Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(Specialist) 2011 TSSM Exam 2 Solutions
Uploaded by
KelleyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(Specialist) 2011 TSSM Exam 2 Solutions
Uploaded by
KelleyCopyright:
Available Formats
SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS
Units 3 & 4 Written examination 2
2011 Trial Examination
SOLUTIONS
SECTION 1: Multiple-choice questions (1 mark each)
Question 1
Answer : A
Explanation :
centre = ( 1,1) , a = (1) (3) = 2
b ( x + 1) 2 ( y 1) 2
=2 b=4 =1
a 4 16
Question 2
Answer : B
Explanation :
y = sin(2 cos 1 (2 x))
2 cos 1 (2 x) cos 1 (2 x)
2 2 4 4
2
But 0 cos 1 (2 x) 0 cos 1 (2 x) 2x 1
4 2
2 1 2 1
x dom = ,
4 2 4 2
TSSM 2011 Page 1 of 17
2011 SPECMATH EXAM 2
Question 3
Answer : B
Explanation :
y = sec ( a (b x ) ) = sec ( a ( x b) )
1
dilation of factor 2 from the y axis, hence a =
2
translation to the right, hence b =
2 2
Question 4
Answer : B
Explanation :
The rays Arg ( z i ) = and Arg ( z 2) = intersect at z = 2 + 3i
4 2
Arg ( z + 1) = Arg (3 + 3i ) =
4
Question 5
Answer : D
Explanation :
1 + i , 1 i and 2
Q( z ) = P (i z )
i z = 1 + i , 1 i and 2
1+ i 1 i 2
z= , and
i i i
z = 1 i , 1 i and 2i
z = 1 + i , 1 + i and 2i
TSSM 2011 Page 2 of 17
2011 SPECMATH EXAM 2
Question 6
Explanation :
2 z 2 (1 + i )
w= , Arg ( z ) = Arg ( z ) =
z2 16 16
Arg ( w) = 2 + 2 = + + =
16 4 16 8 4 8 2
Question 7
Answer : D
Explanation :
T = { z : z + 1 z i , z C} { z : z 2 z i , z C} { z : z 1, z C}
z + 1 z i is the half plane above the left line
z 2 z i is the half plane below the right line
z 1 is the interior of the circle
Question 8
Answer : A
Explanation :
When a, b and c are linearly dependent, one of them, for example c, is a
linear combination of the other two.
Therefore c is in the plane determined by a and b.
TSSM 2011 Page 3 of 17
2011 SPECMATH EXAM 2
Question 9
Answer : C
Explanation :
2 2 2
bc = b + a b bc a b = b b (c a) = b true
ac bc ac + bc
2
c+ 2
c=c 2
c = c true
c c c
ac bc
a c = b c false
c
2 c
2
the vector resolutes of a and b in the direction to c are opposite not equal.
ca c b c ( a + b) cc
2
c+ 2
c=c 2
c=c 2
c = c true
c c c c
2 2
c a = c b c c ( a + b) = c true
Question 10
Answer : B
Explanation :
a = i + 3 j , b = 3k
a =
1
2
(
i + 3 j , b = k )
1
a + b = i + 3 j + k
2
( )
a + b = 2
Hence the required vector is
2
1
2
(i + 3j + ) 1
2
k
TSSM 2011 Page 4 of 17
2011 SPECMATH EXAM 2
Question 11
Answer : B
Explanation :
1 sin ( 2 )
= tan Change to
cos ( 2 ) 4 4
1 sin 2
2 1 + cos ( 2 )
= tan + = cot ( )
4 4 sin ( 2 )
cos 2
2
Question 12
Answer : E
Explanation :
r (t ) = tan(t ) i + sec(t ) j
x = tan(t ) y = sec(t )
sec (t ) tan 2 (t ) = 1 y 2 x 2 = 1
2
hyperbola
Question 13
Answer : D
Explanation :
v 2 = 4 x
d 1 2 d 1
a= v = (4 x) = 2 a = const
dx 2 dx 2
Initially v = 8. Since a < 0 v decreases
TSSM 2011 Page 5 of 17
2011 SPECMATH EXAM 2
Question 14
Answer : D
Explanation :
1
0 x e
3 x2
dx u = x 2 du = 2 xdx
1 1 1 1
du 1
x e dx = x x e dx = u e 2 0
2 2
3 x 2 x u
= u eu du
0 0 0
2
Question 15
Answer : A
Explanation :
r (t ) = sin(2 t ) i + cos( t ) j v(t ) = 2 cos(2 t ) i sin( t ) j
3 3 3
v = 2 cos 2 i sin j
2 2 2
3 3
v = 2 i + j v = 5
2 2
Question 16
Answer : D
Explanation :
For y = const the gradient follows a sin or cos shape
when x = y, gradient is zero, hence sin shape
when x = 1 and y = 0, gradient is positive,
hence sin(x y ) applies
TSSM 2011 Page 6 of 17
2011 SPECMATH EXAM 2
Question 17
Answer : B
Explanation :
1 1
d = at 2 , t = 1 d = a
2 2
1 1 1
d n = an 2 a (n 1) 2 = a ( n 2 (n 1) 2 ) d n = d (2n 1)
2 2 2
Question 18
Answer : C
Explanation :
mg mkv = ma a = g kv
g g
= g kv v =
2 2k
g
2k
dv dv 1
= g kv t = = log e 2
dt 0
g kv k
Question 19
Answer : E
Explanation :
2mg T = 2ma
T mg = ma
g
mg = 3ma a =
3
g 4
T mg = m T = mg
3 3
TSSM 2011 Page 7 of 17
2011 SPECMATH EXAM 2
Question 20
Answer : C
Explanation :
F (m + M ) g mg = Ma
F (m + M ) g mg = mg F = 2 ( M + m) g
mg = ma
Question 21
Answer : A
Explanation :
Q2 = R2 + P2
Q
if = 450 then R = P =
2
Question 22
Answer : A
Explanation :
dp d dv dm
p = mv , F = = ( mv ) F = m + v
dt dt dt dt
dv dm
a= F = ma + v
dt dt
TSSM 2011 Page 8 of 17
2011 SPECMATH EXAM 2
SECTION 2
Question 1
a.
1
z+ = 2sin , 0 z 2 + 2 z sin + 1 = 0
z 4 ........[M1]
z = sin sin 1 z = sin i cos
2
z = sin + i cos or z = sin i cos
........[M1]
But cos + = sin and sin + = cos
2 2
u = cis + as + > 0 w = u ........[M1]
2 2
u = cis + and w = cis as required ........[A1]
2 2
b.
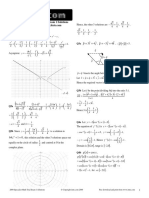
See the diagram to the left
region A ........[A1]
region B ........[A1]
region T ........[A1]
Im(z)
A
T
1
-2 -1 1 2 Re(z)
-1
B
-2
TSSM 2011 Page 9 of 17
2011 SPECMATH EXAM 2
c.
z1 z2 min
= 2i i = 1 ........[A1]
2
z1 z2 max
= cis + 2 = cos + 2 + sin 2 = 2 2 + 5 ........[A1]
4 4 4
d.
i.
u n wn = u n ( u ) = 2i Im(u n ) ........[M1]
n
n
u n wn = 2i sin n + = 2i sin + n as required ........[A1]
2 2
ii.
4
u 4 w4 = 2i sin + 4 = 2i sin(3 ) = 0........[A1]
2 4
Question 2
a.
To show that MNPQ is a parallelogram, it is enough to show that MN =QP
1 1
MN = AB + BC But BC = BA + AD + DC = a + b + c . .. [ M1]
2 2
1 1 1
MN = a + ( a + b + c) MN = (b + c )
2 2 2
1 1 1
QP = AD + DC = (b + c ) MN = QP ... [ A1]
2 2 2
b.
i.
AC = AD + DC AC = 5 i + 3 j
...[ A1]
DB = DA + AB DB = (2 i + 3 j ) + 8 i DB = 6 i 3 j
TSSM 2011 Page 10 of 17
2011 SPECMATH EXAM 2
ii.
AC = 5 i + 3 j DB = 6 i 3 j
AC DB = AC DB cos ...[ M1]
5 6 3 3 = 52 + 32 62 + 32 cos
21
cos = = 57.530 580 ...[ A1]
34 45
c.
i.
AC = 5 i + 3 j DB = 6 i 3 j , AE = m AC and DE = nDB
...[ M1]
AE + EB = AB m AC + (1 n) DB = 8i
m(5i + 3 j ) + (1 n)(6 i 3 j ) = 8 i (5m 6 n + 6) i + (3m + 3n 3) j = 8 i ...[ M1]
5m 6 n + 6 = 8 5m 6 n + 6 = 8 8
11m = 8 m = ...[ A1]
3m + 3n 3 = 0 6m + 6n 6 = 0 11
3
n = 1 m n = ...[ A1]
11
ii.
AC = 5 i + 3 j
24 ...[ M1]
AE = ( 5i + 3 j ) =
8 40
AE = m AC i+ j
11 11 11
1 24 96
A ABE
= 8 = sq. units ...[ A1]
2 11 11
TSSM 2011 Page 11 of 17
2011 SPECMATH EXAM 2
Question 3
a.
See the diagram below
shape (one arm only) ...[ A1]
( y + 3) 2
x 2 = 1 a = 1 and b = 3 ...[ A1]
9
asymptotes y + 3 = 3x ...[ A2]
y + 3 = 3x
2
y + 3 = -3x
-3 -2 -1 1 2 3 x
-2
b.
i.
y + 3 = 3 x 2 + 1 y = 3 + 3 x 2 + 1 as y 0 ...[ M1]
f ( x) =
dy d
=
dx dx
(
3 + 3 x 2 + 1 =) 3x
x2 + 1
as required ...[ A1]
ii.
It can be seen from the graph that the gradient to the hyperbola
changes from 3 to 3 , hence a = 3 and b = 3 ...[ A1]
TSSM 2011 Page 12 of 17
2011 SPECMATH EXAM 2
c.
i.
h
( y + 3) 2
V = x 2 dy , ( y + 3) 2 9 x 2 = 9 x 2 = 1 ...[ M1]
0
9
h
( y + 3) 2
V = 1dy ...[ A1]
0
9
ii
h
( y + 3) 2
h
( y + 3)3 (h + 3)3
V = 1dy = y = h 1
0
9 27 0 27
h3 h 2
V ( h) = + as required ...[ A1]
27 3
d.
Consider dV , a very small change in volume, that produces dh,
a very small change in depth.
dV
dV = A dh A = ...[ A1]
dh
Question 4
a.
ma = W + F
...[ M1]
m( ax i + a y j ) = mg j mk (vx i + v y j )
a x i + a y j = k vx i + ( g k v y ) j
ax = k vx and a y = g k v y ...[ A1]
dvx dv y
= k vx and = g k v y as required
dt dt
TSSM 2011 Page 13 of 17
2011 SPECMATH EXAM 2
b.
dvx dv
= k vx kt = x kt = log e vx + c
dt vx ...[ M1]
At t = 0, vx = u 0 = log e u + c c = log e u
v
kt = log e vx log e u log e x = kt vx (t ) = ue kt ...[ A1]
u
dv y dv y 1
= g k vy t = t = log e ( g k v y ) + c
dt g k vy k
...[ M1]
1
At t = 0, v y = 0 0 = log e ( g ) + c
k
1 1 1 g
t = log e ( g k v y ) + log e ( g ) t = log e
k k k g k v
y
...[ A1]
g g
= e g k v y = ge
kt kt
v y (t ) = (1 e )
kt
g k vy k
c.
g g g 1
v y (t ) =
k
(1 e kt ) y = (1 e kt ) dt y = t + e kt + c ...[ M1]
k k k
g 1 g 1
At t = 0, y=0 0= +c c=
k k k k
...[ A1]
g 1 kt g g g kt
y= t + e 2 y (t ) = t + 2 ( e 1)
k k k k k
d.
i.
gt 2 2h 2 490
h= t= = = 10 s ...[ A1]
2 g 9.8
TSSM 2011 Page 14 of 17
2011 SPECMATH EXAM 2
ii.
10000 0.019.8t
490 = 100t +
9.8
(e 1) t = 11.9 s ...[ A1]
Question 5
a.
N2 N1
F a
Fy
m2 m1
T T Fx
m2 g
m1 g
See the diagram above
Apply Newton's laws on both axes for both objects
N1 + F sin m1 g = 0
F cos T = m1a
...[ M1]
N 2 m2 g = 0
T = m2 a
F cos
F cos = (m1 + m2 ) a a = ...[ M1]
m1 + m2
300cos 450
a= a = 3.5ms 2 ...[ A1]
60
TSSM 2011 Page 15 of 17
2011 SPECMATH EXAM 2
b.
N2 N1
F a
Fy
m2 m1
Ff 2 T T Fx
Ff 1
m2 g
m1 g
Apply Newton's laws on both axes for both objects
N1 + F sin m1 g = 0
F cos T Ff1 = m1a
F f1 = N1
..[ M1]
N 2 m2 g = 0
T Ff 2 = m2 a
F f2 = N 2
N1 = m1 g F sin
F cos T ( m1 g F sin ) = m1a
..[ M1]
N 2 = m2 g
T m2 g = m2 a
F cos ( m1 g F sin ) m2 g = ( m1 + m2 )a
F cos ( m1 g F sin ) m2 g
a=
m1 + m2
F (cos + sin ) m1 g m2 g ..[ M1]
a=
m1 + m2
F (cos + sin )
a= g
m1 + m2
F (cos + tan sin )
= tan a = g tan
m1 + m2
sin ..[ M1]
F cos + sin
a=
cos g tan = F ( cos cos + sin sin ) g tan
m1 + m2 (m1 + m2 ) cos
F cos( )
a= g tan as required..[ A1]
(m1 + m2 ) cos
TSSM 2011 Page 16 of 17
2011 SPECMATH EXAM 2
c.
i.
F cos ( 100 )
a= g tan100
(m1 + m2 ) cos100
a = max when cos ( 100 ) = 1 = 100 ..[ A1]
ii.
F 300
amax = g tan100 = 9.8 tan100 amax = 3.3ms 2 ..[ A1]
( m1 + m2 ) cos100 60cos100
iii.
F cos (1 100 ) F cos ( 2 100 )
a1 = g tan10 and a2 =
0 0
g tan10
(m1 + m2 ) cos100 (m1 + m2 ) cos100 .....[ M1]
a1 = a2 cos (1 100 ) = cos ( 2 100 )
1 100 = 100 2 2 = 200 1 2 = 50 .....[ A1]
d.
The object is on verge of losing contact with the surface
when the normal reaction N1 becomes zero.
N1 = m1 g F sin , N1 = 0 0 = m1 g F sin ..[ M1]
m1 g 40 9.8
F= = = 554.4 N ..[ A1]
sin sin 450
TSSM 2011 Page 17 of 17
You might also like
- The Etteilla Tarot: Majors & Minors MeaningsDocument36 pagesThe Etteilla Tarot: Majors & Minors MeaningsRowan G100% (1)
- Chapter 17 - Essential Mathematical Methods Unit 1&2Document49 pagesChapter 17 - Essential Mathematical Methods Unit 1&2Kelley0% (1)
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Kittel Charles - Introduction To Solid State Physics 8Th Edition - Solution ManualDocument60 pagesKittel Charles - Introduction To Solid State Physics 8Th Edition - Solution Manualnawarajbhandari86% (35)
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsFrom EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- MKT-case StudyDocument7 pagesMKT-case StudyJoe Thampi KuruppumadhomNo ratings yet
- Iit Jee 2005 Maths Sol Screening)Document5 pagesIit Jee 2005 Maths Sol Screening)premsempireNo ratings yet
- Soalan Klon Set D Pelajar (Pra PSPM) SM025Document8 pagesSoalan Klon Set D Pelajar (Pra PSPM) SM025NUR FAHIRA ELIANA BINTI MOHD ZULKIFLI KM-PelajarNo ratings yet
- Practice Qs MTH166 - MergedDocument12 pagesPractice Qs MTH166 - MergedAshish kumarNo ratings yet
- Daniel Sitaru, Claudia N Anut I - RomaniaDocument4 pagesDaniel Sitaru, Claudia N Anut I - RomaniaPerepePereNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 MSDocument24 pagesPaper 1 MSSADIA RAHMAN ANIMA 22S302No ratings yet
- Statics: Edition, Mc-Graw Hill. (/)Document72 pagesStatics: Edition, Mc-Graw Hill. (/)叭叭叭2No ratings yet
- Determinants and Matrices Solutions - Exercise 1 PDFDocument25 pagesDeterminants and Matrices Solutions - Exercise 1 PDFMukesh B HinguNo ratings yet
- Catholic High School Preliminary Examinations (3) Secondary Four Additional Mathematics PaperDocument8 pagesCatholic High School Preliminary Examinations (3) Secondary Four Additional Mathematics PaperJASON_INGHAMNo ratings yet
- IIT JEE 2006 Mathematics Soutions: Time: 2 HoursDocument14 pagesIIT JEE 2006 Mathematics Soutions: Time: 2 HoursSohan PrajapafNo ratings yet
- Problem Set (Headstart AY2022)Document7 pagesProblem Set (Headstart AY2022)Wei Ting ChuiNo ratings yet
- 2021 PypDocument15 pages2021 PypFelicya SugiriNo ratings yet
- Math 1 Question PaperDocument16 pagesMath 1 Question PaperAgkayNo ratings yet
- Mockb1 p2 AnsDocument8 pagesMockb1 p2 Ans。No ratings yet
- Set 1 UPS3 QuestionsDocument7 pagesSet 1 UPS3 Questionsm-6291277No ratings yet
- Ancment638232159769852432 (1)Document21 pagesAncment638232159769852432 (1)suhaas.s.sanshiNo ratings yet
- Final: Problems and AnswersDocument3 pagesFinal: Problems and AnswersDoris riverosNo ratings yet
- Vade Mecum 2002Document168 pagesVade Mecum 2002Irshad HussainNo ratings yet
- 0606 IG MATH MOCK2(2)Document16 pages0606 IG MATH MOCK2(2)Kyle ZhangNo ratings yet
- JEE MAIN APNI KAKSHA STAR BATCH ANSWER KEYDocument41 pagesJEE MAIN APNI KAKSHA STAR BATCH ANSWER KEYBhavadip VamjaNo ratings yet
- VECTOR PRODUCT OF TWO VECTORS PREVIOUS EAMCET BITSDocument2 pagesVECTOR PRODUCT OF TWO VECTORS PREVIOUS EAMCET BITSkeshavareddy mamandurNo ratings yet
- Vectors Imp Questions Paper 1 SolutionsDocument3 pagesVectors Imp Questions Paper 1 Solutionschaynitt30No ratings yet
- JEE-Main-25-07-2021-Shift-2 (Memory Based) PhysicsDocument30 pagesJEE-Main-25-07-2021-Shift-2 (Memory Based) PhysicsSiddhesh DanekarNo ratings yet
- MJC JC2 H2 Maths 2012 Year End Exam Paper 1 SolutionsDocument17 pagesMJC JC2 H2 Maths 2012 Year End Exam Paper 1 SolutionsRyan LeeNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - ELLIP8208C - 20x 2020 - 4E WA1 AMath Question Paper 2022Document9 pagesKami Export - ELLIP8208C - 20x 2020 - 4E WA1 AMath Question Paper 2022Ellipsis Lilo LimNo ratings yet
- N Naf Yad: PrepaDocument7 pagesN Naf Yad: Prepanasru hajiNo ratings yet
- Your Turn 1: 6.8 Condition For Common Root(s)Document50 pagesYour Turn 1: 6.8 Condition For Common Root(s)sanjayb1976gmailcomNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1Document15 pagesMathematics 1keshav GopaulNo ratings yet
- 2122 S6 Math Pre-Mock Exam Paper 2 - AnsDocument5 pages2122 S6 Math Pre-Mock Exam Paper 2 - AnsWinnie SitNo ratings yet
- 0606 IG MATH MOCK1Document16 pages0606 IG MATH MOCK1Kyle ZhangNo ratings yet
- Chapwise Questions Maths IitDocument50 pagesChapwise Questions Maths IitsanchitNo ratings yet
- QE and Complex Numbers DPPDocument9 pagesQE and Complex Numbers DPPsatishmhbdNo ratings yet
- Practice Set 3Document6 pagesPractice Set 3jordanhub05No ratings yet
- Sin Cos Sin 1 Cos 1: Class - Xii Mathematics Ncert SolutionsDocument10 pagesSin Cos Sin 1 Cos 1: Class - Xii Mathematics Ncert SolutionsChetnaNo ratings yet
- Cbse Maths SP Term-1 2021-22Document10 pagesCbse Maths SP Term-1 2021-22Tech BusterNo ratings yet
- 10 0000@Cms Math CA@Crux@v44@n3@Solutions443 PDFDocument11 pages10 0000@Cms Math CA@Crux@v44@n3@Solutions443 PDFAntonio Torres PeñaNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27From EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27No ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Physics Notes Interactions of Light and MatterDocument7 pagesPhysics Notes Interactions of Light and MatterKelleyNo ratings yet
- (Physics) 2010 ITute Unit 3 SolutionsDocument2 pages(Physics) 2010 ITute Unit 3 SolutionsKelleyNo ratings yet
- 3180unit 3 Phys Cheat SheetDocument2 pages3180unit 3 Phys Cheat SheetKelleyNo ratings yet
- (Specialist) 2008 VCAA Exam 2 Itute Solutions PDFDocument4 pages(Specialist) 2008 VCAA Exam 2 Itute Solutions PDFKelleyNo ratings yet
- (Physics) 2010 CSE UNIT 3 SolutionsDocument10 pages(Physics) 2010 CSE UNIT 3 SolutionsKelleyNo ratings yet
- (Specialist) 2008 VCAA Exam 2 PDFDocument28 pages(Specialist) 2008 VCAA Exam 2 PDFKelleyNo ratings yet
- (Physics) 2010 Insight Unit 3 SolutionsDocument53 pages(Physics) 2010 Insight Unit 3 SolutionsKelleyNo ratings yet
- (Physics) 2009 VCAA Unit 3 Exam PDFDocument45 pages(Physics) 2009 VCAA Unit 3 Exam PDFKelleyNo ratings yet
- (Specialist) 2009 Itute Exam 1 Solutions PDFDocument2 pages(Specialist) 2009 Itute Exam 1 Solutions PDFKelleyNo ratings yet
- (Specialist) 2009 Kilbaha Exam 1 Solutions PDFDocument10 pages(Specialist) 2009 Kilbaha Exam 1 Solutions PDFKelley100% (1)
- (Specialist) 2008 VCAA Exam 1 PDFDocument14 pages(Specialist) 2008 VCAA Exam 1 PDFKelleyNo ratings yet
- (Specialist) 2008 VCAA Exam 2 Assessment Report PDFDocument9 pages(Specialist) 2008 VCAA Exam 2 Assessment Report PDFKelleyNo ratings yet
- (Specialist) 2006 Heffernan Exam 2 SolutionsDocument25 pages(Specialist) 2006 Heffernan Exam 2 SolutionsKelleyNo ratings yet
- (Specialist) 2006 Insight Exam 1Document9 pages(Specialist) 2006 Insight Exam 1KelleyNo ratings yet
- (Specialist) 2004 Kilbaha Exam 2Document28 pages(Specialist) 2004 Kilbaha Exam 2KelleyNo ratings yet
- (Specialist) 2006 Heffernan Exam 2Document32 pages(Specialist) 2006 Heffernan Exam 2KelleyNo ratings yet
- (Specialist) 2006 Heffernan Exam 2 SolutionsDocument25 pages(Specialist) 2006 Heffernan Exam 2 SolutionsKelleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document48 pagesChapter 2KelleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document24 pagesChapter 4KelleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document32 pagesChapter 1KelleyNo ratings yet
- Road To Solo Driving Introduction How To Use This Book English PDFDocument29 pagesRoad To Solo Driving Introduction How To Use This Book English PDFKaranbir SinghNo ratings yet
- Impact of Recruitment & Selection on Employee RetentionDocument39 pagesImpact of Recruitment & Selection on Employee RetentiongizawNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Questions & AnswersDocument161 pagesMechanical Questions & AnswersTobaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocument42 pagesChapter 1 - IntroductionShola ayipNo ratings yet
- Migration (LIN 19/051: Specification of Occupations and Assessing Authorities) Instrument 2019Document28 pagesMigration (LIN 19/051: Specification of Occupations and Assessing Authorities) Instrument 2019Ajay palNo ratings yet
- Tupperware India's Perception StudyDocument10 pagesTupperware India's Perception StudyAnmol RahangdaleNo ratings yet
- Homo Sapiens ActivityDocument8 pagesHomo Sapiens ActivityJhon Leamarch BaliguatNo ratings yet
- WA Beretta M92FS Parts ListDocument2 pagesWA Beretta M92FS Parts ListDenis Deki NehezNo ratings yet
- STERNOL Specification ToolDocument15 pagesSTERNOL Specification ToolMahdyZargarNo ratings yet
- The Rich Hues of Purple Murex DyeDocument44 pagesThe Rich Hues of Purple Murex DyeYiğit KılıçNo ratings yet
- Raychem Price ListDocument48 pagesRaychem Price ListramshivvermaNo ratings yet
- No.6 Role-Of-Child-Health-NurseDocument8 pagesNo.6 Role-Of-Child-Health-NursePawan BatthNo ratings yet
- Grade 10Document39 pagesGrade 10amareNo ratings yet
- Ireland in Pre Celtic TimesDocument398 pagesIreland in Pre Celtic TimesGrant MacDonald100% (5)
- PGP TutorialDocument21 pagesPGP TutorialSabri AllaniNo ratings yet
- Credit Risk Management Practice in Private Banks Case Study Bank of AbyssiniaDocument85 pagesCredit Risk Management Practice in Private Banks Case Study Bank of AbyssiniaamogneNo ratings yet
- EPF Passbook Details for Member ID RJRAJ19545850000014181Document3 pagesEPF Passbook Details for Member ID RJRAJ19545850000014181Parveen SainiNo ratings yet
- Application Programming InterfaceDocument12 pagesApplication Programming InterfacesorinproiecteNo ratings yet
- Fiery Training 1Document346 pagesFiery Training 1shamilbasayevNo ratings yet
- Estwani ISO CodesDocument9 pagesEstwani ISO Codesनिपुण कुमारNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics of Advanced Tennis: January 2003Document7 pagesBiomechanics of Advanced Tennis: January 2003Katrien BalNo ratings yet
- 256267a1Document5,083 pages256267a1Елизавета ШепелеваNo ratings yet
- Electrophoresis and Fractionation of Wheat GlutenDocument14 pagesElectrophoresis and Fractionation of Wheat GlutensecucaNo ratings yet
- Obat LasaDocument3 pagesObat Lasaibnunanda29No ratings yet
- Manual - Sentron Pac Profibus Do Modul - 2009 02 - en PDFDocument106 pagesManual - Sentron Pac Profibus Do Modul - 2009 02 - en PDFDante Renee Mendoza DelgadoNo ratings yet
- The Wafer-God and the Bloody History of the VaticanDocument58 pagesThe Wafer-God and the Bloody History of the VaticanMin Hotep Tzaddik BeyNo ratings yet
- D257272 1200 FDD 002 R1 PDFDocument420 pagesD257272 1200 FDD 002 R1 PDFTap Toan100% (1)
- Neonatal SepsisDocument87 pagesNeonatal Sepsisyhanne100% (129)
- The Life and Works of Jose RizalDocument20 pagesThe Life and Works of Jose RizalBemtot Blanquig100% (1)