Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Virus PDF
Uploaded by
Perry Sin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Virus.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views2 pagesVirus PDF
Uploaded by
Perry SinCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Support us at: mobolearner@gmail.
com
Introduction
With the exception of newly discovered prions, viruses are
the smallest agents of infectious disease. Most viruses are
exceedingly and essentially round in shape. They consist
of little more than a small piece of genetic material
surrounded by a thin protein coating. Some viruses are
also surrounded by a thin, fatty envelope. Viruses are
different from all other infectious microorganisms because
they are the only group of microorganisms that cannot
replicate outside of a host cell. Because viruses do not eat
food - instead they seize materials and energy from host
cells by hijacking cellular machinery - some scientists
argue that they are more like complex molecules than
living creatures. Viruses are known to infect nearly every
type of organism on Earth. Some viruses, called
bacteriophages, even infect bacteria.
General Characteristics
Viruses are a cellular, non-cytoplasmic infectious agents.
They are smaller than bacteria, and this can pass through
bacteriological filter. Viruses are transmissible from
disease to healthy organisms. All viruses are obligate
parasites and can multiply only within the living host cells.
Viruses contain only a single type of nucleic acid either
DNA or RNA. Viruses are host specific that they infect only
a single species and definite cells of the host organisms.
Viruses are effective in very small doses. They are highly
resistant to germicides and extremes of physical
conditions.
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- 3850 - Mathematics - Stage - 1 - Question - Paper - Set 1 PDFDocument19 pages3850 - Mathematics - Stage - 1 - Question - Paper - Set 1 PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Full Maths SbaDocument9 pagesFull Maths SbaPerry Sin86% (22)
- Course Outline: Course Title: Linear Algebra Course Code: EDME3201 (ME32A) Level: 3 Semester: 3 Credits: 3Document3 pagesCourse Outline: Course Title: Linear Algebra Course Code: EDME3201 (ME32A) Level: 3 Semester: 3 Credits: 3Perry SinNo ratings yet
- 2004 Csec Chem Paper 01Document10 pages2004 Csec Chem Paper 01Perry SinNo ratings yet
- 3850 Mathematics Stage 1 Marking Guide Set 1Document1 page3850 Mathematics Stage 1 Marking Guide Set 1Perry SinNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan September 24 To 28Document19 pagesLesson Plan September 24 To 28Perry SinNo ratings yet
- Circle Theorem Booklet PDFDocument16 pagesCircle Theorem Booklet PDFPerry Sin100% (1)
- Types of Neurons PDFDocument2 pagesTypes of Neurons PDFPerry Sin100% (2)
- 7B ReproductionDocument31 pages7B ReproductionPerry Sin50% (2)
- White Blood Cells (WBC) PDFDocument3 pagesWhite Blood Cells (WBC) PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Cell Division PDFDocument8 pagesMitosis Cell Division PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System PDFDocument3 pagesThe Nervous System PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- The Menstrual Cycle PDFDocument6 pagesThe Menstrual Cycle PDFPerry Sin100% (1)
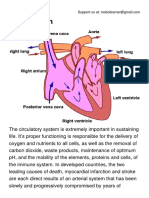
- The Circulatory System PDFDocument4 pagesThe Circulatory System PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Sense Organ PDFDocument5 pagesSense Organ PDFPerry Sin75% (4)
- Skin PDFDocument3 pagesSkin PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Positive and Negative Feedback PDFDocument3 pagesPositive and Negative Feedback PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction PDFDocument4 pagesSexual Reproduction PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System PDFDocument4 pagesMale Reproductive System PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)