Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FSPJFSPJSFPJFSPJFSPJ
Uploaded by
Fatema KhatunOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FSPJFSPJSFPJFSPJFSPJ
Uploaded by
Fatema KhatunCopyright:
Available Formats
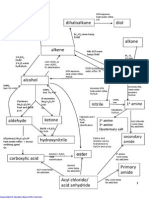
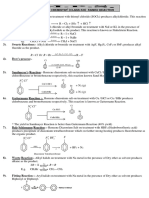
o Cold concentrated H2SO4, followed by heating in the
presence of water
Addition of Hydrogen
o H2(g) with Nickel catalyst, at ~150oC, ~5atm
o H2(g) with Pt or Pd catalyst, at room temperature
Oxidation
o Partial bond cleavage
Cold alkali/ cold, dilute acidified KMnO4
o Total bond cleavage
Hot, acidified KMnO4
Combustion
b. Formation
Dehydration of Alcohols
o Excess, concentrated H2SO4, 180oC
o Al2O3, 400oC
Dehydrohalogenation of halogenoalkane
o Alcoholic KOH, relfux
2. Benzene
a. Reactions
Nitration
o Concentrated HNO3, concentrated H2SO4, reflux at less
than 60oC
Halogenation
o Anhydrous AlCl3 / FeCl3/ Fe power, at room temperature
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation
o Anhydrous AlCl3 / FeCl3/ Fe power, at room temperature
Friedel-Crafts Acylation
o Anhydrous AlCl3 / FeCl3/ Fe power, at room temperature
3. Alkylbenzene
a. Reactions (side-chain)
Halogenation
o Cl2(g)/Br2(l), UV light
Oxidation
o Alkaline/ acidified KMnO4, reflux
o Entire side chain is oxidized into CO 2H
b. Formation
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation
o Anhydrous AlCl3 / FeCl3/ Fe power, at room temperature
4. Alcohols
a. Reactions
Esterification
o Concentrated H2SO4, reflux
Acylation
Halogenation (hydrogen halide)
o NaCl(s), concentrated H2SO4, reflux
o HX, reflux
Halogenation (phosphorus halide)
o Cold PCl5
o Red P and Br2, reflux
o Red P and I2, reflux
Halogenation (Sulfur dichloride oxide)
Done by Nickolas Teo Jia Ming, CG 12/11
o SOCl2, dissolved in pyridine
Dehydration
o Excess, concentrated H2SO4, 180oC
Al2O3, 400oC Organic Chem Reactions
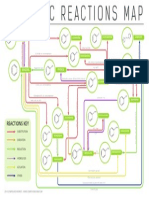
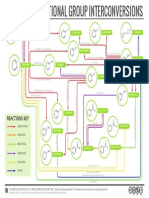
1. Alkanes
a. Reactions
Combustion
Free-radical substitution
o Steps
Initiation
Propagation
Termination
o Conditions
Cl2(g)/Br2(l), UV light
b. Formation
Hydrogenation of Alkenes
o H2(g) with Nickel catalyst, at ~150oC, ~5atm
o H2(g) with Pt or Pd catalyst, at room temperature
Decarboxylation of sodium salt of carboxylic acid
o Heating with sodalime
2. Alkenes
a. Reactions
Addition of bromine
o Br2(l) / Br2 dissolved in CCl4, room temperature
Addition of bromine water
o Bromine water at room temperature
Addition of HBr
o HBr(g)/ HBr dissolved in CCl4, room temperature
Direct hydration
o Steam, H3PO4 catalyst, 300oC, 65 atm
Indirect hydration
o
Formation of alkyl hydrogensulfate
o Concentrated H2SO4, reflux at 80oC
Combustion
Oxidation
o For aldehyde
Acidified K2Cr2O7, heat to distill
o For carboxylic acid/ ketone
Acidified K2Cr2O7/ KMnO4, reflux
b. Formation
Alkaline hydrolysis of halogenoalkane
o Aqueous KOH, reflux
Direct hydration of alkenes
o Steam, H3PO4 catalyst, 300oC, 65 atm
Indirect hydration of alkenes
o Cold concentrated H2SO4, followed by heating in the
presence of water
Reduction of carbonyl compounds
Done by Nickolas Teo Jia Ming, CG 12/11
o H2(g) with Ni catalyst at 140oC
o LiAlH4, dissolved in dry ether at room temperature
c. Test
Tri-iodomethane/ Iodoform test
o Alkaline I2(aq), heat
o Solid I2, NaOH(aq), heat
o NaOI(l), heat
3. Phenol
a. Reactions
Esterification
o Acid chloride and NaOH(aq)
Halogenation
o Br2 dissolved in CCl4
o Chlorine/ Bromine water at room temperature
Nitration
o Dilute HNO3, room temperature
b. Test
Neutral Iron(III) chloride solution at room temperature
o Violet coloration
Bromine water at room temperature
o Decolourisation and white precipitate
4. Aliphatic carbonyl compounds
a. Reactions
Oxidation of aldehydes
o Acidified K2Cr2O7/ KMnO4, heat
o Alkaline KMnO4, heat
o Tollens Reagent, heat
Ammoniacal silver(I) nitrate
o Fehlings Solution, heat
Alkaline copper(II) tartrate
Reduction
o H2(g) with Ni catalyst at 140oC
o LiAlH4, dissolved in dry ether at room temperature
Addition of HCN
o Slightly alkaline HCN (aq) at 10-20oC
o HCN (aq), small amount of KCN, 10-20oC
Condensation reaction with Bradys Reagent
o Bradys Reagent, room temperature.
b. Test
Tri-iodomethane test
o Alkaline I2(aq), heat
o Solid I2, NaOH(aq), heat
o NaOI(l), heat
c. Formation
Oxidation of alcohols
o Acidified K2Cr2O7/ KMnO4, heat (to distill for aldehyde)
5. Aromatic carbonyl compounds
a. Reactions
Oxidation of aldehydes
o Acidified KMnO4, heat
o Alkaline KMnO4, heat
Done by Nickolas Teo Jia Ming, CG 12/11
o Tollens Reagent, heat
Ammoniacal silver(I) nitrate
o NOT Fehlings solution
Reduction
o LiAlH4, dissolved in dry ether at room temperature
Condensation reaction with Bradys Reagent
o Bradys Reagent, room temperature.
Electrophilic substitution of benzene ring
o Fuming HNO, concentrated H2SO4, reflux at 40oC
o Cl2, anhydrous FeCl3, at room temperature
b. Test
Tri-iodomethane test
o Alkaline I2(aq), heat
o Solid I2, NaOH(aq), heat
o NaOI(l), heat
c. Formation
For benzaldehyde
o Excess Cl2 gas and UV light, followed by reflux with
NaOH (aq)
For phenylethanone
o CH3COCl with anhydrous AlCl3 catalyst, 40oC
6. Carboxylic acid
a. Reactions
Metal, metal carbonate, alkali
o Room temperature
Formation of acyl chloride by a halogen atom
o PCl5(s), cold
o PCl3(l), cold
o SOCl2, dissolved in pyridine
Esterification
o Concentrated H2SO4, reflux
Reductions
o LiAlH4, dry ether, room temperature
b. Formation
Oxidation of primary alcohol
o Acidified K2Cr2O7/ KMnO4, reflux
Oxidation of aldehydes
o Acidified K2Cr2O7/ KMnO4, reflux
Oxidation of methyl benzene
o Acidified KMnO4, heat
o Alkaline KMnO4, heat
Acid hydrolysis of nitriles
o Dilute HCl, reflux
Alkali hydrolysis of nitriles
o Dilute NaOH, reflux, followed by acidify
7. Carboxylic acid derivatives
a. Reactions
Hydrolysis
o Ester
Dilute H2SO4, reflux
o Acyl chloride
Done by Nickolas Teo Jia Ming, CG 12/11
Water, room temperature
o Amide
Dilute HCl, reflux
React with alcohol/ phenol
o Acyl chloride
Room temperature
Reaction with NH3
o Ester
Concentrated alcoholic NH3
o Acyl chloride
Room temperature
Reduction
o Ester
LiAlH4, dissolved in dry ether at room
temperature
o Acyl chloride
LiAlH4, dissolved in dry ether at room
temperature
o Amide
LiAlH4, dissolved in dry ether at room
temperature
b. Formation
Acyl chloride
o Formation of acyl chloride by a halogen atom
Ester
o Esterification
Amide
o Acyl chloride, NH3/ RNH2/ R2NH, cold
8. Amine
a. Reactions
Alkylation of amine
o RX dissolved in ethanol in a sealed tube; Heat
Acylation of amine
o Acyl chloride; Cold
b. Formation
Reduction of nitriles
o LiAlH4, dry ether, room temperature
o H2(g) with Ni catalyst at 140oC
o Na and ethanol
Reduction of amides
o LiAlH4, dry ether, room temperature
o H2(g) with Ni catalyst at 140oC
o Na and ethanol
9. Phenylamine
a. Reactions
Alkylation of amine
o RX dissolved in ethanol in a sealed tube; Heat
Acylation of amine
o Acyl chloride; Cold
Halogenation
Done by Nickolas Teo Jia Ming, CG 12/11
o Br2 dissolved in CCl4
o Chlorine/ Bromine water at room temperature
b. Formation
Reduction of nitrobenzene
o Sn, concentrated HCl, reflux followed by addition of
NaOH (aq)
10. Halogenoalkane
a. Reactions
Nucleophilic substitution
o Alkaline hydrolysis
NaOH (aq); Reflux
KOH (aq); Reflux
o Formation of Nitrile
Alcoholic KCN; Reflux
o Formation of ether
Na in excess alcohol; Reflux
o Formation of ester
Silver(I) salt of carboxylic acid in alcohol; Reflux
o Formation of amine
Excess concentrated NH3 in alcohol; Reflux
Elimination
o Dehalogenation of halogenoalkane
Alcoholic KOH; Reflux
Alcoholic CH3O-Na+; Reflux
b. Formation
Free radical substitution of alkane
Halogenation of alcohols
Addition of halogen to alkene
Done by Nickolas Teo Jia Ming, CG 12/11
You might also like
- Organic Chem Reactions: 1. AlkanesDocument6 pagesOrganic Chem Reactions: 1. AlkanesFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Reactions GuideDocument6 pagesOrganic Chemistry Reactions GuideFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem ReactionsDocument7 pagesOrganic Chem ReactionsTeo Jia Ming NickolasNo ratings yet
- Organic Compound Identification ReactionsDocument3 pagesOrganic Compound Identification ReactionsFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Solutions for conversions in Organic ChemistryDocument1 pageSolutions for conversions in Organic ChemistryNIMISH MUTYAPUNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem Identification ReactionsDocument3 pagesOrganic Chem Identification ReactionsTeo Jia Ming NickolasNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions of Alkanes: Mechanism Reaction Reagent Condition Catalysts Product(s)Document9 pagesChemical Reactions of Alkanes: Mechanism Reaction Reagent Condition Catalysts Product(s)Sam LeeNo ratings yet
- Done By: Kaijie, Elias, Chenxi, Ashwini, Sahana, Kelly From 0901 and 0914 Compiled From 2007 and 2008 H2 Chemistry Prelim PapersDocument10 pagesDone By: Kaijie, Elias, Chenxi, Ashwini, Sahana, Kelly From 0901 and 0914 Compiled From 2007 and 2008 H2 Chemistry Prelim Papersdiejunqs sNo ratings yet
- Major organic reactions and their mechanismsDocument9 pagesMajor organic reactions and their mechanismsRajendra ThamerciNo ratings yet
- CIE AS Chemistry: 21.1 Organic SynthesisDocument17 pagesCIE AS Chemistry: 21.1 Organic SynthesisiceforgamingNo ratings yet
- 202004032240234952abha Carbonyl Compounds PDFDocument14 pages202004032240234952abha Carbonyl Compounds PDFSrikeshav BNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes: Short Notes Classification of Halogen DerivativeDocument7 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes: Short Notes Classification of Halogen DerivativeSriram LycanNo ratings yet
- Mod 4 Revision Guide 10 Synthetic RoutesDocument2 pagesMod 4 Revision Guide 10 Synthetic RoutesdufraiscNo ratings yet
- Organic SynthesisDocument1 pageOrganic Synthesiszozoxo0% (1)
- Reaction List v002Document5 pagesReaction List v002cecil3414No ratings yet
- 25 HydrogenDocument53 pages25 HydrogenAbdul MateenNo ratings yet
- Sumary Hydrocarbon AlkeneDocument2 pagesSumary Hydrocarbon AlkeneApple KWNo ratings yet
- Pdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument159 pagesPdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesOmkar Singh Shekhawat100% (2)
- Chapter 4Document10 pagesChapter 4Isabella EhizomohNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds: Aldehydes and KetonesDocument58 pagesCarbonyl Compounds: Aldehydes and KetonesNur Aliyah Abdul RazakNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonDocument25 pagesHydrocarbonSoham NagNo ratings yet
- Organic reactions and conditionsDocument3 pagesOrganic reactions and conditionsAvrinoxNo ratings yet
- 51 Reactions From PDFDocument5 pages51 Reactions From PDFAbhinandan Sinha33% (3)
- Hydrocarbons NotesDocument13 pagesHydrocarbons NotesShivansh Pundir100% (1)
- AldehydeandketoneDocument15 pagesAldehydeandketoneDj Arts Tarpaulin PrintingNo ratings yet
- Important Organic Chemistry Reactions - CopyDocument5 pagesImportant Organic Chemistry Reactions - CopyK VIKASNo ratings yet
- Organic-Chemistry (As Level)Document8 pagesOrganic-Chemistry (As Level)Pirate HunterNo ratings yet
- Named ReactionsDocument5 pagesNamed ReactionsJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Named Reaction Cheatsheet For Organic Chemistry by MeritnationDocument2 pagesNamed Reaction Cheatsheet For Organic Chemistry by Meritnationhanushvenkat6No ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons Formula SheetDocument27 pagesHydrocarbons Formula SheetADARSH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Organic Synthesis Notes (1)Document17 pagesOrganic Synthesis Notes (1)garwade72No ratings yet
- AS OrganicDocument10 pagesAS OrganicTahaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7-10 SM Theory Book 2 EM For 2022GRDocument19 pagesUnit 7-10 SM Theory Book 2 EM For 2022GRThilanka LiyanageNo ratings yet
- WaterDocument7 pagesWaterujwalsrivastava001No ratings yet
- Revision Notes On AlcoholsDocument13 pagesRevision Notes On AlcoholsMuredzwa MuzendaNo ratings yet
- NamereactionorganicDocument13 pagesNamereactionorganicdeykrishna654100% (1)
- Name of Reagent Conditions Uses Oxidising Agent, UsedDocument2 pagesName of Reagent Conditions Uses Oxidising Agent, UsedFsdhdf FbxhNo ratings yet
- Preparations and Reactions of AlkanesDocument25 pagesPreparations and Reactions of AlkanesCarlo ManguilNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-10: Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument6 pagesCBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-10: Haloalkanes and HaloarenesKrishna Moorthy RamaiahNo ratings yet
- JEE+Main+26+July+2022+,+Morning+Shift Chemistry+Document27 pagesJEE+Main+26+July+2022+,+Morning+Shift Chemistry+Nitesh Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Compounds DPP 02Document4 pagesAromatic Compounds DPP 02Rinku Arun JainNo ratings yet
- Organic ReactionsDocument4 pagesOrganic ReactionsRobbing_HoodNo ratings yet
- TEMA Alcoholes 2 PARTEDocument34 pagesTEMA Alcoholes 2 PARTEMaria Jose AramayoNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Chemistry Reactions MapDocument1 pageAromatic Chemistry Reactions MapElectrodeIrresistibleNo ratings yet
- Mapa Químico de Reacciones AromaticasDocument1 pageMapa Químico de Reacciones AromaticasSophiiaNathalyNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesDocument44 pagesReactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesGlen Mangali100% (4)
- Revision Notes On AlcoholsDocument15 pagesRevision Notes On AlcoholsSUSHMANo ratings yet
- Producing Hydrochloric AcidDocument5 pagesProducing Hydrochloric AcidAHMEDNo ratings yet
- 12th - Genral - Named Organic Reaction Sheet Class NotesDocument5 pages12th - Genral - Named Organic Reaction Sheet Class Notesaaravtrivedi313No ratings yet
- Aromatic functional group conversionsDocument1 pageAromatic functional group conversionsMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- Carbonates and bicarbonates reactions properties usesDocument3 pagesCarbonates and bicarbonates reactions properties usesMaulida CitrifoliaNo ratings yet
- Namedreactions H: Aloalkanesandhaloarenes 1Document11 pagesNamedreactions H: Aloalkanesandhaloarenes 1Vishant SinghNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Properties of Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers and EpoxidesDocument14 pagesPreparation and Properties of Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers and Epoxidesitsleochandu21No ratings yet
- Properties and Reactions of Alkanes (38 charactersDocument3 pagesProperties and Reactions of Alkanes (38 charactersidon'tgiveachogiwaNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds Aldehydes and KetonesDocument62 pagesCarbonyl Compounds Aldehydes and KetonesSubhabrata MabhaiNo ratings yet
- Practical Organic ChemistryDocument2 pagesPractical Organic ChemistryRaviNo ratings yet
- Alcohols ChemistryDocument24 pagesAlcohols ChemistryBritney PattersonNo ratings yet
- PPT Haloalkanes & Haloarenes ISC 23-24Document71 pagesPPT Haloalkanes & Haloarenes ISC 23-24jjprakash82chemNo ratings yet
- Annual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1971From EverandAnnual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1971John McMurryNo ratings yet
- The Reactivity SeriesDocument25 pagesThe Reactivity SeriesFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- The Reactivity SeriesDocument25 pagesThe Reactivity SeriesFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- StructureDocument22 pagesStructureFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Rates of ReactionDocument77 pagesRates of ReactionFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table 1Document7 pagesThe Periodic Table 1Fatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction 1Document14 pagesRate of Reaction 1Fatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table 1Document15 pagesThe Periodic Table 1Fatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- The Periodic TableDocument123 pagesThe Periodic TableFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry: Reactions of Group I & VII ElementsDocument107 pagesIGCSE Chemistry: Reactions of Group I & VII ElementsFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- StructureDocument11 pagesStructureFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Separating and AnalisingDocument44 pagesSeparating and AnalisingFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Separating and AnalisingDocument16 pagesSeparating and AnalisingFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction 1Document14 pagesRate of Reaction 1Fatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Rates of ReactionDocument77 pagesRates of ReactionFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- PolymerDocument89 pagesPolymerFatema Khatun100% (1)
- IGCSE polymer questionsDocument59 pagesIGCSE polymer questionsFatema Khatun0% (1)
- Oxygeen & Oxides 1Document11 pagesOxygeen & Oxides 1Fatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Rams & MolesDocument20 pagesRams & MolesFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - Ozone in the AtmosphereDocument87 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Ozone in the AtmosphereFatema Khatun100% (1)
- Oxygeen & Oxides 1Document23 pagesOxygeen & Oxides 1Fatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- MetalsDocument80 pagesMetalsFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- MetalsDocument80 pagesMetalsFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Chemicals 1Document8 pagesManufacturing Chemicals 1Fatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Oxygeen & Oxides 1Document11 pagesOxygeen & Oxides 1Fatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Nitrogenous Fertilisers Increase Crop YieldsDocument59 pagesNitrogenous Fertilisers Increase Crop YieldsFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory and DiffusionDocument42 pagesKinetic Theory and DiffusionFatema Khatun100% (1)
- Oxygeen & Oxides 1Document23 pagesOxygeen & Oxides 1Fatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Chemicals 1Document4 pagesManufacturing Chemicals 1Fatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Making SaltsDocument19 pagesMaking SaltsFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Making SaltsDocument24 pagesMaking SaltsFatema KhatunNo ratings yet