Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thermodynamics MCQ 1800 MCQ With Answers
Uploaded by
swai singhOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thermodynamics MCQ 1800 MCQ With Answers
Uploaded by
swai singhCopyright:
Available Formats
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
Thermodynamics Objective Type (c) tonne
Questions And Answers (Top 150)
(d) quintal
(e) newton.
1. Which of the following variables Answer : a
controls the physical properties of a
perfect gas 5. The unit of length in S.I. units is
(a) pressure (a) meter
(b) temperature (b) centimeter
(c) volume (c) kilometer
(d) all of the above (d) millimeter.
(e) atomic mass.
Answer : a
Answer : d
6. The unit of time in S.I. units is
2. The unit of temperature in S.I. units
(a) second
is
(b) minute
(a) Centigrade (c) hour
(b) Celsius (d) day
(c) Fahrenheit (e) year.
(d) Kelvin
Answer : a
(e) Rankine.
7. The unit of energy in S.I. units is
Answer : d
(a) watt
3. Which of the following laws is
applicable for the behavior of a (b) joule
perfect gas (c) joule/s
(d) joule/m
(a) Boyles law
(e) joule m.
(b) Charleslaw
(c) Gay-Lussac law Answer : b
(d) all of the above
8. According to Gay-Lussac law for a
(e) Joules law.
perfect gas, the absolute pressure of
given mass varies directly as
Answer : d
(a) temperature
4. The unit of mass in S.I. units is
(b) absolute
(a) kilogram (c) absolute temperature, if
(b) gram volume is kept constant
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
(d) volume, if temperature is kept 12. According to Daltons law, the
constant total pres sure of the mixture of
(e) remains constant,if volume gases is equal to
and temperature are kept constant.
(a) greater of the partial
Answer : c pressures of all
(b) average of the partial
9. General gas equation is pressures of all
(c) sum of the partial pressures of
(a) PV=nRT all
(b) PV=mRT (d) sum of the partial pressures
(d) PV = C of all divided by average molecular
weight
(c) PV=KiRT
(e) atmospheric pressure.
(e) Cp-Cv = Wj
Answer : c
Answer : b
13. The unit of pressure in S.I. units is
10. An ideal gas as compared to a
real gas at very high pressure
(a) kg/cm2
occupies
(b) mm of water column
(a) more volume (c) pascal
(b) less volume (d) dynes per square cm
(c) same volume (e) bars
(d) unpredictable behaviour
Answer : c
(e) no such correlation.
14. Temperature of a gas is produced
Answer : a
due to
11. Which of the following can be
(a) its heating value
regarded as gas so that gas laws
could be applicable, within the (b) kinetic energy of molecules
commonly encountered temperature (c) repulsion of molecules
limits. (d) attraction of molecules
(e) surface tension of molecules.
(a) 02, N2, steam, C02
(b) Oz, N2, water vapour Answer : b
(c) S02, NH3, C02, moisture
(d) 02, N2, H2, air 15. A closed system is one in which
(e) steam vapours, H2, C02.
(a) mass does not cross
boundaries of the system, though
Answer : d
energy may do so
(b) mass crosses the boundary
but not the energy
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
(c) neither mass nor energy Answer : a
crosses the boundaries of the system
(d) both energy and mass cross 19. Kinetic energy of the molecules in
the boundaries of the system terms of absolute temperature (T) is
proportional to
(e) thermodynamic reactions take
place.
(a) T
Answer : a (b) j
(c) J2
16. According to kinetic theory of
(d) Vr
gases, the absolute zero temperature
is attained when (e) 1/Vr.
(a) volume of the gas is zero Answer : a
(b) pressure of the gas is zero 20. Superheated vapour behaves
(c) kinetic energy of the
molecules is zero (a) exactly as gas
(d) specific heat of gas is zero (b) as steam
(e) mass is zero. (c) as ordinary vapour
(d) approximately as a gas
Answer : c
(e) as average of gas and
17. The pressureof a gas in terms of vapour.
its mean kinetic energy per unit
volume E is equal to Answer : d
(a) E/3 21. No liquid can exist as liquid at
(b) E/2
(a) 273 K
(c) 3E/4
(b) vacuum
(d)2E/3
(c) zero pressure
(e) 5E/4.
(d) centre of earth
Answer : d (e) in space.
18. Kinetic theory of gases assumes Answer : c
that the collisions between the
molecules are 22. Absolute zero pressure will occur
(a) perfectly elastic (a) at sea level
(b) perfectly inelastic (b) at the center of the earth
(c) partly elastic (c) when molecular momentum of
the system becomes zero
(d) partly inelastic
(d) under vacuum conditions
(e) partly elastic and partly
inelastic. (e) at a temperature of 273 K
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
Answer : c (c) is not dependent on the path
followed but on the state
23. The unit of power in S.I. units is (d) is dependent on the path
followed and not on the state
(a) newton
(e) remains constant.
(b) pascal
(c) erg Answer : b
(d) watt
27. Characteristic gas constant of a
(e) joule. gas is equal to
Answer : d (a) C/Cv
24. The condition of perfect vacuum, (b) Cv/Cp
i.e., absolute zero pressure can be (c) Cp Cv
attained at (d) Cp + Cv
(e) Cp x Cv
(a) a temperature of 273.16C
(b) a temperature of 0C Answer : c
(c) a temperature of 273 K
(d) a negative pressure and 0C 28. The behaviour of gases can be
temperature fully determined by
(e) cant be attained.
(a) 1 law
Answer : a (b) 2 laws
(c) 3 laws
25. Specific heat of air at constant (d) 4 laws
pressure is equal to
Answer : d
(a) 0.17
(b) 0.21 29. Boyles law i.e. pV = constant is
(c) 0.24 applicable to gases under
(d) 1.0
(a) all ranges of pressures
(e) 1.41
(b) only small range of pressures
Answer : c (c) high range of pressures
(d) steady change of pressures
26. Intensive property of a system is (e) atmospheric conditions.
one whose value
Answer : b
(a) depends on the mass of the
system, like volume 30. The ratio of two specific heats of
(b) does not depend on the mass air is equal to
of the system, like temperature,
pressure, etc. (a) 0.17
(b) 0.24
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
(c) 0.1 (a) mass does not cross
(d) 1.41 boundaries of the system, though
energy may do so
(e) 2.71.
(b) neither mass nor energy
Answer : d crosses the boundaries of the system
(c) both energy and mass cross
31. Which law states that the internal the boundaries of the system
energy of a gas is a function of (d) mass crosses the boundary
temperature but not the energy
(e) thermodynamic reactions do
(a) Charles law not occur.
(b) Joules law
Answer : c
(c) Regnaults law
(d) Boyles law 35. Gases have
(e) there is no such law.
(a) only one value of specific heat
Answer : b (b) two values of specific heat
32. Which law states that the specific (c) three values of specific heat
heat of a gas remains constant at all (d) no value of specific heat
temperatures and pressures (e) under some conditions one
value and sometimes two values of
(a) Charles Law specific heat.
(b) Joules Law
Answer : b
(c) Regnaults Law
(d) Boyles Law 36. According to which law, all perfect
(e) there is no such law. gases change in volume by l/273th of
their original volume at 0C for every
Answer : c 1C change in temperature when
pressure remains constant
33. The same volume of all gases
would represent their (a) Joules law
(b) Boyles law
(a) densities
(c) Regnaults law
(b) specific weights
(d) Gay-Lussac law
(c) molecular weights
(e) Charles law.
(d) gas characteristic constants
(e) specific gravities. Answer : e
Answer : c 37. According to Avogadros
Hypothesis
34. An open system is one in which
(a) the molecular weights of all
the perfect gases occupy the same
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
volume under same conditions of (b) Daltons law
pressure and temperature (c) Gas law
(b) the sum of partial pressure of
(d) Law of thermodynamics
mixture of two gases is sum of the two
(e) Joules law.
(c) product of the gas constant
and the molecular weight of an ideal
Answer : a
gas is constant
(d) gases have two values of 41. If a gas is heated against a
specific heat pressure, keeping the volume
(e) all systems can be regarded constant, then work done will be
as closed systems. equal to
Answer : a (a) + v
(b) ve
38. Work done in a free expansion
process is (c) zero
(d) pressure x volume
(a) + ve (e) any where between zero and
(b) -ve infinity.
(c) zero
Answer : c
(d) maximum
(e) minimum. 42. To convert volumetric analysis to
gravimetric analysis, the relative
Answer : c volume of each constituent of the flue
gases is
39. Extensive property of a system is
one whose value (a) divided by its molecular
weight
(a) depends on the mass of the (b) multiplied by its molecular
system like volume weight
(b) does not depend on the mass (c) multiplied by its density
of the system, like temperature,
pressure, etc. (d) multiplied by its specific
weight
(c) is not dependent on the path
followed but on the state (e) divided by its specific weight.
(d) is dependent on the path
Answer : b
followed and not on the state
(e) is always constant. 43. Properties of substances like
pressure, temperature and density, in
Answer : a thermodynamic coordinates are
40. The statement that molecular (a) path functions
weights of all gases occupy the same
volume is known as (b) point functions
(c) cyclic functions
(a) Avogadros hypothesis (d) real functions
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
(e) thermodynamic functions. (a) occupies volume proportional
to its molecular weight
Answer : b (b) occupies volume proportional
to its specific weight
44. An isolated system is one in
(c) occupies volume inversely
which
proportional to its molecular weight
(a) mass does not cross (d) occupies volume inversely
boundaries of the system, though proportional to its specific weight
energy may do so (e) occupies same volume.
(b) neither mass nor energy
crosses the boundaries of the system Answer : e
(c) both energy and mass cross
48. On weight basis, air contains
the boundaries of the system
following parts of oxygen
(d) mass crosses the boundary
but not the energy (a) 21
(e) thermodynamic reactions do (b) 23
not occur.
(c) 25
Answer : b (d) 73
(e) 79.
45. Which of the following quantities
is not the property of the system Answer : b
(a) pressure 49. Which of the following is the
(b) temperature property of a system
(c) specific volume
(a) pressure and temperature
(d) heat
(b) internal energy
(e) density.
(c) volume and density
Answer : d (d) enthalpy and entropy
(e) all of the above.
46. Mixture of ice and water form a
Answer : e
(a) closed system
(b) open system 50. Which of the following is not the
(c) isolated system intensive property
(d) heterogeneous system (a) pressure
(e) thermodynamic system. (b) temperature
Answer : d (c) density
(d) heat
47. According to Avogadros law, for a (e) specific volume.
given pressure and temperature,
each molecule of a gas Answer : d
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
51. Which of the following items is Answer : b
not a path function
55. A perfect gas at 27C is heated at
(a) heat constant pressure till its volume is
(b) work double. The final temperature is
(c) kinetic energy
(a) 54C
(d) vdp
(b) 327C
(e) thermal conductivity.
(c) 108C
Answer : e (d) 654C
(e) 600C
52. Heat and work are
Answer : b
(a) point functions
(b) system properties 56. The value of n = 1 in the
polytropic process indicates it to be
(c) path functions
(d) intensive properties (a) reversible process
(e) extensive properties. (b) isothermal process
(c) adiabatic process
Answer : c
(d) irreversible process
53. Work done in an adiabatic (e) free expansion process.
process between a given pair of end
states depends on Answer : b
(a) the end states only 57. Solids and liquids have
(b) particular adiabatic process
(a) one value of specific heat (ft)
(c) the value of index n
two values of specific heat
(d) the value of heattransferred (c) three values of specific heat
(e) mass of the system. (d) no value of specific heat
Answer : a (e) one value under some
conditions and two values under other
54. Which of the following parameters conditions.
is constant for a mole for most of the
Answer : a
gases at a given temperature and
pressure
58. If value of n is infinitely large in a
polytropic process pV = C, then the
(a) enthalpy
process is known as constant
(b) volume
(c) mass (a) volume
(d) entropy (b) pressure
(e) specific volume. (c) temperature
(d) enthalpy
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
(e) entropy. 62. Change in enthalpy of a system is
the heat supplied at
Answer : a
(a) constant pressure
59. The index of compression n tends (b) constant temperature
to reach ratio of specific heats y
(c) constant volume
when
(d) constant entropy
(a) flow is uniform and steady (e) N.T.P. condition.
(b) process is isentropic
Answer : a
(c) process is isothermal
(d) process is isentropic and 63. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
specific heat does not change with
temperature (a) deals with conversion of mass
(e) process is isentropic and and energy
specific heat changes with (b) deals with reversibility and
temperature. irreversibility of process
Answer : d (c) states that if two systems are
both in equilibrium with a third system,
60. The term N.T.P. stands for they are in thermal equilibrium with
each other
(a) nominal temperature and (d) deals with heat engines
pressure (e) does not exist.
(b) natural temperature and
pressure Answer : c
(c) normal temperature and
64. In an isothermal process, the
pressure
internal energy of gas molecules
(d) normal thermodynamic
practice (a) increases
(e) normal thermodynamic
(b) decreases
pressure.
(c) remains constant
Answer : c (d) may increase/decrease
depending on the properties of gas
61. A heat exchange process in which (e) shows unpredictable
the product of pressure and volume behaviour.
remains constant is known as
Answer : c
(a) heat exchange process
(b) throttling process 65. If a certain amount of dry ice is
(c) isentropic process mixed with same amount of water at
80C, the final temperature of mixture
(d) adiabatic process will be
(e) hyperbolic process.
(a) 80C
Answer : e
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
(b) 0C (a) 100 xlOO5 joules
(c) 40C (b) lxlO5 joules
(d) 20C (c) 10 xlO5 joules
(e) 60C. (d) 10 xlO5 kilo joules
(e) 10xl04ki\ojoules.
Answer : b
Answer : c
66. One watt is equal to
70. For which of the following
(a) 1 Nm/s substances, the gas laws can be used
(b) 1 N/mt with minimum error
(c) 1 Nm/hr
(a) dry steam
(d) 1 kNm/hr
(b) wet steam
(e) 1 kNm/mt.
(c) saturated steam
Answer : a (d) superheated steam
(e) steam at atmospheric
67. Work done is zero for the pressure.
following process
Answer : d
(a) constant volume
(b) free expansion 71. On volume basis, air contains
(c) throttling following parts of oxygen
(d) all Of the above (a) 21
(e) none of the above. (b) 23
Answer : d (c) 25
(d) 77
68. The basis for measuring (e) 79.
thermodynamic property of
temperature is given by Answer : a
(a) zeroth law of thermodynamics 72. The value of the product of
(b) first law of thermodynamics molecular weight and the gas
(c) second law of characteristic constant for all the
thermodynamics gases in M.K.S. unit is
(d) third law of thermodynamics
(a) 29.27 kgfm/molK
(e) Avogadros hypothesis.
(b) 8314kgfm/molK
Answer : a (c) 848kgfm/molK
(d) 427kgfm/molK
69. In a non-flow reversible process (e) 735 kgfm/molK.
for which p = (- 3V+ 15) x 105N/m2,V
changes from 1 m to 2 m3. The work Answer : c
done will be about
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
73. Universal gas constant is defined (b) 83.14J/kmolK
as equal to product of the molecular (c) 848J/kmolK
weight of the gas and
(d) All J/kmol K
(a) specific heat at constant (e) 735 J/kmol K.
pressure
(b) specific heat at constant Answer : b
volume
77. If a gas vapour is allowed to
(c) ratio of two specific heats expand through a very minute
(d) gas constant aperture, then such a process is
(e) unity. known as
Answer : d (a) free expansion
(b) hyperbolic expansion
74. For which of the following
(c) adiabatic expansion
substances, the internal energy and
enthalpy are the functions of (d) parabolic expansion
temperature only (e) throttling.
(a) any gas Answer : e
(b) saturated steam
78. If a fluid expands suddenly into
(c) water vacuum through an orifice of large
(d) perfect gas dimension, then such a process is
(e) superheated steam. called
Answer : d (a) free expansion
(b) hyperbolic expansion
75. In a free expansion process
(c) adiabatic expansion
(a) work done is zero (d) parabolic expansion
(b) heat transfer is zero (e) throttling.
(c) both (a) and (b) above
Answer : a
(d) work done is zero but heat
increases 79. The specific heat of air increases
(e) work done is zero but heat with increase in
decreases.
(a) temperature
Answer : c (b) pressure
(c) both pressure and
76. The value of the product of
molecular weight and the gas temperature
characteristic constant for all the (d) variation of its constituents
gases in S.I. units is (e) air flow
(a) 29.27 J/kmolK Answer : a
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
80. Which of the following processes (b) minimum
are thermodynamically reversible (d) maximum
(d) infinity
(a) throttling
(e) there is no such criterion.
(b) free expansion
(c) constant volume and constant Answer : a
pressure
(d) hyperbolic and pV = C 84. Minimum work in compressor is
(e) isothermal and adiabatic. possible when the value of adiabatic
index n is equal to
Answer : e
(a) 0.75
81. In order that a cycle be reversible, (b) 1
following must be satisfied (c) 1.27
(a) free expansion or friction (d) 1.35
resisted expansion/compression (e) 2.
process should not be encountered
(b) when heat is being absorbed, Answer : b
temperature of hot source and
working substance should be same 85. A gas is compressed in a cylinder
(c) when beat is being rejected, by a movable piston to a volume one-
half its original volume. During the
temperature of cold source and
working sub-stance should be same process 300 kJ heat left the gas and
internal energy remained same. The
(d) all of the above
work done on gas in Nm will be
(e) none of the above.
(a) 300 Nm
Answer : d
(b) 300,000 Nm
82. Which of the following processes (c) 30 Nm
is irreversible process (d) 3000 Nm
(e) 30,000 Nm.
(a) isothermal
(b) adiabatic Answer : b
(c) throttling
86. Molecular volume of any perfect
(d) all of the above
gas at 600 x 103 N/m2 and 27C will
(e) none of the above. be
Answer : c (a) 4.17m3/kgmol
(b) 400 m3/kg mol
83. For a thermodynamic process to
be reversible, the temperature (c) 0.15 m3/kg mol
difference between hot body and (d) 41.7 m3/kg mol
working substance should be (e) 417m3/kgmol.
(a) zero Answer : a
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
87. The more effective way of (e) mass and energy transfer do
increasing efficiency of Carnot not take place.
engine is to
Answer : c
(a) increase higher temperature
(b) decrease higher temperature 91. Energy can neither be created nor
destroyed but can be converted from
(c) increase lower temperature one form to other is inferred from
(d) decrease lower temperature
(e) keep lower temperature (a) zeroth low of thermodynamic
constant. (b) first law of thermodynamics
(c) second law to
Answer : d
thermodynamics
88. For reversible adiabatic process, (d) basic law of thermodynamics
change in entropy is (e) claussius statement.
(a) maximum Answer : b
(b) minimum
92. First law of thermodynamics
(c) zero furnishes the relationship between
(d) unpredictable
(e) negative (a) heat and work
(b) heat, work and properties of
Answer : c the system
(c) various properties of the
89. Entropy change depends on system
(d) various thermodynamic
(a) heat transfer
processes
(b) mass transfer
(e) heat and internal energy.
(c) change of temperature
(d) thermodynamic state Answer : b
(e) change of pressure and
volume. 93. According to first law of
thermodynamics
Answer : a
(a) work done by a system is
90. Isochoric process is one in which equal to heat transferred by the
system
(a) free expansion takes place (b) total internal energy of a
system during a process remains
(b) very little mechanical work is
constant
done by the system
(c) internal energy, enthalpy and
(c) no mechanical work is done
entropy during a process remain
by the system
constant
(d) all parameters remain
(d) total energy of a system
constant
remains constant
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
(e) entropy of a system remains (a) internal energy
constant. (b) entropy
Answer : d (c) thermal capacity
(d) enthalpy
94. In an isothermal process, the (e) thermal conductance.
internal energy
Answer : d
(a) increases
(b) decreases 98. First law of thermodynamics
(c) remains constant
(a) enables to determine change
(d) first increases and then in internal energy of the system
decreases
(b) does not help to predict
(e) first decreases and then whether the system will or not
increases. undergo a change
(c) does not enable to determine
Answer : c
change in entropy
95. Change in enthalpy in a closed (d) provides relationship between
system is equal to heat transferred if heat, work and internal energy
the reversible process takes place at (e) all of the above.
constant
Answer : e
(a) pressure
(b) temperature 99. According to first law of
thermodynamics
(c) volume
(d) internal energy (a) mass and energy are mutually
(e) entropy. convertible
(b) Carnot engine is most
Answer : a efficient
(c) heat and work are mutually
96. Change in internal energy in a convertible
closed system is equal to heat
(d) mass and light are mutually
transferred if the reversible process
convertible
takes place at constant
(e) heat flows from hot substance
(a) pressure to cold substance.
(b) temperature Answer : c
(c) volume
(d) internal energy 100. Addition of heat at constant
pressure to a gas results in
(e) entropy.
(a) raising its temperature
Answer : c
(b) raising its pressure
97. Total heat of a substance is also (c) raising its volume
known as
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
(d) raising its temperature and another engine between T2 and 400K
doing external work For both to do equal work, value of T2
(e) doing external work. will be
Answer : d (a) 650K
(b) 600K
101. Measurement of temperature is (c) 625K
based on
(d) 700K
(a) thermodynamic properties (e) 750K.
(b) zeroth law of thermodynamics
Answer : a
(c) first law of thermodynamics
(d) second law of 105. Carnot cycle efficiency is
thermodynamics maximum when
(e) joules law.
(a) initial temperature is 0K
Answer : b (b) final temperature is 0K
(c) difference between initial and
102. Carnot cycle has maximum
final temperature is 0K
efficiency for
(d) final temperature is 0C
(a) reversible engine (e) initial temperature is minimum
possible.
(b) irreversible engine
(c) new engine Answer : b
(d) petrol engine
(e) diesel engine. 106. If heat be exchanged in a
reversible manner, which of the
Answer : a following property of the working
substance will change accordingly
103. Carnot cycle efficiency depends
upon (a) temperature
(b) enthalpy
(a) properties of the (c) internal energy
medium/substance used
(d) entropy
(b) condition of engine
(e) all of the above.
(c) working condition
(d) temperature range of Answer : d
operation
(e) effectiveness of insulating 107. Which of the following
material around the engine. represents the perpetual motion of
the first kind
Answer : d
(a) engine with 100% thermal
104. An engine operates between efficiency
temperatures of 900Kandr2 and (b) a fully reversible engine
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
(c) transfer of heat energy from (b) constant volume
low temperature source to high (c) constant temperature
temperature source
(d) constant enthaply
(d) a machine that continuously
creates its own energy (e) any one of the above.
(e) production of energy by
Answer : c
temperature differential in sea water at
different levels.
111. A manufacturer claims to have a
heat engine capable of developing 20
Answer : d
h.p. by receiving heat input of 400
108. If a system after undergoing a kcal/mt and working between the
series of processes, returns to the temperature limits of 227 C and 27
initial state then C. His claim is
(a) process is thermodynamically (a) justified
in equilibrium (b) not possible
(b) process is executed in closed (c) may be possible with lot of
system cycle sophistications
(c) its entropy will change due to (d) cost will be very high
irreversibility (e) theroretically possible.
(d) sum of heat and work transfer
will be zero Answer : b
(e) no work will be done by the
system. 112. A diathermic wall is one which
Answer : d (a) prevents thermal interaction
(b) permits thermal interaction
109. An actual engine is to be
(c) encourages thermal
designed having same efficiency as
interaction
the Carnot cycle. Such a proposition
is (d) discourages thermal
interaction
(a) feasible (e) does not exist.
(b) impossible
Answer : b
(c) possible
(d) possible, but with lot of 113. The door of a running
sophistications refrigerator inside a room was left
(e) desirable. open. Which of the following
statements is correct?
Answer : d
(a) The room will be cooled to the
110. In a Carnot cycle, heat is temperature inside the refrigerator.
transferred at (b) The room will be cooled very
slightly.
(a) constant pressure
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
(c) The room will be gradually Answer : d
warmed up.
(d) The temperature of the air in 117. Water contained in a beaker can
room will remain unaffected. be made to boil by passing steam
through it
(e) any one of above is possible
depending on the capacity.
(a) at atmospheric pressure
Answer : c (b) at a pressure below the
firuosphejric pressure
114. An adiabatic wall is one which (c) at a pressure greater than
atmospheric pressure
(a) prevents thermal interaction (d) any pressure
(b) permits thermal interaction (e) not possible.
(c) encourages thermal
interaction Answer : c
(d) discourages thermal
interaction 118. The energy of molecular motion
appears as
(e) dos not exist.
Answer : a (a) heat
(b) potential energy
115. Compressed air coming out from (c) surface tension
a punctured football
(d) friction
(a) becomes hotter (e) increase in pressure.
(b) becomes cooler1
Answer : a
(c) remains at the same
temperature 119. The unitof universal gas
(d) may become hotter or cooler constant is
depend-ing upon the humidity of the
surrounding air (a) watts/K
(e) attains atmospheric (b) dynes/C
temperature. (c) ergscm/K
Answer : b (d)erg/K
(e) none of the above.
116. During throttling process
Answer : d
(a) heat exchange does not take
place 120. A sudden fall in the barometer
(b) no work is done by expanding reading is a sign of approaching
steam
(a) fine weather
(c) there is no change of internal
energy of steam (b) rains
(d) all of the above (c) storm
(e) entropy decreases. (d) cold wave
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
(e) hot wave. 125. The first law of thermodynamics
is the law of
Answer : c
(a) conservation of mass
121. Calorie is a measure of (b) conservation of energy
(c) conservation of momentum
(a) specific heat
(d) conservation of heat
(b) quantity of heat
(e) conservation of temperature.
(c) thermal capacity
(d)entropy Answer : b
(e) work.
126. Kelvin Plancks law deals with
Answer : b
(a) conservation of heat
122. I kgf/cm2 is equal to (b) conservation of work
(c) conversion of heat into work
(a) 760 mm Hg
(d) conversion fo work into heat
(b) zero mm Hg
(e) conservation of mass.
(c) 735.6 mm Hg
(d) 1 mm Hg Answer : c
(e) l00 mm Hg.
127. A perpetual motion machine is
Answer : c
(a) a thermodynamic machine
123. One barometric pressure or 1 (b) a non-thermodynamic
atmospheric pressure is equal to machine
(c) a hypothetical machine
(a) 1 kgf/cnr2
(d) a hypothetical machine whose
(b) 1.033 kgf/cm2
opera-tion would violate the laws of
(c) 0 kgf/cm2 thermodynamics
(d) 1.0197 kgf/cm2 (e) an inefficient machine.
(e) 100 kgf/cm2.
Answer : d
Answer : b
128. According to Clausis statement
124. Barometric pressure is equal to of second law of thermodynamics
(a) 760 mm Hg (a) heat cant be transferred from
low temperature source to high
(b) zero mm Hg
temperature source
(c) 735.6 mm Hg (b) heat can be transferred for
(d) 1 mm Hg low temperature to high temperature
(e) 100mm Hg. source by using refrigeration cycle.
(c) heat can be transferred from
Answer : a low temperature to high temperature
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
source if COP of process is more than 132. For same compression ratio and
unity for same heat added
(d) heat cant be transferred from
low temperature to high temperature (a) Otto cycle is more efficient
source without the aid of external than Diesel cycle
energy (b) Diesel cycle is more efficient
(e) all of the above. than Otto cycle
(c) efficiency depends on other
Answer : d factors
(d) both Otto and Diesel cycles
129. Which of the following is an
are equally efficient
irreversible cycle
(e) none of the above.
(a) carnot
Answer : a
(b) Stirling
(c) ericsson 133. The efficiency of a Carnot engine
(d) all of the above depends on
(e) none of the above.
(a) working substance
Answer : e (b) design of engine
(c) size of engine
130. Thermal power plant works on (d) type of fuel fired
(a) Carnot cycle (e) temperatures of source and
sink.
(b) Joule cycle
(d) Rankine cycle Answer : e
(d) Otto cycle
134. The efficiency of Carnot cycle is
(e) Brayton cycle.
maximum for
Answer : c
(a) gas engine
131. Otto cycle consists of following (b) well lubricated engine
four processes (c) petrol engine
(d) steam engine
(a) two isothermals and two
(e) reversible engine.
isentropics
(b) two isentropics and two Answer : e
constant volumes
(c) two isentropics, one constant 135. Diesel cycle consists of
volume and one constant pressure following four processes
(d) two isentropics and two
constant pres-sures (a) two isothermals and two
(e) none of the above. isentropics
(b) two isentropics, and two
Answer : b constant volumes.
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
(c) two isentropics, one constant (a) reversible cycles
volume and one constant pressure (b) irreversible cycles
(d) two isentropics and two (c) quasi-static cycles
constant pressures
(d) semi-reversible cycles
(e) none of the above.
(e) adiabatic irreversible cycles.
Answer : c
Answer : a
136. Carnot cycle is
140. Brayton cycle consists of
(a) a reversible cycle (ft) an following four processes
irreversible cycle
(a) two isothermals and two
(c) a semi-reversible cycle
isentropics
(d) a quasi static cycle (b) two isentropics and two
(e) an adiabatic irreversible cycle. constant volumes
(c) two isentropics, one constant
Answer : a volume and one constant pressure
(d) two isentropics and two
137. If both Stirling and Carnot cycles
constant pres-sures
operate within the same temperature
limits, then efficiency of Stirling cycle (e) none of the above.
as compared to Carnot cycle
Answer : d
(a) more
141. Reversed joule cycle is called
(b) less
(c) equal (a) Carnot cycle
(d) depends on other factors (b) Rankine cycle
(e) none of the above. (c) Brayton cycle
(d) Bell Coleman cycle
Answer : c
(e) Dual cycle.
138. A cycle consisting of two
adiabatics and two constant pressure Answer : c
processes is known as
142. Which of the following cycles is
(a) Otto cycle not a reversible cycle
(b) Ericsson cycle
(a) Carnot
(c) Joule cycle
(b) Ericsson
(d) Stirling cycle
(c) Stirling
(e) Atkinson cycle.
(d) Joule
Answer : c (e) none of the above.
139. Stirling and Ericsson cycles are Answer : e
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
143. The efficiency of Diesei cycle (d) increase/decrease depending
with decrease in cut off on application
(e) unpredictable.
(a) increases
(b) decreases Answer : a
(c) remains unaffected 147. The following cycle is used for
air craft refrigeration
(d) first increases and then
decreases
(a) Brayton cycle
(e) first decreases and then
(b) Joule cycle
increases.
(c) Carnot cycle
Answer : a (d) Bell-Coleman cycle
(e) Reversed-Brayton cycle.
144. The cycle in which heat is
supplied at constant volume and Answer : e
rejected at constant pressure is
known as 148. The thermodynamic difference
between a Rankine cycle working
(a) Dual combustion cycle with saturated steam and the Carnot
(b) Diesel cycle cycle is that
(c) Atkinson cycle
(a) carnot cycle cant work with
(d) Rankine cycle
saturated steam
(e) Stirling cycle.
(b) heat is supplied to water at
temperature below the maximum
Answer : c
temperature of the cycle
145. Which of the following cycles (c) a rankine cycle receives heat
has maximum efficiency at two places
(d) rankine cycle is hypothetical
(a) Rankine (e) none of the above.
(b) Stirling
Answer : b
(c) Carnot
(d) Brayton 149. The ideal efficiency of a Brayton
(e) Joule. cycle with regeneration, with increase
in pressure ratio will
Answer : c
(a) increase
146. The ideal efficiency of a Brayton (b) decrease
cycle without regeneration with
increase ni pressure ratio will (c) remain unchanged
(d) increase/decrease depending
(a) increase on ap-plication
(b) decrease (e) unpredictable.
(c) remain unchanged
Answer : b
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
150. Gas turbine cycle consists of
4. The amount of heat required to
(a) two isothermals and two raise the temperature of the unit
isentropics mass of gas through one degree at
constant volume, is called
(b) two isentropics and two
constant volumes A.specific heat at constant
(c) two isentropics, one constant volume
volume and one constant pressure B.specific heat at constant
(d) two isentropics and two pressure
constant pressures C.kilo Joule
(e) none of the above. D.none of these
Answer: A
Answer : d
5. There is a loss of heat in an
irreversible process.
Thermodynamics MCQ
A.True
SET-1 B.False
Answer: A
1. All the commercial liquid fuels are 6. An adiabatic process is one in
derived from natural petroleum (or which
crude oil).
A.no heat enters or leaves the
A.True gas
B. False B.the temperature of the gas
changes
Answer: A
C.the change in internal energy is
2. A cycle consisting of one constant equal to the mechanical workdone
pressure, one constant volume and
D.all of the above
two isentropic processes is known as
Answer: D
A.Carnot cycle
7. Water gas is obtained by passing
B.Stirling cycle air and a large amount of steam over
C.Otto cycle waste coal at about 650C.
D.Diesel cycle A.Correct
Answer: D
B.Incorrect
3. The efficiency and work ratio of a Answer: B
simple gas turbine cycle are
8. Which of the following represents
A.low Otto cycle on temperature entropy
B.very low (T s) diagram?
C.high
D.very high
Answer: B
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
C.Nitrogen
D.Carbon
Answer: D
13. Workdone in a free expansion
process is
A.zero
B.minimum
C.maximum
D.positive
Answer: A
14. The pressure exerted by an ideal
gas is __________ of the kinetic
energy of all the molecules contained
in a unit volume of gas.
9. When the gas is heated at constant A.one-half
volume, the heat supplied increases
B.one-third
the internal energy of the gas.
C.two-third
A.True
D.three-fourth
B.False Answer: C
Answer: A
15. The compression ratio for petrol
10. Which of the following is the engines is
lightest and most volatile liquid fuel?
A.3 to 6
A.Gasoline
B.5 to 8
B.Kerosene
C.15 to 20
C.Fuel oil
D.20 to 30
Answer: A
Answer: B
11. The processes occuring in open
system which permit the transfer of
16. The most probable velocity of the
mass to and from the system, are
gas molecules is given by
known as
A.flow processes
B.non-flow processes
C.adiabatic processes
D.none of these
Answer: A
12. Which of the following has the
minimum atomic mass?
A.Oxygen
B.Sulphur
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
Answer: B 21. Carbonisation of coal consists of
17. The efficiency of Diesel cycle A. drying and crushing the coal
approaches to Otto cycle efficiency to a fine powder
when B. moulding the finely ground
coal under pressure with or without a
A. cut-off is increased binding material
B. cut-off is decreased C. heating the wood with a
C. cut-off is zero limited supply of air to temperature not
less than 280C
D. cut-off is constant
D. none of the above
Answer: C
Answer: D
18.The entropy __________ in an
irreversible cyclic process.
22. The efficiency of Stirling cycle is
A. remains constant
__________ Carnot cycle.
B. decreases
C. increases A. greater than
Answer: C B. less than
C. equal to
19. The atomic mass of oxygen is
Answer: C
A. 12
B. 14
C. 16 23. According to Gay-Lussac law for
a perfect gas, p/T = constant, if v is
D. 32 kept constant.
Answer: C
A. True
20. The ratio of specific heat at B. False
constant pressure (Cp) and specific
heat at constant volume (cv) is Answer: A
A. equal to one
B. less than one 24. There is no change in internal
C. greater than one energy in an isothermal process.
D. none of these
A. Correct
Answer: C
B. Incorrect
Answer: A
Thermodynamics MCQ
SET-2 25. If the value of n = 0 in the
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
equation pvn = C, then the process is Answer: A
called
29. The distillation carried out in such
a way that the liquid with the lowest
A. constant volume process boiling point is first evaporated
B. adiabatic process and recondensed, then the liquid with
C. constant pressure process the next higher boiling point is then
evaporated and recondensed, and so
D. isothermal process
on until all the available liquid fuels
are separately recovered in the
Answer: C
sequence of their boiling points.
Such a process is called
26. The value of specific heat at
constant pressure (cp) is __________ A. cracking
that of at constant volume (cv). B. carbonisation
C. fractional distillation
A. less than D. full distillation
B. equal to
C. more than Answer: C
Answer: C
30. Which of the following statement
is incorrect?
27. When coal is strongly heated
continuously for 42 to 48 hours in the A. The liquid fuels consist of
absence of air in a closed vessel, hydrocarbons.
the process is known as __________ B. The liquid fuels have higher
of fuel. calorific value than solid fuels.
C. The solid fuels have higher
A. atomisation calorific value than liquid fuels.
B. carbonisation D. A good fuel should have low
ignition point.
Answer: B
Answer: C
28. Which of the following is correct?
31. Which of the following gas is
A. Absolute pressure = Gauge mostly used in town for street and
pressure + Atmospheric pressure domestic lighting and heating?
B. Gauge pressure = Absolute
pressure + Atmospheric pressure A. Producer gas
C. Atmospheric pressure = B. Coal gas
Absolute pressure + Gauge pressure C. Mond gas
D. Absolute pressure = Gauge D. Coke oven gas
pressure Atmospheric pressure
Answer: B
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
A. equal to
32. The value of gas constant (R) in S. B. directly proportional to
I. units is
C. inversely proportional to
A. 0.287 J/kgK
Answer: B
B. 2.87 J/kgK
C. 28.7 J/kgK
D. 287 J/kgK 37. The kinetic energy of molecules of
a gas becomes zero at absolute zero
Answer: D temperature.
A. Agree
33. In the first law of B. Disagree
thermodynamics, the total energy of
the system remains constant. Answer: A
A. True
B. False 38. One kg of carbon monoxide
requires __________ kg of oxygen to
Answer: A produce 11/7 kg of carbon dioxide
gas.
34. The efficiency of Diesel cycle A. All
increases with B. 4/7
C. 11/4
A. decrease in cut-off
D. 9/7
B. increase in cut-off
C. constant cut-off Answer: B
D. none of these
Answer: A 39. The absolute zero temperature is
taken as
35. Coal gas is obtained by mixing A. -273C
coal and gas at ambient conditions. B. 273C
C. 237C
A. Yes
D. -237C
B. No
Answer: A
Answer: B
40. The specific heat of water is
36. According to Avogadros law, the
density of any two gases is A. 1.817
__________ their molecular masses,
if the gases are at the same B. 2512
temperature and pressure. C. 4.187
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
D. none of these restore the initial conditions at the
end, is known as
Answer: C
A. reversible cycle
B. irreversible cycle
Thermodynamics MCQ
C. thermodynamic cycle
D. none of these
SET-3
Answer: C
41. The constant pressure, constant 45. An isothermal process is
volume and constant pvn processes governed by
are regarded as irreversible process.
A. Boyles law
A. True B. Charles law
B. False C. Gay-Lussac law
D. Avogadros law
Answer: A
Answer: A
42. Stirling and Ericsson cycles are
46. The sum of internal energy (U)
A. reversible cycles
and the product of pressure and
B. irreversible cycles volume (p.v) is known as
C. semi-reversible cycles
D. quasi-static cycles A. workdone
B. entropy
Answer: A C. enthalpy
D. none of these
43. When cut-off ratio is __________
Answer: C
the efficiency of Diesel cycle
approaches to Otto cycle efficiency.
47. The value of 1 mm of Hg is equal
A. zero
to
B. 1/5
C. 4/5 A. 1.333 N/m2
D. 1 B. 13.33 N/m2
C. 133.3 N/m2
Answer: A
D. 1333 N/m2
Answer: C
44. A series of operations, which
takes place in a certain order and
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
whose sole purpose is to convert heat
48. One kg of carbon requires 4/3 kg energy into work
of oxygen and produces __________ C. it is impossible to construct a
kg of carbon monoxide gas. device which operates in a cyclic
process and produces no effect other
A. 8/3 than the transfer of heat from a cold
B. 11/3 body to a hot body
D. none of the above
C. 11/7
D. 7/3 Answer: A
Answer: D
52. According to Gay-Lussac law, the
absolute pressure of a given mass of
49. The behaviour of a perfect gas, a perfect gas varies __________ as its
undergoing any change in the absolute temperature, when the
variables which control physical volume remains constant.
properties, is governed by
A. directly
A. Boyles law
B. indirectly
B. Charles law
C. Gay-Lussac law Answer: A
D. all of these
Answer: D 53. According to Avogadros law
A. the product of the gas
50. The universal gas constant of a constant and the molecular mass of
gas is the product of molecular mass an ideal gas is constant
of the gas and the gas constant. B. the sum of partial pressure of
the mixture of two gases is sum of the
A. Correct two
B. Incorrect C. equal volumes of all gases, at
the same temperature and pressure,
Answer: A contain equal number of molecules
D. all of the above
Answer: C
51. According to Kelvin-Plancks
statement of second law of
thermodynamics, 54. A process, in which the
temperature of the working
A. it is impossible to construct an substance remains constant during
engine working on a cyclic process, its expansion or compression, is
whose sole purpose is to convert heat called
energy into work
B. it is possible to construct an A. isothermal process
engine working on a cyclic process, B. hyperbolic process
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
C. adiabatic process temperature remains constant. This
D. polytropic process statement is known as Charles law.
Answer: A A. Yes
B. No
55. Which of the following gas has a Answer: B
minimum molecular mass?
A. Oxygen 59. The fuel mostly used in steam
B. Nitrogen boilers is
C. Hydrogen
A. brown coal
D. Methane
B. peat
Answer: C C. coking bituminous coal
D. non-coking bituminous coal
56. The total energy of a molecule is Answer: D
shared equally by the various
degrees of freedom possessed by it.
This law is known as 60. The efficiency of Joule cycle is
A. law of equipartition of energy A. greater than Carnot cycle
B. law of conservation of energy B. less than Carnot cycle
C. law of degradation of energy C. equal to Carnot cycle
D. none of these D. none of these
Answer: A Answer: B
57. The thermodynamic property of a
system is said to be an intensive Thermodynamics MCQ
property whose value for the entire
system __________ the sum of their SET-4
value for the individual parts of the
system.
A. is equal to 61. The hyperbolic process is
governed by
B. is not equal to
Answer: B A. Boyles law
B. Charles law
C. Gay-Lussac law
58. The absolute pressure of a given
D. Avogadros law
mass of a perfect gas varies inversely
as its volume, when the
Answer: A
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
A. It is used as the alternate
62. A closed system is one in which standard of comparison of all heat
heat and work crosses the boundary engines.
of the system but the mass of the B. All the heat engines are based
working substance does not crosses on Carnot cycle.
the boundary of the system.
C. It provides concept of
maximising work output between the
A. Yes two temperature limits.
B. No D. all of the above
Answer: A Answer: B
63. The entropy of water at 0C is 67. When two bodies are in thermal
assumed to be equilibrium with a third body, they are
also in thermal equilibrium with each
A. 1 other. This statement is called
B. 0
C. -1 A. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
D. 10 B. First law of thermodynamics
C. Second law of
Answer: B thermodynamics
D. Kelvin Plancks law
64. The greater the pressure
difference in throttling, the lesser is Answer: A
the irreversibility.
A. Yes 68. The area under the temperature-
B. No entropy curve (T s curve) of any
thermodynamic process represents
Answer: B
A. heat absorbed
B. heat rejected
65. During which of the following
C. either (a) or (b)
process does heat rejection takes
place in Carnot cycle? D. none of these
A. Isothermal expansion Answer: C
B. Isentropic expansion
C. Isothermal compression 69. The free expansion process is a
D. Isentropic compression constant enthalpy process.
Answer: C A. Correct
B. Incorrect
66. Which is the incorrect statement Answer: A
about Carnot cycle?
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
Answer: A
70. The specific heat at constant
volume is
74. The blast furnace gas is a by-
A. the amount of heat required to product in the production of pig iron
raise the temperature of unit mass of in the blast furnace.
gas through one degree, at constant
pressure A. Yes
B. the amount of heat required to B. No
raise the temperature of unit mass of
gas through one degree, at constant Answer: A
volume
C. the amount of heat required to
raise the temperature of 1 kg of water 75. The heat supplied to the gaS at
through one degree constant volume is (where m = Mass
D. any one of the above of gas, cv = Specific heat at constant
volume, cp = Specific heat at
Answer: B constant pressure, T2 T1 = Rise in
temperature, and R = Gas constant)
71. One kg of carbon produces A. mR(T2 T1)
__________ kg of carbon dioxide. B. mcv(T2 T1)
C. mcp(T2 T1)
A. 3/7
D. mcp(T2 + T1)
B. 7/3
C. 11/3 Answer: B
D. 3/11
Answer: C 76. Liquid fuels have lower efficiency
than solid fuels.
72. Ericsson cycle consists of two A. True
constant pressure and two isothermal B. False
processes.
Answer: B
A. Agree
B. Disagree
77. The heat absorbed during a
Answer: A polytropic process is
73. The isothermal and isentropic
processes are reversible non-flow
processes.
A. Agree
B. Disagree
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
Thermodynamics MCQ
SET-5
81. The general gas energy equation
is (where Q1 2 = Heat supplied, dU =
Change in internal energy, and W1 2
= Work done in heat units)
78. Liquid fuels consist of
hydrocarbons.
A. True
B. False
Answer: A
Answer: A
79. The expansion ratio (r) is the ratio
of (where v1 = Volume at the
82. The compression ratio for Diesel
beginning of expansion, and v2 =
engines is
Volume at the end of expansion)
A. 3 to 6
B. 5 to 8
C. 15 to 20
D. 20 to 30
Answer: C
83. In an isothermal process,
A. there is no change in
temperature
B. there is no change in enthalpy
80. The dual combustion cycle C. there is no change in internal
consists of one constant pressure, energy
two constant volume and two
D. all of these
isentropic processes.
Answer: D
A. Agree
B. Disagree
84. Which of the following is the
Answer: A
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
correct statement of the second law B. No
of thermodynamics?
Answer: A
A. It is impossible to construct an
engine working on a cyclic process,
whose sole purpose is to convert heat 88. The free expansion process is
energy into work. __________ non-flow process.
B. It is impossible to transfer
heat from a body at a lower A. reversible
temperature to a higher temperature, B. irreversible
without the aid of an external source.
C. There is a definite amount of Answer: B
mechanical energy, which can be
obtained from a given quantity of heat 89. A mixture of gas expands from
energy. 0.03 m3 to 0.06 m3 at a constant
D. all of the above pressure of 1 MPa and absorbs 84 kJ
of heat during the process. The
Answer: D change in internal energy of the
mixture is
85. The heating and expanding of a
gas is called thermodynamic system. A. 30 kJ
B. 54 kJ
A. Yes
C. 84 kJ
B. No
D. 114 kJ
Answer: B
90. The gas constant (R) is equal to
86. Otto cycle efficiency is higher the __________ of two specific heats.
than Diesel cycle efficiency for the
same compression ratio and heat A. sum
input because in Otto cycle B. difference
C. product
A. combustion is at constant
D. ratio
volume
B. expansion and compression Answer: B
are isentropic
C. maximum temperature is 91. Hydrogen is the __________
higher substance.
D. heat rejection is lower
A. lightest
Answer: D
B. heaviest
87. Liquid fuels have higher calorific Answer: A
value than solid fuels.
A. Yes 92. Otto cycle is also known as
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
A. constant pressure cycle Answer: A
B. constant volume cycle
C. constant temperature cycle 96. The efficiency of Diesel cycle
D. constant temperature and depends upon
pressure cycle
A. temperature limits
Answer: B
B. pressure ratio
93. For a perfect gas, according to C. compression ratio
Boyles law (where p = Absolute D. cut-off ratio and compression
pressure, v = Volume, and T = ratio
Absolute temperature)
Answer: D
A. p v = constant, if T is kept
constant 97. Those substances which have so
B. v/T = constant, if p is kept far not been resolved by any means
constant into other substances of simpler form
are called
C. p/T = constant, if v is kept
constant
A. elements
D. T/p = constant, if v is kept
constant B. compounds
C. atoms
Answer: A D. molecules
Answer: A
94. Producer gas is obtained by
A. partial combustion of coal, 98. The measurement of a
coke, anthracite coal or charcoal in a thermodynamic property known as
mixed air steam blast temperature is based on
B. carbonisation of bituminous
coal A. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
C. passing steam over B. First law of thermodynamics
incandescent coke
C. Second law of
D. passing air and a large thermodynamics
amount of steam over waste coal at
D. none of these
about 650C
Answer: A
Answer: A
99. Kelvin-Plancks law deals with
95. The efficiency of a dual
combustion cycle __________ upon A. conservation of work
cut-off ratio. B. conservation of heat
C. conversion of heat into work
A. depends D. conversion of work into heat
B. does not depend
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
Answer: C D. Heat motion
2. The term thermodynamics was first
used in 1849 in the publication of a
A. Rudolph Clausius
B. William Rankine
C. Lord Kelvin
D. Thomas Savery
3. What law asserts that energy is a
thermodynamic property?
A. First law of Thermodynamics
B. Second law of
Thermodynamics
C. Third law of Thermodynamics
D. Zeroth law of
Thermodynamics
4. What law asserts that energy has
quality as well as quantity?
A. First law of Thermodynamics
B. Second law of
Thermodynamics
MCQs Part I
C. Third law of Thermodynamics
1. The term thermodynamics comes
from Greek
D. Zeroth law of
words therme and dynamis which
Thermodynamics
means _______.
5. The macroscopic approach to the
A. Heat power
study of thermodynamics does not
require a knowledge of the behavior of
B. Heat transfer
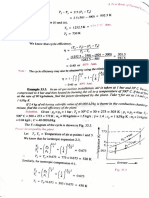
individual particles is called _____.
C. Heat energy
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
A. Dynamic thermodynamics 9. What is the mass or region outside
the system called?
B. Static thermodynamics
A. Surroundings
C. Statistical thermodynamics
B. Boundary
D. Classical thermodynamics
C. Volume
6. What is the more elaborate approach
to the study of thermodynamics and D. Environment
based on the average behavior of large
groups of individual particles? 10. What is the real or imaginary surface
that separates the system from its
A. Dynamic thermodynamics surroundings?
B. Static thermodynamics A. Division
C. Statistical thermodynamics B. Wall
D. Classical thermodynamics C. Boundary
7. What is defined a region in space D. Interface
chosen for study?
11. A system which consists of fixed
A. Surroundings amount of mass and no mass can cross
its boundary called _____.
B. System
A. Equilibrium system
C. Boundary
B. Thermal equilibrium system
D. Volume
C. Open system
8. The first law of thermodynamics is
based on which of the following D. Closed system
principles?
12. A system in which even energy is not
A. Conservation of mass allowed to cross the boundary is called
____.
B. Conservation of energy
A. Closed system
C. Action and reaction
B. Exclusive system
D. The entropy-temperature
relationship C. Isolated system
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
D. Special system C. Phase
13. A system in which there is a flow of D. Cycle
mass is known as _____.
17. How are thermodynamic properties
A. Equilibrium system classified?
B. Isolated system A. Physical and chemical
C. Open system B. Intensive and extensive
D. Closed system C. Real and imaginary
14. Open system usually encloses which D. Homogeneous and
of the following devices? heterogeneous
A. Compressor 18. The thermodynamic properties that
are independent on the size of the
B. Turbine system is called _____.
C. Nozzle A. Extensive property
D. All of the above B. Intensive property
15. The boundaries of a control volume, C. Open property
which may either real or imaginary is
called _____. D. Closed property
A. Control boundary 19. The thermodynamic properties that
are dependent on the size or extent of
B. Control system the system is called _____.
C. Interface A. Extensive property
D. Control surface B. Intensive property
16. Any characteristic of a C. Open property
thermodynamics system is called a
_____. D. Closed property
A. Property 20. Which is NOT an intensive property
of thermodynamics?
B. Process
A. Temperature
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
B. Mass A. Pressure
C. Pressure B. Thermal
D. Density C. Mechanical
21. Which is NOT an extensive property D. Phase
of thermodynamics?
25. If a system involves two phases, it is
A. Density in ______ equilibrium when the mass of
each phase reaches an equilibrium level
B. Mass and stays there.
C. Volume A. Chemical
D. Energy B. Thermal
22. Extensive properties per unit mass C. Mechanical
are called _____.
D. Phase
A. Specific properties
26. A system is in ______ equilibrium of
B. Relative properties its chemical composition does not
change with time, i.e., no chemical
C. Unit properties reaction occurs.
D. Phase properties A. Chemical
23. A system is in ______ equilibrium if B. Thermal
the temperature is the same throughout
the entire system. C. Mechanical
A. Static D. Phase
B. Thermal 27. The state of a simple compressible
system is completely specified by two
C. Mechanical independent, intensive properties. This
is known as ______.
D. Phase
A. Equilibrium postulate
24. A system is in ______ equilibrium if
there is no change in pressure at any B. State postulate
point of the system with time.
C. Environment postulate
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
D. Compressible system B. Phase
postulate
C. Cycle
28. What is the unit of the total energy of
the system? D. Direction
A. Kj 32. How many independent properties
are required to completely fix the
B. Kj/Kg equilibrium state of a pure gaseous
compound?
C. Kg
A. 4
D. g
B. 3
29. Without electrical, mechanical,
gravitational, surface tension and motion C. 2
effects, a system is called _____
system. D. 1
A. Simple 33. What is a process in which the
system remains infinitesimally closed to
B. Simple compressible an equilibrium state at all times?
C. Compressible A. Path equilibrium process
D. Independent B. Cycle equilibrium process
30. What refers to any change that a C. Phase equilibrium process
system undergoes from one equilibrium
state to another equilibrium state? D. Quasi-state or quasi-
equilibrium process
A. Process
34. A closed system may refer to
B. Path ______.
C. Phase A. Control mass
D. Cycle B. Control volume
31. What refers to the series of state C. Control energy
through which a system passes during a
process? D. Control temperature
A. Path
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
35. An open system may refer to D. Isometric process
______.
39. What is a process during which the
A. Control mass pressure remains constant?
B. Control volume A. Isobaric process
C. Control energy B. Isothermal process
D. Control temperature C. Isochoric process
36. A system is said to be in D. Isometric process
thermodynamic equilibrium if it
maintains ______ equilibrium. 40. What is a process during which the
specific volume remains constant?
A. Mechanical and phase
A. Isobaric process
B. Thermal and chemical
B. Isothermal process
C. Thermal, mechanical and
chemical C. Isochoric or isometric process
D. Thermal, phase, mechanical D. Isovolumetric process
and chemical
41. The prefix iso used to designate a
37. What is a process with identical end process means ______.
states called?
A. Cannot be interchanged
A. Cycle
B. Remains constant
B. Path
C. Approximately equal
C. Phase
D. Slight difference
D. Either path or phase
42. What does the term steady
38. What is a process during which the implies?
temperature remains constant?
A. No change with volume
A. Isobaric process
B. No change with time
B. Isothermal process
C. No change with location
C. Isochoric process
D. No change with mass
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
43. What does the tem uniform D. External energy
implies?
47. What form of energy refers to those
A. No change with volume a system possesses as a whole with
respect to some outside reference
B. No change with time frame, such as potential and kinetic
energies?
C. No change with location
A. Macroscopic form of energy
D. No change with mass
B. Microscopic form of energy
44. What is defined as a process during
which a fluid flows through a control C. Internal energy
volume steadily?
D. External energy
A. Transient-flow process
48. Who coined the word energy in
B. Steady and uniform process 1807?
C. Uniform-flow process A. William Rankine
D. Steady-flow process B. Rudolph Clausius
45. The sum of all the microscopic form C. Lord Kelvin
of energy is called _____.
D. Thomas Young
A. Total energy
49. The molecules of a gas moving
B. Internal energy through space with some velocity
possesses what kind of energy?
C. System energy
A. Translational energy
D. Phase energy
B. Spin energy
46. What type of system energy is
related to the molecular structure of a C. Rotational kinetic energy
system?
D. Sensible energy
A. Macroscopic form of energy
50. The electrons in an atom which
B. Microscopic form of energy rotate about the nucleus possess what
kind of energy?
C. Internal energy
A. Translational energy
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
B. Spin energy D. Thermal energy
C. Rotational kinetic energy 54. What is the internal energy
associated with the atomic bonds in a
D. Sensible energy molecule called?
A. Chemical energy
MCQs Part II B. Latent energy
51. The electrons which spins about its C. Phase energy
axis will possess what kind of energy?
D. State energy
A. Translational energy
55. What is the extremely large amount
B. Spin energy of energy associated with the strong
bonds within the nucleus of the atom
C. Rotational kinetic energy itself called?
D. Sensible energy A. Chemical energy
52. What refers to the portion of the B. Latent energy
internal energy of a system associated
with the kinetic energies of the C. Phase energy
molecules?
D. Nuclear energy
A. Translational energy
56. What are the only two forms of
B. Spin energy energy interactions associated with a
closed system?
C. Rotational kinetic energy
A. Kinetic energy and heat
D. Sensible energy
B. Heat transfer and work
53. What is the internal energy
associated with the phase of a system C. Thermal energy and chemical
called? energy
A. Chemical energy D. Latent energy and thermal
energy
B. Latent energy
57. What states that if two bodies are in
C. Phase energy thermal equilibrium with a third body,
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
they are also in equilibrium with each D. Rankine scale
other?
61. What temperature scale is identical
A. Zeroth law of thermodynamics to the Kelvin scale?
B. First law of thermodynamics A. Ideal gas temperature scale
C. Second law of B. Ideal temperature scale
thermodynamics
C. Absolute gas temperature
D. Third law of thermodynamics scale
58. Who formulated the zeroth law of D. Triple point temperature scale
thermodynamics in 1931?
62. The temperatures of the ideal gas
A. A. Celsuis temperature scale are measured by
using a ______.
B. A. Einstein
A. Constant-volume gas
C. R.H. Fowler thermometer
D. G. Fahrenheit B. Constant-mass gas
thermometer
59. What is the thermodynamic
temperature scale in the SI system? C. Constant-temperature gas
thermometer
A. Kelvin scale
D. Constant-pressure gas
B. Celsius scale thermometer
C. Fahrenheit scale 63. What refers to the strong repulsion
between the positively charged nuclei
D. Rankine scale
which makes fusion reaction difficult to
attain?
60. What is the thermodynamic
temperature scale in the English
A. Atomic repulsion
system?
B. Nuclear repulsion
A. Kelvin scale
C. Coulomb repulsion
B. Celsius scale
D. Charge repulsion
C. Fahrenheit scale
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
64. What gas thermometer is based on C. N-m
the principle that at low pressure, the
temperature of a gas is proportional to D. N-m^2
its pressure at constant volume?
68. Which of the following is NOT a
A. Constant-pressure gas value of the standard atmospheric
thermometer pressure?
B. Isobaric gas thermometer A. 1 bar
C. Isometric gas thermometer B. 1 atm
D. Constant-volume gas C. 1 kgf/cm^2
thermometer
D. 14.223 psi
65. What is the state at which all three
phases of water coexist in equilibrium? 69. What is the SI unit of pressure?
A. Tripoint of water A. Atm
B. Triple point of water B. Bar
C. Triple phase point of water C. Pa
D. Phase point of water D. Psi
66. What is defined as the force per unit 70. 1 bar is equivalent to how many
area? pascals?
A. Pressure A. 10^3
B. Energy B. 10^4
C. Work C. 10^5
D. Power D. 10^6
67. The unit pascal is equivalent to 71. 1 atm is equivalent to how many
______. pascals?
A. N/m^2 A. 101,325
B. N/m B. 101,689
C. 101,102
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
D. 101,812 C. Aneroid
72. What is considered as the actual D. Manometer
pressure at a given position and is
measured relative to absolute vacuum? 76. What instrument is used to measure
atmospheric pressure?
A. Gage pressure
A. Pitot tube
B. Absolute pressure
B. Wind vane
C. Atmospheric pressure
C. Barometer
D. Vacuum pressure
D. Manometer
73. What is the pressure below
atmospheric pressure called? 77. Another unit used to measure
atmospheric pressure is the torr. This
A. Gage pressure is named after the Italian physicist,
Evangelista Torrecelli. An average
B. Absolute pressure atmospheric pressure is how many torr?
C. Atmospheric pressure A. 740
D. Vacuum pressure B. 750
74. The difference between the absolute C. 760
pressure and the atmospheric pressure
is called the _____ pressure. D. 770
A. Gage 78. What states that for a confined fluid,
the pressure at a point has the same
B. Normal magnitude in all directions?
C. Standard A. Avogadros Law
D. Vacuum B. Amagat Law
75. Which of the following is NOT an C. Pascals Law
instrument used to measure pressure?
D. Bernoullis Theorem
A. Bourdon tube
79. What pressure measuring device
B. Pitot tube consists of a coiled hollow tube that
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
tends to straighten out when the tube is 83. One calorie is equivalent to how
subjected to an internal pressure? many joules?
A. Aneroid A. 4.448
B. Manometer B. 4.184
C. Bourdon pressure gage C. 4.418
D. Barometer D. 4.814
80. What is an energy that can be 84. One erg is equivalent to how many
transferred from one object to another joules?
causing a change in temperature of
each object? A. 10^-8
A. Power B. 10^-7
B. Heat transfer C. 10^-6
C. Heat D. 10^-5
D. Work 85. The first law of thermodynamics is
the:
81. What is the SI unit of energy?
A. Law of conservation of
A. Newton momentum
B. Btu B. Law of conservation of mass
C. Calorie C. Law of conservation of power
D. Joule D. Law of conservation of energy
82. One joule is equivalent to one 86. What is the study of energy and its
_____. transformations?
A. Kg m/ s^2 A. Thermostatics
B. Kg m^2/s^2 B. Thermophysics
C. Kg m^2/s C. Thermochemistry
D. Kg m/s D. Thermodynamics
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
87. What is considered as the heat 91. The enthalpy change for any
content of a system? chemical reaction is independent of the
intermediate stages, provided the initial
A. Enthalpy and final conditions are the same for
each route. This statement is known as:
B. Entropy
A. Dulongs Law
C. Internal heat
B. Daltons Law
D. Molar heat
C. Hesss Law
88. What refers to the amount of heat
needed to raise the temperature of an D. Petit Law
object by one degree Celsius or 1K?
92. What refers to the measure of the
A. Heat capacity disorder present in a given substance or
system?
B. Specific heat
A. Enthalpy
C. Latent heat
B. Entropy
D. Molar heat
C. Heat capacity
89. What is the heat capacity of one
mole of substance? D. Molar heat
A. Molecular heat 93. Entropy is measured in ______.
B. Specific heat A. Joule/Kelvin
C. Latent heat B. Joule-Meter/Kelvin
D. Molar heat C. Meter/Kelvin
90. What is the heat capacity of one D. Newton/Kelvin
gram of a substance?
94. What is the energy absorbed during
A. Molecular heat chemical reaction under constant
volume conditions?
B. Specific heat
A. Entropy
C. Latent heat
B. Ion exchange
D. Molar heat
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
C. Enthalpy C. Superheated
D. Enthalpy of reaction D. Unsaturated
95. When water exists in the liquid 99. A substance that has a fixed
phase and is not about to vaporize, it is chemical composition is known as
considered as _____liquid. ______ substance.
A. Saturated A. Monoatomic
B. Compressed or subcooled B. Heterogeneous
C. Superheated C. Homogeneous
D. Unsaturated D. Pure
96. A liquid that is about to vaporize is 100. What refers to the temperature at
called ______ liquid. which a pure substance changes phase
at a given pressure?
A. Saturated
A. Equilibrium temperature
B. Compressed or subcooled
B. Saturation temperature
C. Superheated
C. Superheated temperature
D. Unsaturated
D. Subcooled temperature
97. A vapor that is about to condense is
called ______ vapor.
A. Saturated
MCQs Part III
B. Compressed or subcooled 101. What refers to the pressure at
which a pure substance changes phase
C. Superheated at a given temperature?
D. Unsaturated A. Equilibrium pressure
98. A vapor that is not about to B. Saturation pressure
condense is called _____ vapor.
C. Superheated pressure
A. Saturated
D. Subcooled pressure
B. Compressed or subcooled
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
102. What is the amount of heat needed C. 333.7 kJ/kg
to turn 1 kg of the substance at its
melting point from the solid to liquid D. 330.7 kJ/kg
state?
106. What is the latent heat of
A. Heat of fusion vaporization of water at 1 atm?
B. Heat of vaporation A. 2314.8 kJ/kg
C. Heat of condensation B. 2257.1 kJ/kg
D. Heat of fission C. 2511.7 kJ/kg
103. What is the amount of heat needed D. 2429.8 kJ/kg
to turn 1kg of the substance at its boiling
point from the liquid to the gaseous 107. What refers to the point at which
state? the saturated liquid and saturated vapor
states are the same or identical?
A. Heat of fusion
A. Triple point
B. Heat of vaporation
B. Inflection point
C. Heat of condensation
C. Maximum point
D. Heat of fission
D. Critical point
104. What refers to the amount of
energy absorbed or released during a 108. What is defined as the direct
phase-change process? conversion of a substance from the solid
to the vapor state or vice versa without
A. Molar heat passing the liquid state?
B. Latent heat A. Condensation
C. Vaporization heat B. Vaporization
D. Condensation heat C. Sublimation
105. What is the latent heat of fusion of D. Cryogenation
water at 1 atm?
109. The amount of heat required to
A. 331.1 kJ/kg raise the temperature of 1kg of water
through 1 C is called ______.
B. 332.6 kJ/kg
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
A. Calorie 113. The ratio of the mass of vapor to
the total mass of the mixture is called
B. Joule ______.
C. BTU A. Vapor ratio
D. Kilocalorie B. Vapor content
110. The amount of heat required to C. Vapor index
raise the temperature of 1 pound of
water by 1F is called ______. D. Quality
A. Calorie 114. The equation of state refers to any
equation that relates the ______ of the
B. Joule substance.
C. BTU A. Pressure and temperature
D. Kilocalorie B. Pressure, temperature and
specific weight
111. 1 British thermal unit (BTU) is
equivalent to how many joules? C. Temperature and specific
weight
A. 1016
D. Pressure, temperature and
B. 1043 specific volume
C. 1023 115. In the equation Pv = RT, the
constant of proportionality R is known as
D. 1054
______.
112. The term enthalpy comes from
A. Universal gas constant
Greek enthalpen which means ______.
B. Gas constant
A. Warm
C. Ideal gas factor
B. Hot
D. Gas index
C. Heat
116. The gas constant of a certain gas is
D. Cold
the ratio of:
A. Universal gas constant to
molar mass
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
B. Universal gas constant to 120. The ______ of a substance is the
atomic weight amount of heat that must be added or
removed from a unit mass of the
C. Universal gas constant to substance to change its temperature by
atomic number one degree.
D. Universal gas constant to A. Latent heat of fusion
number of moles
B. Molar heat
117. What is the value of the universal
gas constant in kJ/kmol K? C. Specific heat capacity
A. 10.73 D. Specific heat
B. 1.986 121. What is the specific heat capacity
of water in J/kg C?
C. 8.314
A. 4581
D. 1545
B. 4185
118. The mass of one mole of a
substance in grams is known as ______. C. 4518
A. Molar weight D. 4815
B. Molar mass 122. What is the SI unit of specific heat
capacity?
C. Molar volume
A. J/kg
D. Molar constant
B. J/kg F
119. What is defined as the energy
required to raise the temperature of a C. J/kg C
unit mass of a substance by one
degree? D. J/C
A. Latent heat of fusion 123. What is constant for a substance
that is considered incompressible?
B. Molar heat
A. Specific volume of density
C. Specific heat capacity
B. Pressure
D. Specific heat
C. Temperature
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
D. All of the above D. Electrification
124. If there is no heat transferred 128. What refers to the transfer of
during the process, it is called a ______ energy between a solid surface and the
process. adjacent fluid that is in motion?
A. Static A. Conduction
B. Isobaric B. Convection
C. Polytropic C. Radiation
D. Adiabatic D. Electrification
125. The term adiabatic comes from 129. What refers to the transfer of
Greek adiabatos which means ______. energy from the more energetic particles
of a substance to the adjacent less
A. No heat energetic ones as a result of interaction
between particles?
B. No transfer
A. Conduction
C. Not to be passed
B. Convection
D. No transformation
C. Radiation
126. How is heat transferred?
D. Electrification
A. By conduction
130. What states that the net mass
B. By convection transfer to or from a system during a
process is equal to the net change in the
C. By radiation
total mass of the system during that
process?
D. All of the above
A. Third law of thermodynamics
127. What refers to the transfer of
energy due to the emission of
B. Conservation of energy
electromagnetic waves or photons?
principle
A. Conduction
C. Second law of thermodynamic
B. Convection
D. Conservation of mass
principle
C. Radiation
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
131. Which of the following statements 134. What is a measure of the ability of
is TRUE for an ideal gas, but not for a a material to conduct heat?
real gas?
A. Specific heat capacity
A. PV = nRT
B. Coefficient of thermal
B. An increase in temperature expansion
causes an increase in the kinetic
energy of the gas C. Coefficient of thermal
conductivity
C. The total volume of molecules
on a gas is nearly the same as D. Thermal conductivity
the volume of the gas as a whole
135. What refers to the heating of the
D. No attractive forces exists earths atmosphere not caused by direct
between the molecule of a gas sunlight but by infrared light radiated by
the surface and absorbed mainly by
132. How does an adiabatic process atmospheric carbon dioxide?
compare to an isentropic process?
A. Greenhouse effect
A. Adiabatic heat transfer is not
equal to zero; isentropic heat B. Global warming
transfer is zero
C. Thermal rise effect
B. Both heat transfer = 0;
isentropic: reversible D. Ozone effect
C. Adiabatic heat transfer = 0; 136. What is a form of mechanical work
isentropic: heat transfer is not which is related with the expansion and
equal to zero compression of substances?
D. Both heat transfer is not equal A. Boundary work
to zero; isentropic: irreversible
B. Thermodynamic work
133. Which of the following is the Ideal
C. Phase work
gas law (equation)?
D. System work
A. V/T = K
137. Thermal radiation is an
B. V= k*(1/P)
electromagnetic radiation with
C. P1/T1 = P2/T2 wavelengths in _____ range.
D. PV = nRT A. 1 to 100 m
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
B. 0.1 to 100 m A. Gray body
C. 0.1 to 10 m B. Black body
D. 10 to 100 m C. Real body
138. What refers to the rate of thermal D. White body
radiation emitter per unit area of a body?
142. At same temperatures, the
A. Thermal conductivity radiation emitted by all real surfaces is
______ the radiation emitted by a black
B. Absorptivity body.
C. Emissivity A. Less than
D. Emissive power B. Greater than
139. What states that for any two bodies C. Equal to
in thermal equilibrium, the ratios of
emissive power to the absorptivity are D. Either less than or greater
equal? than
A. Kirchhoffs radiation law 143. Which is NOT a characteristic of
emissivity?
B. Newtons law of cooling
A. It is high with most nonmetals
C. Stefan-Boltzmann law
B. It is directly proportional to
D. Hesss law temperature
140. What is considered as a perfect C. It is independent with the
absorber as well as a perfect emitter? surface condition of the material
A. Gray body D. It is low with highly polished
metals
B. Black body
144. What is the emissivity of a black
C. Real body body?
D. White body A. 0
141. What is a body that emits a B. 1
constant emissivity regardless of the
wavelength? C. 0.5
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
D. 0.25 A. Energy conservation
145. What is the absorptivity of a black B. Energy equation
body?
C. Energy balance
A. 0
D. Energy conversion equation
B. 1
149. What remains constant during a
C. 0.5 steady-flow process?
D. 0.25 A. Mass
146. What is sometimes known as the B. Energy content of the control
Fourth-power law? volume
A. Kirchhoffs radiation law C. Temperature
B. Newtons law of cooling D. Mass and energy content of
the control volume
C. Stefan-Boltzmann law
150. Thermal efficiency is the ratio of:
D. Hesss law
A. Network input to total heat
147. What states that the net change in input
the total energy of the system during a
process is equal to the difference B. Network output to total heat
between the total energy entering and output
the total energy leaving the system
during that process? C. Network output to total heat
input
A. Third law of thermodynamics
D. Network input to total heat
B. Conservation of energy output
principle
C. Second law of
thermodynamics MCQs Part IV
D. Conservation of mass 151. What law states that it is impossible
principle to operate an engine operating in a cycle
that will have no other effect than to
148. The equation Ein Eout = Esystem is extract heat from a reservoir and turn it
known as ______. into an equivalent amount of work?
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
A. Zeroth law of thermodynamics 155. What refers to the amount of heat
removed from the cooled space in BTSs
B. First law of thermodynamics for 1 watt-hour of electricity consumed?
C. Second law of A. Cost efficiency rating
thermodynamics
B. Energy efficiency rating
D. Third law of thermodynamics
C. Coefficient of performance
152. Which statement of the second law
of thermodynamics states that no heat D. Cost of performance
engine can have a thermal efficiency of
100 percent? 156. What law states that it is impossible
to build a device that operates in a cycle
A. Kelvin-Planck statement and produces no effect other than the
transfer of heat from a lower-
B. Clausius statement temperature body to a higher-
temperature body?
C. Kevin statement
A. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
D. Rankine statement
B. First law of thermodynamics
153. What is the ratio of the useful heat
extracted to heating value? C. Second law of
thermodynamics
A. Combustion efficiency
D. Third law of thermodynamics
B. Phase efficiency
157. What statement of the second law
C. Heat efficiency of thermodynamics states that it is
impossible to build a device that
D. Work efficiency
operates in a cycle and produces no
effect other than the transfer of heat
154. What is defined as the ratio of the
from a lower-temperature body to a
net electrical power output to the rate of
higher-temperature body?
fuel energy input?
A. Kelvin-Planck statement
A. Combustion efficiency
B. Clausius statement
B. Thermal efficiency
C. Kelvin statement
C. Overall efficiency
D. Rankine statement
D. Furnace efficiency
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
158. A device that violates either the first 161. Carnot cycle is the best known
law of thermodynamics or the second reversible cycle which was first proposed
law of thermodynamics is known as in what year?
_____.
A. 1842
A. Ambiguous machine
B. 1824
B. Universal machine
C. 1832
C. Perpetual-motion machine
D. 1834
D. Unique machine
162. Who proposed the Carnot cycle?
159. A device that violates the first law
of thermodynamics is called a _____. A. Sammy Carnot
A. Perpetual-motion machine of B. Sonny Carnot
the first kind
C. Sadi Carnot
B. Universal machine of the first
kind D. Suri Carnot
C. Ambiguous machine of the 163. The Carnot cycle is composed of
first kind how many reversible processes?
D. Unique machine of the first A. 2
kind
B. 3
160. A device that violates the second
C. 4
law of thermodynamics is called a
______.
D. 5
A. Perpetual motion machine of
164. The Carnot cycle is composed of
the second kind
______ processes.
B. Universal machine of the
A. One isothermal and one
second kind
adiabatic
C. Ambiguous machine of the
B. One isothermal and two
second kind
adiabatic
D. Unique machine of the second
C. Two isothermal and one
kind
adiabatic
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
D. Two isothermal and two 168. Who discovered the
adiabatic thermodynamic property Entropy in
1865?
165. What is the highest efficiency of
heat engine operating between the two A. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
thermal energy reservoirs at
temperature limits? B. First law of thermodynamics
A. Ericson efficiency C. Second law of
thermodynamics
B. Otto efficiency
D. Third law of thermodynamics
C. Carnot efficiency
169. A process during which entropy
D. Stirling efficiency remains constant is called ______
process
166. What is a heat engine that operates
on the reversible Carnot cycle called? A. Isometric
A. Carnot heat engine B. Isochoric
B. Ideal heat engine C. Isobaric
C. Most efficient heat engine D. Isentropic
D. Best heat engine 170. A reversible adiabatic process is
necessarily isentropic but an isentropic
167. What states that thermal process is not necessarily reversible
efficiencies of all reversible heat engines adiabatic process. This statement is:
operating between the same two
reservoirs are the same and that no heat A. True
engine is more efficient than a reversible
one operating between the same two B. False
reservoirs?
C. May be true and may be false
A. Ericson principle
D. Absurd
B. Carnot principle
171. The term isentropic process used
C. Otto principle in thermodynamics implies what?
D. Stirling principle A. Reversible adiabatic process
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
B. Externally reversible, adiabatic C. Entropy balance relation
process
D. Third law of thermodynamics
C. Internally reversible, adiabatic
process 175. What law states that entropy can
be created but it cannot be destroyed?
D. Irreversible adiabatic process
A. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
172. What states that the entropy of a
pure crystalline substance at absolute B. First law of thermodynamics
zero temperature is zero?
C. Second law of
A. Zeroth law of thermodynamics thermodynamics
B. First law of thermodynamics D. Third law of thermodynamics
C. Second law of 176. Entropy is transferred by ______.
thermodynamics
A. Work
D. Third law of thermodynamics
B. Heat
173. What law provides an absolute
reference point for the determination of C. Energy
entropy?
D. Work and heat
A. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
177. During adiabatic, internally
B. First law of thermodynamics reversible process, what is true about
the change in entropy?
C. Second law of
thermodynamics A. It is temperature-dependent
D. Third law of thermodynamics B. It is always greater than zero
174. The entropy change of a system C. It is always zero
during a process is equal to the net
D. It is always less than zero
entropy transfer through the system
boundary and the entropy generated
178. Water boils when:
within the system. This statement is
known as: A. Its saturated vapor pressure
equals to the atmospheric
A. Entropy generation
pressure
B. Entropy change of a system
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
B. Its vapor pressure equals C. Gay-Lussac Law
76cm of mercury
D. Ideal gas law
C. Its temperature reaches 212
degree Celsius 182. Which of the following is the
mathematical representation of the
D. Its vapor pressure is 1 gram Charless law?
per sq. cm
A. V1/V2= P2/P1
179. Which of the following is standard
temperature and pressure (STP)? B. V1/T1=V2/T2
A. 0 degree Celsius and one C. V1/T2=V2/T1
atmosphere
D. V1/V2=P2/P1
B. 32 degree Fahrenheit and zero
pressure 183. Which of the following is the
formula for thermal resistance?
C. 0 degree Kelvin and one
atmosphere A. Thickness of material/ thermal
conductivity of material
D. 0 degree Fahrenheit and zero
pressure B. 2(thickness of
material)/thermal conductivity of
180. What is the value of the work done material
for a closed, reversible isometric
system? C. Thickness of material/
2(thermal conductivity of
A. Zero material)
B. Positive D. Thickness of material x
thermal conductivity of material
C. Negative
184. In the process of radiation, energy
D. Positive or negative is carried by electromagnetic waves.
What is the speed of electromagnetic
181. At constant pressure, the volume waves?
of a gas is inversely proportional to the
pressure. This is known as ______. A. 182,000 miles/second
A. Boyles Law B. 184,000 miles/second
B. Charless Law C. 186,000 miles/second
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
D. 188,000 miles/second A. Third law of thermodynamics
185. For heat engine operating between B. Law of Dulong and Petit
two temperatures (T1>T2), what is the
maximum efficiency attainable? C. Mollier diagram
A. Eff = 1 (T2/T1) D. Pressure-enthalpy diagram
B. Eff = 1 - (T1/T2) 189. Considering one mole of any gas,
the equation of state of ideal gases is
C. Eff = T1 - T2 simply the ______ law.
D. Eff = 1 - (T2/T1)^2 A. Gay-Lussac law
186. Which one is the correct relation B. Dulong and Petit
between energy efficiency ratio (EER)
and coefficient of performance (COP)? C. Avogadros
A. EER = 2.34 COP D. Henrys
B. EER = 3.24 COP 190. An ideal gas whose specific heats
are constant is called _____.
C. EER = 3.42 COP
A. Perfect gas
D. EER = 4.23 COP
B. Natural gas
187. The coefficient of performance
(COP) is the ratio between the: C. Artificial gas
A. Power consumption in watts D. Refined gas
and heat absorbed per hour
191. What are the assumptions of the
B. Heat absorbed per hour and kinetic gas theory?
the power consumption in watts
A. Gas molecules do not attract
C. Work required and the each other
absorbed heat
B. The volume of the gas
D. Absorbed heat and work molecules is negligible compared
required to the volume of the gas
188. What predicts the approximate C. The molecules behave like
molar specific heat at high temperatures hard spheres
from the atomic weight?
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
D. All of the above B. Heel reservoir
192. The total volume of a mixture of C. Toe reservoir
non-reacting gases is equal to the sum
of the partial volumes. This statement is D. Sink reservoir
known as ______.
196. A ______ is a flow in which the gas
A. Law of Dulong and Petit flow is adiabatic and frictionless and
entropy change is zero.
B. Maxwell-Boltzmann law
A. Isentropic flow
C. Amagats law
B. Isobaric flow
D. Avogadros law
C. Steady flow
193. An adiabatic process in which there
is no change in system enthalpy but for D. Uniform flow
which there is a significant decrease in
pressure is called _____. 197. What refers to the minimum
temperature at which combustion can be
A. Isochoric process sustained?
B. Isobaric process A. Burn temperature
C. Throttling process B. Kindle temperature
D. Quasistatic process C. Spark temperature
194. What is defined as the ratio of the D. Ignition temperature
change in temperature to the change in
pressure when a real gas is throttled? 198. What law predicts the dew point of
moisture in the fuel gas?
A. Rankine coefficient
A. Daltons law
B. Kelvin coefficient
B. Law of Dulong and Petit
C. Maxwell-Boltzmann coefficient
C. Ringelman law
D. Joule-Thomson coefficient
D. Amagats law
195. The low temperature reservoir of
the heat reservoirs is known as ______. 199. What law states that one energy
from can be converted without loss into
A. Source reservoir another form?
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
A. Amagats law c. Fahrenheit
B. Joules law d. Rankine
C. Lussacs law 203. The energy that flows from higher
temperature object to a lower
D. Henrys law temperature object because of the
difference in temperature is called
200. Which is NOT a correct statement?
a. heat
A. A superheated vapor will not
condense when small amount of b. temperature
heat re removed
c. thermodynamics cycle
B. An ideal gas is a gas that is
not a superheated vapor d. energy flow
C. A saturated liquid can absorb 204. The amount of heat energy per
as much heat as it can without kilogram that must be added or removed
vaporizing when a substance changes from one
phase to another.
D. Water at 1 atm and room
temperature is subcooled a. specific heat
b. heat of expansion
MCQs Part V c. latent heat
201. Thermodynamics is the study of
heat and its transformation which stems d. useful heat
from Greek words meaning _________.
205. The change in physical size of a
a. transformation of heat substance when its temperature
changes.
b. transformation of energy
a. intensive property
c. movement of heat
b. extensive property
d. movement of matter
c. volume expansion
202. What is the Si unit for temperature?
d. thermal expansion
a. Kelvin
206. A stress which develops within an
b. Celsius object when it attempts to expand or
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
contract in response to a temperature c. Specific Pressure
changes, but cannot, due to being held
rigidly in place. d. Equilibrium Phase Pressure
a. elongation 210. Vapor pressure depends only on
_________.
b. thermal stress
a. pressure
c. expansion contraction
b. force
d. thermal expansion
c. volume
207. The energy associated with
individual molecules in a gas, liquid or d. temperature
solid.
211. A plot of pressure vs. temperature
a. Specific Energy for a given substance showing the
various phases possible for that
b. Molecular Energy particular substance.
c. Internal Energy a. Phase diagram
d. Phase Energy b. P-T diagram
208. The heat Q per unit mass per c. Wein Diagram
degree change in temperature that must
be supplied or removed to change the d. Histogram
temperature of a substance.
212. _________ is the grand total of all
a. Specific Heat Capacity energies inside a substance.
b. Latent Heat a. Internal Energy
c. Heat of Transformation b. Grand Energy
d. Internal Heat c. Atomic Energy
209. The pressure of the vapor phase of d. Elemental Energy
a substance that is in equilibrium with
the liquid or solid phase. 213. The _________ is defined as the
amount of heat required to change the
a. Phase Pressure temperature of 1 gram of water by 1
Celsius degree.
b. Equilibrium Vapor Pressure
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
a. specific heat 217. _________ is a thermodynamic
potential which measures the useful
b. latent heat work obtainable from a closed
thermodynamic system at a constant
c. Joule temperature and volume.
d. calorie a. useful work
214. _________ is a measure of the b. energy consumed
average kinetic energy per molecule in a
substance. c. Helmholtz free energy
a. movement d. Kinetic Energy
b. temperature 218. How much will the length of a 1.0
km section of concrete highway change
c. heat if the temperature varies from -15C in
winter to 41C in summer?
d. mass
a. 0.67 m
215. _________ the very small KE still
present in molecules at absolute zero b. 2.2 m
temperature.
c. 3.1 m
a. internal KE
d. 0.47 m
b. Atomic kinetic energy
219. Two 12 ft. sections of aluminum
c. Zero-Point Energy siding are placed end to end on the
outside wall of house. How large a gap
d. Subliminal Energy
should be left between the pieces to
prevent buckling if the temperature can
216. Convert the change of temperature
change by 55C?
from 20C to 30C to Kelvin scale.
a. 0.21 m
a. 10 K
b. 0.18 m
b. 293 K
c. 0.31 in
c. 303 K
d. 0.18 in
d. 273 K
220. What is the amount of radiant
energy received each second over each
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
square meter that is at right angles to b. relative humidity
the suns rays at the top of the
atmosphere? c. absolute pressure
a. 1400 J d. vapor pressure
b. 6000 J 224. _________ is the transition of a
given substance from the solid to the
c. 10000 J gas phase with no intermediate liquid
stage.
d. 800 J
a. Convection
221. _________ is a thermodynamic
potential that measures the useful or b. Conduction
process-initiating work obtainable from
an isothermal, isobaric thermodynamic c. Radiation
system.
d. Sublimation
a. Du-Pont Potential
225. A process in which heat energy is
b. Gibbs free energy transferred by the flow of fluid.
c. Rabz-Eccles Energy a. Convection
d. Claussius Energy b. Conduction
222. All the energy we consume c. Radiation
ultimately becomes _________.
d. Sublimation
a. heat
226. In order to use a substance to
b. depleted make a thermometer the substance
must _________ with a temperature
c. exhausted change.
d. work a. expand
223. _________is the partial pressure of b. contract
water vapor at the existing temperature
divided by the equilibrium vapor c. change
pressure of water at the existing
temperature. d. increase
a. vacuum pressure
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
227. For most solids, the coefficient of c. the relative humidity remains
volume expansion is _________ the constant
coefficient of linear expansion.
d. the air would eventually
a. unrelated to become saturated
b. proportional to 231. The flow of a fluid when heat is
transferred by convection.
c. twice
a. placidity
d. three times
b. mass flow
228. The volume of a given amount of
water _________ as the temperature c. convection current
decreases from 4C to 0C.
d. heat transfer
a. decreases
232. An idealized perfect absorber and
b. increases perfect emitter of radiation.
c. remains constant a. elastic material
d. none of the above b. transponder material
229. The gas in a constant gas c. Teflon
thermometer cooled to absolute zero
would have _________. d. blackbody
a. no volume 233. A process by which heat is
transferred through a material without a
b. no pressure bulk movement of the material.
c. zero temperature at all scales a. Convection
d. none of the above b. Conduction
230. On a day when the partial pressure c. Radiation
of water vapor remains constant, what
happens as the temperature rises? d. Emission
a. the relative humidity increases 234. Is the amount of a substance that
contains Avogadros number of
b. the relative humidity decreases atoms/molecules.
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
a. mass 238. A _________ is a quantity whose
value depends on the path followed
b. matter during a particular change in state.
c. gram-mole a. path function
d. volume b. point function
235. The distribution of particle speeds c. process
in an ideal gas at a given temperature.
d. cycle
a. velocity of propagation
239. The contact surface shared by both
b. escape velocity the system and the surroundings is
called _________.
c. Maxwell speed Distribution
a. wall
d. terminal velocity
b. boundary
236. A convection process in which an
external device, such as a fan, is used to c. interface
produce the fluid flow.
d. intersection
a. Forced Convection
240. A closed system is also known as
b. External Convection _________.
c. Placid Convection a. isolated system
d. Thermionic Convection b. closed container
237. A _________ is a quantity whose c. control mass
value at any state is independent of the
path or process used to reach that state. d. control volume
a. cycle 241. Open system is also known as
_________.
b. path function
a. isolated system
c. point function
b. closed container
d. process
c. control mass
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
d. control volume c. type of material
242. Liquid hydrogen boils at 17 K. What d. shape of the object
is the temperature in degrees Celsius?
246. Which of the following have the
a. 290 highest thermal conductivities?
b. 63 a. liquids
c. -120 b. gases
d. -256 c. metals
243. When a solid melts, d. solids other than metals
a. the temperature of the 247. Identical objects of four different
substance increases. materials are heated to the same high
temperature. Which of the following
b. the temperature of the would least likely burn your hand if
substance decreases. touched?
c. heat leaves the substance. a. aluminium
d. heat enters the substance. b. brass
244. How many kilocalories of heat are c. glass
required to heat 750 g of water from
35C to 55C. d. concrete
a. 15 248. As we heat a gas at constant
pressure, its volume
b. 1500
a. increases
c. 1.5 x 10^4
b. decreases
d. 6.3 x 10^4
c. stays the same
245. Which of the following does not
determine the amount of internal energy d. none of the above
an object has?
249. The volume of an ideal gas is
a. temperature directly proportional to its
b. amount of material a. pressure
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
b. Celsius temperature d. Lenz Law
c. Kelvin temperature 253. No volume changes occur during
this type of process
d. Fahrenheit temperature
a. Isobaric process
250. An ideal gas is maintained at
constant temperature. If the pressure on b. Isomillimetric process
the gas is doubled, the volume is
c. Isocaloric process
a. increased fourfold
d. Isochoric process
b. doubled
254. The boiling of water into steam in
c. reduced by half an open container is an example of a/an
_________ process.
d. decreased by a quarter
a. adiabatic
b. isochoric
MCQs Part VI c. isobaric
251. If the Kelvin temperature of an ideal
gas is doubled, what happens to the rms d. zero work
speed of the molecules in the gas?
255. When liquid water is converted to
a. it increases by a factor of steam at 100C, the entropy of water
square root of 2
a. increases
b. it increases by a factor of 2
b. decreases
c. it increases by factor of 4
c. remains the same
d. none of the above
d. none of the above
252. A function of state that is
associated with disorder in the system 256. Only energy can cross the
and environment. boundaries.
a. enthalpy a. Closed system
b. entropy b. Open system
c. law of diminishing return c. Isolated system
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
d. Isoenergetic system b. Vaporization
257. The temperature at which the vapor c. fusion
pressure exactly equals one atm is
called _________. d. super heated steam
a. boiling temperature 261. What device measures infrared
radiation below?
b. normal boiling point
a. thermocouple
c. triple point
b. thermopile
d. point of infliction
c. thermodynamic device
258. Mixture of liquid and steam of the
same substance in which both are at d. thermos
saturation temperature.
262. When an object undergoes thermal
a. dry steam expansion,
b. current steam a. any holes in the object expand
as well
c. wet steam
b. any holes in the object remain
d. aerosol the same
259. The term _________ is traditionally c. mass increases
used to describe steam issuing from
condensate receiver vents and open- d. molecular activities would
ended condensate discharge lines from cease
steam traps.
263. _________ is the quantity of heat
a. dry steam required to raise the temperature of one
pound of water 1 F from 63 F to 64 F.
b. wet steam
a. one Joule
c. phase steam
b. one calorie
d. flash steam
c. one watt
260. Defined as the ratio of weight of dry
steam to the weight of stuff. d. one BTU
a. dryness fraction
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
264. Boiling temperature of a material is c. decreasing the volume and
dependent on its _________. increasing the pressure
a. volume d. lowering the temp and raising
the temp
b. power
268. The statement heat cannot by
c. heat itself flow from one body into a hotter
body is governed by _________.
d. pressure
a. the first law of thermodynamics
265. Thermos was invented by
_________. b. the second law of
thermodynamics
a. Sir Arthur Conan Doyle
c. the third law of
b. Sir Fredrich the Great thermodynamics
c. Thomas Edison d. the zeroth law of
thermodynamics
d. Sir James Dewar
269. It is impossible for any process to
266. Most cooking activities involve
have as its sole result the transfer of
_________ process.
heat from a cooler to a hotter body
a. Isochoric
a. Carnots statement
b. Isothermal
b. Clausius statement
c. Isobaric
c. Rankine statement
d. Isovolumic
d. Gauss statement
267. Adiabatic heating and Adiabatic
270. _________ is the average distance
cooling really means _________ and
a molecule moves before colliding with
_________ respectively.
another molecule.
a. raising the temp and lowering
a. mean free path
the temp
b. path allowance
b. maintaining the pressure and
changing the temperature c. compacting factor
d. molecular space
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
271. Find the pressure due to a column c. Newtons Second law
of mercury 74.0 cm high.
d. Pascals law
a. 91.80 x 10^3 N/m^2
275. What type of pressure cannot be
b. 73.56 x 10^2 N/m^2 used for Boyles Law?
c. 9.86 x 10^4 N/m^2 a. Atmospheric Pressure
d. 87.2 x 10^4 N/m^2 b. Gauge Pressure
272. Roughly what is the total weight of c. Surface Pressure
air in the entire earth?
d. Isobaric Pressure
a. 1 x 10^5 tons
276. To displace a cubic foot of fresh
b. 2 x 10^6 tons water, you need _________ force.
c. 6 x 10^15 tons a. 62.4 lb
d. 8 x 10^10 tons b. 9.81 lb
273. _________ is defined as that c. 76 lb
equivalent to the pressure due to a
column of mercury 76cm long. d. 760 lb
a. surface pressure 277. The force per unit length across
such a line in the surface is called
b. gage pressure _________.
c. standard atmospheric pressure a. force per length
d. isobaric pressure b. surface tension
274. If any external pressure is applied c. Pressure
to a confined fluid, the pressure will be
increased at every point in the fluid by d. Density
the amount of the external pressure is
known as _________. 278. The speed at which a liquid
escapes from a vessel through an orifice
a. Torricellis law is given by _________.
b. Barometric law a. Archimedes Principle
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
b. Evangelistas Law 282. _________ is a succession of
changes that ends with the return of the
c. Torricellis Theorem body or system to its initial state.
d. Bernoullis Equation a. process
279. The process of one substance b. system
mixing with another because of
molecular motion is called _________. c. equilibrium
a. diffusion d. cycle
b. viscosity 283. Intensive properties of a system are
called _________.
c. streamline flow
a. Bulk Properties
d. solution
b. Innate Properties
280. When was the Ninth General
Conference on Weights and Measures c. Natural Properties
decided to abandon centigrade and
used Celsius Instead? d. Inside Properties
a. 1950 284. In thermodynamics, a throttling
process, also called a _________, is a
b. 1936 type of isenthalpic process where a
liquid or gas is cooled as it passes from
c. 1957 a higher pressure state to a lower
pressure state.
d. 1948
a. Rankine Process
281. _________ is the temperature to
which the air must be cooled, at b. Carnot Cycle
constant pressure, to produce
saturation. c. Joule-Thomson process
a. relative humidity d. Refrigeration process
b. triple point temperature 285. Gasoline and Diesel Engines are
best described by the _________.
c. dew point
a. Otto Cycle
d. critical point
b. Burnign Cycle
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
c. Shikki Cycle 289. A gas is enclosed in a cylinder with
a weighted piston as the top boundary.
d. Shapa R Elli Cycle The gas is heated and expands from a
volume of 0.04 m3 to 0.10 m3 at a
286. Twenty grams of ice at 0C melts to constant pressure of 200 kPa. Find the
water at 0C. How much does the work done on the system.
entropy of the 20g change in this
process? a. 5 kJ
a. 30.5 J/K b. 15 kJ
b. 24.6 J/K c. 10 kJ
c. 21.3 J/K d. 12 kJ
d. 15.7 J/K 290. A simple steam engine receives
steam from the boiler at 180C and
287. The first law of thermodynamics is exhausts directly into the air at 100C.
based on which of the following What is the upper limit of its efficiency?
principles?
a. 11.28 %
a. conservation of mass
b. 36.77 %
b. the enthalpy-entropy
relationship c. 20.36 %
c. action reaction d. 17.66 %
d. conservation of energy 291. Heat which causes a change in
temperature of a substance.
288. If a system absorbs 500 cal of heat
at the same time does 400J of work, find a. Latent heat
the change in internal energy of the
system. b. Sensible heat
a. 1400 J c. Specific heat
b. 1700 J d. Heat of Fusion
c. 1900 J 292. Who coined the term latent heat?
d. 1500 J a. John Thompson
b. Studey Baker
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
c. Joe di Maggio a. Polytropic process
d. Joseph Black b. Entropy
293. Which of the following cannot be c. Ideal Gas Law
measured by a thermometer?
d. Carnot Cycle
a. Latent Heat
297. The flow through an open system is
b. Sensible Heat _________ if all properties at each point
within the system remain constant with
c. Specific Heat respect to time.
d. Heat of Fusion a. streamline flow
294. It is generally accepted as a law of b. steady flow
nature that although one may closely
approach 0 Kelvin it is impossible c. constant flow
actually to reach it.
d. algebraic flow
a. First Law of thermodynamics
298. The most efficient cycle that can
b. Second Law of operate between two constant
thermodynamics temperature reservoir is the _________.
c. Third Law of thermodynamics a. Otto Cycle
d. Zeroth Law of thermodynamics b. Lazare Cycle
295. One calorie is equal to _________. c. Isothermal Cycle
a. 1/180 W.h d. Carnot Cycle
b. 1/860 W.h 299. The flow energy of 150 L of a fluid
passing a boundary to a system is 110
c. 1/360 W.h kJ. Determine the pressure at this point
d. 1/250 W.h a. 733.33 kPa
296. A _________ is a reversible b. 833.33 kPa
process in which there is transfer of heat
and takes place according to the relation c. 933.33 kPa
pVn = C where n is any constant.
d. 633.33 kPa
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
300. Who is the father of Formula: h= u+ pV u= h pV
thermodynamics?
303. 3.0 lbm of air are contained at 25
psia and 100 F. Given that Rair = 53.35
a. Lazare Carnot
ft-lbf/lbm- F, what is the volume of the
b. Sadi Carnot container?
c. William Thompson A.10.7 ft^3
d. Rudolf Classius B.14.7 ft^3
C.15 ft^3
D.24.9 ft^3
MCQs Part VII
301. If air is at pressure, p, of 3200 Formula: use the ideal gas law
lbf/ft2, and at a temperature, T, of 800 R, pV = mRT
what is the specific volume, v? (R=5303
ft-lbf/lbm-R, and air can be modeled as T = (100 +460) R
an ideal gas.) V = mRT/p
A.9.8 ft^3/lbm 304. The compressibility factor, x, is
used for predicting the behavior of non-
B.11.2 ft^3/lbm ideal gases. How is the compressibility
ty factor defined relative to an ideal gas?
C.13.33 ft^3/lbm (subscript crefers to critical value)
D.14.2 ft^3/lbm A. z = P / Pc
Formula: pv = RT v = RT / p B. z = pV/ RT
302. Steam at 1000 lbf/ft^2 pressure and
C. z = T /Tc
300R has specific volume of 6.5
ft^3/lbm and a specific enthalpy of 9800 D. z = RT / pV
lbf-ft/lbm. Find the internal energy per
pound mass of steam. Hint: for an real gases the
compressibility factor, x, is an
A.2500 lbf-ft/lbm dimensionless constant given by pV=
zRT. Therefore z = pV / RT
B.3300 lbf-ft/lbm
305. From the steam table, determine
C.5400 lbf-ft/lbm the average constant pressure specific
heat (c) of steam at 10 kPa and45.8 C
D.6900 lbf-ft/lbm
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
A.1.79 kJ/ kg-C steam table, calculate the mass of the
water vapor.
B.10.28 kJ/ kg-C
A. 0.99kg
C.30.57 kJ/ kg-C
B. 1.57 kg
D. 100.1 kJ/ kg-C
C. 2.54 kg
Formula: h = cT
D. 3.16 kg
From the steam table
At 47.7 C h= 2588.1 kJ/ kg Formula: from the steam table at 600kPa
At 43.8 C h= 2581.1 kJ/ kg v = 0.001101 m^3 / kg
306. A 10m^3 vessel initially contains 5 vg = 0.3157 m^3 / kg
m^3 of liquid water and 5 m^3 of
Vtot = m v + mg vg
saturated water vapor at 100 kPa.
Calculate the internal energy of the mg = (tot-m v) / vg
system using the steam table. 308. Calculate the entropy of steam at
60psiawith a quality of 0.8
A. 5 x10^5 kJ
A. 0.4274 BTU/lbm-R
B. 8x10^5 kJ
B. 0.7303 BTU/lbm-R
C. 1 x10^6 kJ
C. 1.1577 BTU/lbm-R
D. 2 x10^6 kJ
D. 1.2172 BTU/lbm-R
Formula: fromthe steamtable
v = 0.001043 m^3 / kg Formula: fromthe steamtable at 60 psia:
vg = 1.6940 m^3 / kg s = 0.4274 BTU/lbm-R
u = 417.3 kJ/kg ug= 2506kJ/kg sg = 1.2172 BTU/lbm-R)
formula: Mvap = V vap/vg s = s + x sg where x = is the quality
M liq = Vliq/ v 309. Find the change in internal energy
of 5 lb. of oxygen gas when the
u =uM liq + ug M vap
temperature changes from 100 F to 120
307. A vessel with a volume of cubic F. CV = 0.157 BTU/lbm-R
meter contains liquid water and water
vapor ion equilibrium at 600 kPa. The A.14.7 BTU
liquid water has mass of1kg. Using the
B.15.7 BTU
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
C. 16.8 BTU D. 2374.23 N
D. 15.9 BTU Formula :
M = wk / g
Formula: U= mcvT
F = ma /k
310. Water (specific heat cv= 4.2 kJ/ kg
K ) is being heated by a 1500 W h eater. 313. A problem Drum ( 3 ft. diameter ; 6
What is the rate of change in ft. height ) is field with a fluid whose
temperature of 1kg of the water? density is 50 lb/ft^3. Determine the total
volume of the fluid.
A. 0.043 K/s
A. 42.41 ft^3
B. 0.179 K/s
B.44.35 ft^3
C. 0.357 K/s
C.45.63 ft^3
D. 1.50 K/s
D.41.23 ft^3
Formula: Q = mcv (T)
Formula: Vf = (pi d^2 h) / 4
311. A system weighing 2kN. Determine
the force that accelerate if to 12 m/s^2. 314. What is the resulting pressure
when one pound of air at 15 psia and
a. vertically upward when g = 9.7 m/s^2
200 F is heated at constant volume to
A. 4474.23 N 800 F?
B.5484.23 N A.15 psia
C.4495.23 N B. 28.6 psia
D.5488.23 N C. 36.4 psia.
Formula: F = m/k (a +g) D. 52.1 psia
312. Refer to problem # 11. Determine Formula :
the force that accelerates if to 12 m/s^2.
T1/p1 = T2/p2
horizontally along frictionless plane.
p2= p1T2 / T1
A. 2474.23 N
315. What horse power is required to
B. 2574.23 N isothermally compress 800 ft^3 of Air
per minute from 14.7 psia to 120 psia?
C. 3474.23 N
A. 28 hp
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
B.108 hp and 68 F. The compression ratio is 1:4.
Calculate the work done by the gas.
C.256 hp
A. 1454 BTU/lbm
D.13900 hp
B. -364 BTU/lbm
Formula: W= p1V1 ln (p1/p2)
C.-187BTU/lbm
Power = dW / dt
316. What is the equation for the work D.46.7 BTU/lbm
done by a constant temperature system?
Formula: W = RT ln (V2/V1)
A. W = mRTln(V2-V1)
319. Gas is enclosed in a cylinder with a
weighted piston as the stop boundary.
B. W = mR( T2-T1 ) ln( V2/V1)
The gas is heated and expands from a
C. W = mRTln (V2/V1) volume of 0.04 m^3 to 0.10 m^3 at a
constant pressure of 200kPa.Calculate
D. W = RT ln (V2/V1) the work done by the system.
Formula : W= pdV lim1,2 A. 8 kJ
= mRT / V B. 10 kJ
317. Twenty grams of oxygen gas are
C.12 kJ
compressed at a constant temperature
of 30 C to 5%of their original volume.
D.14 kJ
What work is done on the system.
Formula: W = p(V2-V1)
A.824 cal
320. refer to problem no.13. Determine
B.924 cal the specific volume.
C.944 cal A. 0.02 ft^3/lbm
D.1124 cal B. 0.05 ft^3/lbm
Formula: C. 1.0 ft^3/lbm
W = -mRTln (V2/V1)
D. 1.2 ft^3/lbm
Where R = (1.98 cal/gmoleK) (32
g/gmole) Formula :
318. Helium ( R= 0.4698 BTU/lbm-R ) is Vf = ( pi d^2 h) / 4
compressed isothermally from 14.7 psia Pf = mf / vf
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
Specific volume= Vf /mf b. 543.68 kPa (gauge)
321. What is the weight of a66-kgm man
c. Both a & b
at standard condition?
(Formula: Fg= mg / k) d. None of the above
a. 66 kgf 325. Ten cu ft. of air at 300 psia 400F is
cooled to 140F at constant volume.
b. 66 kgm What is the final pressure?
(formula: p2 = p1T2/T1)
c. 66 lbm
a. 0
d. 66 gf
b. 209 psia
322. What is the specific weight of water
at standard condition?
c. - 420 psia
(Formula: = g / k)
d. None of the above
a. 1000 kgm/m3
326. 876 R = _____ F
b. 9.8066 m/s 2
a. 335
c. 1000 kgf/m 3
b. 416
d. None of the above
c. 400
323. 746 R = ______ F
d. None of the above
a. 254
327. There are 1.36 kg of gas, for which
b. 345 R = 377 J/kg.k and k = 1.25, that
undergo a nonflow constant volume
c. 286 process from p1 = 551.6 kPa and t1 =
60C to p2 = 1655 kPa. During the
d. None of the above process the gas is internally stirred and
there are also added 105.5 kJ of heat.
324. A 30-m vertical column of fluid Determine t2.
(density 1878 kg/m3 ) is located where g=
9.65 mps2. Find the pressure at the base (Formula: T2= T1p2/ p1)
of the column.
a. 999 K
(Formula: pg= ghg/k )
b. 888 K
a. 543680 N/m 2
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
c. 456 K a. 214
d. One of the above b. 121
328. 5 atm = ____mmHg c. 213
a. 8300 d. None of the above
b. 3800 332. 212 F = _____ C
c. 3080 a. 200
d. None of the above b. 150
329. A certain gas, with cp = c. 100
0.529Btu/lb.R and R = 96.2 ft.lb/lb.R,
expands from 5 cu ft and 80F to 15 cu d. None of the above
ft while the pressure remains constant at
15.5 psia. Compute for T2. 333. Let a closed system execute a state
change for which the heat is Q = 100 J
(Formula: T2= T1V2/V1) and work is W = -25 J. Find E.
a. 460R (Formula: E = Q- W)
b. 270R a. 125 J
c. 1620 R b. 123 J
d. None of the above c. 126 J
330. In the above problem, compute for d. None of the above
the mass.
334. A pressure gage registers 50 psig
(Formula: m = p1V1 / RT1) in a region where the barometer is 14.25
psia. Find absolute pressure in psia, Pa.
a. 0.2148 lb
(Formula; p = patm+ pg)
b. 0.2134 lb
a. 433 kPa
c. 0.1248 lb
b. 443 kPa
d. None of the above
c. 343 kPa
331. 710R= ______ C
d. None of the above
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
335. A mass of 5kg is 100m above a b. 1
given datum where local g = 9.75 m/s2.
Find the gravitational force in newtons. c. 350
(Formula: Fg= mg/k ) d. None of the above
a. 48.75 N 339. 212 C = _____ K
b. 50 N a. 485
c. 45 N b. 435
d. None of the above c. 498
336. In the above problem, find the d. None of the above
potential energy of the mass with
respect to datum. 340. 212 F = _____R
(Formula: P = mgz/k )
a. 567
a. 4875 j
b. 672
b. 0.51 j
c. 700
c. 0.46 j
d. None of the above
d. None of the above
341. An automobile tire has a gauge
pressure of 200 kpa at 0C assuming no
337. The combined mass of car and
air leaks and no change of volume of the
passengers travelling at 72 km/hr is
tire, what is the gauge pressure at 35C.
1500 kg. Find the kinetic energy of this
combined mass.
a. 298.645
(Formula: K =mv / 2k )
2
b. 398.109
a. 300 kJ
c. 291.167
b. 200 kJ
d. 281.333
c. 500 kJ
Pg = Pabs - Patm
d. None of the above
342. An ideal gas at 45psig and 80F is
heated in the close container to 130F.
338. 14.696 psia = _____ mmHg
What is the final pressure?
a. 760
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
a. 65.10 psi c. 981.6 N
b. 65.11 psi d. 980.1N
c. 65.23 psi F = ma
346. The volume of the gas held at
d. 61.16 psi
constant pressure increases 4 cm at
P1V1/T1= P2V2/T2;V = Constant 0C to 5cm. What is the final pressure?
343. A wall of the firebrick has an inside a. 68.65C
temperature of 313F and an outside
temperature of 73F. What is the b. 68.25C
difference in the surface temperature in
Rankin? c. 70.01C
a. 70 d. 79.1C
b. 68 t2= T2T1
347. A certain gas with cp =
c. 72
0.529Btu/lbR and R = 96.2ft/lbR
expands from 5 ft and 80F to 15 ft while
d. 94
the pressure remains constant at 15.5
R = F + 460 psia.
344. What is the force required to a. T2=1.620R, H = 122.83 Btu
accelerate amass of 30kg at a rate of
15m/s. b. T2 = 2R, H = 122.83 Btu
a. 460 N c. T2 = 2.620R, H = 122.83 Btu
b. 380 N d. T2 = 1R, H = 122.83 Btu
c. 560 N T2= V2(t2)/V1 and H = mcp (T2-T1)
348. A vacuum is connected to a tank
d. 450 N
reads 3kpa at a location w/ the
F = ma barametric pressure reading is 75mmhg.
Determined the P absolute in the tank
345. How much does an object having
the mass of 100kg weight in newton. a. 70.658 kpa
a. 981 N b. 68 kpa
b. 991 N
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
c. 58.78 kap meter per second does it strike the
ground assume g = 10m/s.
d. None of the above
a. 11m/s
Pabs = Patm Pvacuum
b. 12m/s
349. Calculate:
a. Mass flow rate in lb/hr. c. 13m/s
b. The velocity at section 2 in fps d. 10m/s
a. 800,000lb/hr;625ft/s KE = mV2/2gc
b. 900,000lb/hr;625 ft/s 352. While swimming a depth of 13m in
a fresh water lake a fish emits an air
c. 888,000lb/hr;269 ft/s bubble of volume 2 mm atmospheric
pressure is 100kpa what is the original
d. 700,000lb/hr;269 ft/s pressure of the bubble.
m = A1V!/V1 a. 217.17 kpa
350. A 600kg hammer of a pile driver is
b. 119 kpa
lilted 2m the pilling head. What is the
change of potential energy? If the
c. 326.15 kpa
hammer is realest. What will be its
velocity and the instant if it sticks the d. 210 kap
pilling?
Pabs = Pg + Patm
a. 10,772 N-m and 5.26m/s
353. Oxygen at 15C and 10.3 Mpa
b. 13,200 N-m and 5.26m/s gauge pressure occupies 600L. What is
the occupied by the oxygen at 8.28 Mpa
c. 11,772 N-m and 6.26m/s gauge pressure and 35C?
d. 11,77 2N-m and5.26m/s a. 789.32 L
PE = mgo(Z)/gc b. 796.32 L
c. 699 L
MCQs Part VIII d. 588 L
351. A bayabas falls from a branch 5m
V2= P1V1/T1P2
above the ground with what speed in
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
354. Water is flowing through a 1 foot t2= T2T1
diameter pipe at the rate of 10ft/sec.
357. Water flow to a terminal 3 mm
What is the volume flow rate of water in
diameter and has an average speed of 2
ft/sec?
m/s. What is the rate of flow in cubic
meter/mm?
a. 7.85
a. 0.0001m/min
b. 6.85
b. 0.076 m/min
c. 8.85
c. 0.085 m/min
d. 5.85
d. 0.097 m/min
V = A
355. A certain fluid is flowing in a 0.5m x 358. Water flowing at a 6m/s through a
0.3 channel at the rate of 3 m/s and has 60 mm pipe is suddenly channeled into
a specific volume of 0.012 m/kg. a 30 mm pipe. What is the velocity in the
Determined the mass of water flowing in small pipe?
kg/s.
a. 34m/s
a. 267 kg/s
b. 24m/s
b. 378 kg/s
c. 15m/s
c. 375 kg/s
d. 27m/s
d. 456.5 kg/s
359. A vertical column of water will be
m = A/V supported to what height by standard
atmospheric pressure.
356. A gas having a volume of100 ft at
27C is expanded to 120 ftby heated at
a. 33.9 ft
constant pressure to what temperature
has it been heated to have this new b. 45 ft
volume?
c. 67 ft
a. 87C
d. 25.46 ft
b. 85C
ho= Po/Yo
c. 76C
360. A fluid flows in a steady manner
d. 97C between two section in a flow line at
section 1: A 1 = 1ft, V1 = 100fpm,
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
volume1 of 4ft/lb. at sec2: A2 = 2 ft, p= b. 1.37
0.20 lb/ft calculate the velocity at
section 2. c. 1.38
a. 625 fpm d. 1.39
b. 567 fpm formula: k= R / cv+1
364. Ten cu. ft of air at 300psia and
c. 356 fpm
400F is cooled to 140F at constant
volume. What is the transferred heat?
d. None of the above
a.-120Btu
361. The weight of an object is 50lb.
What is its mass at standard condition?
b. -220Btu
a. 50 lbm
c.-320Btu
b. 60 lbm
d. -420Btu
c. 70 lbm
formula: Q= mcv(T2-T1)
d. 80 lbm 365. Utilizing the answer to the previous
problem, estimate the overall or average
formula: m = Fgk /g increase in temperature ( T) of the
362. A vertical column of water will be concrete roof from the energy absorbed
supported to what height by standard from the sun during a12hour day.
atmospheric pressure. If the Y w = Assume that all of the radiation
62.4lb/ft3 po = 14.7 psi. absorbed goes into heating the roof. The
specific heat of concrete is about 900
a. 44.9 ft J/kg, and the density is about 2,300
kg/m3.
b. 33.9 ft
a. 7.9 C
c. 22.9 ft
b. 8.9C
d. 55.9 ft
c. 9.9C
formula: ho= po/Yw
d. 10.9C
363. For a certain gas R = 320 J/kg.K
and cv= 0.84kJ/kg.K. Find k? formula: Q = m c T
a. 1.36 366. The concrete roof of a house is 10
m by 8 m and 10 cm thick (4"). Estimate
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
the total heat the roof would absorb over to 100 kmph in 5 sec. Find the driving
the 12 day? force in Newtons.
a. 1.3 x 108 J a. 11,120 N
b 2.3 x 108 J b. 11,320 N
c. 3.3 x 108 J c. 11,420 N
d. 4.3 x 108 J d. 11520 N
formula: Q = Q/tx t formula: F= ma / k
367. The value for the U of a system is 370. An ideal gas of volume 1liter and
-120 J. If the system is known to have pressure 10 bar undergoes a quasistatic
absorbed 420 J of heat, how much work adiabatic expansion until the pressure
was done? drops to 1 bar. Assume to be 1.4 what
is the final volume?
a. -540 J
a. 3.18 l
b. -640 J
b. 4.18 l
c. -740 J
c. 5.18 l
d. -840 J
d. 6.18 l
formula: U = q +w
371. Two masses, one of the 10kg and
368. When the pressure on a 1 kg liquid
the other unknown, are placed on a
is increased isothermally from 1 bar to
scale in a region where g = 9.67 m/sec2.
3000 bar the Gibbs free energy
The combined weight of these two
increases by 360 kJ. Estimate the
masses is 174.06 N. Find the unknown
density of the liquid.
mass in kg.
a. 0.66 kg liter-1
a. 20 kg
b. 0.77 kg liter-1
b. 19 kg
c. 0.88 kg liter-1
c. 18 kg
d. 0.99 kg liter-1
d. 17 kg
369. A car whose mass is 2 metric tons
formula: m=Fg k / g
is accelerated uniformly from stand hill
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
372. The flow energy of 5 ft3 of a fluid /kgK,k= 1.67) at 105 k/Paa, 27C and
passing a boundary to a system is delivers it at 630kPaa: P = 0, K= 0.
80,000 ft-lb. Determine the pressure at Find the work if the process is
this point. isentropic?
a. 222 psi a. 1664 kJ/min
b. 333 psi b. 1774 kJ/min
c. 444 psi c. 1884 kJ/min
d. 111 psi d. 1994 kJ/min
formula: Ef= pV formula: WSF = Q- H m=p1V1/RT1
T2= T1(p2/p1)(k-1)/k
373. Find for steam at 100 psia and
600F.If h = 1329.6 and v = 6.216 376. A carnot power cycle operates on 2
lb of air between the limits of 71 F and
a. 1214 Btu / lb 500F. The pressure at the beginning of
isothermal expansion is 400 psia and at
b. 1234 Btu /lb the end of isothermal expansion is
185psig. Determine the volume at the
c. 1342 Btu / lb
end of isothermal compression.
d. 1324 Btu /lb
a. 7.849 ft3
formula: = h pv/ J
b. 7.850 ft3
374. What mass of nitrogen is contained
in a10 ft3 vessel at a pressure of 840atm c. 7.851 ft3
and 820R? Make a computation by
using ideal gas equation. d. 7852 ft3
a. 194lb formula: V= mRT/ P P3= P2[T3/ T2]
377. During a polytropic process,10lb of
b. 214lb an ideal gas, whose R= 40ft.lb/lb.R and
cp = 0.25Btu/lb.R, changes state from
c. 394 lb
20 psia and 40F to 120psia and 340F.
Determine n?
d. 413lb
a. 1.234
formula: m=pV /RT
375. A rotary compressor receives 6m3/ b. 1.345
min of a gas(R=410J/ kgK, cp=1.03kJ
c. 1.456
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
d. 1.356 d. 710R
formula: [ p2/p1]n-1 / n = T2/T1 formula: R= F + 460
378. A perfect gas has a value of R= 381. Steam with a specific volume of
319.2 J/ kf.K and k= 1.26. If 120 kJ are 0.09596 m/kg undergoes a constant
added to 2.27 kf\g of this gas at constant pressure process at 1.70 MPa until the
pressure when the initial temp is specific volume becomes 0.13796
32.2C? Find T2. m/kg. What are (a) the final
temperature, (b) u, (c) W, (d)s, and
a. 339.4 K (e) Q?
b. 449.4 K a) 265.4C, 430.7kJ/kg,
71.4kJ/kg, 1.0327kJ/(kg)
c. 559.4K (K),502.1 kJ/kg
d. 669.4K b) 204.2C, -703.2 kJ/kg, -84.15
kJ/kg, -1.7505 kJ/(kg)(K), -787.4
formula: cp = kR/ k-1 Q= mcp(T2-T1)
kJ/kg
379. A certain gas, with cp = 0.529Btu/
lb. Rand R = 96.2ft.lb/lb. R, expands c) 304.2C, -803.2 kJ/kg, -89.15
from 5 cu ft and 80F to 15 cu ft while kJ/kg, -2.7505 kJ/(kg)(K), -987.4
the pressure remains constant at kJ/kg
15.5psia. Compute for T2.
d) 279.4C, 439.7kJ/kg,
a.1520R 79.4kJ/kg, 3.0327kJ/(kg)
(K),602.1 kJ/kg
b. 1620R
382. Steam with an enthalpy of 2843.5
c. 1720R kJ/kg undergoes a constant pressure
process at 0.9 MPa until the enthalpy
d. 1820R becomes 2056.1 kJ/kg. What are (a) the
initial temperature or quality, (b) u,
formula: T2= T1V2/V1 (c)W, (d) s, and(e) Q?
380. A System has a temperature of
a) 265.4C, 430.7kJ/kg,
250F. Convert this Value to R?
71.4kJ/kg, 1.0327kJ/(kg)
a. 740R (K),502.1 kJ/kg
b.730R b) 204.2C, -703.2 kJ/kg, -84.15
kJ/kg, -1.7505 kJ/(kg)(K),-787.4
c. 720R kJ/kg
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
c) 304.2C, -803.2 kJ/kg, -89.15 Heat is added until the pressure rises to
kJ/kg, -2.7505 kJ/(kg)(K), -987.4 3.5 MPa and the temperature to 400.
kJ/kg Determine the heat added.
d) 279.4C, 439.7kJ/kg, a) 1378.7 kJ
79.4kJ/kg, 3.0327kJ/(kg)(K),
602.1 kJ/kg b) 1348.5 kJ
Formula of #1and #2: u = u2 u1, W = c) 1278,7 kJ
p(v2-v1), s =s2-s1, Q = h2 h1
d) 1246,5 kJ
383. At throttling calorimeter receives
steam from a boiler drum at0.11MPa Formula: Q = (h2 p2v2) (h1 p1v1)
and is superheated by 10 degrees. If the
386. Water vapor at 100 KPa and 150C
boiler drum pressure is 1.55 MPa, what
is compressed isothermally until half the
is the quality of the steam generated by
vapor has condensed. How much work
the boiler?
must be performed on the steam in this
a) 95.20% compression process per kilogram?
b) 70.10% a) -1384.7 kJ
c) 65.60% b) 1384.7 kJ
d) 95.56% c) -2384.7 kJ
Formula: h1 = hf1 + x1hfg1 d) 2384.7 kJ
384. A steam calorimeter receives steam 387. Wet steam at 1 MPa flowing
from a pipe at 0.1 MPa and 20SH. For through a pipe is throttled to a pressure
a pipe steam pressure of 2 MPa, what is of 0.1 MPa. If the throttling temperature
the quality of the steam? is110C, What is the quality of the steam
in the pipe?
a) 95.56%
a) 96%
b) 70.10%
b) 86%
c) 95.20%
c) 76%
d) 85.10%
d) 66%
Formula: h1 = hf1 + x1hfg1
388. Steam is throttled to 0.1 MPa with
385. A 1-kg steam-water mixture at 1.0
20 degrees of superheat. (a) What is the
MPa is contained in an inflexible tank.
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
quality of throttled steam if its pressure 391. A Gas tank registers1000 kPa.
is 0.75 MPa (b) What is the enthalpy of After some gas has been used, the
the process? gauge registers 500 kPa. What percent
of the gas remains in the tank?
a) 97.6%,2713 kJ/kg
a) 64.40%
b) -97.6%, 2713 kJ/kg
b) 74.60%
c) 87.6%,3713 kJ/kg
c) 58.40%
d) -87.6%, 3713 kJ/kg
d) 54.60%
389. The pressure gauge on a 2000 m
tank of oxygen gas reads 600 kPa. How Formula: Pabs = Patm + Pgage & %=
much volumes will the oxygen occupied P2/P1 * 100%
at pressure of the outside air 100 kPa?
392. The volume of a gas under
standard atmospheric pressure & 76
a) 14026.5 m
cmHg is 200m. What is the volume
b) 15026.5 m when pressure is 80 cmHg if the
temperature is unchanged?
c) 13026.5 m
a) 180 in
d) 16026.5 m
b) 170 in
Formula: P1V1/T1 =P2V2/T2
c) 160 in
390. Assuming compression is
according to the Law PV = C, Calculate d) 190 in
the initial volume of the gas at a
pressure of 2 bars w/c will occupy a Formula: P2V2 = P1V1
volume of 6m when it is compressed to
393. While swimming at depth of120m in
a pressure of 42 Bars.
a fresh water lake, A fish emits an air
bubbles of volume 2.0mm atmospheric
a) 130m
pressure is 100kPa. What is the
b) 136m pressure of the bubble?
c) 120m a) 217.7 kPa
d) 126m b) 317.7 kPa
Formula: P1V1/T1 =P2V2/T2 c) 417.7 kPa
d) 517.7 kPa
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
Formula: P= h Formula: 1hp= 746 watts
394. How many joules of work is the 397. How many Newtons (N) in 900,000
equivalent of 15000 cal of heat? dynes?
a) 62850 joules a) 8 Newtons
b) 3579.95 joules b) 9 Newtons
c) 14995.81 joules c) 7 Newtons
d) 15004.19 joules d) 6 Newtons
Formula: J =Work/Heat Formula: 1Newton (N)=100,000dynes
J = mechanical equivalent of heat whose 398. Calculate the power output in
value is 4.19 joules/calorie horsepower of an 80-kg man that climbs
a flight of stairs 3.8 m high in 4.0 s.
395. Two thick slices of bread, when
completely oxidized by the body, can
a) 744.8 hp
supply 200,000 cal of heat. How much
work is this equivalent to? b) 0.998 hp
a) 4,190,000 joules c) 746 hp
b) 8,390,000 joules d) 1.998 hp
c) 839,000 joules Formula: Power = Fd/t = mgh/t
d) 419 000 joules F = W = mg
d=h
Formula: J =Work/Heat
399. How many calories of heat will be
J = mechanical equivalent of heat whose
needed to raise the temperature of 200
value is 4.19 joules/calorie
g of iron from 27C to 80C? (c = 0.11
396. 3 horsepower (hp) = cal/g. C)
_____________watts?
a) 1.16 kcal
a) 1492 watts
b) 2166 cal
b) 2238 watts
c) 3.16 kcal
c) 746 watts
d) 4166 cal
d) 2238 kilowatts
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
Formula: H = mcT b. Boyles Law
400. 100g of iron was heated to 100C
c. Daltons Law
and mixed with 22g of water at 40C.
The final temperature of the mixture was d. Amagats Law
60C. Show that the heat given off by
the iron equals the heat absorbed by the 403. Avogadros Number NA
water.
a. 6.2205 x 10^23 mol-1
a) 440 cal
b. 6.2025 x 10^23 mol-1
b) 540 cal
c. 6.0225 x 10^23 mol-1
c) 340 cal
d. 6.2250 x 10^23 mol-1
d) 640 cal
404. The first law of thermodynamics
Formula: H (given off by iron) = H may be expressed in the following
(absorbed by water), equivalent
mcT(iron)= mcT(water)
a. the net heat transfer id equal to
the network
b. the sum of the total energy
MCQs Part IX forms leaving the system
401. An engineering science primarily boundary is always equal to the
concerned with heat and work energy input
conversions.
c. energy can neither be created
a. Thermodynamics nor destroyed but only converted
from one form to another
b. Mechanics
d. all of the above
c. Physics
405. A system whose boundary does not
d. Electromagnetic allow the exchange of either matter or
energy with the surrounding
402. If the temperature o f a fixed
quantity of a gas is held constant during a. open system
a change of state, the volume varies
inversely with the absolute pressure. b. closed system
a. Charles Law c. isolated system
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
d. none of the above d. when a body is inversed in a
fluid, the fluid exerts a downward
406. The specific terms used in phase force on the body whose
transitions magnitude is lower than the
weight of the displaced fluid.
a. melting
409. Types of system except one
b. evaporation
a. closed
c. freezing
b. open
d. sublimation
c. isolated
407. The density of water at 4C is
d. solid
a. 1 gm/cm
410. Isometric process is
b. 2 gm/cm
a. T = P
c. 3 gm/cm
b. P = C
d. 4 gm/cm
c. V = C
408. Archimedes principle states that
d. T = V
a. when a body is inversed in a
fluid, the fluid exerts a downward 411. The ratio of the change in energy in
force on the body whose the form of the heat
magnitude is equal to the weight
of the displaced fluid a. relative density
b. when a body is inversed in a b. specific heat
fluid, the fluid exerts a upward
force on the body whose c. specific gravity
magnitude is equal to the weight
of the displaced fluid. d. none of the above
c. when a body is inversed in a 412. Specific heat ratio is always
fluid, the fluid exerts a downward
a. > 1
force on the body whose
magnitude is greater than the
b. < 1
weight of the displaced fluid.
c. = 1
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
d. none of the above c. Gabriel Danelle Fahrenheit
413. It states that mass is a commodity d. Danelle Gabriel Fahrenheit
that can neither be heated nor destroyed
with the exception of nuclear processes 417. Developed the centigrade or
where the conversion of mass into Celsius
energy is a fundamental principle
a. Andres Celsius
a. Law of Conservation of Mass
b. Anders Celsius
b. Law of Conservation of Energy
c. Andrew Celsius
c. Law of Conservation of Power
d. Anthony Celsius
d. Law of Conservation of Heat
418. Instrument used to measure the
414. The energy that stored in a system absolute pressure of the atmosphere
as a result of its position in the earths
gravitational field a. galvanometer
a. elastic energy b. thermometer
b. kinetic energy c. barometer
c. potential energy d. pressure gages
d. flow energy 419. A vector quantity whose direction is
the same as the direction of the velocity
415. It involves a force deforming a solid
body a. Force
a. non-elastic work b. Momentum
b. non-flow work c. Friction
c. flow work d. Resultant
d. elastic work 420. Conceptualize that the heat was an
energy form and that there was a
416. Developed the Fahrenheit scale precise relationship between heat and
work.
a. Gabriel Daniel Fahrenheit
a. Count Rumford
b. Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
b. Sir Humpry Davey c. Work
c. James Prescott d. None of the above
d. all of the above 425. Amount of heat needed to rate the
temperature of a substance by 1C
421. Which is true:
a. Heat Exchange
a. Energy is a scalar quantity
b. Heat Engine
b. Energy is a vector quantity
c. Specific Heat
c. Energy is vector & scalar
d. None of the above
d. None of the above
426. Study of transformation of heat
422. It is a region enclosed by specified energy to mechanical energy to other
boundaries, which may be imaginary, forms of energy.
either fixed or moving
a. Thermodynamics
a. Isolated system
b. Physics
b. Open system
c. Mechanics
c. System
d. None of the above
d. None of the above
427.Heat cannot be created, nor
423. Amount or volume of liquid that destroyed, but it can be changed from
pass in a given limit of time one form to another. The energy in the
universe remains constant.
a. Flow rate
a. 1st Law of Energy Conservation
b. Volume
b. 2nd Law of Energy
c. Time Conservation
d. None of the above c. 3rd Law of Energy Conservation
424. Ability to do work d. None of the above
a. Power 428. Quantities that describe both
magnitude & direction
b. Energy
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
a. Physical Quantity b. Barometer
b. Scalar Quantity c. Manometer
c. Vector Quantity d. None of the above
d. None of the above 433. Work done in pushing a fluid across
a boundary, Usually into or out of a
429. The sum of energies of all the system
molecules in a system, energies that
appear in several complex forms. a. Flow Work
a. External Energy b. Flow Energy
b. Internal Energy c. Both a & b
c. Kinetic Energy d. None of the above
d. None of the above 434. Which is not true about Heat (Q):
430. The value of atomic charge e is a. Q is positive when heat is
added to the body or system
a. 1.60210 x 10-19 coulomb
b. Q is negative when heat is
b. 1.68910 x 10 coulomb
-19
rejected by the body or system
c. 1.20160 x 1019 coulomb c. Q is positive when heat is
rejected by the body or system
d. None of the above
d. None of the above
431. p1V1= p2V2
435. The standard reference
a. Charle's Law atmospheric pressure
b. Boyle's Law a. 760 mmHg
c. Ideal Gas Law b. 1 atm
d. Joule's Law c. 14.696 psia
432. A _______ is used to measure d. All of the above
atmospheric pressure.
436. ______ is that property of a
a. Thermometer substance which remains constant if no
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
heat enters or leaves the substance, c. Specific Heat
while it does work or alters its volume,
but which increases or diminishes d. None of the above
should a small amount of heat enter or
leave. 440. A classification of system in which
mass does not cross its boundaries.
a. Entrophy
a. Nonflow System
b. Enthalpy
b. Open System
c. Specific Heat
c. Closed System
d. None of the above
d. None of the above
437.The acceleration of a particular
body is directly proportional to the 441. Gas being heated at constant
resultant force acting on it & inversely volume is undergoing the process of.
proportional to its mass.
a. isometric
a. Pascal's Law
b. specific heat
b. Joule's Law
c. enthalpy
c. Newton's Law
d. isothermal
d. None of the above
442. The heat per unit mass per degree
438. Mass (not weight) per unit volume change in temperature
a. Specific Weight a. specific heat
b. Specific Volume b. isometric
c. Density c. conservation of energy
d. None of the above d. none of the above
439. Composite property applicable to 443. A unit of pressure used in high
all fluids vacuum technology, which is equal to
1mmhg.
a. Entropy
a. specific heat
b. Enthalpy
b. isometric
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
c. isobaric c. Isolated System
d. torr d. Enthalpy
444. The gas constant is equal to 448. The ratio of the weight of a
substance to the weight of some
a. Cp Cv standard substance is called?
b. Cp + Cv a. Specific Heat
c. Cp Cv + k b. Specific Gravity
d. None of the above c. Isothermal
445. The 1st Law of Thermodynamics on d. Specific Weight
what principle?
449. Specific heat capacity in SI unit.
a. Conservation of Energy
a. kJ / kg.k
b. Conservation of mass
b. kJ / kg
c. Enthalpy
c. kN / kg
d. Isometric
d. None of the above
446. A system having a rigid boundary
that energy, work and mass does not 450. The Law of Thermodynamics that
cross its boundaries provides the basis for measuring the
thermodynamic property of temperature.
a. Specific Heat
a. Charles Law
b. Specific Gravity
b. Boyles Law
c. Isolated System
c. Zeroth Law
d. Enthalpy
d. Gas Law
447. Sum of the internal energy of a
substance and the product of pressure
and volume.
a. Specific Heat
b. Specific Gravity
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
b. Closed System
c. Surrounding
MCQs Part X
451. The pressure of the confined gas is d. Isentropic
held constant, the volume directly
proportional to the absolute temperature. 455. A state occurs in isentropic process
a. Charles Law a. The change in entropy is 0
b. Boyles Law b. The change in entropy is 1
c. Zeroth Law c. The change in enthalpy is 0
d. Gas Law d. The change in enthalpy is 1
452. Regardless of the process, the 456. The SI unit of mass
change in enthalpy firm moles of ideal
gas is a. kg
a. Heat b. g
b. Enthalpy c. N
c. Entropy d. None of the above
d. Density 457. Anything that is outside the system
boundary is called ________.
453. Ideal process are ________
process a. Surrounding
a. Irreversible b. Natural Environment
b. Reversible c. Closed System
c. Isothermal d. Open System
d. Isometric 458. A Thermodynamic Term That refers
to any fixed region in a space
454. A state occurs when a system is in
equilibrium a. Control Volume
a. Natural Environment b. Volume
c. Density
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
d. Natural Gas 463. The law of conservation of mass
states that ______.
459. The process that has no heat
transfer a. mass is indestructible
a. Density b. mass is destructible
b. Isentropic Process c. mass is indestructible
c. Isometric Process d. none of the above
d. Adiabatic 464. __________ is the energy stored
within a body or substance by virtue of
460. Another name of reversible the activity and configuration of its
adiabatic process molecules.
a. Isentropic Process a. Internal Energy
b. Isometric Process b. External Energy
c. Isobaric Process c. Kinetic Energy
d. Isothermal Process d. Potential Energy
461. ______ of a Body is the absolute 465. The Product of the displacement of
quantity of a matter in it. the body and the component if the force
in the direction of the displacement.
a. Mass
a. Nonflow Work
b. Weight
b. Flow Work
c. Density
c. Work
d. Volume
d. None of the above
462. _______ of a body means the force
of the gravity Fg on the body 466. Is the energy in transit (on the
move) from the one body or system to
a. Mass another solely because of a temperature
between the bodies or systems.
b. Weight
a. Work
c. Density
b. Heat
d. Volume
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
c. Energy c. Multistaging
d. None of the above d. None of the above
467. A classification of a system in 471 Is define as the ratio of the actual
which mass crosses its boundaries. pressure of the vapor
a. Closed System a. Relative Humidity
b. Open System b. Humidity Ratio
c. Isolated System c. Dew Point
d. None of the above d. Adiabatic Saturation
468. The SI unit of pressure 472. Heat engine deriving its power from
the energy liberated by the explosion of
a. Pa a mixture of some hydrocarbon, in a
gaseous or vaporized form.
b. N
a. Dual Combustion Engine
c. J
b. Internal Combustion Engine
d. None of the above
c. External Combustion Engine
469. The volume of a confined gas is
held constant, the pressure is directly d. None of the above
proportional to the absolute temperature.
473. Also called absolute humidity and
a. Charles Law specific humidity.
b. Boyles Law a. Related humidity
c. Joules Law b. Humidity ratio
d. Specific Heat c. Dew point
470. The compression of the gas in two d. Adiabatic ratio
or more cylinders in place of a single
cylinder compressor 474. Is a steady flow process at total
constant pressure through a control
a. Single Staging volume for which there is no heat?
b. Double Staging a. Adiabatic Saturation Process
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
b. Dew point a. Banometer
c. Adiabatic Ratio b. Nanometer
d. None of the above c. Thermometer
475. Fuels that may classified d. Manometer
conveniently in solid, liquid and
gaseous. 479. If any one or more properties of a
system change, the system is said to
a. Unleaded fuel have undergone a _______.
b. Diesel fuel a. Cycle
c. Fossil fuel b. System
d. All of the above c. Process
476. Is a general name, without specific d. None of the above
meaning unless the way in which it is
measured or define by the context. 480. Is a thermodynamic system that
operates continuously with only energy
a. Natural Value (heat and work) crossing its boundaries?
b. Heating Value a. Heat Engine
c. Burning Value b. Heat Reservoir
d. Internal Value c. Heat Source
477. Is the force of gravity on unit d. Heat Sink
volume?
481. _______________ is the
a. Specific Weight temperature at which liquids start to boil
or the temperature at which vapors
b. Specific Heat begin to condense.
c. Specific Pressure a. Saturation Temperature
d. Specific Volume b. Sub cooled Liquid
478. Give a reading as the length of c. Compressed Liquid
some liquid column: water, alcohol, etc.
d. Saturated Liquid
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
482. ________________ is one which a) Vapor
has a temperature lower than the
saturation temperature corresponding to b) Saturated Vapor
the existing pressure.
c) Superheated Vapor
a. Saturation Temperature
d) Wet Vapor
b. Sub cooled Liquid
486. ___________________ is a vapor
c. Compressed Liquid at the saturation conditions (saturation
temperature and saturation pressure).
d. Saturated Liquid
a) Vapor
483. _________________ is one which
has a pressure higher than the b) Saturated Vapor
saturation pressure corresponding to the
existing temperature. c) Superheated Vapor
a. Saturation Temperature d) Wet Vapor
b. Sub cooled Liquid 487. ___________________ is a vapor
having a temperature higher than the
c. Compressed Liquid saturation temperature corresponding to
the existing pressure.
d. Saturated Liquid
a) Vapor
484. __________________ is a liquid at
the saturations which has temperature b) Saturated Vapor
equal to the boiling point corresponding
to the existing pressure. c) Superheated Vapor
a. Saturation Temperature d) Wet Vapor
b. Sub cooled Liquid 488. __________________ is a
combination of saturated vapor and
c. Compressed Liquid saturated liquid.
d. Saturated Liquid a) Vapor
485. __________________ is the name b) Saturated Vapor
given to a gaseous phase that is in
contact with the liquid phase, or that is in c) Superheated Vapor
the vicinity of a state where some of it
d) Wet Vapor
might be condensed.
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
489. ___________________ represents d) None of the above
the highest pressure and highest
temperature at which liquid and vapor 493. What is the formula to convert F to
can coexist in equilibrium. C?
a) Critical Point a) C = F + 273
b) Boiling Point b) C = 5/9 (F - 32)
c) Quality Point c) C = 9/5 (F)+32
d) None of the above d) None of the above
490. Heat that cause change in 494. ______________ is the base unit
temperature at without a change in of thermodynamics temperature.
phase.
a) Celsius
a) Sensible Heat
b) Fahrenheit
b) Latent Heat
c) Kelvin
c) Thermo Heat
d) None of the above
d) None of the above
495. __________ is the unit of force.
491. Heat that cause change in phase
without a change in temperature. a) Newton
a) Sensible Heat b) Pascal
b) Latent Heat c) Hertz
c) Thermo Heat d) Joule
d) None of the above 496. __________ is the unit of pressure
and stress.
492. What is the formula to convert C to
F? a) Newton
a) F = C + 273 b) Pascal
b) F = 5/9 (C - 32) c) Hertz
c) F = 9/5 (C)+32 d) Joule
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
97. _____________ is the difference c) Vapor
between the actual temperature of
superheated vapor and the saturation c) Liquid
temperature for the existing pressure.
a) Degrees of Superheat, SH
MCQs Part XI
b) Degrees of Sub cooled, SB
501. How many independent properties
c) Both a and b are required to completely fix the
equilibrium state of a pure gaseous
d) None of the above compound?
498. ____________is the difference a. 4
between the saturation temperature for
the given pressure and the actual sub b. 3
cooled liquid temperature.
c. 2
a) Degrees of Superheat, SH
d. 1
b) Degrees of Sub cooled, SB
502. What is the value of the work done
c) Both a and b for a closed, reversible isometric
system?
d) None of the above
a. zero
499. ___________ is the percent by
weight that is saturated vapor. b. positive
a) Quality, x c. negative
b) Percent Moisture, y d. positive or negative
c) Vapor 503. The first law of thermodynamics is
based on which of the following
d) Liquid principles?
500. ____________ is the percent by a. Conservation of mass
weight that is saturated liquid.
b. Conservation of energy
a) Quality, x
c. Action and reaction
b) Percent Moisture, y
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
d. The entropy-temperature c. Reversible properties
relationship
d. Irreversible properties
504. Which of the following cycle is used
in vapor cycle power plant? 508. What refers to the thermodynamic
properties which are independent on the
a. Brayton cycle amount of the substance present?
b. Diesel cycle a. Extensive property
c. Ericson cycle b. Intensive properties
d. Rankine cycle c. Reversible properties
505. Which of the following is not a d. Irreversible properties
thermodynamic property?
509. What is known as the total heat and
a. Pressure heat content at various times in the
history?
b. Temperature
a. enthalpy
c. Volume
b. entropy
d. Phase
c. internal energy
506. Which of the following
compressibility factor of ideal gas d. latent heat
a. 1 510. What is the measure of the energy
that is no longer available to perform
b. 2 useful work within the current
environment?
c. 1.5
a. enthalpy
d. 0
b. entropy
507. What refers to the thermodynamic
properties which are dependent on the c. internal energy
amount of the substance present?
d. latent heat
a. Extensive property
511. What is the temperature when
b. Intensive properties water and vapor are in the equilibrium
with the atmospheric pressure?
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
a. Ice point 515. What is defined as the quantity of
heat needed to raise the temperature of
b. Steam point one kilogram of water by one degrees
Celsius?
c. Critical point
a. Kilojoule
d. Freezing point
b. Btu
512. What is the unique state at which
solid, liquid and gaseous phase can go c. Kilocalorie
co-exist in equilibrium?
d. Latent heat
a. Triple point
516. To what conditions does a gas
b. Critical point behave like an ideal gas?
c. Boiling point a. low temperature and low
pressure
d. Pour point
b. low temperature and high
513. What refers to the state at which pressure
liquid and gaseous phases are
indistinguishable? c. high temperature and low
pressure
a. Triple point
d. high temperature and high
b. Critical point pressure
c. Boiling point 517. What Law states that the pressure
of gas is inversely proportional to its
d. Pour point
volume at constant temperature?
514. What refers to the heat needed to
a. Charles law
change the temperature of the
substances without changing its b. Gay-Lussacs Law
phases?
c. Boyles Law
a. Latent heat
d. Daltons Law
b. Sensible heat
518. What do you call a system in which
c. Specific heat there is a flow of matter through the
boundary?
d. entropy
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
a. Closed system c. the enthalpy of reactants is
lower than the enthalpy of
b. Open system products.
c. Isolated system d. The enthalpy of the product is
lower than the enthalpy of the
d. All of these reactant
519. Which of the following best 522. The phenomenon of melting under
describes heat? pressure and freezing again when the
pressure is reduced is known as
a. The capacity to do work
a. sublimation
b. Forces times distances
b. condensation
c. Sum of thermal and chemical
energy c. deposition
d. An energy transfer due to d. regelation
temperature difference
523. Which of the following events is
520. The mechanical equivalent of heat heat exchange involved?
is
a. when there is a phase change
a. joule
b. when there is a chemical
b. calorie reaction
c. Btu c. when the gas expands
adiabatically
d. Specific heat
d. when there is difference in
521. Burning of Gasoline initially
temperature
requires heat before it burns
spontaneously. Which of the following 524. What is the entropy of a pure
does not give a good explanation of this substance at a temperature of absolute
phenomenon? zero?
a. the initial heat rises the a. unity
enthalpy of the reactant
b. zero
b. the initial heat lowers the
activation of energy of the c. infinity
reactants
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
d. undefined b. halves
525. What is the area under the curve c. quadruples
on a temperature entropy diagram?
d. triples
a. Heat
529. When the expansion of
b. work compression of gas takes place without
transfer of heat or from the gas the
c. entropy process is called;
d. volume a. Isometric process
526. What happens to the internal b. Isothermal process
energy of water at reference
temperature where enthalpy is zero? c. Isobaric process
a. Becomes negative d. Adiabatic process
b. Becomes positive 530. Which of the following best
describes both Stirling and Ericson
c. Remains constant engines?
d. Cannot be defined a. Internal combustion engine
527. Which of the following is the work b. External combustion engine
done for a closed reversible isometric
system? c. Diesel cycle
a. negative d. Rankine cycle
b. positive 531. At steam point, the temperature of
water and its vapor at standard pressure
c. zero are:
d. undefined a. Extremes or maximum
528. If the initial volume of an ideal gas b. unity
is compressed to one-half its original
volume and to twice its original c. in equilibrium
temperature, the pressure:
d. undefined
a. doubles
532. Who coined the word Entropy?
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
a. Rudolf Clausius d. Compressed liquid
b. Lord Kelvin 536. Which law that states Entropy of
all perfect crystalline solids is zero at
c. Gabriel Volks absolute zero temperature?
d. Rudolf Diesel a. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
533. What is the temperature when b. First law of thermodynamics
water and vapor are in equilibrium with
the atmospheric pressure? c. Second law of
thermodynamics
a. Ice point
d. Third law of thermodynamics
b. Steam point
537. A 0.064 kg of octane vapor (MW =
c. Critical point 114) is mixed with0.91 kg of air (MW =
29.0) in the manifold of an Engine. The
d. Freezing point total pressure in the manifold is 86.1
kPa, and a temperature is 290 K.
534. When the expansion of
assume octane behaves ideally. What is
compression of gas takes place without
the partial pressure of the air in the
transfer of heat to or from the gas the
mixture in KPa?
process is called
a. 46.8
a. reversible
b. 48.6
b. adiabatic
c. 84.6
c. polytropic
d. 64.8
d. isothermal
538. Which of the following occurs in a
535. What refers to a liquid whose
reversible polytrophic process?
temperature is lower than saturation
temperature corresponding to the a. Enthalpy remains constant
existing pressure?
b. Internal energy does not
a. Subcooled liquid change
b. Saturated liquid c. Some heat transfer occurs
c. Pure liquid d. Entropy remains constant
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
539. The change that the system that c. Isolated system
undergoes from one equilibrium state to
another is known as d. All of these
a. oath 543. What is referred to by control
volume?
b. process
a. An isolated system
c. enthalpy change
b. Closed system
d. entropy change
c. Fixed region in space
540. What refers to the series of states
through which a system passes during d. Reversible process only
the process?
544. Which of the following is used in
a. path thermal power plant?
b. quasi- static steps a. Brayton cycle
c. reversibility moves b. Reversed carnot cycle
d. irreversibility moves c. Rankine cycle
541. Which of the following relations is d. Otto cycle
not applicable in a free expansion
process? 545. A Bell-Coleman cycle is a reversed
of which the following cycles?
a. Heat is rejected to zero
a. Stirling cycle
b. Work done is zero
b. Joule cycle
c. Change in temperature is zero
c. Carnot cycle
d. Heat supplied is zero
d. Otto cycle
542. What system in which neither mass
nor energy cross the boundaries and is 546. An ideal gas is compresses
not influenced by the surroundings? isothermally. The enthalpy change is
a. Closed system a. Always negative
b. Open system b. Always positive
c. zero
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
d. undefined c. Isolated system
547. The state of a thermodynamic d. Non-flow system
system is always defined by its:
a. Absolute temperature
b. process
MCQs Part XII
551. Which of the following cannot be a
c. properties property of a gas?
d. temperature and pressure a. density
548. Entropy is the measure of: b. pressure
a. The internal energy of a gas c. viscosity
b. The heat capacity of a d. temperature
substance
552. During the adiabatic process, which
c. Randomness or disorder of the following is the change in
entropy?
d. The change of enthalpy of a
system a. zero
549. What system in which there is no b. greater than zero
exchange of matter with the surrounding
or mass does not cross its boundaries? c. less than zero
a. Open system d. infinity
b. Closed system 553. Which of the following values
characterize the state of the system?
c. Isolated system
a. cycle
d. Non-flow system
b. process
550. What refers to a system in which
there is a flow of mass across its c. property
boundaries?
d. enthalpy
a. Open system
554. Which of the following is least
b. Closed system efficient?
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
a. Gas turbine b. Second law
b. Diesel engine c. Third law
c. Carnot engine d. Law of conservation of energy
d. Gasoline engine 559. Which of the following is the other
term used for enthalpy-entropy diagram?
555. Which of the following engines is
the most efficient? a. Enthalpy diagram
a. Gas turbine b. Mollier diagram
b. Diesel engine c. Steam diagram
c. Carnot engine d. Entropy chart
d. Gasoline engine 560. What is used for predicting the
behavior of non-ideal gases?
556. Which of the following engines is
the most efficient? a. Compressibility factor
a. Isobaric expansion b. Expansivity factor
b. Adiabatic compression c. Emissivity factor
c. Adiabatic expansion d. Van-d-whals factor
d. Isothermal expansion 561. Which of the following
thermodynamic devices operates the
557. Who coined the word energy? reverse of the heat engine?
a. James Joule a. Thermal pump
b. Thomas Young b. Thermal evaporator
c. Rudolf Diesel c. Thermal condenser
d. Lord Kelvin d. Thermal equilibrant
558. Which of the following laws of 562. What is another term used for
thermodynamic which leads to the isometric processes?
definition of entropy?
a. Isochoric process
a. First law
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
b. Iolytropic process d. Latent Heat Of Condensation
c. Isothermal process 566. A thermodynamic process in which
entropy is conserved
d. Reversible process
a. isentropic
563. Which of the following engines was
introduced by a German engineer, b. adiabatic
Nickolas Otto?
c. isothermal
a. Gasoline engine
d. polytropic
b. Diesel engine
567. A control volume refers to what?
c. Gas turbine
a. A fixed region in space
d. Thermal engine
b. A reversible process
564. If two systems are in the thermal
equilibrium with a third system, then they c. an isolated system
must be in thermal equilibrium with each
other. d. a specified mass
a. Zeroth Law of 568. Which of the following is commonly
Thermodynamics used as liquid absorbent?
b. First Law of Thermodynamics a. Silica gel
c. Second Law of b. Activated alumina
Thermodynamics
c. Ethylene glycol
d. Third Law of Thermodynamics
d. None of these
565. The heat absorbed by a unit mass
569. One for which no heat is gained or
of a material at its holding point in order
lost
to convert the material into a gas at the
same temperature.
a. Isentropic
a. Latent Heat of Sublimation
b. Adiabatic
b. Latent Heat of Vaporization
c. Isothermal
c. Latent Heat of Fusion
d. Polytropic
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
570. A law relating the pressure, c. decreases
temperature and volume of an ideal gas
d. is basically zero
a. Gay-Lussacs Law
574. Occurring at fixed temperature
b. Ideal gas Law
a. isentropic
c. Charles Law
b. Adiabatic
d. Boyles Law
c. Isothermal
571. Occurs when the vapor pressure
equals the atmospheric pressure d. polytropic
a. Boiling 575. The changing of solid directly to
vapor without passing through liquid
b. Melting state is called
c. Freezing a. Evaporation
d. Vaporizing b. Vaporization
572. As temperature goes to 0, the c. Sublimation
entropy approaches a constant
d. Condensation
a. Zeroth Law of
Thermodynamics 576. The phase transition of a liquid to a
solid
b. First Law of Thermodynamics
a. Solidification
c. Second Law of
Thermodynamics b. Freezing
d. Third Law of Thermodynamics c. Fusion
573. An ideal gas is compressed in a d. All of these
cylinder so well insulated that there is
essentially no heat transfer. The 577. It is an energy flux, equal to the
temperature of gas rate of energy flow per unit area per unit
time across some surface.
a. Remains constant
a. Irradiance
b. increases
b. Radiant Intensity
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
c. Luminosity a. Gamma Radiation
d. Brightness b. Black Body Radiation
578. The volume of a gas under c. Electromagnetic Radiation
constant pressure increases or decrease
with temperature. d. Alpha Radiation
a. Gay- Lussacs Law 582. The radiation emitted by a body as
a result of its temperature.
b. Ideal Gas Law
a. Blackbody Radiation
c. Charles Law
b. Thermal Inversion
d. Boyles Law
c. Thermionic Inversion
579. The molecular number density of
an ideal gas at standard temperature d. Thermal Radiation
and pressure in cm3
583. At Equilibrium, the radiation emitted
a. Froude number must equal the radiation absorbed.
b. Loschmidt number a. Boyles Law
c. Mach number b. Plancks Law
d. Reynold number c. Kirchoffs Law
580. A temperature scale whose zero d. Joules Law
point is absolute zero, the temperature
of 0 entropy at which all molecular 584. The theory that heat consisted of a
motion stops. fluid, which could be transferred from
one body to another, but not created or
a. Celsius destroyed.
b. Fahrenheit a. Clausius Theorem
c. Kelvin b. Caloric Theory
d. Rankine c. Joules Law
581. The thermal radiation emitted by a d. Newtons Law of cooling
blackbody heated to a given
temperature.
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
585. The volume of a gas is directly b. First Law of Thermodynamics
proportional to the number of molecules
of the gas. c. Second Law of
Thermodynamics
a. Ideal gas law
d. Third Law of Thermodynamics
b. Boyle-Mariotte Law
589. A cylinder contains oxygen at a
c. Avogadros Hypothesis pressure of 10 atm and a temperature of
300 K. The volume of the cylinder is 10
d. Gay-Lussacs Law of liters. What is the mass of the oxygen in
combining Volumes grams? Molecular weight (MW) of
oxygen is 32 g/mole?
586. For a body cooling in a draft, the
rate of heat loss is proportional to the a. 125.02
difference in temperature between the
body and its surroundings. b. 130.08
a. Nemst Effect c. 135.05
b. Caloric Theory d. 120.04
c. Joules Law 590. It is the deposition of radiant energy
as heat into an absorbing body.
d. Newtons Law of Cooling
a. Radiation
587. It is the intensity of a radiating
source. b. Ionization
a. Specific Brightness c. Convection
b. Radiance d. Insolation
c. Surface Brightness 591. It is a process during which the
pressure remains constant
d. All of these
a. Adiabatic
588. This law of thermodynamics
prohibits the construction of a perpetual b. Isentropic
motion machine of the second kind
c. Isobaric
a. Zeroth Law of
Thermodynamics d. Isotropic
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
592. Diffusion due to thermal motion is c. Four-stroke engine
called
d. Eight-stroke engine
a. dilation
596. It is the unbalanced force
b. infusion developed in a turbo jet engine that is
caused by the difference in the
c. effusion momentum of the low-velocity air
entering the engine and the high velocity
d. dispersion exhaust gases leaving the engine.
593. The rate at which this is quantity a. Fall
passes through a fixed boundary per
unit time b. Lift
a. Flux c. Drag
b. Existence d. Thrust
c. Irradiance 597. Which of the engine is used for
fighter bombers?
d. All of these
a. Turbojet
594. Energy can neither created nor
destroyed. It can only change forms. b. Pulsejet
a. Conservation of Mass Principle c. Rockets
b. Conservation of Energy d. Ramjet
Principle
598. The Science of Energy
c. Conservation of Momentum
Principle a. Thermionics
d. Conservation of Heat Principle b. Kinetics
595. Executes the entire cycle in just two c. Thermodynamics
strokes the power stroke and the
compression stroke. d. Geophysics
a. One-stroke engine 599. It is used for gas turbines which
operates on an open cycle where both
b. Two-stroke engine the compression and expansion
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
processes take place in rotating 11. Closed system
machinery.
12. Isolated system
a. Dual Cycle 13. Open system
b. Otto Cycle 14. All of the above
15. Control surface
c. Carnot Cycle
16. Property
d. Brayton Cycle
17. Intensive and extensive
600. Which of the following laws of 18. Intensive property
thermodynamic which leads to the
19. Extensive property
definition of entropy?
20. Mass
a. First law
21. Density
b. Second law 22. Specific properties
c. Third law 23. Thermal
24. Mechanical
d. Law of conservation of energy
25. Phase
26. Chemical
Answers Sheet 27. State postulate
28. Kj
MCQs Part I
29. Simple compressible
1. Heat power
30. Process
2. Lord Kelvin
31. Path
3. First law of Thermodynamics
32. 2
4. Second law of Thermodynamics
33. Quasi-state or quasi- equilibrium
5. Classical thermodynamics
process
6. Statistical thermodynamics
34. Control mass
7. System
35. Control volume
8. Conservation of energy
36. Thermal, phase, mechanical and
9. Surroundings chemical
10. Boundary 37. Cycle
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
38. Isothermal process 64. Constant-volume gas thermometer
39. Isobaric process 65. Triple point of water
40. Isochoric or isometric process 66. Pressure
41. Remains constant 67. N/m^2
42. No change with time 68. 14.223 psi
43. No change with location 69. Pa
44. Steady-flow process 70. 10^5
45. Internal energy 71. 101,325
46. Microscopic form of energy 72. Absolute pressure
47. Macroscopic form of energy 73. Vacuum pressure
48. Thomas Young 74. Gage
49. Translational energy 75. Pitot tube
50. Rotational kinetic energy 76. Barometer
77. 760
MCQs Part II 78. Pascals Law
51. Spin energy 79. Bourdon pressure gage
52. Sensible energy 80. Heat
53. Latent energy 81. Joule
54. Chemical energy 82. Kg m^2/s^2
55. Nuclear energy 83. 4.184
56. Heat transfer and work 84. 10^-7
57. Zeroth law of thermodynamics 85. Law of conservation of energy
58. R.H. Fowler 86. Thermodynamics
59. Kelvin scale 87. Enthalpy
60. Rankine scale 88. Heat capacity
61. Ideal gas temperature scale 89. Molar heat
62. Constant-volume gas thermometer 90. Specific heat
63. Coulomb repulsion 91. Hesss Law
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
92. Entropy 116. Universal gas constant to molar
mass
93. Joule/Kelvin
117. 8.314
94. Enthalpy
118. Molar mass
95. Compressed or subcooled
119. Specific heat
96. Saturated
120. Specific heat capacity
97. Saturated
121. 4185
98. Superheated
122. J/kg C
99. Pure
123. Specific volume of density
100. Saturation temperature
124. Adiabatic
125. Not to be passed
MCQs Part III 126. All of the above
101. Saturation pressure 127. Radiation
102. Heat of fusion 128. Convection
103. Heat of vaporation 129. Conduction
104. Latent heat 130. Conservation of mass principle
105. 333.7 kJ/kg 131. PV = nRT
106. 2257.1 kJ/kg 132. Both heat transfer = 0; isentropic:
107. Maximum point reversible
108. Sublimation 133. PV = nRT
109. Kilocalorie 134. Thermal conductivity
110. BTU 135. Greenhouse effect
111. 1054 136. Boundary work
112. Heat 137. 0.1 to 100 m
113. Quality 138. Emissive power
114. Pressure, temperature and specific 139. Kirchhoffs radiation law
volume 140. Black body
115. Gas constant 141. Gray body
142. Less than
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
143. It is independent with the surface 166. Carnot heat engine
condition of the material
167. Carnot principle
144. 1
168. Second law of thermodynamics
145. 1
169. Isentropic
146. Stefan-Boltzmann law
170. True
147. Conservation of energy principle
171. Internally reversible, adiabatic
148. Energy balance process
149. Mass and energy content of the 172. Third law of thermodynamics
control volume
173. Third law of thermodynamics
150. Network output to total heat input
174. Entropy balance relation
175. Second law of thermodynamics
176. Heat
MCQs Part IV
151. Second law of thermodynamics 177. It is always zero
152. Kelvin-Planck statement 178. Its saturated vapor pressure equals
to the atmospheric pressure
153. Combustion efficiency
179. 0 degree Celsius and one
154. Overall efficiency atmosphere
155. Energy efficiency rating 180. Zero
156. Second law of thermodynamics 181. Boyles Law
157. Clausius statement 182. V1/T1=V2/T2
158. Perpetual-motion machine 183. Thickness of material/ thermal
159. Perpetual-motion machine of the conductivity of material
first kind 184. 186,000 miles/second
160. Perpetual motion machine of the 185. Eff = 1 (T2/T1)
second kind
186. EER = 3.42 COP
161. 1824
187. Absorbed heat and work required
162. Sadi Carnot
188. Law of Dulong and Petit
163. 4
189. Avogadros
164. Two isothermal and two adiabatic
190. Perfect gas
165. Carnot efficiency
191. All of the above
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
192. Amagats law 217. Helmholtz free energy
193. Throttling process 218. 0.67 m
194. Joule-Thomson coefficient 219. 0.18 in
195. Sink reservoir 220. 1400 J
196. Isentropic flow 221. Gibbs free energy
197. Ignition temperature 222. heat
198. Daltons law 223. relative humidity
199. Joules law 224. Sublimation
200. An ideal gas is a gas that is not a 225. Convection
superheated vapor
226. change
227. three times
228. increases
MCQs Part V
201. movement of heat 229. no pressure
202. Kelvin 230. the relative humidity decreases
203. heat 231. convection current
204. latent heat 232. blackbody
205. thermal expansion 233. Conduction
206. thermal stress 234. gram-mole
207. Internal Energy 235. Maxwell speed Distribution
208. Specific Heat Capacity 236. Forced Convection
209. Equilibrium Vapor Pressure 237. point function
210. temperature 238. path function
211. Phase diagram 239. boundary
212. Internal Energy 240. control mass
213. calorie 241. control volume
214. temperature 242. -256
215. Zero-Point Energy 243. heat enters the substance.
216. 10 K 244. 15
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
245. shape of the object 269. Clausius statement
246. metals 270. mean free path
247. glass 271. 9.86 x 10^4 N/m^2
248. increases 272. 6 x 10^15 tons
249. Kelvin temperature 273. standard atmospheric pressure
250. reduced by half 274. Pascals law
275. Gauge Pressure
276. 62.4 lb
MCQs Part VI
277. surface tension
251. it increases by a factor of square
root of 2 278. Torricellis Theorem
252. entropy 279. diffusion
253. Isochoric process 280. 1948
254. isobaric 281. dew point
255. increases 282. cycle
256. Closed system 283. Bulk Properties
257. normal boiling point 284. Joule-Thomson process
258. wet steam 285. Otto Cycle
259. flash steam 286. 24.6 J/K
260. dryness fraction 287. conservation of energy
261. thermopile 288. 1700 J
262. any holes in the object expand as 289. 12 kJ
well 290. 17.66 %
263. one BTU 291. Sensible heat
264. pressure 292. Joseph Black
265. Sir James Dewar 293. Latent Heat
266. Isobaric 294. Third Law of thermodynamics
267. raising the temp and lowering the 295. 1/860 W.h
temp
296. Polytropic process
268. the second law of thermodynamics
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
297. steady flow 323. 286
298. Carnot Cycle 324. Both a & b
299. 733.33 kPa 325. 209 psia
300. Sadi Carnot 326. 416
327. 999 K
328. 3800
MCQs Part VII
329. 1620 R
301. 13.33 ft^3/lbm
330. 0.2148 lb
302. 3300 lbf-ft/lbm
331. 121
303. 24.9 ft^3
332. 100
304. z = pV/ RT
333. 125 J
305. 1.79 kJ/ kg-C
334. 443 kPa
306. 2 x10^6 kJ
335. 48.75 N
307. 3.16 kg
336. 4875 j
308. 1.1577 BTU/lbm-R
337. 300 kJ
309. 15.7 BTU
338. 1
310. 0.179 K/s
339. 485
311. 4474.23 N
340. 672
312. 2474.23 N
341. 298.645
313. 42.41 ft^3
342. 65.23 psi
314. 28.6 psia
343. 70
315. 108 hp
344. 450 N
316. W = mRTln (V2/V1)
345. 900,000lb/hr;625 ft/s981 N
317. 1124 cal
346. 981 N
318. -364 BTU/lbm
347. T2=1.620R, H = 122.83 Btu
319. 12 kJ
348. 70.658 kpa
320. 0.02 ft^3/lbm
349. 900,000 lb/hr;625 ft/s
321. 66 kgf
350. 11,772 N-m and 6.26m/s
322. 1000 kgf/m3
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
377. 1.356
378. 339.4 K
MCQs Part VIII
379. 1620R
351. 10m/s
380. 710R
352. 217.17 kpa
381. 265.4C, 430.7kJ/kg, 71.4kJ/kg,
353. 796.32 L 1.0327kJ/(kg)(K),502.1 kJ/kg
354. 7.85 382. 204.2C, -703.2 kJ/kg, -84.15
355. 375 kg/s kJ/kg, -1.7505 kJ/(kg)(K),-787.4 kJ/kg
356. 87C 383. 95.20%
357. 0.085 m/min 384. 95.56%
358. 24m/s 385. 1378.7 kJ
359. 33.9 ft 386. -1384.7 kJ
360. 625 fpm 387. 96%
361. 50 lbm 388. 97.6%,2713 kJ/kg
362. 33.9 ft 389. 14026.5 m
363. 1.38 390. 126m
364. -420Btu 391. 54.60%
365. 7.9 C 392. 190 in
366. 1.3 x 108 J 393. 217.7 kPa
367. -540 J 394. 62850 joules
368. 0.77 kg liter-1 395. 419 000 joules
369. 11,120N 396. 2238 watts
370. 5.18 l 397. 9 Newtons
371. 18 kg 398. 0.998 hp
372. 111 psi 399. 1.16 kcal
373. 1214Btu / lb 400. 440 cal
374. 394 lb
375. 1664 kJ/min
376. 7.849 ft3
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
425. Specific Heat
426. Thermodynamics
MCQs Part IX
427. 1st Law of Energy Conservation
401. Thermodynamics
428. Vector Quantity
402. Boyles Law
429. Internal Energy
403. 6.0225 x 10^23 mol-1
430. 1.60210 x 10-19 coulomb
404. all of the above
431. Boyle's Law
405. isolated system
432. Barometer
406. evaporation
433. Both a & b
407. 1 gm/cm
434. Q is positive when heat is rejected
408. when a body is inversed in a fluid, by the body or system
the fluid exerts a upward force on the
body whose magnitude is equal to the 435. All of the above
weight of the displaced fluid. 436. Entrophy
409. solid 437. Newton's Law
410. V = C 438. Density
411. specific heat 439. Enthalpy
412. > 1 440. Closed System
413. Law of Conservation of Mass 441. isometric
414. potential energy 442. specific heat
415. elastic work 443. torr
416. Gabriel Daniel Fahrenheit 444. Cp Cv
417. Anders Celsius 445. Conservation of Energy
418. barometer 446. Isolated System
419. Momentum 447. Enthalpy
420. all of the above 448. Specific Gravity
421. Energy is a scalar quantity 449. kJ / kg.k
422. System 450. Zeroth Law
423. Flow rate
424. Energy
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
477. Specific Weight
478. Manometer
MCQs Part X
479. Process
451. Charles Law
480. Heat Engine
452. Heat
481. Saturation Temperature
453. Reversible
482. Sub cooled Liquid
454. Natural Environment
483. Compressed Liquid
455. The change in entropy is 0
484. Saturated Liquid
456. kg
485. Vapor
457. Surrounding
486. Saturated Vapor
458. Control Volume
487. Superheated Vapor
459. Adiabatic
488. Wet Vapor
460. Isentropic Process
489. Critical Point
461. Mass
490. Sensible Heat
462. Weight
491. Latent Heat
463. mass is indestructible
492. momentum
464. Internal Energy
493. C = 5/9 (F - 32)
465. Work
494. Kelvin
466. Heat
495. Newton
467. Open System
496. Pascal
468. Pa
497. Degrees of Superheat, SH
469. Boyles Law
498. Degrees of Sub cooled, SB
470. Multistaging
499. Quality, x
471. Relative Humidity
500. Percent Moisture, y
472. Internal Combustion Engine
473. Humidity ratio
474. Adiabatic Saturation Process MCQs Part XI
475. Fossil fuel 501. 2
476. Heating Value 502. zero
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
503. Conservation of energy 530. External combustion engine
504. Rankine cycle 531. in equilibrium
505. Phase 532. Rudolf Clausius
506. 1 533. Steam point
507. Extensive property 534. adiabatic
508. Intensive properties 535. Subcooled liquid
509. enthalpy 536. Third law of thermodynamics
510. entropy 537. 84.6
511. Steam point 538. Some heat transfer occurs
512. Triple point 539. process
513. Critical point 540. path
514. Sensible heat 541. Change in temperature is zero
515. Kilocalorie 542. Isolated system
516. high temperature and low pressure 543. Fixed region in space
517. Boyles Law 544. Rankine cycle
518. Open system 545. Joule cycle
519. An energy transfer due to 546. zero
temperature difference
547. properties
520. joule
548. Randomness or disorder
521. the enthalpy of reactants is lower
549. Closed system
than the enthalpy of products.
550. Open system
522. regelation
523. when the gas expands adiabatically
524. zero MCQs Part XII
525. Heat
526. Becomes negative 551. viscosity
527. zero 552. zero
528. quadruples 553. enthalpy
529. Adiabatic process 554. Gasoline engine
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
555. Carnot engine 583. Kirchoffs Law
556. Isobaric expansion 584. Caloric Theory
557. Thomas Young 585. Avogadros Hypothesis
558. Second law 586. Newtons Law of Cooling
559. Mollier diagram 587. All of these
560. Compressibility factor 588. Second Law of Thermodynamics
561. Thermal pump 589. 130.08 {(10atm)(10)(32)/(0.0821)
(300K)}
562. Isochoric process
590. Insolation
563. Gasoline engine
591. Isobaric
564. Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
592. effusion
565. Latent Heat of Vaporization
593. All of these
566. isentropic
594. Conservation of Energy Principle
567. A fixed region in space
595. Two-stroke engine
568. Ethylene glycol
596. Thrust
569. Adiabatic
597. Turbojet
570. Ideal gas Law
598. Thermodynamics
571. Boiling
599. Brayton Cycle
572. Third Law of Thermodynamics
600. Second law
573. increases
574. Isothermal
575. Sublimation
576. All of these
577. Luminosity
578. Charles Law
579. Loschmidt number
580. Kelvin
581. Black Body Radiation
582. Thermal Radiation
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
Mechanical Engineering MCQ
Thermodymics
Swai Singh Godara 9414532268, 9414532269, 9462974849, 9509974849,
8005603009, 8441976502
You might also like
- 300+ TOP THERMODYNAMICS Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersDocument43 pages300+ TOP THERMODYNAMICS Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersSasi Ravi100% (1)
- 152 TOP Thermodynamics - Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers ListDocument30 pages152 TOP Thermodynamics - Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers ListSampat AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- THERMOCHEMISTRY MCQsDocument5 pagesTHERMOCHEMISTRY MCQsAnonymous hh6RRWHHh367% (3)
- Thermodynamics MCQDocument13 pagesThermodynamics MCQBhaskar jyoti BhuyanNo ratings yet
- MCQ in Thermodynamics 000ANSDocument33 pagesMCQ in Thermodynamics 000ANSjenny92% (13)
- Mcq-Thermodynamics Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesMcq-Thermodynamics Second Law of ThermodynamicsTochi Krishna Abhishek91% (11)
- MCQ Thermodynamics First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesMCQ Thermodynamics First Law of ThermodynamicsTochi Krishna Abhishek82% (11)
- Thermodynamics Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersDocument21 pagesThermodynamics Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersPadmavathi C50% (2)
- 103 Top Heat Transfer Question and Answers PDFDocument11 pages103 Top Heat Transfer Question and Answers PDFbenny narrido67% (6)
- Fluid Mechanics (MCQ)Document17 pagesFluid Mechanics (MCQ)John WilmarNo ratings yet
- Physics First Year FSC Solved MCQsDocument36 pagesPhysics First Year FSC Solved MCQsFahad Rehman Khan74% (215)
- 136 TOP Engineering Mechanics - Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers - MCQs Preparation For Engineering Competitive ExamsDocument21 pages136 TOP Engineering Mechanics - Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers - MCQs Preparation For Engineering Competitive ExamsNagaraj Muniyandi50% (2)
- Solved - Problems in ThermodynamicsDocument29 pagesSolved - Problems in ThermodynamicsAngelica Joyce Benito100% (6)
- Internal Combustion Engines MCQ PDFDocument14 pagesInternal Combustion Engines MCQ PDFShakir ullah87% (53)
- Mcqs With Answers Waves and OscillationDocument18 pagesMcqs With Answers Waves and OscillationGovt.GraduateCollege TobaTekSinghNo ratings yet
- BSC Phy, Thermodynamics, HRK PDFDocument60 pagesBSC Phy, Thermodynamics, HRK PDFAbrar Ahmed Awan92% (12)
- Top 250 I.C. Engine Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersDocument24 pagesTop 250 I.C. Engine Multiple Choice Questions and Answersswai singh79% (14)
- Thermodynamics 1Document21 pagesThermodynamics 1Jo Ces100% (1)
- Fluid Dynamics-MCQ'sDocument13 pagesFluid Dynamics-MCQ'sfrost50% (2)
- Engineering Materials 74 Important MCQDocument10 pagesEngineering Materials 74 Important MCQaditya100% (4)
- Fuels and Combustion MCQs PDFDocument55 pagesFuels and Combustion MCQs PDFZubair Malik67% (6)
- Torque and Equilibrium McqsDocument2 pagesTorque and Equilibrium McqsFaraz Ahmad63% (8)
- Projectile Motion MCQS PhysicsDocument10 pagesProjectile Motion MCQS PhysicsZamaan Haidri80% (69)
- Tom MCQ VISemDocument5 pagesTom MCQ VISempurukumar32250% (2)
- MCQ Questions From Simple MachineDocument15 pagesMCQ Questions From Simple Machinefotick100% (3)
- 300 Multiple Choice Question Bank On Power Plant EngineringDocument27 pages300 Multiple Choice Question Bank On Power Plant Engineringramkrishna77% (39)
- Powerplant MCQ 1200 QnsDocument103 pagesPowerplant MCQ 1200 QnsSaranya S100% (2)
- Fluid Mechanics MCQ - Bundle 1 - SampleDocument9 pagesFluid Mechanics MCQ - Bundle 1 - SampleMohamed Salah Yassin100% (1)
- Physics XII The Nuclear Physics MCQDocument12 pagesPhysics XII The Nuclear Physics MCQSyed Mairaj Ul Haq72% (18)
- Mcq's Thermal and Statistical Physics-1Document6 pagesMcq's Thermal and Statistical Physics-1Ehtasham AhmadNo ratings yet
- Me 6301 Engineering Thermodynamics Short Questions and AnswersDocument43 pagesMe 6301 Engineering Thermodynamics Short Questions and AnswersBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHAN83% (29)
- 255 TOP FLUID MECHANICS Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDFDocument38 pages255 TOP FLUID MECHANICS Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDFAshish Agarwal70% (10)
- For All Sanfoundry MCQ (1000+ MCQ) JOIN Telegram GroupDocument472 pagesFor All Sanfoundry MCQ (1000+ MCQ) JOIN Telegram GroupRitesh DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Thyristor MCQDocument6 pagesThyristor MCQnandhakumarme0% (3)
- Felows Specimen1Document2 pagesFelows Specimen1Ahmad Faraz Khan100% (2)
- MCQ Thermodynamics Compressible FlowDocument4 pagesMCQ Thermodynamics Compressible FlowTochi Krishna Abhishek100% (1)
- Statistical Mechanics TEST QuestionsDocument2 pagesStatistical Mechanics TEST QuestionsAbhijit Kar Gupta83% (42)
- MCQ QuestionsDocument29 pagesMCQ Questionsj setty70% (63)
- Questions and Answers in ThermodynamicsDocument14 pagesQuestions and Answers in ThermodynamicsD.Viswanath100% (24)
- Alternator MCQDocument30 pagesAlternator MCQKhealMaeL.Enagordaf50% (4)
- Physics MCQ Solid State PhysicsDocument15 pagesPhysics MCQ Solid State PhysicsRams Chander88% (25)
- Homeostasis McqsDocument8 pagesHomeostasis Mcqsharistxt92% (12)
- Mcqs Solid State Physics (Chapter 3-5) by Mansoor SultanDocument7 pagesMcqs Solid State Physics (Chapter 3-5) by Mansoor SultanMansoor AslamNo ratings yet
- MCQ On VibrationsDocument18 pagesMCQ On VibrationsAbhijit Dakare100% (4)
- Chapter # 7 Work Power and EnergyDocument13 pagesChapter # 7 Work Power and EnergySIR USMAN KHAN86% (7)
- Sample questions for training: geα+βE geα+βE−1 geα+βE+1 geα+βE+kDocument13 pagesSample questions for training: geα+βE geα+βE−1 geα+βE+1 geα+βE+kHamza Maher100% (4)
- 75 MCQ of PhysicsDocument47 pages75 MCQ of PhysicsFarah Anjum94% (35)
- Engineering Mechanics MCQ QuestionsDocument116 pagesEngineering Mechanics MCQ QuestionsMiral_Kagathra100% (2)
- SUM ACADEMY LARKANA - MCQ TEST Chapter 1 - HOMEOSTASISDocument24 pagesSUM ACADEMY LARKANA - MCQ TEST Chapter 1 - HOMEOSTASISAjay96% (25)
- IC Engine MCQDocument16 pagesIC Engine MCQAkshat Singh Jhala100% (2)
- 195 TOP Engineering Materials - Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers - MCQs Preparation For Engineering Competitive ExamsDocument20 pages195 TOP Engineering Materials - Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers - MCQs Preparation For Engineering Competitive Examssabya51278% (9)
- MCQ Aero ThermodynamicsDocument88 pagesMCQ Aero ThermodynamicskkonthenetNo ratings yet
- UPDA Questions For Mechanical (Thermodynamics)Document22 pagesUPDA Questions For Mechanical (Thermodynamics)Romal MathewNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Questions MCqsDocument6 pagesThermodynamics Questions MCqsGoverdhan ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Mech Material 1 199 LogoDocument199 pagesMech Material 1 199 LogoSuchitKNo ratings yet
- 300+ TOP Thermodynamics Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersDocument1 page300+ TOP Thermodynamics Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersBhutto WaqarNo ratings yet
- Thermal Multiple Short QuestionDocument18 pagesThermal Multiple Short QuestionMohammad FahimNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics - Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers For Compitative ExamsDocument243 pagesThermodynamics - Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers For Compitative Examsahmish kabbaxeNo ratings yet
- Course Objective QuestionDocument243 pagesCourse Objective Questionahmish kabbaxeNo ratings yet
- UPDA (From Islam)Document133 pagesUPDA (From Islam)riswanNo ratings yet
- Khanna's Objective Questions in Petroleum EngineeringDocument396 pagesKhanna's Objective Questions in Petroleum EngineeringTouhid Islam92% (13)
- D 0415 Paper III Psychology 2015Document40 pagesD 0415 Paper III Psychology 2015swai singhNo ratings yet
- Timetable 3rd Test 2ndPEDocument1 pageTimetable 3rd Test 2ndPEswai singhNo ratings yet
- Swai Singh PE202 3rd TestDocument1 pageSwai Singh PE202 3rd Testswai singhNo ratings yet
- Material FileDocument14 pagesMaterial FileAso SerwanNo ratings yet
- Swai Singh PE201 3rd TestDocument4 pagesSwai Singh PE201 3rd Testswai singhNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas: Processing, Transportation, Storage and Custody TransferDocument2 pagesNatural Gas: Processing, Transportation, Storage and Custody Transferswai singhNo ratings yet
- Heat TreatmentDocument3 pagesHeat Treatmentswai singhNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas Supply Chain Vs 2Document1 pageNatural Gas Supply Chain Vs 2swai singhNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Booster: What Are The Main Parts of An Automobile Engine?Document9 pagesMechanical Booster: What Are The Main Parts of An Automobile Engine?swai singhNo ratings yet
- Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument40 pagesSecond Law of ThermodynamicscaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Top 250 I.C. Engine Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersDocument24 pagesTop 250 I.C. Engine Multiple Choice Questions and Answersswai singh79% (14)
- Age Related QuestionsDocument9 pagesAge Related Questionsswai singhNo ratings yet
- Caste Certificate DirectionsDocument28 pagesCaste Certificate Directionsswai singhNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Dictionary-Automotive Vehicles - ObjectiveBooksDocument13 pagesMechanical Engineering Dictionary-Automotive Vehicles - ObjectiveBooksswai singhNo ratings yet
- 3-Process Flow Chart and Plant Layout Dairy and Food EngineeringDocument3 pages3-Process Flow Chart and Plant Layout Dairy and Food Engineeringswai singhNo ratings yet
- Nptel - Iitm.ac - in Courses Webcourse-Contents IISc-BANG Basic Thermodynamics PDF Module 1Document32 pagesNptel - Iitm.ac - in Courses Webcourse-Contents IISc-BANG Basic Thermodynamics PDF Module 1lakumas15No ratings yet
- Nuclear Science General Knowledge GK Practice Test: Question Set 01Document2 pagesNuclear Science General Knowledge GK Practice Test: Question Set 01swai singhNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Science General Knowledge GK Practice Test: Question Set 01Document2 pagesNuclear Science General Knowledge GK Practice Test: Question Set 01swai singhNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document1 pagePaper 1swai singhNo ratings yet
- Border Security ForceDocument7 pagesBorder Security Forceswai singhNo ratings yet
- Programming XML in Java, Part 1 - JavaWorld2Document7 pagesProgramming XML in Java, Part 1 - JavaWorld2swai singhNo ratings yet
- IitmailerDocument20 pagesIitmailerswai singhNo ratings yet
- Java - Decision MakingDocument2 pagesJava - Decision Makingswai singhNo ratings yet
- Ignou PDFDocument2 pagesIgnou PDFswai singhNo ratings yet
- ME 1991 Unsolved PDFDocument13 pagesME 1991 Unsolved PDFSathya ThyaguNo ratings yet
- Air Cycle Refrigeration Systems Gas Turbine CyclesDocument32 pagesAir Cycle Refrigeration Systems Gas Turbine Cyclesswai singhNo ratings yet
- StringDocument2 pagesStringswai singhNo ratings yet
- Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument40 pagesSecond Law of ThermodynamicscaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Engine Torque, Power and Mean Piston SpeedDocument13 pagesEngine Torque, Power and Mean Piston SpeedJayath BogahawatteNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power Generation MCQDocument37 pagesElectrical Power Generation MCQsalman bhatti100% (3)
- Gas Turbine Numerical PDFDocument5 pagesGas Turbine Numerical PDFWaseem KhanNo ratings yet
- Pipe Problems Part 1Document100 pagesPipe Problems Part 1Sheena BejasaNo ratings yet
- JMS 624 GS-N.L: Technical Description Cogeneration UnitDocument11 pagesJMS 624 GS-N.L: Technical Description Cogeneration Unitsmartleo_walo100% (1)
- Practice Problems For Thermal Engineering: September 2019Document24 pagesPractice Problems For Thermal Engineering: September 2019Roderick VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Unjuk Kerja Turbin Uap Pembangkit Listrik Tenaga Panas Bumi Dalam Pandangan Pendidikan IslamDocument6 pagesUnjuk Kerja Turbin Uap Pembangkit Listrik Tenaga Panas Bumi Dalam Pandangan Pendidikan Islamalkhawarizmi vebriNo ratings yet
- Lec27 Problem Solution PDFDocument22 pagesLec27 Problem Solution PDFmaya singhNo ratings yet
- Effect of Excess Air in Boiler OperationDocument5 pagesEffect of Excess Air in Boiler OperationGovindarajan Chandrasekaran100% (1)
- Energy Management & Audit 1Document25 pagesEnergy Management & Audit 1Avinaba BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- SSC JE Mechanical SyllabusDocument6 pagesSSC JE Mechanical SyllabusPrince SethiNo ratings yet
- Otto, Brayton and Rankine Cycles: ObjectiveDocument7 pagesOtto, Brayton and Rankine Cycles: ObjectivepappuNo ratings yet
- Reeds Vol. 12 Motor Engineering Knowledge For Marine EngineersDocument385 pagesReeds Vol. 12 Motor Engineering Knowledge For Marine Engineershzhchina168No ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EngineDocument40 pagesInternal Combustion EngineMingNo ratings yet
- ,esson Plan Cot 2Document25 pages,esson Plan Cot 2Kwen Ann OrtigzNo ratings yet
- Power Plant QuestionsDocument20 pagesPower Plant QuestionsSubhransu Mohapatra50% (2)
- PhysicsMCQ XII PDFDocument190 pagesPhysicsMCQ XII PDFSunder KumarNo ratings yet
- Code No: 13006Document4 pagesCode No: 13006SRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Hermal Efficiency: Thermal Efficiency Providing Ways of Improvement of Thermal EnginesDocument2 pagesHermal Efficiency: Thermal Efficiency Providing Ways of Improvement of Thermal EnginesVohid KadirzhanovNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Plant: (Coal-Fired)Document94 pagesSteam Power Plant: (Coal-Fired)Gabriel ApolonioNo ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering - Ii: 111. What Is Steam Nozzle? How Are They Classified?Document61 pagesThermal Engineering - Ii: 111. What Is Steam Nozzle? How Are They Classified?karthiyuvenNo ratings yet
- Spontaneously Not Vice Versa: Second-Law - PPT Modified 10/9/02Document37 pagesSpontaneously Not Vice Versa: Second-Law - PPT Modified 10/9/02T Hari PrasadNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine Performance Evaluation and Emission Analysis Using Gmelina Seed Oil BiodieselDocument8 pagesDiesel Engine Performance Evaluation and Emission Analysis Using Gmelina Seed Oil BiodieselInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Tech Data: Heat Transfer OilDocument4 pagesTech Data: Heat Transfer OilNokiabhre WijayaNo ratings yet
- Engine Test Sample Question(s)Document4 pagesEngine Test Sample Question(s)Anup ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Power Plant QuestionsDocument11 pagesPower Plant QuestionssebinNo ratings yet
- Question Phase 3Document115 pagesQuestion Phase 3Noel Capillan OcapNo ratings yet
- Basic Mechanical Engg. Assigenment No. 2Document1 pageBasic Mechanical Engg. Assigenment No. 2niyatisonimgNo ratings yet
- 2007 Advanced EngineDocument340 pages2007 Advanced EngineGolden PerfectNo ratings yet
- Vapor and Combined Power Cycles: TopicsDocument52 pagesVapor and Combined Power Cycles: TopicsAshlin Augusty100% (1)