Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment 12 (Synthesis of Acetylsalicylic Acid)
Uploaded by
Cheng BauzonCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment 12 (Synthesis of Acetylsalicylic Acid)
Uploaded by
Cheng BauzonCopyright:
Available Formats
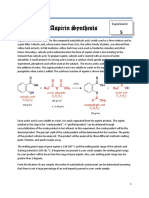
SYNTHESIS OF ACETYLSALICYLIC ACID (ASPIRIN)
Adolfo, Angela Nicole G., Alcaraz Frances Jillian F., Aliman, Stephanie T., Astor, Jashmin D.,
Bauzon, Franchesca D., Cabral, Danica Rose G.
Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Pharmacy
University of Santo Tomas
ABSTRACT
Acetylsalicylic acid, or commonly known as Aspirin, is one of the most widely used drugs
to reduce fever. It is under the drug classification of a Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug or
NSAID in short, Anticoagulant, Antiplatelet, Non-Opioid Analgesic, Antipyretic & Fibrinolytic
(Thrombolytic). Aspirin is formed through the combination of salicylic acid and acetic anhydride.
Both salicylic acid and acetic anhydride are mixed to create a crude product. In this experiment
Aspirin was studied of how it was produced and how the product would react to different reagents.
A commercial aspirin went through a procedure producing a synthesized aspirin, making up
different results from the reactants and products seeing the differences of the results from each.
INTRODUCTION
Acetylsalicylic Acid commonly known
as Aspirin is among the most widely used
medicine. Aspirin is also among the oldest. It
has the ability to reduce swelling, redness,
and soreness, it also acts as an analgesic to
reduce pain. The synthesis of aspirin is
acquired from salicylic acid which can be
extracted in willow trees. The boiling point of
Structural Formula of Aspirin
salicylic acid is 211C, a melting point of
(Acetylsalicylic Acid)
159C and a density of 1.44 g/mol.
Acetic anhydride is an organic
compound also known as a type of acetic
Crystallization refers to the formation
anhydride. The molecular formula for acetic
of solid crystals from a homogeneous
anhydride is C4H6O3. The synthesis of acetic
solution. It is one of the most used purifying
anhydride is quite simple as long as you
methods inorganic experiments. The
remember the term 'carboxylic acid.' A
substance to be purified is dependent to its
carboxylic acid is a functional group whose
solubility in change of temperature whether
molecular formula is defined as RCOOH.
in a hot or cold solvent. It is the main factor
Acetic anhydride is useful as a building block
that affects crystallization. The substance to
for other chemicals, such as the household
be crystallized should show the ideal
staple item vinegar. This usefulness also
solubility. It is essentially a solid-liquid
carries into the pharmaceutical industry.
separation technique and a very important
Acetic anhydride is used to make aspirin. As
one at that. Organic compounds that are
we see in the equation below, when acetic
solid in room temperature are usually purified
anhydride reacts with salicylic acid, aspirin is
by crystallization. The desired substance will
produced.
crystallize on cooling, but the impurities will
not. The objectives of experiment are the
following: (1) to explore the chemical process
in the synthesis of aspirin; (2) to be able to
calculate for the percentage yield of the
synthesized aspirin.
Structural Formula of Acetic Anhydride
METHODOLOGY
The materials needed for this experiment
are test tubes, beakers, glass rod, iron
ring/tripod, plastic wash bottle, Bunsen
burner, clamp, pipette, and watch glass. The
samples and reagents needed are salicylic
acid, acetic anhydride, conc. H2SO4,
Formation of Acetylsalicylic Acid commercial aspirin, benzoic acid, benzyl
alcohol, 2& FeCl3, iodine solution, and mL of ice-cold water to the beaker, stir
methyl alcohol. then pack the beaker in ice for 10
minutes for the aspirin to crystallize. Filter
A. Reaction of Acetic Anhydride and
the crystals using filter paper and allow to
Salicylic Acid
dry overnight, then measure the weight of
Get exactly 2.00g of salicylic acid
dried aspirin and compute for percentage
and place it in a clean, dry 20-cm test
yield.
tube. Place exactly 5.00 mL of acetic
anhydride and 5 drops of conc. H2SO4
B. Ferric Chloride Test for Salicylic Acid
into the same test tube. Stir it until the
In a 6 clean 10-cm test tubes,
salicylic acid dissolves.
place 1 mL of water each. Put a crystal of
Prepare the set-up for the
salicylic acid in the first test tube,
preparation of aspirin by bringing a 250-
powdered commercial aspirin in the
mL beaker three-fourths full of tap water
second test tube, synthesized aspirin in
to a boil; support it in a ring stand. Fill the
the third, benzoic acid in the fourth, 1 mL
wash bottle with distilled water and pack
of benzyl alcohol in the fifth, and dont
it in ice contained in a large beaker. Once
add anything in the last test tube because
the water begins to boil, turn the burner
it will serve as the control. Shake the test
off and place the test tube in a water bath;
tubes to dissolve the solid and place 2
stir well for 1 minute.
drops of 2% ferric chloride. Observe the
Let the reaction mixture to remain
color changes.
in the water bath for 20-30 minutes.
Remove the test tube from the water
C. Starch Test
bath, then cautiously pour the contents
In a three 10-cm test tubes, place
into 5 mL of water in a 150-mL beaker.
2 mL of water each. Put a small amount
Stir for 1 minute once the reaction in the
of synthesized aspirin in the first test
beaker subsides. Slowly add water until
tube, powdered commercial aspirin in the
a maximum of 40 drops until the solution
second, and dont add anything in the
becomes cloudy. If the solution returns to
third because this will serve as the
being clear, continue to add water.
control. Add 1 drop of iodine solution to
Rinse the test tube with ice-cold
each test tube. The presence of starch
water once the crystals of aspirin appear
will be indicated by blue or blue-black
in the beaker, adding the rinse to the
color change.
solution in the 150-mL beaker. Place 20
D. Preparation of Methyl Salicylate Table 1 - Reaction of Acetic Anhydride and
Place exactly 1.00g of salicylic Salicylic Acid
acid in a 20-cm test tube. Place 5 mL of
methyl alcohol and 3 drops of conc.
H2SO4 in the same test tube. Stir to
dissolve the salicylic acid in the alcohol.
Place it in a water bath for 15 minutes. A
mint aroma will indicate the presence of
methyl salicylate.
The formation of Acetylsalicylic Acid
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION is seen through the figure (Figure 1) below,
The experiment performed has 4 which went through a reaction of Salicylic
portions of experiments performed. First of is Acid and Acetic Anhydride. Also forming
the Reaction of Acetic Anhydride and Acetic Acid along with ASA or Aspirin.
Salicylic Acid which was performed/finished
the longest, wherein the second objective
would be accomplished. Then there is
theres the Ferric Chloride Test for Salicylic
Acid, Starch Test, and lastly Preparation of
Methyl Salicylate where the first objective will
take part. For the results of the first part of
the experiment the group was instructed to Figure 1. Formation of Acetylsalicylic Acid
collect 1g of Salicylic Acid. And to collect the
right or exact amount, they used a watch
glassed. Firstly, they calibrated the watch Limiting Reagent: Salicylic Acid (C7H6O3)
glass (93g) and they weighed an addition of
1g (94g) to achieve the specified amount.
After that the members collected 5mL of
Acetic Anhydride and 5 drops of conc. H2SO4
(Sulfuric Acid) with caution. Through these
they have collected the reagents they
needed to use for the experiment.
Acetic Anhydride:
Salicylic Acid:
Theoretical Yield:
Figure 2. Reaction of Acetic Anhydride
with Alicylic Acid
Percentage Yield: In the second portion of the
experiment, six chosen samples were
tested. And out of all the samples only three
had a reaction with Ferric Chloride. And
those are Salicylic Acid, Commercial Aspirin,
and Synthesized Aspirin. In conclusion that
Ferric Chloride has a rapid reaction with
In this part of the experiment, the Salicylic Acid knowing that all three consists
members witnessed the synthesize of of the reagent. And comparing from the
aspirin, wherein the percentage yield was results (seen from Table 2) Salicylic gave a
obtained from. Coming from the calculations more rapid reaction with Ferric Chloride
(seen above) the amount of acetic anhydride regarding the value or hue of the three
and salicylic acid used was calculated samples. As for the other samples they gave
through Stoichiometric calculations. There no reaction, as they maintained a colorless
we obtained the limiting reagent. And then reaction.
computed for the limiting reagent.
Table 2 Ferric Chloride Test for Salicylic In the third part of the experiment the
Acid Starch Test was performed. Wherein only
Commercial Aspirin was the only sample to
give a reaction with iodine solution, creating
a dark-green solution as seen from the
results from Table 3.
Table 3 Starch Test
As seen from Figure 3 (below) only 5
samples were immediately observed,
And as seen from Figure 4 the
because of the reason that the Synthesized
Synthesized Aspirin sample was still not
Aspirin was still being done by the other
tested. But later on gave a colorless solution
members. The experiment was completely
as a result. And as seen from the figure,
achieved in the second meeting.
Commercial Aspirin still had a light hue for
the color green. But after standing, the
sample gave a dark-green solution
Figure 4. Starch Test (without Synthesized
Figure 3. Ferric Chloride Test for Salicylic
Aspirin)
Acid (without Synthesized Aspirin)
The last portion of the experiment thus eliminated. Recrystallization removed
performed was Preparation of Methyl impurities from the formed aspirin, which
Salicylate which should give a minty aroma involved salicylic acid. To test for purity, a
to say that the experiment was a success. number of tests were conducted. One of
And from the given results, the sample did which was the ferric chloride test. A complex
give a efficacent oli-like smell or a minty with an intense violet color is formed when
aroma. But after a few moments, the smell ferric chloride is added to salicylic acid.
could not be much perceived anymore as it When ferric chloride is added to pure aspirin
was in the first moment when it was however, no reaction will occur. Another test
accomplished. is the starch test, which is used to detect the
presence of starch in the samples: prepared
aspirin, commercially available aspirin, and
control. Commercially available aspirin
should react to the iodine solution (it should
turn blue-violet or purple) because most
pharmaceutical companies add starch to
their products for aesthetic appeal.
Methyl salicylate, commonly known as oil of
wintergreen, is another ester of salicylic acid.
It is synthesized in a manner similar to
aspirin, but at a lower temperature. Similar to
aspirin, it also contains compounds that have
analgesic and antipyretic properties. It was
Figure 5. Preparation of Methyl Salicylate first isolated in 1843 by extraction from a
plant (Gaultheria spp.) which is in the mint
family, which explains the characteristic
CONCLUSION minty odor of methyl salicylate.
In the experiment, aspirin was prepared
from the chemical reaction of salicylic acid
and acetic anhydride. Upon the addition of
cold water, acetic acid was formed and was
REFERENCES
Website:
The Synthesis of Organic Aspirin. (2008,
February 28). Retrieved from
http://www.studymode.com/essays/Lab-
Report-Synthesis-Organic-Aspirin-First-
Year-Chemistry-65188753.html
Acetic anhydride. (2015, May 15). Retrieved
from
http://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?ID=C
108247&Mask=8
Books:
Bathan, G.I., Bayquen, A.V., Crisostomo,
A.B.C., Cruz, C.T., de Guia, R.M., Farrow,
F.L., Pea G.T., Sarile, A.S., Torres, P.C..
(2014). Laboratory Manual in Organic
Chemistry Revised Edition. Quezon City,
Manila: C & E Publishing, Inc.
You might also like
- Synthesis of Aspirin (2EMT - Group 1, 2009)Document8 pagesSynthesis of Aspirin (2EMT - Group 1, 2009)Mary Christelle90% (10)
- Synthesis of Aspirin-Formal ReportDocument6 pagesSynthesis of Aspirin-Formal ReportStephanie ButedNo ratings yet
- Formal Report Synthesis of AspirinDocument4 pagesFormal Report Synthesis of AspirinEdrick Ramoran0% (1)
- Aspirin SythesisDocument4 pagesAspirin Sythesiskramnuj92% (12)
- Synthesis of Aspirin From Salicylic Acid and Acetic AnhydrideDocument6 pagesSynthesis of Aspirin From Salicylic Acid and Acetic AnhydrideChristine71% (7)
- Classification Tests For Carboxylic Acids and Their DerivativesDocument9 pagesClassification Tests For Carboxylic Acids and Their DerivativesAngelyka Cabalo100% (1)
- Synthesis of Aspirin and Oil of WintergreenDocument5 pagesSynthesis of Aspirin and Oil of WintergreenJason Raquin Roque100% (4)
- Experiment 9 Formal Laboratory ReportDocument5 pagesExperiment 9 Formal Laboratory ReportNathaniel Argelio Dimaano100% (1)
- Classification Tests For Organic Halides Formal ReportDocument4 pagesClassification Tests For Organic Halides Formal ReportJessa Mateum VallangcaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Aspirin Lab ReportDocument12 pagesSynthesis of Aspirin Lab ReportJasmeetSingh63% (8)
- Nitration of Methyl BenzoateDocument7 pagesNitration of Methyl BenzoateJanel Pauline G. Chua100% (1)
- Synthesis of Acetanilide and Its Purification Through RecrystallizationDocument4 pagesSynthesis of Acetanilide and Its Purification Through RecrystallizationTeresa Saylo100% (1)
- AcetanilideDocument7 pagesAcetanilideepsonme101No ratings yet
- Synthesis of Aspirin LabDocument5 pagesSynthesis of Aspirin LabSisilia Devi NNo ratings yet
- Classification Tests For Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDocument5 pagesClassification Tests For Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesMaggie Quinto100% (6)
- Experiment 9 Classification Tests For Hydroxyl - & Carbonyl-Containing CompoundsDocument8 pagesExperiment 9 Classification Tests For Hydroxyl - & Carbonyl-Containing CompoundsPatricia Isabel Tayag100% (7)
- Classification Tests For Organic HalidesDocument3 pagesClassification Tests For Organic HalidesRhone Roque100% (6)
- Recrystallization of Acetanilide (2EMT - Group 1, 2009)Document7 pagesRecrystallization of Acetanilide (2EMT - Group 1, 2009)Mary Christelle100% (2)
- Lab Report 5 Protein Solubility and PHDocument3 pagesLab Report 5 Protein Solubility and PHDan Floyd FernandezNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology Laboratory Worksheet UST - Faculty of PharmacyDocument3 pagesPharmaceutical Microbiology Laboratory Worksheet UST - Faculty of PharmacyPRINCESS JULIENNE YUNo ratings yet
- The Synthesis of AspirinDocument4 pagesThe Synthesis of AspirinMarieya Elizabeth ZantuaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8 - Classification Tests For Organic HalidesDocument6 pagesExperiment 8 - Classification Tests For Organic HalidesNICOLE GEA DIVINASFLORESNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Aspirin Results and DiscussionDocument9 pagesSynthesis of Aspirin Results and DiscussionGellie Dela Rosa Valencia33% (3)
- Syntheses of Soap and DetergentDocument3 pagesSyntheses of Soap and DetergentAnghel Santos DimaandalNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of AcetanilideDocument4 pagesSynthesis of AcetanilideMich Tolentino50% (2)
- Synthesis of AspirinDocument4 pagesSynthesis of Aspirinホアキン 印33% (3)
- Acyl Compunds: Soaps and DetergentsDocument4 pagesAcyl Compunds: Soaps and DetergentsLucile BronzalNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Salicylic AcidDocument2 pagesSynthesis of Salicylic AcidHarly Kabut100% (1)
- Formal Report, Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDocument4 pagesFormal Report, Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesVicente Romeo M Macatangay88% (8)
- MODULE 6 Alkalimetric AnalysisDocument16 pagesMODULE 6 Alkalimetric AnalysisMrl AshiaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Reactions of Carboxylic Acid DerivativesDocument5 pagesComparative Reactions of Carboxylic Acid DerivativesMark Manalang SerranoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 PH Measurement and Buffer PreparationDocument5 pagesExperiment 1 PH Measurement and Buffer PreparationAnonymouscatNo ratings yet
- Classification Tests For Hydroxyl - and Carbonyl - Containing CompoundsDocument6 pagesClassification Tests For Hydroxyl - and Carbonyl - Containing CompoundsShaira Jhann L. Rosales50% (2)
- Full Report: Synthesis of AspirinDocument3 pagesFull Report: Synthesis of AspirinNor Ashikin IsmailNo ratings yet
- Chem 9Document4 pagesChem 9Emmanuel PlazaNo ratings yet
- Separation and Identification of Amino Acids by Paper ChromatographyDocument4 pagesSeparation and Identification of Amino Acids by Paper Chromatographyroxannediana86% (14)
- Experiment 9 Formal Report On Classification Test of Hydroxyl-Containing and Carbonyl-Containing Organic CompoundsDocument16 pagesExperiment 9 Formal Report On Classification Test of Hydroxyl-Containing and Carbonyl-Containing Organic CompoundsLuisGabito100% (1)
- Experiment 9Document6 pagesExperiment 9clairedemotica100% (1)
- Formal Report-Proteins and Amino AcidsDocument10 pagesFormal Report-Proteins and Amino AcidsQuenieMarielIlar100% (1)
- Biochem Laboratory MidtermDocument15 pagesBiochem Laboratory MidtermNica DonioNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Synthesis of AspirinDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Synthesis of AspirinClarissa Macanas100% (1)
- Experiment 8 - The Preparation of AcetanlideDocument12 pagesExperiment 8 - The Preparation of AcetanlideMark Ryan Tripole92% (13)
- Classification Tests For Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDocument3 pagesClassification Tests For Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesJohn Emmanuel SyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 - General and Specific Tests For CarbohydratesDocument18 pagesExperiment 5 - General and Specific Tests For CarbohydratesArthur Lorenz Paraguison100% (1)
- Solubility of Organic CompoundsDocument4 pagesSolubility of Organic CompoundsJeremy Noceda100% (1)
- Experiment 8 Classification of Organic Halides Formal ReportDocument5 pagesExperiment 8 Classification of Organic Halides Formal ReportRoxine Florentino56% (9)
- Activity No.5: Notre Dame of Dadiangas UniversityDocument10 pagesActivity No.5: Notre Dame of Dadiangas Universitydenshang 10No ratings yet
- Classification Tests For Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDocument4 pagesClassification Tests For Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesAJ Pasciolco50% (2)
- Experiment No.7 Potassium AcetateDocument2 pagesExperiment No.7 Potassium AcetateBlazy InhumangNo ratings yet
- Experiment 13 (Syntheses of Soap and Detergent)Document5 pagesExperiment 13 (Syntheses of Soap and Detergent)Cheng Bauzon100% (1)
- 123Document4 pages123JC Cayanan0% (1)
- Activity 12 Group 69Document4 pagesActivity 12 Group 69Abdulrahman Amlih0% (1)
- Classification Tests For Hydroxyl and Carbonyl Containing CompoundsDocument5 pagesClassification Tests For Hydroxyl and Carbonyl Containing CompoundsAcener Padua100% (1)
- Quantitative Analysis of Acetylsalicylic Acid in Aspirin Tablets by Back-TitrationDocument2 pagesQuantitative Analysis of Acetylsalicylic Acid in Aspirin Tablets by Back-TitrationSheenly Anne SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of AspirinDocument8 pagesSynthesis of AspirinwishingdustNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6: Synthesis of AspirinDocument8 pagesExperiment 6: Synthesis of AspirinMicahNo ratings yet
- Exp 5 - AspirinF11-1Document5 pagesExp 5 - AspirinF11-1Mesfen MeleseNo ratings yet
- Exp 5 - Aspirinf11Document5 pagesExp 5 - Aspirinf11alhattab tempNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Acetylsalicylic AcidDocument7 pagesSynthesis of Acetylsalicylic Acidjeniccax17No ratings yet
- Orgchem Formal ReportDocument6 pagesOrgchem Formal ReportKATHLEEN CALALANGNo ratings yet
- Toxic o KineticsDocument35 pagesToxic o KineticsCheng BauzonNo ratings yet
- Exp 4 BauzonDocument3 pagesExp 4 BauzonCheng BauzonNo ratings yet
- PHISTCONS (1st Shifting Reviewer)Document5 pagesPHISTCONS (1st Shifting Reviewer)Cheng BauzonNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument9 pagesIlovepdf MergedCheng BauzonNo ratings yet
- Pharma 7 ImmunoDocument48 pagesPharma 7 ImmunoCheng BauzonNo ratings yet
- Phil Lit Batch 3Document7 pagesPhil Lit Batch 3Cheng BauzonNo ratings yet
- Phil Lit Batch 2Document10 pagesPhil Lit Batch 2Cheng BauzonNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1. Results and Discussion (Phys 201)Document3 pagesExperiment 1. Results and Discussion (Phys 201)Cheng BauzonNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document5 pagesExperiment 1Cheng BauzonNo ratings yet
- Experiment 13 (Syntheses of Soap and Detergent)Document5 pagesExperiment 13 (Syntheses of Soap and Detergent)Cheng Bauzon100% (1)
- Abstract - Density, Is The Mass of Unit Volume of A Substance, An Absolute Value Independent of The Gravitating ForceDocument1 pageAbstract - Density, Is The Mass of Unit Volume of A Substance, An Absolute Value Independent of The Gravitating ForceCheng BauzonNo ratings yet
- p6 Abstract (Exp3)Document1 pagep6 Abstract (Exp3)Cheng BauzonNo ratings yet
- Conclusion ReferenceDocument1 pageConclusion ReferenceCheng Bauzon0% (1)
- Phar 5 Lab Activity 1 (Reviewer)Document5 pagesPhar 5 Lab Activity 1 (Reviewer)Cheng BauzonNo ratings yet
- Theology Assignment 110716 (Bauzon)Document2 pagesTheology Assignment 110716 (Bauzon)Cheng BauzonNo ratings yet
- Cathartic Article CH Go MedDocument4 pagesCathartic Article CH Go MedCheng BauzonNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 (Simple and Fractional Distillation)Document6 pagesExperiment 1 (Simple and Fractional Distillation)Cheng BauzonNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 (Chromatography)Document7 pagesExperiment 5 (Chromatography)Cheng Bauzon100% (1)
- Experiment 3 (Sublimation and Melting Point Determination)Document13 pagesExperiment 3 (Sublimation and Melting Point Determination)Cheng BauzonNo ratings yet
- Revised Mod2 With Cover UpdateDocument19 pagesRevised Mod2 With Cover UpdateJerome Rivera CastroNo ratings yet
- Exp 4 Formal ReportDocument3 pagesExp 4 Formal ReportCheng BauzonNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Defect of TabetsDocument7 pagesManufacturing Defect of TabetsDhirendra KumarNo ratings yet
- CNS&PNSDocument62 pagesCNS&PNSVincent ManganaanNo ratings yet
- Paper Chromatography Formal Report ORG ChemDocument5 pagesPaper Chromatography Formal Report ORG ChemCheng BauzonNo ratings yet
- PsychologyDocument27 pagesPsychologyCheng BauzonNo ratings yet
- Exp1 Simple and Fractional DistillationDocument12 pagesExp1 Simple and Fractional DistillationCheng BauzonNo ratings yet
- Paper Chromatography Formal Report ORG ChemDocument5 pagesPaper Chromatography Formal Report ORG ChemCheng BauzonNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems (An Overview) PDFDocument9 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery Systems (An Overview) PDFCheng BauzonNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems (An Overview) PDFDocument9 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery Systems (An Overview) PDFCheng BauzonNo ratings yet
- PHE971 SGP EngDocument12 pagesPHE971 SGP EngAndreiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Real GasesDocument10 pagesChapter 8 - Real Gasescarleston thurgoodNo ratings yet
- Tunnelling Topic 3Document23 pagesTunnelling Topic 3MMM-2012No ratings yet
- An Intelligent Feedback Controller Design For EnerDocument8 pagesAn Intelligent Feedback Controller Design For EnerJocian VefNo ratings yet
- Light Metals 2012Document5 pagesLight Metals 2012Sinan YıldızNo ratings yet
- A Consistent World Model For Consciousness and PhysicsDocument12 pagesA Consistent World Model For Consciousness and PhysicsGeorge PetreNo ratings yet
- Microspectroscopic Analysis of Traditional Oil Paint: Jaap Van Der WeerdDocument193 pagesMicrospectroscopic Analysis of Traditional Oil Paint: Jaap Van Der WeerdAndra Ch123No ratings yet
- Worksheet 4 Vertical MotionDocument1 pageWorksheet 4 Vertical MotionCJ BonitaNo ratings yet
- Rme Pec Module 3 - Sept 2015Document2 pagesRme Pec Module 3 - Sept 2015Bianca SañezNo ratings yet
- Extraction, Isolation, Purification and Identification CurcuminDocument16 pagesExtraction, Isolation, Purification and Identification CurcuminRaisyIkrimahNo ratings yet
- Original PDF An Introduction To Medicinal Chemistry 6th by Graham Patrick PDFDocument51 pagesOriginal PDF An Introduction To Medicinal Chemistry 6th by Graham Patrick PDFkathleen.jones449100% (33)
- EST Emergency Scrubber Products1Document32 pagesEST Emergency Scrubber Products1ca_perez75No ratings yet
- Oil & Gas Industry Waste Management: Prof. Dr. Mamdouh F. Abdel-SabourDocument28 pagesOil & Gas Industry Waste Management: Prof. Dr. Mamdouh F. Abdel-SabourKawooya AloysiusNo ratings yet
- Slip Agents Extended Performance Range For Polyolefin FilmsDocument2 pagesSlip Agents Extended Performance Range For Polyolefin Filmsanti blocking additiveNo ratings yet
- Momentum and Impulse-Egg DropDocument8 pagesMomentum and Impulse-Egg Dropapi-317253969No ratings yet
- Journal 2.2.5Document2 pagesJournal 2.2.5Estella Reyes0% (1)
- Geologic HazardsDocument26 pagesGeologic HazardsTrisha May Flores67% (9)
- Assignment 7 - Wastewater TreatmentDocument2 pagesAssignment 7 - Wastewater TreatmentJohn Feil JimenezNo ratings yet
- Leakfinder Wv622nvwkitDocument20 pagesLeakfinder Wv622nvwkitPaul ZiddyNo ratings yet
- Determination of Radionuclide Content in Agricultural Lands Using ResRad Off-Site Computer Model in Nasarawa State, NigeriaDocument10 pagesDetermination of Radionuclide Content in Agricultural Lands Using ResRad Off-Site Computer Model in Nasarawa State, NigeriaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Blending - IBCDocument2 pagesBlending - IBCRoyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Particle PhysicsDocument101 pagesIntroduction To Particle PhysicsДарко Симић100% (6)
- MEC126 - COMBUSTION - List 3 / Reactors: 1 Problem 6.12 (Turns, 2013) - Fixed Volume ReactorDocument17 pagesMEC126 - COMBUSTION - List 3 / Reactors: 1 Problem 6.12 (Turns, 2013) - Fixed Volume ReactorGiovanni AndradeNo ratings yet
- Chairul 2023 IOP Conf.Document9 pagesChairul 2023 IOP Conf.chairulNo ratings yet
- Pourbaix Diagrams For Copper at 25 To 300°CDocument8 pagesPourbaix Diagrams For Copper at 25 To 300°CfesooNo ratings yet
- FMDS0798Document12 pagesFMDS0798A NNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document18 pagesChapter 5J.K HomerNo ratings yet
- Thermal Cracking Reaction Kinetics - Hemendra KhakharDocument21 pagesThermal Cracking Reaction Kinetics - Hemendra Khakhargolden retrieverNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL 2D Work Energy Power Momentum & ImpulseDocument3 pagesTUTORIAL 2D Work Energy Power Momentum & ImpulseLeago LeagoNo ratings yet
- History of Electronics: Year Person WorksDocument2 pagesHistory of Electronics: Year Person WorksRoy AngelesNo ratings yet