Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Neurons PDF
Uploaded by
Perry SinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Neurons PDF
Uploaded by
Perry SinCopyright:
Available Formats
Support us at: mobolearner@gmail.
com
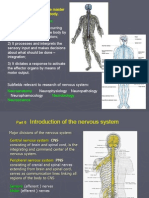
Introduction
There are three types of neurons in the body. We have
sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons.
Neurons are a major class of cells in the nervous system.
Neurons are sometimes called nerve cells, though this
term is technically imprecise, as many neurons do not form
nerves. In vertebrates, neurons are found in the brain, the
spinal cord and in the nerves and ganglia of the peripheral
nervous system. Their main role is to process and transmit
information. Neurons have excitable membranes, which
allow them to generate and propagate electrical impulses.
Sensory neuron takes nerve impulses or messages right
from the sensory receptor and delivers it to the central
nervous system. A sensory receptor is a structure that can
find any kind of change in it's surroundings or environment.
Structure of a neuron
Neurons have three different parts to them. They all have
an axon, a cell body and dendrites. The axon is the part of
the neuron that conducts nerve impulses. Axons can get to
be quite long. When an axon is present in nerves, it is
called a nerve fiber. A cell body has a nucleous and it also
has other organelles. The dendrites are the short pieces
that come off of the cell body that receive the signals from
sensory receptors and other neurons.
Myelin Sheath
Schwann cells contain a lipid substance called myelin in
their plasma membranes. When schwann cells wrap
around axons, a myelin sheath forms. There are gaps that
have no myelin sheath around them; these gaps are called
nodes of Ranvier. Myelin sheathes make excellent
insulators. Axons that are longer have a myelin sheath,
while shorter axons do not. The disease multiple sclerosis
is an autoimune disease where the body attacks the
myelin sheath of the central nervous system.
You might also like
- Structure of NeuronsDocument6 pagesStructure of NeuronsMusdiqJavedNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesNervous SystemLeon MarkoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Nervous System PDFDocument11 pagesIntroduction To The Nervous System PDFEmanuel DragomirescuNo ratings yet
- Ervous Ystem: Structural ClassificationDocument95 pagesErvous Ystem: Structural ClassificationJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Discuss Action Potential of The Axon and Nerve ImpulseDocument3 pagesDiscuss Action Potential of The Axon and Nerve ImpulsePink PastaNo ratings yet
- Biological NeuronsDocument37 pagesBiological NeuronsCharles TaylorNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Notes: Cognitive Approach To Undersatding BehaviourDocument38 pagesUnit 2 Notes: Cognitive Approach To Undersatding BehaviourAdvait MadanalNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience & Biological Foundations: Powerpoint Lecture Notes PresentationDocument49 pagesNeuroscience & Biological Foundations: Powerpoint Lecture Notes PresentationNabilah FarhanahNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Science 6 - Second QuarterDocument25 pagesNervous System: Science 6 - Second QuarterRegin BaguioNo ratings yet
- Tutorial On Helmholtz MachineDocument26 pagesTutorial On Helmholtz MachineNon SenseNo ratings yet
- NeuronsDocument32 pagesNeuronsDesadaNo ratings yet
- Three Main Functions:: The Nervous System Is The Master Controlling System of The BodyDocument34 pagesThree Main Functions:: The Nervous System Is The Master Controlling System of The Bodyapi-19641337No ratings yet
- Introduction To Psychology PSY 101: Lecture 3/ Modules 3 & 4 Biological Psychology Lecturer: Catherine SesayDocument48 pagesIntroduction To Psychology PSY 101: Lecture 3/ Modules 3 & 4 Biological Psychology Lecturer: Catherine SesayNgaima SesayNo ratings yet
- NeuronsDocument22 pagesNeuronsmanuelNo ratings yet
- Nervous TissueDocument29 pagesNervous TissueKaruna PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves Important To SpeechDocument3 pagesCranial Nerves Important To SpeechMike SwiesNo ratings yet
- Nervous System PDFDocument91 pagesNervous System PDFGayathri SNo ratings yet
- Bilology XII 2014 Ch-17 Nervous CoordinationDocument26 pagesBilology XII 2014 Ch-17 Nervous CoordinationMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 The Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument77 pagesUnit 2 The Peripheral Nervous SystemKemoy FrancisNo ratings yet
- Neuron: Structure and Function: B.A.II PsychologyDocument9 pagesNeuron: Structure and Function: B.A.II Psychologyvpilania2008100% (1)
- 1 Anatomy of The Nervous SystemDocument41 pages1 Anatomy of The Nervous SystemFarhan HaleemNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT On Action PotentialDocument8 pagesASSIGNMENT On Action PotentialRinta Moon100% (1)
- Action Potential - Communication Within NeuronsDocument6 pagesAction Potential - Communication Within NeuronsPeehuNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous System WordDocument4 pagesPeripheral Nervous System WordJesi QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System NotesDocument6 pagesThe Nervous System NotesDhea Angela A. CapuyanNo ratings yet
- NeuronsDocument9 pagesNeuronsMuhammad Junaid SialNo ratings yet
- Neurons and NeurotransmittersDocument16 pagesNeurons and NeurotransmittersBedussa NuritNo ratings yet
- Brain and BehaviourDocument9 pagesBrain and BehaviourKenya BaileyNo ratings yet
- Physiological Basis of Behavior ScribDocument12 pagesPhysiological Basis of Behavior ScribJJ WoodruffNo ratings yet
- Cranial and Spinal NervesDocument5 pagesCranial and Spinal NervesEijunNo ratings yet
- Obedience To AuthorityDocument37 pagesObedience To AuthorityABDOULIENo ratings yet
- (W3) Cell CycleDocument6 pages(W3) Cell CycleRednaxela Mejico TarucNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Memory: Introduction To PsychologyDocument6 pagesChapter 5: Memory: Introduction To PsychologyRoseNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Nerve ImpulseDocument7 pagesPhysiology of Nerve ImpulseBryan tsepang Nare100% (1)
- Experiments in PsychologyDocument25 pagesExperiments in PsychologyAnanya GulatiNo ratings yet
- Kedar Mirchandani - Dissertation Final PDFDocument61 pagesKedar Mirchandani - Dissertation Final PDFJasleen KaurNo ratings yet
- 2 - Mod 2-Theories of AttentionDocument31 pages2 - Mod 2-Theories of AttentionPhaguni KatariaNo ratings yet
- NeuronDocument4 pagesNeuroniris danielle barolaNo ratings yet
- Frog's AnatomyDocument13 pagesFrog's AnatomyMark Tolentino100% (1)
- Stanley Milgrams Experiments - Gang Stalking MethodsDocument12 pagesStanley Milgrams Experiments - Gang Stalking MethodsSimon BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Theories of Learning 2022Document59 pagesTheories of Learning 2022Nashawn Brown100% (1)
- Calculate Mean, Median, Mode, Variance and Standard Deviation For Column ADocument22 pagesCalculate Mean, Median, Mode, Variance and Standard Deviation For Column AAmol VirbhadreNo ratings yet
- Notes - MeiosisDocument3 pagesNotes - Meiosisapi-238421605100% (1)
- NppcityDocument63 pagesNppcityMohammad JoharNo ratings yet
- Journal of Experimental Social PsychologyDocument4 pagesJournal of Experimental Social PsychologyJayanth Philip MarottipuzhaNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes: Chapter Three Memory and ForgetingDocument65 pagesLearning Outcomes: Chapter Three Memory and ForgetingDiego Abdi NasiibNo ratings yet
- Muller-Lyer Illusion: PsychophysicsDocument6 pagesMuller-Lyer Illusion: PsychophysicsPradyot HegdeNo ratings yet
- Division of Brain On The Basis of HemisphereDocument24 pagesDivision of Brain On The Basis of HemisphereAnushka Ridhi Hira100% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemSumaira Noreen100% (1)
- Unit 1Document15 pagesUnit 1Nitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Variation of Conductance With Temperature in ElectrolytesDocument20 pagesVariation of Conductance With Temperature in Electrolyteshuha818100% (1)
- Mutation: Prof. Harshraj. S. Shinde K. K. Wagh College of Agril. Biotech, Nashik. IndiaDocument24 pagesMutation: Prof. Harshraj. S. Shinde K. K. Wagh College of Agril. Biotech, Nashik. IndiaMonika shankarNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesThe Nervous SystemRokas Kibelis100% (1)
- Research Methods in Psychology - Indian Perspective (P.lodha, A.desousa)Document14 pagesResearch Methods in Psychology - Indian Perspective (P.lodha, A.desousa)AnneNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Human EarDocument5 pagesAnatomy of Human EarSharanz Twentyfour SevenNo ratings yet
- Week-1 PSYDocument38 pagesWeek-1 PSYHina MalikNo ratings yet
- Adolescents' Introversion and Extroversion As A Corrleates of Their Social Adjustment in Edo South Senatorial District of Edo State PDFDocument11 pagesAdolescents' Introversion and Extroversion As A Corrleates of Their Social Adjustment in Edo South Senatorial District of Edo State PDFAgustina Izehiuwa Efosa-EhioghirenNo ratings yet
- 9SUMMARYNERVOUSSYSTEMDocument24 pages9SUMMARYNERVOUSSYSTEMArvenBitasNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesNervous SystemxoxogeloNo ratings yet
- 3850 - Mathematics - Stage - 1 - Question - Paper - Set 1 PDFDocument19 pages3850 - Mathematics - Stage - 1 - Question - Paper - Set 1 PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan September 24 To 28Document19 pagesLesson Plan September 24 To 28Perry SinNo ratings yet
- Course Outline: Course Title: Linear Algebra Course Code: EDME3201 (ME32A) Level: 3 Semester: 3 Credits: 3Document3 pagesCourse Outline: Course Title: Linear Algebra Course Code: EDME3201 (ME32A) Level: 3 Semester: 3 Credits: 3Perry SinNo ratings yet
- Full Maths SbaDocument9 pagesFull Maths SbaPerry Sin86% (22)
- Circle Theorem Booklet PDFDocument16 pagesCircle Theorem Booklet PDFPerry Sin100% (1)
- 2004 Csec Chem Paper 01Document10 pages2004 Csec Chem Paper 01Perry SinNo ratings yet
- 3850 Mathematics Stage 1 Marking Guide Set 1Document1 page3850 Mathematics Stage 1 Marking Guide Set 1Perry SinNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System PDFDocument4 pagesThe Circulatory System PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- 7B ReproductionDocument31 pages7B ReproductionPerry Sin50% (2)
- The Nervous System PDFDocument3 pagesThe Nervous System PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- White Blood Cells (WBC) PDFDocument3 pagesWhite Blood Cells (WBC) PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- The Menstrual Cycle PDFDocument6 pagesThe Menstrual Cycle PDFPerry Sin100% (1)
- Mitosis Cell Division PDFDocument8 pagesMitosis Cell Division PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction PDFDocument4 pagesSexual Reproduction PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Skin PDFDocument3 pagesSkin PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Sense Organ PDFDocument5 pagesSense Organ PDFPerry Sin75% (4)
- Positive and Negative Feedback PDFDocument3 pagesPositive and Negative Feedback PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System PDFDocument4 pagesMale Reproductive System PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Bio 124 Lab SensesDocument20 pagesBio 124 Lab SensesJuliaNo ratings yet
- Transverse Myelitis: A Guide For Patients and CarersDocument36 pagesTransverse Myelitis: A Guide For Patients and CarersMartina Acosta RamaNo ratings yet
- Herniated Nucleus PulposusDocument13 pagesHerniated Nucleus PulposusLorebell100% (4)
- Unsupervised Learning Networks: "Principles of Soft Computing, 2Document44 pagesUnsupervised Learning Networks: "Principles of Soft Computing, 2جرح الماضيNo ratings yet
- Indirect Speech Act1Document13 pagesIndirect Speech Act1darkcardNo ratings yet
- A Trip I Will Never ForgetDocument1 pageA Trip I Will Never ForgetIuliana ȚigănașuNo ratings yet
- Stenger Test GuideDocument2 pagesStenger Test GuideAnonymous iftX7wVPCNo ratings yet
- Notes On Paediatrics (Aindrani Akka)Document220 pagesNotes On Paediatrics (Aindrani Akka)Lasantha RathnayakeNo ratings yet
- Birth TraumaDocument57 pagesBirth TraumaAbu HajerahNo ratings yet
- Janardana Reddy OCDDocument155 pagesJanardana Reddy OCDDrAvik ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Sub - Medical Surgical Nursing: Assignment On Neurological AssessmentDocument11 pagesSub - Medical Surgical Nursing: Assignment On Neurological Assessmentkamini Choudhary100% (1)
- DREAM11 Final-CompressedDocument12 pagesDREAM11 Final-Compressedayaz sheikhNo ratings yet
- Initial Evaluation Consultation Chief Complaint: Name: History of Present Illness: RoomDocument4 pagesInitial Evaluation Consultation Chief Complaint: Name: History of Present Illness: RoomwhitneyagNo ratings yet
- 15 - Mahima Bhatia - MyalgiaDocument14 pages15 - Mahima Bhatia - MyalgiaApoorvNo ratings yet
- Asd Inclusive Ed Essay Mulen Hayley A110751Document10 pagesAsd Inclusive Ed Essay Mulen Hayley A110751api-501465610No ratings yet
- Jurding Elmo H3a021009Document39 pagesJurding Elmo H3a021009Elmo KrisnawanNo ratings yet
- Types of Anxiety DisordersDocument5 pagesTypes of Anxiety DisordersCindy Mae de la TorreNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument3 pagesDaftar PustakaAchmad SaktyNo ratings yet
- Hearing 2nd YearDocument20 pagesHearing 2nd YearAliaa MahamadNo ratings yet
- Crash Course Disorder WorksheetsDocument11 pagesCrash Course Disorder WorksheetsKaitlyn SimmonsNo ratings yet
- Michelle Ty - On The Cognitive Turn in Lit StudiesDocument17 pagesMichelle Ty - On The Cognitive Turn in Lit StudiesJimmy NewlinNo ratings yet
- Ranga SNC PDFDocument287 pagesRanga SNC PDFcoolathea100% (1)
- Visual Pathway - Lecture SlidesDocument11 pagesVisual Pathway - Lecture SlidesSimphiwe CebisaNo ratings yet
- A Psychiatric Classification of PossessionsDocument2 pagesA Psychiatric Classification of PossessionsColin P. CollinsNo ratings yet
- The EyeDocument22 pagesThe Eyeapi-309893409No ratings yet
- Sexual Connections Builder WorkbookDocument171 pagesSexual Connections Builder WorkbookPiero Mauricio Pesantes Escobar100% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Vestibuler SystemDocument54 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Vestibuler SystemAndri Adma Wijaya100% (1)
- 54 The Brain From Inside Out 15: Chapter 1. e ProblemDocument20 pages54 The Brain From Inside Out 15: Chapter 1. e ProblemjuannnnNo ratings yet
- Effects of GABA On Brain and BehaviourDocument6 pagesEffects of GABA On Brain and BehaviourRay TakazaNo ratings yet
- Lab Act 1 - Motor AssessmentDocument6 pagesLab Act 1 - Motor AssessmentZgama AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)From EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (82)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (32)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesFrom EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1412)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (254)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceFrom EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (51)
- Critical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsFrom EverandCritical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (39)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlFrom EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (60)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingFrom EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1138)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)