Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter: Work, Energy & Power Work: Case Description Work Done? Explanation
Uploaded by
Yenny TigaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter: Work, Energy & Power Work: Case Description Work Done? Explanation
Uploaded by
Yenny TigaCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER: WORK, ENERGY & POWER
WORK
1.
a. In Physics, explain what is considered to be work done. [1]
b. Write down the equation to calculate work, and its SI unit. [2]
2. Identify which of the following cases is considered work. Explain you answer. [3]
Case Description Work done?
Explanation
(a) A woman lifts a shopping bag vertically from
the floor and places it on her shoulder.
(b) A worker supports a bag of grain on his
shoulder and walks horizontally.
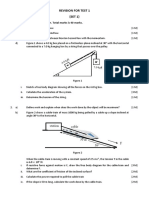
3. The figure shows a load that is to be lifted from the ground to a higher level along three different paths J, K
and L, with a crane. Which path requires the least amount of work?
Explain. [2]
Higher levelJ K L
load
ground
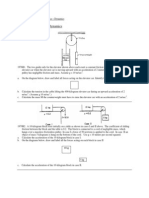
4. Sam pushes a shopping trolley of mass 30 kg for 16 m. The work done by him is 2 kJ.
a. What is the force exerted by Sam on the trolley? [2]
b. Some additional groceries are added to the trolley. The trolley is then lifted vertically off the ground
for 25 m by a lift system that did 10 kJ of work. The lift moves at a constant speed.
i. What is the force exerted by the lift in raising the trolley? [2]
ii. Calculate the mass of the added groceries. [3]
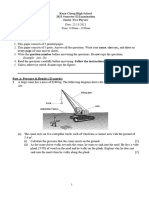
5. A tractor is pulling a fallen tree trunk along a rough road horizontally. The tree trunk weights
2 500 N. The tractor is moving at a constant speed of 1.2 m/s for 5 s. The pull force exerted by tractor on
trunk is 11 kN.
a. Calculate the distance travelled by the trunk for 5s. [2]
b. Calculate the work done against friction between tree trunk and the rough road. [3]
You might also like
- Half Yearly Examination 2020 Class 7 PhysicsDocument3 pagesHalf Yearly Examination 2020 Class 7 Physicsmanoj sharmaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 - General PhysicsDocument3 pagesWorksheet 1 - General PhysicsDaniel Ngenokesho WandyaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Work, Energy, Power & EfficiencyDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Work, Energy, Power & EfficiencyEric MitchellNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2.6 ForceDocument2 pagesExercise 2.6 ForceCart KartikaNo ratings yet
- SC f3 CHP 7Document7 pagesSC f3 CHP 7ROSNI BINTI ISMAIL MoeNo ratings yet
- Revision For Test 1 (SET 1) : Answer All Question Within 1 Hour. Total Marks Is 40 MarksDocument3 pagesRevision For Test 1 (SET 1) : Answer All Question Within 1 Hour. Total Marks Is 40 MarkshadassahhadidNo ratings yet
- 5 WEP (2014 J2H2PH Prelim)Document6 pages5 WEP (2014 J2H2PH Prelim)CHUA XIN YING CELESTENo ratings yet
- Test 4-1Document6 pagesTest 4-1Brãñdøn DzîñgáíNo ratings yet
- Energy Calculations PPQDocument1 pageEnergy Calculations PPQperkinsluke5No ratings yet
- WORK ENERGY & POWER Exam Style QuestionsDocument7 pagesWORK ENERGY & POWER Exam Style QuestionsChi Nguyễn PhươngNo ratings yet
- WEP Energy Question BankDocument2 pagesWEP Energy Question BankAJ SkybornNo ratings yet
- A2AS MATH Past Papers Mark Schemes Standard January Series 2011 7812 PDFDocument8 pagesA2AS MATH Past Papers Mark Schemes Standard January Series 2011 7812 PDFJoshua HallNo ratings yet
- Physics Questions - Moment and Hooke's LawDocument2 pagesPhysics Questions - Moment and Hooke's LawSamson MuchinduNo ratings yet
- Physics - WorkDocument2 pagesPhysics - WorkLionelkeneth12No ratings yet
- Worksheet on Work, Power and Energy CalculationsDocument3 pagesWorksheet on Work, Power and Energy CalculationsMahad Asim100% (2)
- HK 09 Sec 4Sc Phy Prelim P2Document11 pagesHK 09 Sec 4Sc Phy Prelim P2topcatNo ratings yet
- Assignment Work Power EnergyDocument2 pagesAssignment Work Power EnergyPeggy BellNo ratings yet
- WorkDocument5 pagesWorkAlex noslenNo ratings yet
- Physics Question BankDocument20 pagesPhysics Question BankJoshNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Resolution of Forces + 1.3 Equilibrium of Forces 2021Document13 pages1.2 Resolution of Forces + 1.3 Equilibrium of Forces 2021pravin manikamNo ratings yet
- Important Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th PhysicsDocument3 pagesImportant Question ICSE 2010 Class 10th Physicspavan kumarNo ratings yet
- 2b-Dynamics FR Practice ProblemsDocument24 pages2b-Dynamics FR Practice ProblemsTiff VoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Work, Energy and PowerDocument4 pagesChapter 5: Work, Energy and PowerPriyaa JayasankarNo ratings yet
- PHY1 June 2006Document2 pagesPHY1 June 2006api-3726022No ratings yet
- Worksheet Phy 11Document10 pagesWorksheet Phy 11kcricketer75No ratings yet
- Physics - Work - NumericalsDocument2 pagesPhysics - Work - NumericalsLionelkeneth12No ratings yet
- ICSE Sample Papers For Class 10 On WORKDocument3 pagesICSE Sample Papers For Class 10 On WORKSoha ghodeswarNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - Work, Energy and PowerDocument18 pagesTopic 4 - Work, Energy and Powerche syakirNo ratings yet
- Jr2 Physics Sem II Exam 2021Document5 pagesJr2 Physics Sem II Exam 2021aman97881234No ratings yet
- 11th PT-1Document6 pages11th PT-1ABHISHEK PANDANo ratings yet
- Class - XI Subject - Physics: o o o oDocument3 pagesClass - XI Subject - Physics: o o o oRafia AqueelaNo ratings yet
- FORCESDocument4 pagesFORCESTani JNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 2Document13 pagesPhysics Paper 2Adam K C Tiong100% (1)
- Time: 50 Minutes Total: 40 Marks: Lower Sixth Revision Test: Work, Energy and PowerDocument2 pagesTime: 50 Minutes Total: 40 Marks: Lower Sixth Revision Test: Work, Energy and PowerDilan NyaririNo ratings yet
- Physics Trial ExamDocument17 pagesPhysics Trial Examda_reaper_dasNo ratings yet
- Hkcee Physics - Section 2 Mechanics - P.1Document33 pagesHkcee Physics - Section 2 Mechanics - P.1Y AdaNo ratings yet
- KMS Fly High Set 3Document6 pagesKMS Fly High Set 3Ahya NatasyaNo ratings yet
- T4 - Work, Energy & PowerDocument6 pagesT4 - Work, Energy & Powerdayang ishamNo ratings yet
- Question's FOR YOUDSADocument22 pagesQuestion's FOR YOUDSAHAFIZ ABDUL HASEEB ADNANNo ratings yet
- GR 9 ICSE Final Exam Question Paper PhysicsDocument4 pagesGR 9 ICSE Final Exam Question Paper PhysicsanjalimenonNo ratings yet
- 1.3.2 Forces 00-10Document5 pages1.3.2 Forces 00-10Murray PhysicsNo ratings yet
- STPM 2017 Physics Trial ExamDocument19 pagesSTPM 2017 Physics Trial ExamLee Shi HockNo ratings yet
- 5 Worksheet (AS) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Document3 pages5 Worksheet (AS) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Almas TalibNo ratings yet
- 期中复习答案Document14 pages期中复习答案IDKNo ratings yet
- Test 1: Bus velocity and projectile motion problemsDocument7 pagesTest 1: Bus velocity and projectile motion problemstaekim btsNo ratings yet
- Past Paper Questions Energy Work and PowerDocument11 pagesPast Paper Questions Energy Work and PowerAhmed JomaaNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Momentum Edexel Physics Past Papers Questions & Mark Scheme 2001-2009Document53 pagesUltimate Momentum Edexel Physics Past Papers Questions & Mark Scheme 2001-2009kyred100% (2)
- Forces on blocks and passengers in trains and liftsDocument7 pagesForces on blocks and passengers in trains and liftshahaNo ratings yet
- HKCEE PHYSICS | Section 2 Mechanics Key ConceptsDocument33 pagesHKCEE PHYSICS | Section 2 Mechanics Key Conceptslavina rachelNo ratings yet
- Physics Assinm22Document3 pagesPhysics Assinm22Syrus ZambiaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 05 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 05 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (1)
- Edexcel A-LEVEL PHY1 June 2001 QPDocument2 pagesEdexcel A-LEVEL PHY1 June 2001 QPapi-3726022No ratings yet
- Unit 4 EnergyDocument13 pagesUnit 4 EnergySuperBrainy SuperkidsNo ratings yet
- Mechanics SummaryDocument27 pagesMechanics Summaryuse otherNo ratings yet
- Physics - Chapter - 1 - Work and EnergyDocument11 pagesPhysics - Chapter - 1 - Work and EnergyAman LilaniNo ratings yet
- DynDocument7 pagesDynRyan LumNo ratings yet
- Theme: Force and Motion: Learning Area: 1.0 DynamicsDocument9 pagesTheme: Force and Motion: Learning Area: 1.0 DynamicsChee Jin TangNo ratings yet
- CA 2 MomentsDocument3 pagesCA 2 MomentsOctavius_19930% (5)
- Notes - Radiation Related TermsDocument7 pagesNotes - Radiation Related TermsYenny TigaNo ratings yet
- Decay equations for elementsDocument1 pageDecay equations for elementsYenny TigaNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic NotesDocument9 pagesElectrostatic NotesYenny TigaNo ratings yet
- Physics Presentation - Haadi & AqilDocument11 pagesPhysics Presentation - Haadi & AqilYenny Tiga100% (1)
- Calibrating a Thermometer - SOASC Physics ClassDocument1 pageCalibrating a Thermometer - SOASC Physics ClassYenny TigaNo ratings yet
- Revision Checklist For O Level Physics 5054 FINALDocument24 pagesRevision Checklist For O Level Physics 5054 FINALYenny Tiga100% (3)
- Cie o Level Physics Syllabus For Year 2012Document46 pagesCie o Level Physics Syllabus For Year 2012Sakib Ex-rccNo ratings yet
- Exercise: Use The Table Above As A Guide To Answer The Following QuestionsDocument1 pageExercise: Use The Table Above As A Guide To Answer The Following QuestionsYenny TigaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics, VectorDocument1 pageKinematics, VectorYenny TigaNo ratings yet
- Transformers Simply ExplainedDocument2 pagesTransformers Simply ExplainedYenny TigaNo ratings yet
- Examiner Tips For O Level Physics 5054Document10 pagesExaminer Tips For O Level Physics 5054muzaahNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Additional Results Reporting June 20101Document4 pagesA Guide To Additional Results Reporting June 20101Mohsin SadiqNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Cartoon DiscussionDocument2 pagesWork Energy Cartoon DiscussionYenny TigaNo ratings yet
- Transformer 1Document1 pageTransformer 1Yenny TigaNo ratings yet
- Physics Resistance ExDocument1 pagePhysics Resistance ExYenny TigaNo ratings yet
- TransformerDocument3 pagesTransformerYenny TigaNo ratings yet
- Maths Igcse Scheme of Work 0580 - 2011Document6 pagesMaths Igcse Scheme of Work 0580 - 2011Yenny TigaNo ratings yet
- Pressure ExerciseDocument2 pagesPressure ExerciseYenny TigaNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion and ConservationDocument4 pagesEnergy Conversion and ConservationYenny TigaNo ratings yet
- Index of Refraction& Snells WorksheetDocument1 pageIndex of Refraction& Snells WorksheetYenny Tiga0% (1)
- Uses of RadioactivityDocument2 pagesUses of RadioactivityYenny TigaNo ratings yet
- Maths Igcse Scheme of Work 0580 - 2012Document3 pagesMaths Igcse Scheme of Work 0580 - 2012Yenny TigaNo ratings yet
- Maths Igcse Scheme of Work 0580 - 2010Document6 pagesMaths Igcse Scheme of Work 0580 - 2010Yenny Tiga100% (2)
- ResistanceDocument1 pageResistanceYenny TigaNo ratings yet
- Travel and Tourism SOW - Front Page (Word 97-2003)Document38 pagesTravel and Tourism SOW - Front Page (Word 97-2003)Yenny Tiga100% (3)
- Maths Introduction CoverDocument1 pageMaths Introduction CoverYenny TigaNo ratings yet
- Maths Introduction Igcse Extended 3 YrsDocument9 pagesMaths Introduction Igcse Extended 3 YrsYenny TigaNo ratings yet
- Maths Introduction Igcse Extended 3 YrsDocument9 pagesMaths Introduction Igcse Extended 3 YrsYenny TigaNo ratings yet
- Maths IGCSE Scheme of Work 0580 - 2012Document3 pagesMaths IGCSE Scheme of Work 0580 - 2012Yenny TigaNo ratings yet