/dd
n neutron + uus 0 0 uds dds 0 0 uu
/dd
938 MeV eta + 135 MeV mixture
sigma du
ud
K kaon 0
lambda 0 uss dss n0 = u d
Pions carry
d ss
xi K 0
K the nuclear
neutron udd su
sd
force between
++ uuu + uud 0 udd ddd 940 MeV
nucleons.
nucleons spin 1 nonet K*0 K*+
spin 32 decuplet ds us
*+ uus *0 uds * dds rho
delta omega 0 0 uu
/dd
sigma +
*0 uss * dss phi du
0 ud
xi K kaon ss
omega-minus sss K* *0
K
su
sd
2005-2014 Keith Enevoldsen elements.wlonk.com
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Particles PDFDocument1 pageParticles PDFEnrique Escalante EchagüeNo ratings yet
- 1 RamblamapDocument2 pages1 RamblamapEnrique Escalante EchagüeNo ratings yet
- Cliff YoungDocument56 pagesCliff YoungMario Schiano100% (5)
- Cliff YoungDocument56 pagesCliff YoungMario Schiano100% (5)
- Ubs Pricesandearnings 2015 enDocument44 pagesUbs Pricesandearnings 2015 enAlejandro Méndez MartínezNo ratings yet
- Tuneles de Buenos AiresDocument156 pagesTuneles de Buenos AiresCarlos Sosa EscaladaNo ratings yet