Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elec Reviewer
Uploaded by
Charles Marx Vargas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views5 pageselectronics 2 reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentelectronics 2 reviewer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views5 pagesElec Reviewer
Uploaded by
Charles Marx Vargaselectronics 2 reviewer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
//ELEC1 Minority carriers: holes
Net charge: Neutral
Electronics branch of science and Negative Temperature Coefficient as
engineering that deals with the study temperature increases, resistance
of the movement and behaviour of decreases
electrons and its application Depletion Region region of
Types of Elements uncovered positive and negative ions
Passive (RLC) not capable of Barrier Potential knee voltage of a
generating energy diode
Active capable of generating PN Junctions NPN, PNP
energy Diode Models (Forward Biased close
Types of Materials switch, Reversed Biased open
Insulator does not allow flow switch)
of current even under pressure Ideal diode model
- Consists of 8 valence Practice diode model (with
electrons (most) barrier potential)
Semiconductor characteristics Complex diode model (with
between insulator and internal resistance)
conductor Breakdown voltage voltage where
- Consists of 4 valence avalanche occurs
electrons Clippers diodes to clip away portion
Conductor allows generous
of input signal w/o distorting the
flow of current under pressure remaining parts
- Consists of 1-3 valence
Clampers diodes and capacitors that
electrons (least)
shifts input signal to a different level
Enery Gap distance between the
w/o changing its appearance
conduction bond and valence bond
Block Diagram of Power Supply
Semiconductor
Signal > Xformer > Rectifier >
Intrinsic made as pure as
Filter > Voltage Regulator > Load
possible Vpripp N 1
@ absolute zero temp (-273C) Xformer: =
Vsec N2
very good insulator
@ room temp (27C) vibration Rectifier: @ Half Wave =
occurs 0.318(Vsecp)
@ net charge: neutral @ Full Wave =
Extrinsic made pure by doping 0.636(Vsecp)
process (a process of adding Filter: Capacitor Filter, AC Filter
impurities to a pure Voltage Regulator: Load
semiconductor) Regulation, Line Regulation
@ P-type (BIG, boron-indium- Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)
gallium) trivalent/acceptor - Linear amplifier
atoms - Fast acting switch
Majority carriers: holes - Current driven device
Minority carriers: free Regions of operation
electrons 1. Linear/Active
Net charge: Neutral 2. Saturation
@ N-type (PAA, phosphorus- 3. Cut-off
antimony-arsenic) Terminal Configurations
pentavelent/donor atoms 1. Common Emitter (universal
Majority carriers: free amp)
electons 2. Common Base (voltage amp)
3. Common Collector (current (Op-Amps are voltage amplifier, BJTs
amp, impedance matching are current amplifier, FETs are
device) transconductance amplifer)
DC Biasing application of DC power a. Voltage amplifier
to establish a fixed level of current and b. Current amplifier
voltage to determine level of c. Transconductance amplifier
d. Transimpedance amplifier
amplification
Classes of Amplifiers
a. Fixed Bias
a. Class A amount of output signal
b. Emitter Stabilized
c. Voltage Divider (Exact, flow varies for a full 360 of the
Approximate) cycle
d. Voltage Feedback b. Class B amount of output signal is
e. Miscellaneous Configurations 180
Field Effect Transistor (FET) c. Class AB output signal flows for
- Linear amplifier more than 180 but less than 360
- Faster acting switch d. Class C output signal flows less
- Voltage driven device than 180
- Unipolar devices e. Class D
Types of FET f. Class S
Junction FET (JFET) Other Classification of Amplifiers
Metal Oxide Semiconductor FET a. Accdg to Frequency Amplified
- D-MOSFET - DC amplifier
- E-MOSFET - RF amplifier
- Video amplifier
Shockleys Equation: b. Accdg to Signal Amplified
- Small signal amplifier
2
Vgs - Large signal amplifer
(
Id=Idss 1
Vp ) c. Accdg to Coupling Method
- Resistive-coupled amplifier
- Inductive-coupled amplifier
Pinch-off conditions where Id = 0A - Direct-coupled amplifier
Quiescent Point point that will be Other Amplifier Circuit Configurations
employed for amplification of the a. Cascaded amplifier stages of
applied signal amplifiers connected in series
fashion
//ELEC2 b. Cascode amplifier
c. Darlington amplifier
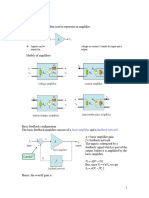
AMPLIFIERS an electronic circuit that is d. Differential amplifier
capable of increasing the signal amplitude e. Push-Pull amplifier two similar
w/o altering the signal waveform circuits operating in phase
characteristics opposition
f. Complementary-symmentry
Amplifier Classification amplifier
1. By Function g. Quasi-complementary amplifier
a. Voltage amplifier
b. Power amplifier OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
2. By Frequency Response
a. Audio amplifier 15Hz-20 KHz - One of the most versatile
b. RF amplifier (Radio Frequency) and widely used electronic
10K-100,000MHz device. Intended to perform
c. Video amplifier 10Hz-6MHz mathematical operation in
Types of Amplifiers analog computers
@ Open loop produces square - Large # of comparators
waveform (squaring circuit) provides fast conversion
@ Closed loop time
- (-) inverting, for control of of comparators=2n 1
gain
- (+) non-inverting, for Summing Amplifiers has two or more
reduction of noise inputs, and its output voltage is
Mode of Operations proportional to the negative of the
- Single Mode algebraic sum of the input voltages
- Common Mode (Noise) Digital-to-Analog Conversion (Scaling
- Differential Mode (Desired)
Adder Apllication)
Op-Amp Properties:
- An important interference
- Voltage between inverting
process for converting digital
and non-inverting is zero
signals to analog (linear)
making them equal
signals
- Current between inverting
and non-inverting is zero INTEGRATOR simulates mathematical
making them equal integration, basically a summing process that
determines the total area under the curve of
Design of Op-Amp Circuit
fuction
- Case 1: Rx is infinite (z is
positive) DIFFERENTIATOR simulates mathematical
- Case 2: Ry is infinite (z is differentiation, process of determining the
negative) instantaneous rate of change of a function
- Case 3: Rx and Ry is infinite
(z is zero) ACTIVE FILTERS
Z=xy1 - Uses transistors/op-amps combined
with passive RL,RC or RLC circuits
COMPARATORS - Active devices produce voltage gain,
passive circuits produce frequency
- Used to compare the
selectivity
amplitude of one voltage to
Filters circuits that are capable of
another passing signals w/ certain selected
a. Zero Level Detection determines
frequencies while rejecting signals w/
when an input voltage exceeds a other frequencies. This property is
certain level called selectivity.
b. Non-Zero Level Detection detects Categories of Active Filters (Basic Filter
voltages other than zero Response)
Hysteresis circuit at the positive Low Pass Fiter Response
feedback for noise reduction - Pass Band ( 0 Hz up to critical
Schmitt Trigger comparator with frequency, fc)
hysteresis - Output voltage is 70.7% of pass band
Output Bounding process of limiting voltage
the output range High Pass Filter Response
Analog-to-Digital Conversion - Attenuates all frequencies below fc
and passes all frequencies above fc.
(Comparator Application)
Band Pass Filter Response
- Common interfacing process
- Passes all signals between lower and
often used when a linear
upper frequencies, and rejects all
analog system must provide
other frequencies that are outside the
inputs to a digital system is specified band.
A/D conversion
- Center frequency pass band is - Widely used in most communication
centered, fo systems
fo= fc 1 fc 2 - Based on principle of positive
feedback (portion of output voltage id
- Quality Factor an indication of the fed back to the input w/o phase shift,
selectivity of a band pass filter. resulting in a reinforcement of output
o Higher Q, narrower BW, better signal)
selectivity
o BPF are narrowband (Q>10) or Conditions for oscillations
wide-band (Q<10) - Phase shift around feedback loop must
fo 1 be 0 degrees.
Q= or
Q=
BW DF - Voltage gain around closed feedback
loop must equal to 1 (unity)
where DF= dampling factor
Band Stop Filter Response Oscillators with RC feedback circuits
- Also known notch, band-reject, band- (frequency up to 1MHz)
elimination 1 Wien-bridge oscillator (most widely
- Opposite of band pass filter, as used)
frequencies between certain 2 Phase-shift oscillator
bandwidth are rejected and outside 3 Twin-T oscillator
bandwidth are passed.
Butterworth Characteristics Oscillators with LC feedback circuits
- Provides very flat amplitude in pass (higher frequency)
band 1 Colpitts (BJT as the gain element)
- Roll-off rate of 20 dB/decade/pole 2 Clapp
- Used when frequency in the pass band 3 Hartley
must have same gain 4 Armstrong
- Referred as maximally flat response 5 Crystal-Controlled (most stable and
accurate type that uses
Chebyshev Characteristics piezoelectric crystal in the
- Roll-off rate greater than feedback loop to control frequency)
20dB/decade/pole
- Characterized by overshoot/ripple in
the pass band(depending on # of
poles) Non-sinusoidal Oscillator
- Less linear phase response than 1 Triangular wave oscillator uses
butterworth dual-polarity switched input
Bessel Characteristics 2 Square wave relaxation oscillator
- Exhibits linear phase characteristics, its operation is based on the
meaning phase shift increases linearly charging/discharging of a capacitor
with frequency.
- No overshoot on the output w/ a pulse
input DIGITAL TIMER/CONTROL CIRCUITS
- Used for altering pulse waveform w/o
distorting the shape of waveform. - Timing (everything in digital circuits)
- Clock oscillator (generates square
OSCILLATORS wave clock signal)
- Circuits that generate output signal 1 Astable Multivibrator
w/o an input signal - Commonly used as clock oscillator
- Used as signal sources - Used to produce an alternating two-
- Produces types of outputs/repetitive state square or rectangular output
waveforms (sine, square, triangular, waveform
sawtooth wave)
- Called as free-running multivibrator,
because it requires no input signal to 3 Bistable multivibrator
start its operation. - A digital control device that can either
set or reset
2 Monostable Multivibrator - Two-stable state
- When triggered, will generate a - Two inputs, set and reset
rectangular pulse of a fixed duration. - A pulse on the set input will flip the
- One-stable state circuit into set state, while a pulse on
- Will remain in stable state indefinitely the reset input will flop the circuit
until a trigger is applied and forces it into its reset state.
into its unstable state
- Called as one-shot multivibrator
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Documentary ReviewDocument2 pagesDocumentary ReviewCharles Marx VargasNo ratings yet
- DreamDocument2 pagesDreamCharles Marx VargasNo ratings yet
- Diocese of Cubao Liturgical Affairs Ministry: 41 Lantana Street, Cubao, Quezon City, 1109, Metro ManilaDocument1 pageDiocese of Cubao Liturgical Affairs Ministry: 41 Lantana Street, Cubao, Quezon City, 1109, Metro ManilaCharles Marx VargasNo ratings yet
- Act 3Document2 pagesAct 3Charles Marx VargasNo ratings yet
- Mateo, Joshua Philip C. 20130200838Document3 pagesMateo, Joshua Philip C. 20130200838Charles Marx VargasNo ratings yet
- BienDocument9 pagesBienCharles Marx VargasNo ratings yet
- Procedure A: 2Document3 pagesProcedure A: 2Charles Marx VargasNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Design of 8 Bit Alu Using Microwind 3.1Document6 pagesDesign of 8 Bit Alu Using Microwind 3.1ijaert100% (1)
- BJT Circuit Analysis: CollectorDocument5 pagesBJT Circuit Analysis: CollectorHarithZakariaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Feedback AmplifiersDocument5 pagesLecture 7 Feedback AmplifiersengmsaudanNo ratings yet
- Microelectronics Journal: Ali Nejati, Sara Radfar, Parviz Amiri, Mohammad Hossein MaghamiDocument12 pagesMicroelectronics Journal: Ali Nejati, Sara Radfar, Parviz Amiri, Mohammad Hossein MaghamiReza RezaNo ratings yet
- Clipper & ClamperDocument7 pagesClipper & ClamperARUN100% (1)
- RFIC Design and Testing For Wireless CommunicationsDocument17 pagesRFIC Design and Testing For Wireless CommunicationsPraveen Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- General Purpose Type Photocoupler: (Unit: MM)Document5 pagesGeneral Purpose Type Photocoupler: (Unit: MM)Narendra Bhole100% (1)
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityJMehtNo ratings yet
- Mini Bench PSU (Elektor)Document2 pagesMini Bench PSU (Elektor)dardosordiNo ratings yet
- ECA FinalDocument4 pagesECA Final143ramyaNo ratings yet
- Ler para CCIDocument114 pagesLer para CCIjonas1446No ratings yet
- Psoc Range FinderDocument3 pagesPsoc Range FinderHelloprojectNo ratings yet
- Sop For MSDocument2 pagesSop For MSSaiGoutham SunkaraNo ratings yet
- Ed & I Lab 18ecl37 ManualDocument29 pagesEd & I Lab 18ecl37 Manualcharan mNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: ANA Log Ic Design LabDocument14 pagesLab Report: ANA Log Ic Design LabNitishNo ratings yet
- MOSFETDocument23 pagesMOSFETRahulKushwahaNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 Requires Respondus LockDown Browser PDFDocument6 pagesExam 2 Requires Respondus LockDown Browser PDFMeryam BakkarNo ratings yet
- TLC 7225Document21 pagesTLC 7225tajpan77No ratings yet
- BI Technologies R2R Resistor Ladder NetworksDocument6 pagesBI Technologies R2R Resistor Ladder NetworksRianKunNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Slides 6Document9 pagesCH 2 Slides 6QuynhNhu TranNo ratings yet
- Multiplexer 4 Inputs and Test BenchDocument7 pagesMultiplexer 4 Inputs and Test BenchsagarNo ratings yet
- Differentiator and IntegratorDocument5 pagesDifferentiator and Integratorvinit.vermaNo ratings yet
- 74HC/HCT11 Triple 3-Input AND Gate DatasheetDocument5 pages74HC/HCT11 Triple 3-Input AND Gate DatasheetNICOLAS STEVEN AVENDA�O RAMOSNo ratings yet
- RF and Radio Engineering Interview QuestionsDocument1 pageRF and Radio Engineering Interview Questionskrisravi9No ratings yet
- ST - Anne'S College of Engineering and Technology: (For Ii B.E Electronics and Communication Engineering)Document20 pagesST - Anne'S College of Engineering and Technology: (For Ii B.E Electronics and Communication Engineering)shankarNo ratings yet
- Principles & ApplicationsDocument37 pagesPrinciples & Applicationsdhea aftariNo ratings yet
- Silicon NPN Power Transistors: Inchange Semiconductor Product SpecificationDocument4 pagesSilicon NPN Power Transistors: Inchange Semiconductor Product SpecificationDjalma MotaNo ratings yet
- A.C. Network Anaylsis: Learning ObjectivesDocument28 pagesA.C. Network Anaylsis: Learning ObjectivesDio Ilham Tirta AdiNo ratings yet
- MM74C926Document9 pagesMM74C926Marco NochebuenaNo ratings yet