Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mesenteric Doppler Protocol 14
Uploaded by
api-349402240Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mesenteric Doppler Protocol 14
Uploaded by
api-349402240Copyright:
Available Formats
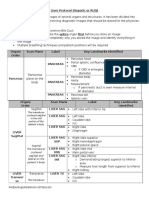
Mesenteric Doppler Protocol
Structure Scan Label Landmarks Identified Images Stored
Plane
On
Body
Sagittal AORTA Proximal aorta Gray scale
Celiac artery
SMA
Proximal aorta Color Doppler
Aorta Celiac artery
SMA
Proximal aorta Color & spectral Doppler with
Celiac artery peak systolic velocity and end
SMA diastolic velocity
Transver CELIAC AT Proximal aorta Color Doppler
se ORIGIN Celiac artery
Splenic artery
Celiac Common hepatic
Axis artery
Proximal aorta Color & spectral Doppler with
Celiac artery peak systolic velocity and end
diastolic velocity
Splenic Transver SPLENIC Proximal aorta Color & spectral Doppler with
Artery se ARTERY Celiac artery peak systolic velocity and end
Splenic artery diastolic velocity
Common Transver HEPATIC Proximal aorta Color & spectral Doppler with
Hepatic se ARTERY Celiac artery peak systolic velocity and end
Artery Hepatic artery diastolic velocity
Sagittal SMA AT Proximal aorta Color Doppler
ORIGIN SMA
Proximal aorta Color & spectral Doppler with
SMA peak systolic velocity and end
Superior
diastolic velocity
Mesenter
SMA PROX Mid aorta Color Doppler
ic Artery
Proximal SMA
Mid aorta Color & spectral Doppler with
Proximal SMA peak systolic velocity and end
diastolic velocity
Transver IMA AT Distal aorta Color Doppler
Inferior se ORIGIN IMA
Mesenter Distal aorta Color & spectral Doppler with
ic Artery IMA peak systolic velocity and end
diastolic velocity
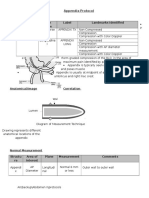
Anatomical/Image Correlation
Celiac axis Superior Mesenteric
Artery
Inferior Mesenteric
Artery
AK\backup\Vascular I\protocols
Mesenteric Doppler Protocol
Artery with
Tips
Doppler
Scan planes listed above refer to transducer orientation on the body. You will be evaluating
each vessel in the sagittal plane of the vessel, even if your transducer is in a more
transverse plane on the body.
It is extremely important that the patient has been fasting prior to the exam. If the patient
has not been NPO, that information must be relayed to the interpreting physician because
the criteria for evaluating waveforms will not be accurate.
If a site includes pre- and postprandial imaging, the postprandial images must be labeled
accordingly.
Color Doppler
Will vary with the presence/absence of pathology & curvature of the vessel
Color images should relay the same information as your gray scale & spectral images
Using a curved transducer will not allow you to steer your color box with the vessel direction
Color bruit in any vessel is indicative of a stenosis
Pay close attention to flow direction in splenic and hepatic arteries when stenosis is
suspected in the celiac artery
Spectral Doppler
Have patient hold their breath when obtaining spectral waveforms to decrease movement
Must use angle correct - Angle correct must be less than 60 degrees
Gate (SV length) must be in center of vessel & small width
Normal celiac artery is low-resistive, with PSV <125 cm/s
Normal SMA is high-resistive, with PSV <125 cm/s
Normal IMA is high-resistive
SMA and IMA should change to low-resistive after a patient eats
Elevated velocities with spectral broadening indicate a stenosis
Velocities will be increased in patients with stents compare to previous studies
AK\backup\Vascular I\protocols
You might also like
- Advanced Endovascular Therapy of Aortic DiseaseFrom EverandAdvanced Endovascular Therapy of Aortic DiseaseAlan B. LumsdenNo ratings yet
- Echocardiography in Pediatric and Congenital Heart Disease: From Fetus to AdultFrom EverandEchocardiography in Pediatric and Congenital Heart Disease: From Fetus to AdultNo ratings yet
- Renal Doppler Protocol 14 1Document4 pagesRenal Doppler Protocol 14 1api-349402240100% (1)
- Upper Extremity Arterial Protocol 14 PDFDocument2 pagesUpper Extremity Arterial Protocol 14 PDFapi-390240132No ratings yet
- Lower Extremity Arterial Protocol 14 1Document2 pagesLower Extremity Arterial Protocol 14 1api-3494022400% (1)
- Lower Extremity Arterial Protocol 14 PDFDocument2 pagesLower Extremity Arterial Protocol 14 PDFapi-390240132No ratings yet
- Upper Extremity Arterial Protocol 14Document3 pagesUpper Extremity Arterial Protocol 14api-349402240No ratings yet
- Doppler Ultrasound of The KidneysDocument23 pagesDoppler Ultrasound of The KidneysivoklarinNo ratings yet
- Fetal Echocardiogram ProtocolDocument4 pagesFetal Echocardiogram Protocolapi-349402240No ratings yet
- Scrotum Protocol 14Document2 pagesScrotum Protocol 14api-349402240No ratings yet
- Upper Extremity Venous Protocol 14Document2 pagesUpper Extremity Venous Protocol 14api-349402240No ratings yet
- Lower Extremity Venous Incompetence Protcol 14Document5 pagesLower Extremity Venous Incompetence Protcol 14api-349402240No ratings yet
- Abdominal US in Hepatobiliary DiseasesDocument76 pagesAbdominal US in Hepatobiliary DiseasesSyafari D. MangopoNo ratings yet
- Liver Protocol 14 1Document5 pagesLiver Protocol 14 1api-349402240No ratings yet
- Ob Biophysical Profile Protocol r14 PDFDocument3 pagesOb Biophysical Profile Protocol r14 PDFapi-390240132No ratings yet
- LiverultrasoundDocument62 pagesLiverultrasoundiuliia94No ratings yet
- Appendix Protocol 14 1Document2 pagesAppendix Protocol 14 1api-349402240No ratings yet
- Abdomen Protocol 14 PDFDocument6 pagesAbdomen Protocol 14 PDFapi-390240132No ratings yet
- Policies and Statements: Peripheral Arterial UltrasoundDocument5 pagesPolicies and Statements: Peripheral Arterial UltrasoundJing CruzNo ratings yet
- Allen Test Protocol 14 1Document2 pagesAllen Test Protocol 14 1api-349402240No ratings yet
- Gynecoloical Ultrasound Doppler AssessmentDocument17 pagesGynecoloical Ultrasound Doppler AssessmentKinzaNo ratings yet
- 14 Clauss Pediatric Echocardiography PDFDocument159 pages14 Clauss Pediatric Echocardiography PDFSergiu NiculitaNo ratings yet
- Color and Power DopplerDocument114 pagesColor and Power DopplerThuraiya Al MasoudiNo ratings yet
- ISUOG Basic Training: Writing The Gynecological Ultrasound ReportDocument29 pagesISUOG Basic Training: Writing The Gynecological Ultrasound ReportsandrogvaladzeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18Document17 pagesChapter 18George LeahuNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Spine 14Document2 pagesPediatric Spine 14api-349402240No ratings yet
- Handbook of Transrectal Ultrasound and Biopsy of The ProstateDocument126 pagesHandbook of Transrectal Ultrasound and Biopsy of The ProstateIván RomeroNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Blok GI Tract - USG Abd - September 2010Document65 pagesKuliah Blok GI Tract - USG Abd - September 2010Natallia BatuwaelNo ratings yet
- Renal Ultrasound: Diana Pancu, MDDocument76 pagesRenal Ultrasound: Diana Pancu, MDReza Angga PratamaNo ratings yet
- Doppler Echocardiography: Dr.S.R.Sruthi Meenaxshi MBBS, MD, PDFDocument38 pagesDoppler Echocardiography: Dr.S.R.Sruthi Meenaxshi MBBS, MD, PDFsruthimeena6891No ratings yet
- Breast Procedures Ultrasound Only EditedDocument107 pagesBreast Procedures Ultrasound Only EditedDanaNo ratings yet
- 超声进展2020 10 8最终版Document160 pages超声进展2020 10 8最终版Wai Kwong ChiuNo ratings yet
- Ardms Spi Exam PDFDocument336 pagesArdms Spi Exam PDFSanjida Piya100% (1)
- Biophysical Profile& Color Doppler Ultrasound in The High Risk PregnancyDocument56 pagesBiophysical Profile& Color Doppler Ultrasound in The High Risk Pregnancykhadzx100% (4)
- Basic Ultasonograph yDocument56 pagesBasic Ultasonograph yshashwathhNo ratings yet
- Penile US and Doppler USDocument2 pagesPenile US and Doppler UShardrocker_2007No ratings yet
- Small Parts USDocument58 pagesSmall Parts USWaqas AliNo ratings yet
- Us Vasos RetroperitonealesDocument101 pagesUs Vasos RetroperitonealesLourdes MarcosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34Document12 pagesChapter 34Haba HenrikNo ratings yet
- ECR2014 - Ultrasound Evaluation of Scrotal PathologyDocument76 pagesECR2014 - Ultrasound Evaluation of Scrotal PathologyMicNo ratings yet
- Coursebook-Echoscopy ch30Document23 pagesCoursebook-Echoscopy ch30Сергей СадовниковNo ratings yet
- Renal Ultrasound ProtocolDocument4 pagesRenal Ultrasound Protocolfouad tabetNo ratings yet
- #Normal #Tubes On #UltrasoundDocument1 page#Normal #Tubes On #UltrasoundDr Pankaj TalwarNo ratings yet
- Articulo Tesis 6Document130 pagesArticulo Tesis 6Lourdes MarcosNo ratings yet
- Scanning Technique of KidneysDocument103 pagesScanning Technique of KidneysPhuntsho OngmoNo ratings yet
- D5 PolicyDocument5 pagesD5 PolicyDenis PogoreviciNo ratings yet
- Procedure of UltrasoundDocument1 pageProcedure of UltrasoundDr Pankaj TalwarNo ratings yet
- To Review The Imaging Anatomy of Peritoneal Spaces: Poster No.: Congress: Type: Authors: Keywords: DoiDocument20 pagesTo Review The Imaging Anatomy of Peritoneal Spaces: Poster No.: Congress: Type: Authors: Keywords: DoiradiologirsckNo ratings yet
- Doppler US and GrowthDocument43 pagesDoppler US and GrowthAulia rahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck Gastrointestinal Lung Pelvic Renal and BladderDocument10 pagesHead and Neck Gastrointestinal Lung Pelvic Renal and BladderAmir AliNo ratings yet
- Artifacts and Pitfalls in Doppler VelocimetryDocument39 pagesArtifacts and Pitfalls in Doppler VelocimetryEileen del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound of Srotal Emergency in PediatricDocument53 pagesUltrasound of Srotal Emergency in PediatricIsti Iryan PriantiNo ratings yet
- Obstetric EcoDocument35 pagesObstetric EcomemecedarNo ratings yet
- Apr 28 Ultrasound Chawla PDFDocument85 pagesApr 28 Ultrasound Chawla PDFAna-Maria PopaNo ratings yet
- Normal Ovaries On UltrasoundDocument1 pageNormal Ovaries On UltrasoundDr Pankaj TalwarNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound in Obstetrics: Ramon M. Gonzalez MD FPOGS Professor UST Faculty of Medicine and SurgeryDocument102 pagesUltrasound in Obstetrics: Ramon M. Gonzalez MD FPOGS Professor UST Faculty of Medicine and Surgeryaldeeray01No ratings yet
- Lower Extremity Venous Protocol 14Document3 pagesLower Extremity Venous Protocol 14api-276847924No ratings yet
- Ecbse ch08 SpleenDocument46 pagesEcbse ch08 SpleenMitulsinh M RavaljiNo ratings yet
- ISUOGMidTrimester Guidelines 2011 PresentationDocument22 pagesISUOGMidTrimester Guidelines 2011 Presentationmihaela8023No ratings yet
- Practice Guidlines For Performance First Trimester USDocument95 pagesPractice Guidlines For Performance First Trimester USOxy GenNo ratings yet
- Female Pelvis Protocol r16 1Document2 pagesFemale Pelvis Protocol r16 1api-349402240No ratings yet
- Clinical Totals 2Document1 pageClinical Totals 2api-349402240No ratings yet
- Clinical EvaluationsDocument1 pageClinical Evaluationsapi-349402240No ratings yet
- Hollie Poe Summer 2016 Research Paper GynecomastiaDocument14 pagesHollie Poe Summer 2016 Research Paper Gynecomastiaapi-349402240No ratings yet
- Clinical TotalsDocument1 pageClinical Totalsapi-349402240No ratings yet
- Hepatic Doppler Protocol 14Document4 pagesHepatic Doppler Protocol 14api-349402240No ratings yet
- Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Protocol 14Document2 pagesThoracic Outlet Syndrome Protocol 14api-349402240No ratings yet
- Upper Extremity Venous Protocol 14Document2 pagesUpper Extremity Venous Protocol 14api-349402240No ratings yet
- Lower Extremity Venous Incompetence Protcol 14Document5 pagesLower Extremity Venous Incompetence Protcol 14api-349402240No ratings yet
- Lower Extremity Venous Protocol 14Document3 pagesLower Extremity Venous Protocol 14api-349474075No ratings yet
- Fetal Echocardiogram ProtocolDocument4 pagesFetal Echocardiogram Protocolapi-349402240No ratings yet
- Pediatric Spine 14Document2 pagesPediatric Spine 14api-349402240No ratings yet
- Carotid Protocol 14 1Document4 pagesCarotid Protocol 14 1api-349402240No ratings yet
- Graft Doppler Protocol 14Document3 pagesGraft Doppler Protocol 14api-349402240No ratings yet
- Breast Protocol 14 1Document4 pagesBreast Protocol 14 1api-349402240No ratings yet
- Scrotum Protocol 14Document2 pagesScrotum Protocol 14api-349402240No ratings yet
- Thyroid Protocol 14 1Document3 pagesThyroid Protocol 14 1api-349402240No ratings yet
- Pediatric Hip Protocol 14Document3 pagesPediatric Hip Protocol 14api-349402240No ratings yet
- Neonatal Head Protocol 14Document5 pagesNeonatal Head Protocol 14api-349402240No ratings yet
- Pyloric Stenosis 14Document3 pagesPyloric Stenosis 14api-349402240No ratings yet
- Allen Test Protocol 14 1Document2 pagesAllen Test Protocol 14 1api-349402240No ratings yet
- Adult Echocardiography Protocol 14 2Document10 pagesAdult Echocardiography Protocol 14 2api-349402240No ratings yet
- Abdomen ProtocolDocument8 pagesAbdomen Protocolapi-349474075No ratings yet
- Urinary Protocol 14 1Document4 pagesUrinary Protocol 14 1api-349402240No ratings yet
- Pancreas Protocol 14 2Document2 pagesPancreas Protocol 14 2api-349402240No ratings yet
- Prostate Protocol 14 1Document3 pagesProstate Protocol 14 1api-349402240No ratings yet
- Introduction To Sonography and Patient Care First Edition Ebook PDFDocument61 pagesIntroduction To Sonography and Patient Care First Edition Ebook PDFjose.waller368100% (44)
- Https Cghs - Nic.in Reports View Hospital - JSPDocument36 pagesHttps Cghs - Nic.in Reports View Hospital - JSPRTI ActivistNo ratings yet
- Siui Smartor UTDocument6 pagesSiui Smartor UTJohn Choquemaque Mendoza100% (2)
- Current Concepts in Orthopedic Management of Multiple TraumaDocument8 pagesCurrent Concepts in Orthopedic Management of Multiple TraumanellieauthorNo ratings yet
- Lmo1fphy Copy 5Document5 pagesLmo1fphy Copy 5angelesreanzelNo ratings yet
- Inventory Japan Medical WO PriceDocument5 pagesInventory Japan Medical WO PriceAmin KhanNo ratings yet
- Final PC & PNDT ActDocument52 pagesFinal PC & PNDT ActChandra Mohan100% (1)
- EndoscopeDocument12 pagesEndoscopemamjoud mustaphaNo ratings yet
- Ge AviationDocument30 pagesGe Aviationpriyansh256No ratings yet
- Mukund Sadashiv Joshi (1942-2020) : Snehalata DeshmukhDocument1 pageMukund Sadashiv Joshi (1942-2020) : Snehalata DeshmukhKriti KumariNo ratings yet
- Abortion Doctors Fail To Call AmbulancesDocument29 pagesAbortion Doctors Fail To Call AmbulancesCarole Novielli0% (1)
- Lung and Airway Ultrasound in Pediatric AnesthesiaDocument7 pagesLung and Airway Ultrasound in Pediatric Anesthesiaema moralesNo ratings yet
- Planned Maintenance 2Document18 pagesPlanned Maintenance 2Ramanjaneya goudNo ratings yet
- 240 243Document5 pages240 243Rika WulandariNo ratings yet
- Oapowopdk ADocument33 pagesOapowopdk AraissaNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Machine Brochure - 221003 - 152159Document3 pagesUltrasound Machine Brochure - 221003 - 152159joseNo ratings yet
- 10introduction To EchocardiographyDocument21 pages10introduction To EchocardiographyMaria EdelNo ratings yet
- Field Trip 2Document13 pagesField Trip 2Raghvendra Singh KhichiNo ratings yet
- Scanner HydroFORM - en PDFDocument2 pagesScanner HydroFORM - en PDFaldeanucuNo ratings yet
- The Swollen Extremit A Systematic Approach To The Evaluation of A Common ComplaintDocument28 pagesThe Swollen Extremit A Systematic Approach To The Evaluation of A Common ComplaintnyjonesNo ratings yet
- Individual and Organizational Ethics: Social ResponsibilityDocument4 pagesIndividual and Organizational Ethics: Social ResponsibilityJulianaNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need, Nothing You Don't: ACUSON Juniper Ultrasound SystemDocument16 pagesEverything You Need, Nothing You Don't: ACUSON Juniper Ultrasound SystemEdwar Andreiv Polanco BeltranNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument21 pagesQuestionsashaaman0325No ratings yet
- Pitfalls in Femur Length Measurements: Ruth B. Goldstein, MD, Roy A. Filly, MD, Gary Simpson, MotDocument5 pagesPitfalls in Femur Length Measurements: Ruth B. Goldstein, MD, Roy A. Filly, MD, Gary Simpson, MotMoe Wai MyintNo ratings yet
- PAUT, TOFD, AUT in Lieu of Radiography PDFDocument111 pagesPAUT, TOFD, AUT in Lieu of Radiography PDFmahesh100% (12)
- Caution!: Portable Digital Color Doppler Ultrasound SystemDocument177 pagesCaution!: Portable Digital Color Doppler Ultrasound SystemDaniel Galindo100% (1)
- IOTA Risk Assessment Model-Ovarian Tumor Analysis (2019)Document1 pageIOTA Risk Assessment Model-Ovarian Tumor Analysis (2019)Tunlanan LekbornvornwongNo ratings yet
- PICO Field SERVICE MANUALDocument169 pagesPICO Field SERVICE MANUALEcomedical Pluss100% (2)
- Pictorial Essay B-Scan Ultrasonography in Ocular ADocument7 pagesPictorial Essay B-Scan Ultrasonography in Ocular ASugumar YathavanNo ratings yet
- CV Dr. Dr. Jacub Pandelaki 2016 (Edit Jan 2017)Document6 pagesCV Dr. Dr. Jacub Pandelaki 2016 (Edit Jan 2017)hasanuddinNo ratings yet