Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Brophy Notes
Uploaded by
api-350262169Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Brophy Notes
Uploaded by
api-350262169Copyright:
Available Formats
Brophy Notes
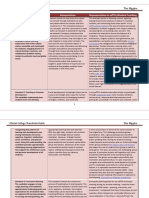
A supportive classroom climate
To create a climate for molding their students into a cohesive and supportive learning
community, teachers need to display personal attributes that will make them effective as models
and socializers: a cheerful disposition, friendliness, emotional maturity, sincerity, and caring
about students as individuals as well as learners.
Opportunity to learn
Research indicates that teachers who approach management as a process of establishing an
effective learning environment tend to be more successful than teachers who emphasize their
roles as disciplinarians.
Curricular alignment
Research indicates that educational policy-makers, textbook publishers and teachers often
become so focused on content coverage or learning activities that they lose sight of the larger
purposes and goals that are supposed to guide curriculum planning.
Establishing learning orientations
Research indicates the value of establishing a learning orientation by beginning lessons and
activities with advance organizers or previews.
Coherent content
Research indicates that networks of connected knowledge structured around powerful ideas can
be learned with understanding and retained in forms that make them accessible for application.
Thoughtful discourse
They use questions to stimulate students to process and reflect on content, recognize
relationships among and implications of its key ideas, think critically about it, and use it in
problem solving, decision making or other higher-order applications.
Practice and application activities
There are three main ways in which teachers help their students to learn. First, they present
information, explain concepts and model skills. Second, they ask questions and lead their
students in discussion and other forms of discourse surrounding the content. Third, they engage
students in activities or assignments that provide them with opportunities to practise or apply
what they are learning.
Scaffolding students task engagement
Research on learning tasks suggests that activities and assignments should be sufficiently varied
and interesting to motivate student engagement, sufficiently new or challenging to constitute
meaningful learning experiences rather than needless repetition, and yet sufficiently easy to
allow students to achieve high rates of success if they invest reasonable time and effort
Strategy teaching
General learning and study skills as well as domain-specific skills (such as constructing meaning
from text, solving mathematical problems or reasoning scientifically) are most likely to be
learned thoroughly and become accessible for application if they are taught as strategies to be
brought to bear purposefully and implemented with metacognitive awareness and self-regulation.
Co-operative learning
Co-operative learning promotes affective and social benefits such as increased student interest in
and valuing of subject matter, and increases in positive attitudes and social interactions among
students who differ in gender, race, ethnicity, achievement levels and other characteristics.
Goal-oriented assessment
These assessment components are aligned with the curriculums goals, and so they are integrated
with its content, instructional methods and learning activities, and designed to evaluate progress
towards its major intended outcomes.
Achievement expectations
Research indicates that effective schools feature strong academic leadership that produces
consensus on goal priorities and commitment to instructional excellence, as well as positive
teacher attitudes towards students and expectations regarding their abilities to master the
curriculum.
You might also like
- Teaching StrategiesDocument24 pagesTeaching StrategiesRania MohammedNo ratings yet
- Classroom-Ready Resources for Student-Centered Learning: Basic Teaching Strategies for Fostering Student Ownership, Agency, and Engagement in K–6 ClassroomsFrom EverandClassroom-Ready Resources for Student-Centered Learning: Basic Teaching Strategies for Fostering Student Ownership, Agency, and Engagement in K–6 ClassroomsNo ratings yet
- 14 Learner Teaching PrincipleDocument4 pages14 Learner Teaching Principlemaela pollen yemaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Self-Regulated LearningDocument17 pagesThe Role of Self-Regulated LearningMikail KayaNo ratings yet
- Learning & Teaching StrategiesDocument12 pagesLearning & Teaching StrategiesFerra FilaNo ratings yet
- Professional Learning CommunityDocument21 pagesProfessional Learning CommunityemanNo ratings yet
- Advanced PedagogyDocument5 pagesAdvanced PedagogyRahul Sharma100% (3)
- Module 5Document43 pagesModule 5John Joseph EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Teaching Strategies Preferred Most by The BSHRM Students of CDDDocument16 pagesTeaching Strategies Preferred Most by The BSHRM Students of CDDSharlene BiananNo ratings yet
- Teaching StrategiesDocument14 pagesTeaching Strategieseden barredaNo ratings yet
- Teaching StrategiesDocument8 pagesTeaching StrategiesMark Jade PanisNo ratings yet
- Remedial Program in MathematicsDocument2 pagesRemedial Program in MathematicsDolores Espinosa100% (1)
- What Is Active LearningDocument17 pagesWhat Is Active LearningGedionNo ratings yet
- Becoming a Better Science Teacher: 8 Steps to High Quality Instruction and Student AchievementFrom EverandBecoming a Better Science Teacher: 8 Steps to High Quality Instruction and Student AchievementNo ratings yet
- Learning Process: Wilma R. CamiñaDocument51 pagesLearning Process: Wilma R. CamiñaJohn Joseph Enriquez100% (1)
- MODULE 5 Building and Enhancing New Literacies Across The CurriculumDocument13 pagesMODULE 5 Building and Enhancing New Literacies Across The CurriculumLance Austria100% (1)
- 21 Century SUSD CharacteristicsDocument10 pages21 Century SUSD Characteristicscresta2014No ratings yet
- Reflection Paper 6Document5 pagesReflection Paper 6Ofwono LukeNo ratings yet
- Why Is Active Learning Important?Document3 pagesWhy Is Active Learning Important?AlexxaNo ratings yet
- LEARNER CENTERED PEDAGOGICAL APPROACHES NotesDocument8 pagesLEARNER CENTERED PEDAGOGICAL APPROACHES NotesfantasticlyrgNo ratings yet
- TsediDocument3 pagesTsediluweta125No ratings yet
- ArtifactsDocument7 pagesArtifactsScherasid VillejoNo ratings yet
- (A) Teaching StrategesDocument5 pages(A) Teaching StrategesIan KunNo ratings yet
- Paradigm Shift - WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesParadigm Shift - WPS Officetakena PowNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument7 pagesReflectionAriane Grace LopezNo ratings yet
- CM - PagdilaoDocument4 pagesCM - PagdilaoIvy PacateNo ratings yet
- HLPDocument6 pagesHLPPAULNo ratings yet
- 754 Ed 74Document6 pages754 Ed 74Nchimunya Guy- ScottNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Teaching MethodDocument5 pagesPart 2 Teaching MethodJOHN LLOYD VINLUANNo ratings yet
- Q.1. Define Teaching. Discuss in Detail The Components of TeachingDocument10 pagesQ.1. Define Teaching. Discuss in Detail The Components of TeachingZeeshan NasirNo ratings yet
- Action Research ProposalDocument11 pagesAction Research ProposalTroy AlonzoNo ratings yet
- MATC Prog Goals StandardsDocument2 pagesMATC Prog Goals Standardsdavidsonkl713No ratings yet
- Midterm - Act 1.Document5 pagesMidterm - Act 1.Lynnah SibongaNo ratings yet
- Q.1 Discuss With Any Educationist, The Permissive Style of Teaching and Prepare A Report of The Outcomes of Your Discussion. AnswerDocument14 pagesQ.1 Discuss With Any Educationist, The Permissive Style of Teaching and Prepare A Report of The Outcomes of Your Discussion. Answerinformation pointNo ratings yet
- Principles of Teachin1Document5 pagesPrinciples of Teachin1AbigailsuiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument15 pagesUntitledAyesha MalickkNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: 8601-1 General Method of TeachingDocument28 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: 8601-1 General Method of TeachingMasooma IshratNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 01 8601Document18 pagesAssignment No. 01 8601humairarahim764591No ratings yet
- Project of Element, Need and Nature ofDocument29 pagesProject of Element, Need and Nature ofZain SaeedNo ratings yet
- Other Teaching Strategies Suited in Teaching Philippine History and Related Subject in Social StudiesDocument6 pagesOther Teaching Strategies Suited in Teaching Philippine History and Related Subject in Social StudiesELEONOR DE JESUSNo ratings yet
- Standards Guide Edtpa HigginsDocument6 pagesStandards Guide Edtpa Higginsapi-292659346No ratings yet
- Midterm ReportDocument3 pagesMidterm Reportapi-296128579No ratings yet
- Combining Constructivict and Empowerment TeoriDocument15 pagesCombining Constructivict and Empowerment Teoridaqril81No ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Cooperative Learning Approach in Developing Critical Thinking Skills of Secondary StudentsDocument9 pagesEffectiveness of Cooperative Learning Approach in Developing Critical Thinking Skills of Secondary StudentsHạnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Understanding BriefDocument6 pagesUnderstanding BriefMi RoNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Psychological Principles: Center For Excellence in Teaching and LearningDocument6 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological Principles: Center For Excellence in Teaching and LearningJayson BasiagNo ratings yet
- SOETDocument11 pagesSOETArdelianda AugeslaNo ratings yet
- Costructivist Learning TheoriesDocument3 pagesCostructivist Learning TheoriesSofia BolivarNo ratings yet
- Reiser and BalderasDocument3 pagesReiser and BalderasRham BlaimNo ratings yet
- Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument4 pagesLearner-Centered Psychological Principles愛No ratings yet
- The Learning Environment Is Supportive and ProductiveDocument8 pagesThe Learning Environment Is Supportive and Productiveasiano_24No ratings yet
- LearnerDocument3 pagesLearnerZaira Michaela CamposNo ratings yet
- Best PracticeDocument4 pagesBest Practiceapi-229152558No ratings yet
- Students' Approaches To LearningDocument5 pagesStudents' Approaches To LearningDedi SofyanNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument5 pagesReportLei Andrew BalmacedaNo ratings yet
- Hist 122 Handout 1Document11 pagesHist 122 Handout 1Sandrex A. AgbayaniNo ratings yet
- Eea 532 Instructional Strategies Comparison Eryn WhiteDocument9 pagesEea 532 Instructional Strategies Comparison Eryn Whiteapi-617772119No ratings yet
- Teaching Methodology in Elementary EducationDocument4 pagesTeaching Methodology in Elementary EducationRochelle AnneNo ratings yet
- Principles of Learning and Teaching PDocument30 pagesPrinciples of Learning and Teaching Proneldayo62No ratings yet
- Goals of Teaching 1Document22 pagesGoals of Teaching 1joannNo ratings yet
- Reflections For SteppingstoneDocument2 pagesReflections For Steppingstoneapi-350262169No ratings yet
- Solon Powerpoint PresentationDocument7 pagesSolon Powerpoint Presentationapi-350262169No ratings yet
- Reflection For FennemaDocument1 pageReflection For Fennemaapi-350262169No ratings yet
- Reflection For Entry PointsDocument1 pageReflection For Entry Pointsapi-350262169No ratings yet
- Reflection For BrophyDocument1 pageReflection For Brophyapi-350262169No ratings yet
- Reflection For Act of TeachingDocument1 pageReflection For Act of Teachingapi-350262169No ratings yet
- Steppingstone Notes Chapter 1Document6 pagesSteppingstone Notes Chapter 1api-350262169No ratings yet
- Act of Teaching NotesDocument11 pagesAct of Teaching Notesapi-350262169No ratings yet
- Itc Lesson Plan To WeeblyDocument3 pagesItc Lesson Plan To Weeblyapi-350262169No ratings yet
- Fennema NotesDocument2 pagesFennema Notesapi-350262169No ratings yet
- Entry Points NotesDocument3 pagesEntry Points Notesapi-350262169No ratings yet
- Verb TensesDocument3 pagesVerb Tensesapi-350262169No ratings yet
- Article Review 2 1Document2 pagesArticle Review 2 1api-350262169No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Irregular Verbs WeeblyDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Irregular Verbs Weeblyapi-350262169No ratings yet
- Emt501 Task 1 Action PlanDocument5 pagesEmt501 Task 1 Action Planapi-238497149No ratings yet
- Edu 201 Portfolio Project 12Document2 pagesEdu 201 Portfolio Project 12api-609317321No ratings yet
- English For Young LearnersDocument3 pagesEnglish For Young LearnersYoskapelaNo ratings yet
- Tes IQDocument112 pagesTes IQHandre PutraNo ratings yet
- Course Plan: Mohammed Imran SK Asst. Professor B.TechDocument25 pagesCourse Plan: Mohammed Imran SK Asst. Professor B.TechImranNo ratings yet
- SCHOOL BASED ACTION PLAN in READINGDocument3 pagesSCHOOL BASED ACTION PLAN in READINGGirly GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Clinicals Socialstudies Observation Form-2Document2 pagesClinicals Socialstudies Observation Form-2api-381662166No ratings yet
- Task 1 Part B Lesson Plans For Learning Segment-14Document12 pagesTask 1 Part B Lesson Plans For Learning Segment-14api-500386111No ratings yet
- LP Still PicturesDocument8 pagesLP Still PicturesJoan JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Sose Lesson 4pDocument5 pagesSose Lesson 4papi-263184946No ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log DLL New JoanDocument10 pagesDaily Lesson Log DLL New JoanPrinces Domenden ConsueloNo ratings yet
- Agreement CircleDocument11 pagesAgreement CircleIan BetosNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka PDFDocument18 pagesDaftar Pustaka PDFZeinor RahmanNo ratings yet
- Improving Students Reading Comprehension On Narrative Text Using Narrative Video To The Sixth Grade Students of SDN 01 Banyuasin IDocument5 pagesImproving Students Reading Comprehension On Narrative Text Using Narrative Video To The Sixth Grade Students of SDN 01 Banyuasin IAam SevenfoldismeNo ratings yet
- Educ 106aDocument1 pageEduc 106aMaryjoy PaladanNo ratings yet
- Course Handout Template With Guidelines CommentsDocument7 pagesCourse Handout Template With Guidelines CommentsPathivadaSantoshNaiduNo ratings yet
- Eleot WPDocument3 pagesEleot WPNehad El LeithyNo ratings yet
- Action Research FilDocument19 pagesAction Research Fillimboy15No ratings yet
- Grade 8: Sections: Evergreen Madre Cacao Liptong Mangrove Golden Shower and Teak TreeDocument2 pagesGrade 8: Sections: Evergreen Madre Cacao Liptong Mangrove Golden Shower and Teak TreeJuvelito ChicoNo ratings yet
- The Use of A Bar Model Drawing To Teach Word Problem Solving To Students With Mathematics Difficulties - Lisa LDocument7 pagesThe Use of A Bar Model Drawing To Teach Word Problem Solving To Students With Mathematics Difficulties - Lisa Lapi-518387243No ratings yet
- Edu 412 Disciplinary Literacy Lesson Segment TemplateDocument15 pagesEdu 412 Disciplinary Literacy Lesson Segment Templateapi-549570505No ratings yet
- Be Guided by These Tasks As You Do Your Observation. Then Accomplish The Matrix To RecordDocument1 pageBe Guided by These Tasks As You Do Your Observation. Then Accomplish The Matrix To RecordELMERNo ratings yet
- Monitoring and AssesmentDocument2 pagesMonitoring and AssesmentAzizah NurNo ratings yet
- Cainta Senior High School: Division of RizalDocument5 pagesCainta Senior High School: Division of Rizaljollibee torresNo ratings yet
- PIR (Program Implementation Review) Related To BE-LCP: Lack of Knowledge On ICT Some Teachers Have Not CreatedDocument74 pagesPIR (Program Implementation Review) Related To BE-LCP: Lack of Knowledge On ICT Some Teachers Have Not CreatedJOSELITO AGUANo ratings yet
- Lesson 15 Oral Presentation of Achievement StoryDocument2 pagesLesson 15 Oral Presentation of Achievement Storyapi-265593610No ratings yet
- Authentic Assessment: Benefits To Learning and Implementation ChallengesDocument10 pagesAuthentic Assessment: Benefits To Learning and Implementation ChallengesMissia H. SabtalNo ratings yet
- ARC - 14 - 408.3 - IV - VIII - Digital Design - Poonam RathoreDocument3 pagesARC - 14 - 408.3 - IV - VIII - Digital Design - Poonam RathoreKripa SriramNo ratings yet
- Basic Course Outline of AssessmentDocument8 pagesBasic Course Outline of AssessmentRinartika Risma MelatiNo ratings yet