Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Combustion in CI Engines
Uploaded by
Ayman EsaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Combustion in CI Engines
Uploaded by
Ayman EsaCopyright:
Available Formats
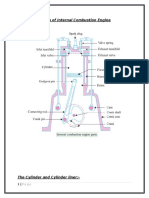
Lecture: 1
Combustion in Compression
Ignition Engine
Dr. Ismail Mahmoud Metwally El.semary 1 3/14/2017
Combustion in C I Engine
Working Principle: 4-stroke
1. Induction
Pure air is drawn into the cylinder
2. Compression
The air is compressed to high temperature and pressure
3. Power Stroke
Around TDC fuel is injected, which self-ignites and burns, further increasing
pressure and there by forcing the piston down.
4. Exhaust
The hot gas is released to the surrounding
Dr. Ismail Mahmoud Metwally El.semary 2 3/14/2017
Combustion in C I Engine
Working Principle: 4-stroke
Dr. Ismail Mahmoud Metwally El.semary 3 3/14/2017
Combustion in C I Engine
The importance of CI engines is due to:
Its higher thermal efficiency than SI engines.
CI engines fuels being less expensive than SI engine fuels.
Due to these factors the running cost of CI engine s much less than SI engines and
make them attractive for all industrial and transport applications.
Why Passenger cars did not use CI engines?????
Because of the CI engine are heavier weight, noise , vibration, smoke and odour
than the SI engines.
The compression ratio of SI (6:1 to 11:1) but in CI (12:1 to 22:1) this factor affect
on the parts of engine be heavier and increase engine weight.
The smoke and odour are the result of the nature of diesel combustion
phenomena, i.e., incomplete combustion of a heterogeneous mixture, and droplet
combustion.
Dr. Ismail Mahmoud Metwally El.semary 4 3/14/2017
Combustion in C I Engine
Combustion in CI engine:
In SI engine,
a homogeneous carbureted mixture of petrol vapor and air, in nearly
stoichiometric or chemically correct ratio, is compressed in the compression
stroke through a small compression ratio (6:1 to 11:1) and the mixture is
ignited at one place before the end of the compression stroke by means of an
electric spark. After ignition a single definite flame front progresses through
the air fuel mixture, and entire mixture being in the combustible range.
In CI engine,
air alone is compressed through a large compression ratio (12:1 to 22:1) during
the compression stroke raising highly its temperature and pressure. In this
highly compressed and highly heated air in the combustion chamber one or
more jets of fuel are injected in the liquid state, compressed to high pressure of
110 to 200 bar by means of a fuel pump. Each minute droplet as it enters the
hot air (temperature 450-550 oC and pressure 30-40 bar) is quickly surrounded
by an envelope of its own vapor.
Dr. Ismail Mahmoud Metwally El.semary 5 3/14/2017
Combustion in C I Engine
As the fuel vapor and air in contact reach a certain temperature and the local
air fuel ratio is within combustible range, ignition takes place. Once ignition
has taken place and a flame established, the heat required for further
evaporation will be supplied from that released by combustion.
In CI engine the fuel is not injected at once, but is spread over a definite
period of time corresponding to 20-40 degrees of crank travel.
The initial fuel droplets meet air whose temperature is only little above
their self ignition temperature and they ignite after the ignition delay.
The subsequent fuel droplets find air already heated to a much higher
temperature by the burning of initial droplets and light up much more
quickly but their subsequent progress is handicapped because of less
quantity of oxygen available.
Dr. Ismail Mahmoud Metwally El.semary 6 3/14/2017
Combustion in C I Engine
Stages of Combustion:-
In CI engine combustion as taking place
in three distinct stages:-
1. Ignition delay period.
2. Rapid or uncontrolled combustion.
3. Controlled combustion.
The third stage is followed by after
burning, which may be the fourth
stage.
Dr. Ismail Mahmoud Metwally El.semary 7 3/14/2017
Combustion in C I Engine
First stage.
Ignition delay period during which some fuel has been admitted but has not yet
been ignited.
The ignition delay is counted from the start of injection to the point where the
p- curve separates from the pure air compression curve.
Second stage.
Rapid or uncontrolled combustion following ignition. In this second stage the
pressure rise is because during the delay period the fuel droplet have had time
to spread themselves over a wide area and they have fresh air all around them.
This stage is counted from the end of delay period to the point of maximum
pressure on indicator diagram.
about one-third of the heat is evolved during this stage.
Dr. Ismail Mahmoud Metwally El.semary 8 3/14/2017
Combustion in C I Engine
Third stage.
Controlled combustion, at the end of second stage the temperature and pressure
are so high than the fuel droplets injected during the last stage burn almost as
they enter and any further pressure rise can be controlled by purely mechanical
means.
The heat evolved by the end of controlled combustion is about 70 to 80 percent
of the total heat of the fuel supplied during cycle.
Fourth stage.
After burning, theoretically it is expected that combustion process shall end
after the third stage.
Because of poor distribution of the fuel particles, combustion continues during
part of the remainder of the expansion stroke.
The duration of after burning may correspond to 70-80 degree of crank travel
from tdc and the total heat evolved by the end of entire combustion process is
95 to 97% and 3 to 5% of heat goes as unburned fuel in exhaust.
Dr. Ismail Mahmoud Metwally El.semary 9 3/14/2017
Combustion in C I Engine
Delay Period or Ignition Lag:-
The delay period exerts a very great influence on both engine design and
performance .
The delay period can be divided into two parts:
Physical delay. Is the time between the beginning of injection and the
attainment of chemical relation conditions. Here the fuel is atomized,
vaporized, mixed with air and raised in temperature.
Chemically delay. Is the second part of delay period at which reaction start
slowly and then accelerate until ignition take place.
Chemical delay is longer than the physical delay.
In SI engine the ignition lag is basically equivalent to the chemical delay only
because the charge consist of homogeneous mixture of vapor fuel and air.
Dr. Ismail Mahmoud Metwally El.semary 10 3/14/2017
Combustion in C I Engine
The effect of delay period in CI engine:-
The delay period affect the rate of pressure rise , knocking and engine startability.
The longer the delay period the more rapid and higher is the pressure rise, more
fuel will be in cylinder before the rate of burning come under control so it cause
engine knock.
The factor affecting on Delay Period in CI engine:-
1. fuel 7. Fuel temperature.
2. Injection pressure or size of droplet. 8. Intake temperature.
3. Injection advance angle. 9. Speed.
4. Compression ratio. 10. Air to fuel ratio.
5. Intake pressure. 11. Engine size.
6. Jacket water temperature. 12. Type of combustion chamber.
Dr. Ismail Mahmoud Metwally El.semary 11 3/14/2017
Combustion in C I Engine
1. Fuel properties:-
Self ignition temperature. Is the most important property of fuel which affect
delay period .
The lower self ignition temperature mean a wider margin between it and
the temperature of compressed air and here lower delay period.
The higher cetane number mean a lower delay period, and smoother
engine operation because the cetane number depend on the chemical
composition of the fuel.
The other fuel properties which affect on delay period:
i) Volatility, ii) latent heat, iii) viscosity, and surface tension.
Volatility and latent heat affect on time taken to form an envelope of
vapor.
Viscosity and surface tension influence the fineness of atomization.
Dr. Ismail Mahmoud Metwally El.semary 12 3/14/2017
Combustion in C I Engine
2. Injection pressure or size of droplet:-
The rate of burning depends on the relative movement of the burning droplets
to the surrounding air charge.
The time taken to establish and ignite a film of vapor surrounding a liquid
droplet is practically independent of the size of the droplet. So that, the rate of
burning and pressure rise following ignition will dependent upon the exposed
surface face area of the vaporizing liquid droplets.
It is possible, to control the droplet size by the injection needle spring closing
load. Generally the greater the injector spring load, the smaller and finer
droplet size.
As the size of droplet depend on the injection pressure, it can be said that
lower the injection pressure the lower the rate of pressure rise during the
uncontrolled phase and smoother the engine running.
Dr. Ismail Mahmoud Metwally El.semary 13 3/14/2017
Combustion in C I Engine
3. Injection advance angle:-
The delay period increase with increase in injection advance angle, because of
the temperature and pressure are lower when the injection begins.
When the injection advance angles are small , the delay period reduces and
operation of engine is smoother but power is reduced because large amount of
fuel burns during expansion stroke.
The optimum angle of injection be 12 to 20 degree before tdc, to cause peak
pressure to occur 10 to 15 degree after tdc.
Dr. Ismail Mahmoud Metwally El.semary 14 3/14/2017
Combustion in C I Engine
4. Compression ratio:-
Increase in compression ratio reduce the delay period as it raises both
temperature and density.
Increase in compression ratio lead to:
The cylinder compression pressure and temperature increase, the ignition
time lag between the point of injection to the instant when ignition first
commences reduces.
The density and turbulence of the charge increase, and increase rate of
burning and increase the rate of pressure rise and the magnitude of peak
cylinder pressure reduced.
Thermal efficiency and specific fuel consumption are improved.
The mechanical efficiency and volumetric efficiency are reduced.
Dr. Ismail Mahmoud Metwally El.semary 15 3/14/2017
Combustion in C I Engine
Dr. Ismail Mahmoud Metwally El.semary 16 3/14/2017
Combustion in C I Engine
Dr. Ismail Mahmoud Metwally El.semary 17 3/14/2017
Combustion in C I Engine
5. Intake temperature:-
Increasing the intake temperature would result in increase in the compressed
air temperature, which would reduce the delay period. But also it reduce the
density of air and hence the volumetric efficiency and power output.
Preheating the air by 100 oC reduces the delay angle by 2o.
6. Jacket water temperature:-
Increase in jacket water temperature also increase compressed air temperature
so it reduce delay period.
7. Fuel temperature:-
Increase in fuel temperature would reduce both physical and chemical delay
period.
Dr. Ismail Mahmoud Metwally El.semary 18 3/14/2017
Combustion in C I Engine
8. Intake pressure or supercharger:-
Increasing the intake pressure or supercharger reduces the auto ignition
temperature and reduce the delay period.
9. speed:-
At constant speed, delay time is proportional to delay angle.
At variable speed, delay period decrease in term of milliseconds but increase
in term of crank angle.
Dr. Ismail Mahmoud Metwally El.semary 19 3/14/2017
Combustion in C I Engine
10. Air fuel ratio:-
Increase in air fuel ratio the combustion temperature are lowered and cylinder
wall temperature are reduced and the delay period increases.
11. Engine size:-
The engine size has little effect on the delay period in milliseconds. As large
engines operate at low rpm because of inertia stress limitations, the delay
period in term of crank angle is smaller .
12. Type of combustion chamber :-
In general, a pre-combustion chamber gives shorter delay period to open type
combustion chamber.
Dr. Ismail Mahmoud Metwally El.semary 20 3/14/2017
Combustion in C I Engine
Diesel Knock:-
If the delay period is long a large amount of fuel will be injected and
accumulated in the chamber, at the ignition of this large amount of fuel may
cause high rate of pressure rise and high maximum pressure which may cause
knock in diesel engine.
The comparison between the detonation in SI engine and knock in CI engine:
In SI engine, the detonation occurs near the end of combustion.
In CI engine, the detonation occurs near the beginning of combustion.
In SI engine, the detonation of a homogeneous charge causing very high
rate of pressure rise.
In CI engine, the fuel and air are imperfectly mixed and the rate of
pressure rise is normally lower than in the detonation in SI engine.
In SI engine, it is easy to distinguish between detonation and non
detonation operation as the human ear easy find the distinction.
In CI engine, it is difficult because all CI engine have a sufficiently high
rate of pressure rise per degree of
Dr. Ismail Mahmoud Metwally El.semary 21
crank angle to cause audible noise. 3/14/2017
Combustion in C I Engine
Methods of Controlling Diesel Knock (Reducing Delay Period) :-
The diesel knock can be controlled by reducing delay period.
The delay period is reduced by the following:
High charge temperature.
High fuel temperature.
Increase the cetane number, by adding chemical dopes, called ignition
accelerators.
A fuel with a short induction period, by arranging the injector so only a
small amount of fuel is injected at first.
Dr. Ismail Mahmoud Metwally El.semary 22 3/14/2017
You might also like
- Lec. 2 Combustion Champer in CI EngineDocument43 pagesLec. 2 Combustion Champer in CI EngineAhmed QasemNo ratings yet
- Combustion in CI EnginesDocument34 pagesCombustion in CI EnginesJayant SisodiaNo ratings yet
- ME6016 - Advance IC Engines NotesDocument106 pagesME6016 - Advance IC Engines NotesDHILEEPAN100% (1)
- COMBUSTION PROCESS IN CI ENGINESDocument11 pagesCOMBUSTION PROCESS IN CI ENGINESSathistrnpcNo ratings yet
- Lec 2.the Combustion Chambers of C I EDocument21 pagesLec 2.the Combustion Chambers of C I EAyman Esa100% (1)
- Thermal Engineering Key 2 UnitsDocument29 pagesThermal Engineering Key 2 UnitsB. selvababuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Combustion and Combustion Chamber Design NotesDocument18 pagesChapter 4 Combustion and Combustion Chamber Design Notesahmed jemalNo ratings yet
- Compression Ignition Engines: 2.1 Combustion Process in Ci EnginesDocument33 pagesCompression Ignition Engines: 2.1 Combustion Process in Ci EnginessuriyaNo ratings yet
- IC ENGINES Unit-1&2Document38 pagesIC ENGINES Unit-1&2parameshNo ratings yet
- Bustion in IC EnginesDocument56 pagesBustion in IC EnginesRam27092003 GermanNo ratings yet
- SI and CI Engine Combustion StagesDocument10 pagesSI and CI Engine Combustion StagesprasanthiNo ratings yet
- Combustion Engines Iit KanpurDocument20 pagesCombustion Engines Iit Kanpurabhigoyal1989No ratings yet
- Chpter Seven Combustion Process in Si EnginesDocument16 pagesChpter Seven Combustion Process in Si EnginesMohammed SohailNo ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering - Combustion in SI EnginesDocument22 pagesThermal Engineering - Combustion in SI EnginesBASIL BENNYNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine Basics ExplainedDocument33 pagesDiesel Engine Basics ExplainedMubarek TeshomeNo ratings yet
- UPDATED COMBUSION IN SI ENGINE .pdf MICROPROJECTDocument21 pagesUPDATED COMBUSION IN SI ENGINE .pdf MICROPROJECTgjumde940No ratings yet
- Combustion in Si EnginesDocument40 pagesCombustion in Si EnginesPolireddi Gopala Krishna100% (4)
- Combustion Process in Ci Engines: Ignition Delay Period /pre-Flame CombustionDocument16 pagesCombustion Process in Ci Engines: Ignition Delay Period /pre-Flame CombustionA'raf Bin Islam SwapnilNo ratings yet
- Combustion in SI - FancsaliDocument5 pagesCombustion in SI - FancsaliFancsali IstvánNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Combustion in CI EngineDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Combustion in CI EnginePrakash KatdareNo ratings yet
- Advanced IC Engines Unit GuideDocument5 pagesAdvanced IC Engines Unit GuiderajapratyNo ratings yet
- Improtant QuestionsDocument133 pagesImprotant Questionsmech mceNo ratings yet
- Level 7 TwoDocument7 pagesLevel 7 TwoSire MkubwaNo ratings yet
- Combustion in CI EnginesDocument3 pagesCombustion in CI EnginesKiran Jot SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Combustion and Combustion Chamber DesignDocument40 pagesChapter 4 Combustion and Combustion Chamber Designahmed jemalNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument42 pagesFinal ReportNimish PandeNo ratings yet
- Combustion Processes in SI and CI EnginesDocument20 pagesCombustion Processes in SI and CI EnginesJo EyNo ratings yet
- Stagesofcombustion 171031161412Document28 pagesStagesofcombustion 171031161412RamanvlrNo ratings yet
- Advanced Internal Combustion EngineDocument17 pagesAdvanced Internal Combustion Engineaerochandru.87No ratings yet
- HSD Term 22-23 EvenDocument38 pagesHSD Term 22-23 EvenViraj ParmarNo ratings yet
- Combustion AnalysisDocument28 pagesCombustion AnalysisPrateek Singh SahniNo ratings yet
- Noise Level Reduction in Four Stroke Ci Engine Effecting Modifications in Fuel Injection EquipmentDocument55 pagesNoise Level Reduction in Four Stroke Ci Engine Effecting Modifications in Fuel Injection EquipmentBhavaniNo ratings yet
- 1cylinder CombustionDocument23 pages1cylinder CombustionBharatiyulamNo ratings yet
- Combustion in CI Engines 1409Document21 pagesCombustion in CI Engines 1409Shriram SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- MikikoDocument12 pagesMikikoMamush FikreNo ratings yet
- Wind Tubine 1234 (1)Document20 pagesWind Tubine 1234 (1)gjumde940No ratings yet
- Combustion Stages SI EnginesDocument25 pagesCombustion Stages SI Enginesshubhamgautam56_6497No ratings yet
- Combustion in CI EnginesDocument65 pagesCombustion in CI EnginesNamandeep Singh OberoiNo ratings yet
- Theories of Combustion in SI EngineDocument4 pagesTheories of Combustion in SI EngineBALAMBAL RNo ratings yet
- Combustion & Combustion ChamberDocument40 pagesCombustion & Combustion ChamberGODNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5: Normal CombustionDocument9 pagesChapter - 5: Normal CombustionYohannes GideyNo ratings yet
- Notes Ic Engines RGPVDocument13 pagesNotes Ic Engines RGPVnitinNo ratings yet
- Combustion & Combustion Chamber: Lecture-8Document73 pagesCombustion & Combustion Chamber: Lecture-8TERMUZE MUSANo ratings yet
- New 5 LectureDocument28 pagesNew 5 LectureMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- 5 Units of I.C EngineDocument55 pages5 Units of I.C Engineguna sekaranNo ratings yet
- M603 Thermal Engineering II - Lecture Notes - Module 4Document19 pagesM603 Thermal Engineering II - Lecture Notes - Module 4xeradementaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Combustion in CI Engines-Stages of Combustion and Ignition DelayDocument19 pagesLecture 9 Combustion in CI Engines-Stages of Combustion and Ignition Delaydivyansh vermaNo ratings yet
- Unit - Ii Combustion: Difficulty of Combustion in CI EnginesDocument3 pagesUnit - Ii Combustion: Difficulty of Combustion in CI Engineskkat2010sanNo ratings yet
- Combustion & Combustion Chamber Design: Lecture-5 by Zewdie Alemayehu Automotive Engineering December 2021Document68 pagesCombustion & Combustion Chamber Design: Lecture-5 by Zewdie Alemayehu Automotive Engineering December 2021ahmed jemalNo ratings yet
- Combustion in IC EnginesDocument10 pagesCombustion in IC EnginesSethu ramNo ratings yet
- Combustion Process in CI and SI EnginesDocument95 pagesCombustion Process in CI and SI EnginesAkashdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Nandha Engineering College (Autonomous) : 17mex12 - Internal Combustion EnginesDocument36 pagesNandha Engineering College (Autonomous) : 17mex12 - Internal Combustion EnginesSugumar MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- CI Engine CombustionDocument14 pagesCI Engine CombustionRahul MeenaNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation of IC Engine With Preheated DieselDocument4 pagesPerformance Evaluation of IC Engine With Preheated DieselInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 17-18 - Combustion in CI EnginesDocument19 pages17-18 - Combustion in CI EnginesRISHAB KABDI JAINNo ratings yet
- HCCI, Emission, Auto-Ignition, Etc.: KeywordsDocument8 pagesHCCI, Emission, Auto-Ignition, Etc.: KeywordsAllaboyinamahidharNo ratings yet
- 3.10 Combustion in CiDocument22 pages3.10 Combustion in CirkNo ratings yet
- Ic Engines Fuel RatingDocument74 pagesIc Engines Fuel RatingKodanda RamaraoNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesFrom EverandComparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Naval Diesel Engineering: The Fundamentals of Operation, Performance and EfficiencyFrom EverandNaval Diesel Engineering: The Fundamentals of Operation, Performance and EfficiencyNo ratings yet
- Iveco - Euro Trakker 4 - 5 - Manual PDFDocument1,702 pagesIveco - Euro Trakker 4 - 5 - Manual PDFFranciscoOliveira92% (88)
- BobcatTroubleshooting Method 2018Document17 pagesBobcatTroubleshooting Method 2018Ayman Esa100% (1)
- Cargador 950 G PDFDocument14 pagesCargador 950 G PDFEdison Pfoccori Barrionuevo100% (1)
- Section 3 Hydraulic SystemDocument3 pagesSection 3 Hydraulic SystemAyman EsaNo ratings yet
- TA2test For S-O-S: Status Description CommentsDocument3 pagesTA2test For S-O-S: Status Description CommentsAyman EsaNo ratings yet
- TA1 Test For Steering SystemDocument6 pagesTA1 Test For Steering SystemAyman EsaNo ratings yet
- TA1 Test For Engine: Status Description CommentsDocument3 pagesTA1 Test For Engine: Status Description CommentsAyman EsaNo ratings yet
- Cf.966h Sist - Elect.Document25 pagesCf.966h Sist - Elect.rmatico1234100% (5)
- 220 ElectricalDocument17 pages220 ElectricalAyman EsaNo ratings yet
- 220 ElectricalDocument17 pages220 ElectricalAyman EsaNo ratings yet
- TA1 Test For Hydraulic System: Status Description CommentsDocument6 pagesTA1 Test For Hydraulic System: Status Description CommentsAyman EsaNo ratings yet
- TA1 Test For Power TrainDocument6 pagesTA1 Test For Power TrainAyman EsaNo ratings yet
- TA1 Test For Electrical System: Status Description CommentsDocument6 pagesTA1 Test For Electrical System: Status Description CommentsAyman EsaNo ratings yet
- Frame inspection report for TA1 loaderDocument6 pagesFrame inspection report for TA1 loaderAyman EsaNo ratings yet
- Cooling SystemDocument6 pagesCooling SystemAyman EsaNo ratings yet
- TA1 Test For Fuel SystemDocument6 pagesTA1 Test For Fuel SystemAyman EsaNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar Compactor Air Inlet Exhaust TA1 TestDocument6 pagesCaterpillar Compactor Air Inlet Exhaust TA1 TestAyman EsaNo ratings yet
- TA1 Test For Operator StationDocument6 pagesTA1 Test For Operator StationAyman EsaNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar Compactor Air Inlet Exhaust TA1 TestDocument6 pagesCaterpillar Compactor Air Inlet Exhaust TA1 TestAyman EsaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Drawing SampleD155A-2Document1 pageHydraulic Drawing SampleD155A-2Ayman EsaNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Components ActuatorDocument10 pages3.1 Components ActuatorAyman EsaNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Components PumpDocument16 pages2.2 Components PumpAyman EsaNo ratings yet
- Hands-On Training: Power of ColorsDocument18 pagesHands-On Training: Power of ColorsAyman EsaNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Components ValveDocument25 pages2.3 Components ValveAyman Esa50% (2)
- Example of ICE DesigneDocument6 pagesExample of ICE DesigneAyman EsaNo ratings yet
- FluidPower Chapters1-4Document61 pagesFluidPower Chapters1-4Ayman EsaNo ratings yet
- What Is Comparative Politics?: Theory of Comparative Political SystemsDocument47 pagesWhat Is Comparative Politics?: Theory of Comparative Political SystemsAyman EsaNo ratings yet
- Week 6Document8 pagesWeek 6Ayman EsaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Machines Problems on Turbines and Draft TubesDocument2 pagesHydraulic Machines Problems on Turbines and Draft TubesAyman EsaNo ratings yet
- Design of Internal Combustion EngineDocument17 pagesDesign of Internal Combustion EngineAyman EsaNo ratings yet
- Walk-Behind-Mower-Brochure-En Walk Behind LawnmowerDocument6 pagesWalk-Behind-Mower-Brochure-En Walk Behind LawnmowerThong KimNo ratings yet
- Type 202221Document2 pagesType 202221api-3779075No ratings yet
- Instrukcja Pellets Fuzzy Logic - ENGDocument53 pagesInstrukcja Pellets Fuzzy Logic - ENGxilef84No ratings yet
- DM30 Series: Atlas Copco Blasthole DrillsDocument4 pagesDM30 Series: Atlas Copco Blasthole Drillscristian garciaNo ratings yet
- At 402 502 504 602 Pilot Training CourseDocument128 pagesAt 402 502 504 602 Pilot Training CourseEtienne Gerber100% (1)
- Artigo Nasa Sugar VoltDocument233 pagesArtigo Nasa Sugar Voltraphael EliasNo ratings yet
- STRATOS MGM 160 Biogas Cogeneration UnitDocument11 pagesSTRATOS MGM 160 Biogas Cogeneration UnitGeorge PircalabuNo ratings yet
- 11 Normal Vs AbnormalCombustionDocument4 pages11 Normal Vs AbnormalCombustionDhananjay BaviskarNo ratings yet
- Gamma Engine - I20Document20 pagesGamma Engine - I20Reza Varamini100% (3)
- P329 12Document1,132 pagesP329 12BlueSkyMasterNo ratings yet
- Prime 4 0 0 e K W 5 0 0 K V A 50 HZ 1500 RPM 415 Volts: Diesel Generator SetDocument6 pagesPrime 4 0 0 e K W 5 0 0 K V A 50 HZ 1500 RPM 415 Volts: Diesel Generator SetMontaserNo ratings yet
- 1 5118668111280603310Document44 pages1 5118668111280603310Jéssica Tupy Paulo HenriqueNo ratings yet
- TU5J4 (NFU) 1.6 16V Petrol Engine Wiring TU5J4 (NFU) 1.6 16V Petrol Engine Wiring Diagram DiagramDocument6 pagesTU5J4 (NFU) 1.6 16V Petrol Engine Wiring TU5J4 (NFU) 1.6 16V Petrol Engine Wiring Diagram DiagramRuiNo ratings yet
- Performance Test On Two-Stage Reciprocating Air CompressorDocument6 pagesPerformance Test On Two-Stage Reciprocating Air CompressorAji V s100% (2)
- Design of Electric ScooterDocument22 pagesDesign of Electric ScooterRithik Gowda80% (5)
- ICEMESM-2018 - Automation Umbrella and Smart Garbage Using IOTDocument6 pagesICEMESM-2018 - Automation Umbrella and Smart Garbage Using IOTWael AlmahdiNo ratings yet
- UNOPS-AFG-RFQ-017-003 GN Parts RAIP-IVDocument16 pagesUNOPS-AFG-RFQ-017-003 GN Parts RAIP-IVمهيب سعيد الشميريNo ratings yet
- 8281 SRi27 DS P4A048014E Jan04 PDFDocument2 pages8281 SRi27 DS P4A048014E Jan04 PDFSamuel CanelónNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar c15 Dissasembly and AssemblyDocument20 pagesCaterpillar c15 Dissasembly and AssemblyDavid100% (57)
- MBL Staff 2010Document52 pagesMBL Staff 2010Victor NdlovuNo ratings yet
- English For Aircraft - Question Bank With Answer KeysDocument120 pagesEnglish For Aircraft - Question Bank With Answer Keyslightjp133% (6)
- Astra D.truck ChecklistDocument9 pagesAstra D.truck ChecklistEyobNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Motor Perkins 1300Document2 pagesData Sheet Motor Perkins 1300Jhonny Castro Pallares100% (2)
- Study On Double Sided Axial Flux Switched Reluctance Motor and Its Application As A Direct Wheel DriveDocument2 pagesStudy On Double Sided Axial Flux Switched Reluctance Motor and Its Application As A Direct Wheel DriveAalok Dyuti SahaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document33 pagesChapter 7kuma alemayehuNo ratings yet
- Tomasetto Alaska 09Document11 pagesTomasetto Alaska 09Quarmina HesseNo ratings yet
- Traffic Laws, Rules and RegulationDocument27 pagesTraffic Laws, Rules and Regulationjovz castillonesNo ratings yet
- Komatsud65ex 16dozerbulldozerservicerepairmanualsn80001andup 200727063646Document26 pagesKomatsud65ex 16dozerbulldozerservicerepairmanualsn80001andup 200727063646juan santa cruzNo ratings yet
- LEBW4971-04 Engine Room VentilationDocument36 pagesLEBW4971-04 Engine Room VentilationBadar Ud Duja100% (1)
- Kato HD820-III Service ManualDocument234 pagesKato HD820-III Service Manualmacthree381% (21)