Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Zebrafish Poster Portrait Eupfi Sep 2106 Final Submitted
Uploaded by
api-266268510Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Zebrafish Poster Portrait Eupfi Sep 2106 Final Submitted
Uploaded by
api-266268510Copyright:
Available Formats
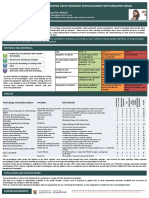
Development of a Zebrafish Model for Bitter Taste Assessment.
J. Bennett2, A. Coburn1 , A. Coupe2, D. Stedman1,, A. Taylor1, A. Tyler1
1 Pfizer Global R & D, Groton, CT, 06340, USA
2 Pfizer Global R & D, Ramsgate Road, Sandwich, Kent, CT13 9NJ, UK
Introduction Fig 4 Effect of concentration on mean food uptake response in zebrafish in initial trial 1
and subsequent repeat trials 2 and 3
Development of simple models to predict bitter taste in humans (paediatrics) is
required to enable improvements in formulation development of paediatric
medicines. A limited number of models are available for evaluating taste e.g. e-
tongue, rat Brief Access Taste Aversion (BATA) model. Although these models
have been shown to have some utility they have a number of limitations and
their application in the drug development process has been limited (1). Juvenile
zebrafish have recently been shown to recognise bitter tastes and further
development of this model could offer a simple alternative to current models
(2,3). In these studies work was undertaken with adult zebrafish (Fig.2) where
feeding was more well established to further understand whether this model
could be used to identify bitter tastes of five compounds with known taste data
in humans.
Materials and Methods
Log doses of test compounds quinine, caffeine, carbamazepine, sildenafil
(1,10,100 mM) and paracetamol (1, 10 and 50 mM) were fed to wild-type
adult zebrafish in a gelatin based food source. Prior to the study zebrafish
were familiarised with eating a gelatin diet in addition to their standard diet. Fig. 5 Effect of concentration on mean food uptake response in zebrafish
The gelatin based food source, Gelly BellyTM(GB), contains a mixture of (combined data from Trials 1,2,3)
vitamins, minerals, krill meal, special mixture of fish and invertebrate feeds,
microalgae and pigment enhancers. The GB was dissolved in hot water,
cooled prior to adding test compounds at concentrations of 1,10,50,100 mM
and allowed to solidify prior to storage at -20C (Fig 3). Each dose of GB was
cut into pieces small enough for fish to eat. Each tank contained five adult
zebrafish (3 females, 2 males) and 3 tanks were used per concentration. The
effect of repeat dosing was examined with zebrafish being given 3 doses
(32.5mg GB + drug) at time 0h, 4h and 24h (Trial 1,2,3). A simple scoring
system was introduced to assess food uptake (Fig.1). Following dosing of the
GB control (no compound) and GB containing test compound fish were
observed for 1 minute and the response scored accordingly.
Fig 1. Scoring System
Scoring System
Observation @ 1 minute Score (Response)
Did not eat GB 0
Ate some of GB 1
Ate all GB 2
Conclusion
Fig 2. Adult Zebrafish
These preliminary studies indicate that adult zebrafish may be a useful model to
identify and evaluate bitter compounds. The presence of quinine, caffeine,
carbamazepine, sildenafil in the food source significantly reduced uptake in a
Fig 3. Drug GB Aliquots
concentration dependent manner. In contrast paracetamol did not impact food
uptake. The data for paracetamol is consistent with human taste panel data where it
was shown to be less bitter than quinine and sildenafil (4).
Acknowledgements
This work was conducted as part of the SPaeDD-UK (Smarter Paediatric Drug
Development-UK) project which is co-funded by Innovate UK and industrial partners:
AZ, Glaxo, Juniper, BMS, Pfizer
Results References
Zebrafish showed a dose response effect for caffeine,
1. Mohamed-Ahmed, A., Soto, J., Ernest, T., Tuleu, C. (2016),Non-human tools for
carbamazepine, sildenafil with reduced GB consumption at higher the evaluation of bitter taste in the design and development of medicines: a
doses and on repeat dosing. The fish consumed less GB on systematic review. Drug Discovery Today,21,7, 1170-1180.
repeat dosing in trial 2 and 3 relative to the initial dose (Fig.4). 2. Okada, S.,(2015), The taste system of small fish species. Biosci Biotechnol
Initial studies with quinine were variable (data not shown) and Biochem, 79, 1039-1043.
optimisation of the dose preparation was undertaken. Subsequent 3. Boyer, B., S. Ernest, and F. Rosa (2013), Egr-1 induction provides a genetic
findings for quinine also showed a dose response effect. In response to food aversion in zebrafish.Front Behav Neurosci, 7, 51.
4. Soto, J., Winzenburg G, Turner R., Desset-Brthes, S., Sheng ,Y., Orlu Gul,M.,
contrast paracetamol showed no consistent dose response effect
Tuleu, C. Assessing the aversive taste of medicines: a comparison between rat
(up to 50mM) Fig. 5 shows the overall dose response data taste panels (via the brief-access taste aversion (BATA) model) and human
obtained for all 5 compounds using combined data from trial 1-3. taste panels. Presented at 7th EuPFI conference, 16th and 17th September
2015 in Antwerp (Belgium)
You might also like
- Effects of Chronic IngestionDocument7 pagesEffects of Chronic IngestionYusrinabilla -No ratings yet
- Gastroprotective Effect of Zingerone On Ethanol-Induced Gastric Ulcers in RatsDocument9 pagesGastroprotective Effect of Zingerone On Ethanol-Induced Gastric Ulcers in RatsRihabNo ratings yet
- EFSA Journal - 2010 - Scientific Opinion On The Re Evaluation of Brilliant Blue FCF E 133 As A Food AdditiveDocument36 pagesEFSA Journal - 2010 - Scientific Opinion On The Re Evaluation of Brilliant Blue FCF E 133 As A Food AdditivebabithyNo ratings yet
- Can Intestinal Absorption of Dietary Protein Be Improved Through Early Exposure To Plant-Based DietDocument16 pagesCan Intestinal Absorption of Dietary Protein Be Improved Through Early Exposure To Plant-Based Diethossainimam0079No ratings yet
- Asam KandisDocument5 pagesAsam KandisRahma NovinisaNo ratings yet
- Bignay Chap 1 3 2Document22 pagesBignay Chap 1 3 2Ralph AJ BalmesNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Penambahan Sukun Muda (Artocarpus Communis) Terhadap Mutu Fisik, Kadar Protein, Dan Kadar Air Abon Lele Dumbo (Clarias Gariepinus)Document5 pagesPengaruh Penambahan Sukun Muda (Artocarpus Communis) Terhadap Mutu Fisik, Kadar Protein, Dan Kadar Air Abon Lele Dumbo (Clarias Gariepinus)Sie ningsihNo ratings yet
- AD ErythrosinDocument9 pagesAD ErythrosinsalmaNo ratings yet
- Food ChemistryDocument9 pagesFood ChemistryEdwin RizoNo ratings yet
- Histoprotective Effects of Curcumin On Bisphenol-A Induced Testicular Toxicity in Adult Albino RatsDocument11 pagesHistoprotective Effects of Curcumin On Bisphenol-A Induced Testicular Toxicity in Adult Albino Ratsrabia ToorNo ratings yet
- Ijpr 19 113 1Document8 pagesIjpr 19 113 1suhandinataNo ratings yet
- Effect of Dietary Acidification in Broil PDFDocument6 pagesEffect of Dietary Acidification in Broil PDFdarioNo ratings yet
- Formulation and Evaluation of Gabapentin Mucoadhesive Gastro Retentive Tablets.Document13 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Gabapentin Mucoadhesive Gastro Retentive Tablets.Sriram NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Scopus Database Journal 02 NovDocument25 pagesScopus Database Journal 02 Novnaresh kotraNo ratings yet
- Shelf Life Prediction For Non-Accelerated StudiesDocument4 pagesShelf Life Prediction For Non-Accelerated StudiesANDREAMIBNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Administration The Highrise Dosage of Monosodium Glutamate Towards The Level of Serum Urea-Creatinine On Wistar RatsDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Administration The Highrise Dosage of Monosodium Glutamate Towards The Level of Serum Urea-Creatinine On Wistar Ratsferry gunawanNo ratings yet
- 2019 Parul NJPPP 2019Document7 pages2019 Parul NJPPP 2019maloymandalNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0271531712000176 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0271531712000176 MainEdwin RizoNo ratings yet
- Gastroproteção EAbDocument13 pagesGastroproteção EAbMeelsNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Ejps 2019 104988Document8 pages10 1016@j Ejps 2019 104988jose noel garcia perezNo ratings yet
- Artículo BiodisponibilidadDocument9 pagesArtículo BiodisponibilidadLuis Enrique SanchezNo ratings yet
- PharmacognJ-13-6-1384 Toxicity 2021Document5 pagesPharmacognJ-13-6-1384 Toxicity 2021Khaira Rusdi NumlilNo ratings yet
- Combination of PPI With A Prokinetic Drug in Gastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseDocument19 pagesCombination of PPI With A Prokinetic Drug in Gastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseFebyan AbotNo ratings yet
- J Efsa 2014 3768Document51 pagesJ Efsa 2014 3768Thùy TrangNo ratings yet
- Formulation and Characterization of Chitosanpeg Nanoparticles Based On Cork Fish Channa Striata Protein Hydrolysate As ADocument7 pagesFormulation and Characterization of Chitosanpeg Nanoparticles Based On Cork Fish Channa Striata Protein Hydrolysate As AfajrulNo ratings yet
- Hepatoprotective Activity of Berberisaristata Root Extract Against Chemical Induced Acute Hepatotoxicity in RatsDocument4 pagesHepatoprotective Activity of Berberisaristata Root Extract Against Chemical Induced Acute Hepatotoxicity in RatsAmit patelNo ratings yet
- Spesialis Penyakit Dalam 2 (Additive Effects of Rebamipide Plus Proton Pump PDFDocument5 pagesSpesialis Penyakit Dalam 2 (Additive Effects of Rebamipide Plus Proton Pump PDFfildzah amalyaNo ratings yet
- Paper Butirato Doença RenalDocument9 pagesPaper Butirato Doença RenalRafael PereiraNo ratings yet
- Thambi (2014)Document9 pagesThambi (2014)Lyka MahrNo ratings yet
- Ameliorating Effect of Olive Oil On Fertility of Male Rats Fed On Genetically Modified Soya BeanDocument6 pagesAmeliorating Effect of Olive Oil On Fertility of Male Rats Fed On Genetically Modified Soya Bean--No ratings yet
- Abbey 2014Document7 pagesAbbey 2014kiệt lêNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Human Hazards Associated With Excessive Intake of Amino AcidsDocument7 pagesThe Nature of Human Hazards Associated With Excessive Intake of Amino Acidsblend.preniqiNo ratings yet
- Iai 68 4 2386-2389 2000Document4 pagesIai 68 4 2386-2389 2000nurullahfatihNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Gastrointestinal Toxicity of Ibuprofen UsingDocument6 pagesEvaluation of Gastrointestinal Toxicity of Ibuprofen UsingRangwani NesbitNo ratings yet
- Jefo 35th Celebrations - CIRAA PostersDocument13 pagesJefo 35th Celebrations - CIRAA PostersEmilie FontaineNo ratings yet
- Volume3-1 Glyphosat 05Document45 pagesVolume3-1 Glyphosat 05Claire RobinsonNo ratings yet
- NXZ 328Document12 pagesNXZ 328Sara DeleuNo ratings yet
- Dietary Grape Seed Proanthocyanidins (GSPS) Improve Weaned Intestinal Microbiota and Mucosal Barrier Using A Piglet ModelDocument14 pagesDietary Grape Seed Proanthocyanidins (GSPS) Improve Weaned Intestinal Microbiota and Mucosal Barrier Using A Piglet ModelGina PistolNo ratings yet
- 7f68009926b7ac41e70e70769ad8bc70Document14 pages7f68009926b7ac41e70e70769ad8bc70Cibelle FigueiredoNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument11 pages1 PBZikry ChannelNo ratings yet
- Foods: Biological E in Vitro Model SystemsDocument19 pagesFoods: Biological E in Vitro Model SystemsViraj SenavirathneNo ratings yet
- Ability of Lactobacillus and Propionibacterium Strains To Remove Aflatoxin B From The Chicken DuodenumDocument4 pagesAbility of Lactobacillus and Propionibacterium Strains To Remove Aflatoxin B From The Chicken DuodenumdaniellesilvavvieiraNo ratings yet
- 1088 1176 1 PBDocument5 pages1088 1176 1 PBRista MoraNo ratings yet
- Determination of Feeding Stimulants in Shrimp Using A Solid Matrix BioassayDocument6 pagesDetermination of Feeding Stimulants in Shrimp Using A Solid Matrix BioassayPuri RahmaNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Ibuprofen NanoparticlesDocument1 pageComparison Between Ibuprofen NanoparticlesAiman ShoiabNo ratings yet
- Protective Effects of Saffron (Crocus Sativus Linn.) On Genotoxins-Induced Oxidative Stress in Swiss Albino MiceDocument4 pagesProtective Effects of Saffron (Crocus Sativus Linn.) On Genotoxins-Induced Oxidative Stress in Swiss Albino MiceArlaaNo ratings yet
- 84 - Ijbpr 2011, 2 (2), 80-84Document5 pages84 - Ijbpr 2011, 2 (2), 80-84Sujith KuttanNo ratings yet
- Beta Alanina Revision Sistematica 2019Document12 pagesBeta Alanina Revision Sistematica 2019griego81No ratings yet
- Simbai Muchabaiwa Hit 400 ProposalDocument9 pagesSimbai Muchabaiwa Hit 400 ProposalsimbaiNo ratings yet
- Effects of Encapsulated Organic Acids and Essential Oils On Inte - 2019 - PoultrDocument8 pagesEffects of Encapsulated Organic Acids and Essential Oils On Inte - 2019 - PoultrCristian José CardozoNo ratings yet
- Tmp973e TMPDocument6 pagesTmp973e TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Mycotoxin Effects On AnimalsDocument4 pagesMycotoxin Effects On AnimalsYusraNo ratings yet
- AttachmentDocument4 pagesAttachmentLawliet FardiNo ratings yet
- AR101 Oral Immunotherapy For Peanut Allergy: Original ArticleDocument11 pagesAR101 Oral Immunotherapy For Peanut Allergy: Original ArticleWXXI NewsNo ratings yet
- Ciclosporina - AtopiaDocument14 pagesCiclosporina - AtopiaWania Clelia Brito ParanaibaNo ratings yet
- 2018-Hadrich-Apigertin Inhibits Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 CellsDocument8 pages2018-Hadrich-Apigertin Inhibits Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 CellsAthanasios S. ArampatzisNo ratings yet
- Aab 131 PDFDocument4 pagesAab 131 PDFAjuogu PeterNo ratings yet
- Efecto de Diferentes Dosis de Ácido Butírico Recubierto en El Rendimiento Del Crecimiento y La Utilización de Energía en Pollos de Engorde 2016Document9 pagesEfecto de Diferentes Dosis de Ácido Butírico Recubierto en El Rendimiento Del Crecimiento y La Utilización de Energía en Pollos de Engorde 2016Cristian José CardozoNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 0278691595000844 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 0278691595000844 MainChirag EducationNo ratings yet
- Success Factors for Fish Larval ProductionFrom EverandSuccess Factors for Fish Larval ProductionLuis ConceicaoNo ratings yet
- FL - Poster - Eupfi Lisbon 2016Document1 pageFL - Poster - Eupfi Lisbon 2016api-266268510No ratings yet
- Eupfi Lisbon 2016 Multi Particulates Poster Presentation Pmistry v1Document1 pageEupfi Lisbon 2016 Multi Particulates Poster Presentation Pmistry v1api-266268510No ratings yet
- Age Dependent Biorelevant Dissolution Eupfi Lisbon 2016Document1 pageAge Dependent Biorelevant Dissolution Eupfi Lisbon 2016api-266268510No ratings yet
- Eupfi Poster Eunice 002Document1 pageEupfi Poster Eunice 002api-266268510No ratings yet
- Pharmasci Presentation Final 02092015Document19 pagesPharmasci Presentation Final 02092015api-266268510No ratings yet
- PBP Glasgow 2016 Pro-Poster Final To PrintDocument1 pagePBP Glasgow 2016 Pro-Poster Final To Printapi-266268510No ratings yet
- The Challenges of Performing in Vivo Studies For Taste or Acceptability Aps 2015 Final Modified No LogosDocument19 pagesThe Challenges of Performing in Vivo Studies For Taste or Acceptability Aps 2015 Final Modified No Logosapi-266268510No ratings yet
- Eupfi Abstract v1 2015 Punam MistryDocument1 pageEupfi Abstract v1 2015 Punam Mistryapi-266268510No ratings yet
- Aps Uk Pharm Sci Poster 2014 PDFDocument1 pageAps Uk Pharm Sci Poster 2014 PDFapi-266268510No ratings yet
- Astrazeneca TSB Poster 2015 UpdatedDocument1 pageAstrazeneca TSB Poster 2015 Updatedapi-266268510No ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka-1Document3 pagesDaftar Pustaka-1Anggi Rizky Adhi PratamaNo ratings yet
- Ellinger 1971Document7 pagesEllinger 1971Mohammed TarekNo ratings yet
- The Galeniko-Noone MethodDocument82 pagesThe Galeniko-Noone MethodLouFerrignoNo ratings yet
- Initial Nurse Patient InteractionDocument1 pageInitial Nurse Patient InteractionBryan Jay Carlo PañaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Leprosy AssociationDocument142 pagesJournal of Leprosy AssociationWahyuni Tri Lestari100% (1)
- Bariatric SurgeryDocument252 pagesBariatric SurgeryEdward-Dan Buzoianu100% (2)
- PBL Oral BiologyDocument12 pagesPBL Oral BiologyhusunasanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Language Practice: Grammar Progress Test 6b (Units 27-28)Document3 pagesAdvanced Language Practice: Grammar Progress Test 6b (Units 27-28)Ramona TudorNo ratings yet
- Materi Sjs LoratadineDocument8 pagesMateri Sjs LoratadineLala Rahma Qodriyan SofiakmiNo ratings yet
- Journal of Food Composition and AnalysisDocument11 pagesJournal of Food Composition and AnalysisJessica WeaverNo ratings yet
- Confidentiality - A Case ScenarioDocument4 pagesConfidentiality - A Case ScenarioimmaNo ratings yet
- Psychodaynamic Guide For Essential Treatment PlanningDocument24 pagesPsychodaynamic Guide For Essential Treatment PlanningLina SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Ears Nose Mouth and ThroatDocument3 pagesChapter 12 Ears Nose Mouth and ThroatKhanh HoangNo ratings yet
- Bali Cyclosporine Reduces Sclerosis in (Morphea, Systemic Sclerosis)Document8 pagesBali Cyclosporine Reduces Sclerosis in (Morphea, Systemic Sclerosis)Azmi FadhlihNo ratings yet
- Tumors of Salivary GlandDocument28 pagesTumors of Salivary Glandrameshparajuli14100% (1)
- Dumaguete Case-Study On The Socio-Economic Spillover Effects From FSMDocument7 pagesDumaguete Case-Study On The Socio-Economic Spillover Effects From FSMADBI EventsNo ratings yet
- Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Concise Guidance 1Document6 pagesComplex Regional Pain Syndrome Concise Guidance 1roooNo ratings yet
- CystoclysisDocument29 pagesCystoclysisKate PedzNo ratings yet
- Organizational DevelopmentDocument16 pagesOrganizational Developmentsagar09No ratings yet
- Handbook of AnesthesiologyDocument176 pagesHandbook of AnesthesiologyarmelzahfauziNo ratings yet
- Zhang Zhuang ThesisDocument120 pagesZhang Zhuang ThesisSilviu MihaiNo ratings yet
- Hot Tips For Master Plumber Boards2Document8 pagesHot Tips For Master Plumber Boards2jcedricaquino100% (1)
- Blood Warmer ValidationDocument5 pagesBlood Warmer ValidationulgenyNo ratings yet
- Role of Chlorhexidine in Caries PreventionDocument7 pagesRole of Chlorhexidine in Caries PreventionHarry ArdiyantoNo ratings yet
- 02 NST Icu Intake 0007Document8 pages02 NST Icu Intake 0007anariela kityNo ratings yet
- Yacon SyrupDocument40 pagesYacon SyrupTrilceNo ratings yet
- Post TestDocument9 pagesPost TestPradnya Paramitha100% (2)
- Ds OresolDocument1 pageDs OresolShannie Padilla100% (1)
- Asperger Syndrome and AdultsDocument4 pagesAsperger Syndrome and Adultschinkshady100% (1)
- Nclex PNDocument416 pagesNclex PNSandhu Sdhu100% (9)