Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Crib Sheet
Uploaded by
Marc M0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesCrib Sheet
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCrib Sheet
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesCrib Sheet
Uploaded by
Marc MCrib Sheet
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
CFX-9850GB Calculator
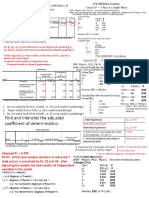
Conduct the global F-test of model usefulness at Lesson. teat ohana, Meen
€1=0.05 level of significance STAT ten) £26) F3).shen eerste feloningitrs
Wet: Orv age the Ete ater ren dpa enn. Ofer, use the cursor ¥ arrow. vou
swovee Sede eee AEN a esas
iat es eagan
= gine | at |nemsgael/“e | & Y) © BONY
Y regener] yy ea ie) to oO oe
: in ae
“ an Ste
wa 78368) "| Now key EXE or FA{Calc)
ESSE TERT STS PSTN TESTOR TOSS — the actor willow show the eat
SORSLIEEINE SLES AoE esuenatposey Samples
Ho: B,=Bs=B,~0 (All model terms are not important for predicting Y) > Baseseos
Fa: At least one f+ 0 (At least one model tem is useful for predicting Y) Sa 2
Blue preach pvle-2000s lr han 2-095 eect CEX-9850GB Calculator
Condlude that the model i statistically useful Lesson 10 — Z-Test of a single Proportion
Conduct t-test on these fi parameters STAT Fa{tes) F1(2) F(LP)_ then entor the fllowing items:
(ote: Only use the EXEkey after anew data entry. Otherwsse, use the cursor
Coote ‘arrow WFyou accidantaly hit the wrong key, ze AC/ON oe EXIT to go bse
Tinie 1 Prop ZTest STAT Fa(lest) FAR)
V Ecce | contin Prop 2b)
owe ower | ew | «| og | 2 1050 EXE es
: — es St ie 2 tos xe 2-Sample Frest
powrasesineaie | ate] org] a} tcf said 1300 KE Data :Fa(va ¥
otepereny ot“ F4(¢02) ¥
popesso vast sm] an] ase] asze] aor] Nowkey EXE or Fa{cale) xtont 3.8 EXE
ce /M 380 EXE
Kerctunesssce | rose] _osee] are acne] a] THe aMeuatorllnowshow the resus oon4 23.2 EXE
SLES TAGE SHE SIGE TET eos mn :40 EXE
2 =L732 Now key EXE oF F4(Cal)
1. Do not reject Ho:81=0 at =0.05, i.e. X1 isnot useful in predicting Y —p —=0.041632————~ Bake Pabacts-2ae
2. Reject Ho:B2-0 at a=0.05, i.e. K2 is useful in predicting ¥ Dp 20.55, earn
3. Do not reject Ho:83=0 at 0=0.05, i.e. X3 is not useful in predictingY 309,
Find and interpret the adjusted ZNaiypomess
coefficient of determination. Tore than 4 00 ours? _
Alternate hypothesis Hy 4.00
ode sonnary Memanetyponess
3 Determine the appropriate tex (reer | Test
{othe fowchart)-not given
hose ® rsqae | sguasesque | “ESL | “F Whatassumplion(s)are made to [None sncen>30,
ae zi THEA] perform this test?
FRESE OST Ra oR TT SET FSET
mgrovemerts on fe groper 5. Determine the critical value that divide | Given 5% significance level.
the rejection and norvrejection region | a one tated test
Adjusted R? = 0.878 Test tor Diterance Between Two Means (3 known)
87.8% of the total sample variation of sale price Y From tne Main Menu select
(sale prices) is explained by X1,X2 and X3, after S7AT Fadesi) FIZ) F2(2-S) then enler ihe folowing fers:
2-Sample ZTest
adjusting for sample size and number of independent Data F2(var) ¥
variables in the model. uw Fa?)
Information required: a gore EXE
u and degrees of freedom 1 3023 EXE
ny-1= degrees of freedom from sample 1 at 100 EXE
2 5.031 EXE
(ie. the numerator degrees of freedom) 2 Sasi EXE
ng: T= degrees of freedom from sample 2
(ie. the denominator degrees of freedom) Now key EXE or F1(Calc)
»b) Use 555 to estimate the unknown parameters ByB1,s, Bsin the ,
ms Po Interpretation of b
model
Y=BotBiXatBaXatBaXat® b1=0.814 ; Estimate the mean sale price of a
couficientee property to increase 0.814 dollar for every $1
— increase in appraised land value (XL} when both
Uniniowee |S X2 and X2 aro held constant (fixcd).
owl ea b2=0.820: Estimate the mean sale orice of a
je Tone Tas] sis] S$a] property to increase 0.820 dollar for every $1
spasectndraie | rs] eta] sea]_ieo]_ ss] increase in appraised improvements(X2] when
oheoonety both X1 and X3 are held constant (fixed).
feasesmees, | tz] 2n| sss] 1] $)3-15.529: Estimate ttre meant sale price of a
sara property to increase 15.529 dollar for each
Aesetimanae | sx ess] am 20s] os] additional square foot of living area(X3} when
[DSRS SE Pree oS SENT
both X1 and X2 arc held constant (fix
Caution
The regression line (prediction line) is:
YA=1470.276+0.814X,+0.820X,+13.529X,
Inferences About the B parameters
Test of an individual Parameter Coefficient in the Multiple
If you fail to reject Ho: fi, =0, several conclusions
are possible:
1. There is no relationship between y and Xi.
2. Amore complex than “linear” relationship
between Y and Xi.
Regression Model.
oneratee est were et
forge epee
ft oT tapi 0 The most you can say about a B parameter
test is that there is either sufficient (if reject
Ho: f, =0) or insufficient (if you do net rejec
Rejection Region: [t |< ta Ho: B; =0) evidence of a linear relationship
Where tuand tes are based on (nk) degressoffieedomand between y and X
n= Number of observations The multiple Coefficient of
ict = Number off perameters inthe model — ,
Stop 7; Finally, if the model is deemed adequate, use the fitted Determination, R
‘model to estimate the mean value of y or to predict a particular
value of y for a given valuas of the independent variables, ani Call r? (called coefficient of determination) is a
measure of how well a straight-line model fits
Using the Model for Estimation and Prediction: # d@ta set.
1. Confidence Interval the mean value of Y _R’ (called the multiple coefficient of
SPSS printout: LMCI and UMCI determination) measure how well a multiple
regression model fits a set of data.
2. Prediction Interval for ¥
SPSS printout: LICI and UIC!
2
Test Statistics: t=
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Finance Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesFinance Cheat SheetMarc MNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- FIN300 Notes - Class 1Document1 pageFIN300 Notes - Class 1Marc MNo ratings yet
- ECN Midterm ReviewDocument3 pagesECN Midterm ReviewMarc MNo ratings yet
- CMN279 Notes - Class 3Document2 pagesCMN279 Notes - Class 3Marc MNo ratings yet
- FIN300 Notes: Financial Planning Process and ComponentsDocument1 pageFIN300 Notes: Financial Planning Process and ComponentsMarc MNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Torts Chapter ObjectivesDocument4 pagesIntroduction to Torts Chapter ObjectivesMarc MNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives:: Larger Slice of Sales ResultDocument2 pagesLearning Objectives:: Larger Slice of Sales ResultMarc MNo ratings yet
- Crib Sheet 2Document1 pageCrib Sheet 2Marc MNo ratings yet
- FIN300 Notes Class 2Document1 pageFIN300 Notes Class 2Marc MNo ratings yet
- ECN 204 Notes Class 2Document3 pagesECN 204 Notes Class 2Marc MNo ratings yet
- CMN279 Notes - Class 4Document1 pageCMN279 Notes - Class 4Marc MNo ratings yet
- CMN279 Notes - Class 2Document3 pagesCMN279 Notes - Class 2Marc MNo ratings yet
- COGS: Income Statement (Expense) Inventory SystemsDocument1 pageCOGS: Income Statement (Expense) Inventory SystemsMarc MNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Law 122Document2 pagesCH 5 Law 122Marc MNo ratings yet
- ACC 100 Notes Sep 23Document1 pageACC 100 Notes Sep 23Marc MNo ratings yet
- CMN279 Notes - Class 1Document2 pagesCMN279 Notes - Class 1Marc MNo ratings yet
- PCS 181 Notes Class 2Document2 pagesPCS 181 Notes Class 2Marc MNo ratings yet
- Intentional Torts and Defences ExplainedDocument3 pagesIntentional Torts and Defences ExplainedMarc MNo ratings yet
- PCS 181 Notes Class 1Document1 pagePCS 181 Notes Class 1Marc MNo ratings yet
- PCS181 Class 3Document2 pagesPCS181 Class 3Marc MNo ratings yet
- PCS181 Notes Class 6Document3 pagesPCS181 Notes Class 6Marc MNo ratings yet
- PCS181 Notes Class 4Document3 pagesPCS181 Notes Class 4Marc MNo ratings yet
- PCS181 Notes Class 7Document2 pagesPCS181 Notes Class 7Marc MNo ratings yet
- PCS181 Notes Class 5Document1 pagePCS181 Notes Class 5Marc MNo ratings yet