Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Credit Concept Map I - Credit and Credit Transactions
Uploaded by
Donna Cel IsubolCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Credit Concept Map I - Credit and Credit Transactions
Uploaded by
Donna Cel IsubolCopyright:
Available Formats
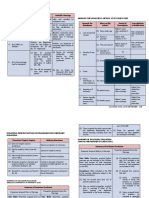
The gratuitous lending of an object for the use of the
Definition borrower (bailee), who has the obligation to return
the same to the lender (bailor) without damage.
Art. 1935: Contract ceases to be commodatum if
Bailor Liberality bailee pays compensation to bailor -> becomes a
Consideration lease
Bailee Permissive Use
GR: Non-consumable thing
EX: Consumable thing, if purpose is not
consumption (ex. exhibition; Art. 1936)
Concepts
Art. 1937: Movables or immovables may be the
As a Contract subject of a commodatum
Object
SGS: SC is wrong here; ownership had to pass for
Producers Bank v. CA: Agreement in this case was a
the purpose stated (because incorporators must own
contract of commodatum, even if money was the
the capital to be used). And if ownership over the
object since it was only used to show that there was
object passes, then it is mutuum. There is the same
enough capitalization for incorporation (i.e.,
obligation to repay in this case, however, whether
exhibition)
mutuum or commodatum
Both parties must consent
Consent Not a consensual contract, however, but a real
contract, perfected by delivery
Art. 1938: Bailor in commodatum need not be the
owner of the thing loaned
But, as against the bailee, he is considered the
owner
Bailor
Retains ownership over the thing, even after delivery
Primary obligation in a contract of commodatum is
the delivery of the object to be loaned
GR (Art. 1935): Permissive use is only as to the
object loaned and does NOT include its fruits
Contract of loan wherein the creditor delivers money Parties As to fruits
or consumable property to the debtor, upon the EX (Art. 1940): Unless the parties stipulate
condition that the same amount of the same kind otherwise; such stipulation is considered valid
and quality shall be paid back
The main consideration of the bailee is the GR: Commodatum is personal in character; bailee
Necessary since the use of the property involved in a permissive use of the object loaned cannot lend nor lease the thing loaned to a third
Bailee
mutuum generally results in its extinguishment person
As to third persons using the object loaned (Art.
Art. 1953: Debtor acquires ownership of the money
The obligation of the debtor is then to pay an equal 1939)
or the consumable property delivered EX to the EX: Unless there is a stipulation to the
EX: Members of the bailee's household may make
amount of the same kind and quality, eectively contrary OR the nature of the property forbids its use
use of the property loaned
replacing or substituting the property loaned by anyone other than the bailee
It is paid as compensation in a simple loan
Involves consumable and fungible property, which Art. 1945: Two or more bailees to whom a thing is
It is that interest agreed upon by the parties, makes it commercially interchangeable with other loaned in the same contract are liable solidarily.
Definition and Concept
distinguished from that prescribed by law property of the same kind.
Art. 1941: Bailee is liable for ordinary expenses
The conventional interest paid in a simple loan Concept This is the most common of all credit commercial arising from use and preservation
Monetary Interest credit transactions, which comes in the form of a Ordinary Expenses
Viewed as the cost of money fixed, savings, or current deposit account with a Art. 1943: However, this does NOT include
bank (Art. 1980) deterioration arising from ordinary wear and tear.
Also, a document may contain two or more legally- SGS on Frias v. San Diego-Sison: Conventional
binding contracts interest is the payment for the use of money SGS: This is the most common credit transaction GR: Since Bailor retains the ownership, he is liable
Concept
since it involves money for extraordinary expenses
Loan of money, goods, or credits (simple loan)
People v. Puig and Porras: The relationship between Arising From Preservation EX to the EX: General rule applies if the need for
Forbearance, or the act of refraining, tolerating, or banks and depositors are that of debtor and creditor. EX: Bailee becomes liable if he incurs them without these extraordinary expenses are so urgent that
Applies To Extraordinary Expenses (Art. 1949) first informing the bailor and securing his approval waiting for bailor's approval would endanger the
abstaining from enforcing a right or obligation of The bank acquires ownership of the money
money, goods, or credits even if the principal deposited by its clients. property loaned
obligation is not a simple loan
Gratuitous GR: BOTH bailor and bailee are liable
Agreed upon by parties Conventional Creditor Arising From Use
Onerous Consideration EX: Unless stipulated otherwise
Kinds
Amount or rate supplied by law in absence of
Legal Permissive Use Debtor If bailee incurs expenses from use, other than those
stipulation
ordinary and extraordinary expenses for use and
Other Expenses (Art. 1950)
Clauses in long-term credit transactions that Money preservation, he is liable for them without right to
Consumables Liability for Expenses and Damages
authorise the increase in conventional interest rates Conventional Interest reimbursement
Goods and Other Consumables
A means to maintain fiscal stability and retaining the Art. 1952: Bailor cannot exempt himself from
value of money Concept SGS and Art. 1954: If the purpose of the contract is Object Commodatum obligation of reimbursing the bailee for expenses and
the transfer of ownership of a non-fungible property indemnifying the latter for damages by abandoning
SGS on Concepcion v. CA: An important clause and payment is made by giving something of the Abandonment by Bailor the property to the bailee
since most credit transactions subsist over long same kind, quantity and quality, it is a contract of
periods of time barter The bailee has the right to compel the bailor for
expenses that he duly owes
GR: Generally valid. Value of payment of the principal is generally
determined at the time of the establishment of the This is the primary obligation of the debtor GR (Art. 1950): Bailee has no right of retention over
EX: Clause is voided if it allows for unconsented obligation (i.e., the delivery of the principal) the property if bailor refuses to pay; he only has a
increase in interest rates, which transgresses the Escalation Clauses Mutuum (Simple Loan) right to demand payment
mutuality principle of contracts. Rule Written promise by the maker to the payee or to
the bearer, or a written promise to pay a specified EX (Art. 1951 and 1944): If the bailor, who has Object is to guarantee payment
There must be a de-escalation clause that amount to a certain person on demand or on a Right of Retention by Bailee
Note knowledge of the flaws of the property loaned, does
authorises a corresponding reduction in the interest specified date Has an accessory character to the principal
not advise the bailee of the same and the latter
rates obligation of the bailor to pay damages
suers damages by reason thereof, then the bailee
SGS: Payable to a specific person
shall have a right of retention over the property until Not considered a coercive measure but a means of
1. Must have a de-escalation clause
Written promise by the issuer to pay money to the bailor indemnifies him for damages. obtaining compensation
2. Escalation must be pegged to the "prevailing holders; or,
Sereno Rules from Concurring Op. After the expiration of the period stipulated
market rates"
in Spouses Juico v. China Banking Written promise issued by a government or Jurisprudence: A sum credited on the books of a GR (Art. 1946): Bailee's obligation to return only
"Transaction by which a creditor mitigates non-
3. The proposed modification must be the result of corporation to holders, to pay the principal amount Obligation to Pay company to a person who appears to be entitled to arises... After accomplishment of the use for which the
payment of a debt by equating a sum of money
an agreement between the parties of the loan at maturity and a specified sum of money it. It presupposes a creditor-debtor relationship, commodatum was constituted
owed with property or another person's undertaking
usually at intervals (Interest-bearing or discounted Bond Evidences Definition Security and may be said to imply ability, by reason of
to pay." Neither duration nor the use to which the thing
GR: Conventional interest applies on the principal government or corporate securities) property or estates, to make a promised Art. 1947: Commodatum is a precarium, wherein
amount only (i.e., conventional interest) CONCEPT OF CREDIT Credit Definition payment." bailor may demand return at will. Commodatum is a should be devoted to was stipulated
SGS: Mitigates the risk of loss
SGS: Payable to any holder. Hence, bonds are precarium in the cases:
EX: Contracting parties, may, by stipulation, On Application of Interest (Art. 1959) easier to trade due to this nature. With notes, the Justice Malcolm in People v. Concepcion: "The Use of the thing is merely tolerated by the owner
SGS: "Any transaction that comes about from the
capitalise the interest due and unpaid, which as holder has to prove that he/she derives his/her ability to borrow money by virtue of the confidence
evaluation of an individual's ability to borrow Definition Credit Transaction Demand the return of the property, extinguishing
added principal, shall earn new interest (i.e., interest rights from the person named in the note or trust reposed by a lender that he will pay what
(credit)." the commodatum
on interest/compound interest) he may promise."
Art. 1946: Bailor has urgent need of the property, in
Instrument acknowledging a debt secured only by
GR: Interest on interest is generally NOT which case he may... Demand the temporary use of the property,
the issuer's earning power and NOT by a lien, legal
demandable temporarily suspending the commodatum while the
right or interest that a creditor has, on any specific Debenture bailor possesses the thing
asset or an unsecured bond.
1. There is an express stipulation in writing to pay
Interest on Interest Bailee commits some oense against the person,
interest. SGS: Basically an "unsecured bond"
the honor, or property of the bailor, or the bailors
By stipulation, compounding/capitalising of interest Fixed Amount EX: Bailor may demand return of the property in the wife, or the children under parental authority of the
Obligation to Return bailor
is agreed upon (compound interest) Money . cases:
How Applied (Art. 1959 and 2212)
2. Any or both of the following instances are present: EX: Interest on interest becomes demandable in the Interest Rate
This demand is reckoned from the date of filing and When the conventional interest due and unpaid is Payable in... Concept Bailee imputes to the bailor any criminal oense,
presence of the . requisites: Art. 765: Bailee commits the acts of ingratitude or any act involving moral turpitude, even though it
the rate shall be the legal rate (6%) judicially demanded, whether or not there was an Value is appraised at the time of the payment
agreement/stipulation to this eect In Kind against bailor be proved, unless the crime or act has been
SGS: It's good to state the appraised value committed against the bailee, or the bailees wife, or
Interest
SGS: In Art. 1959, it is still the principal that earns children under parental authority of the bailee
the interest; the interest unpaid shall just be added to 1. There is an express stipulation for the payment of
the principal, making the base amount larger interest Bailee unduly refuses the bailor support when the
Interest former is legally or morally bound to give support
Compensatory interest is the indemnity for 2. Such stipulation is in writing to the latter
damages arising from delay on the part of the
debtor of an obligation consisting in the payment of Creditor obliged to return the amount paid by SGS: These exceptions recognise that the liberality
Borrower paid by mistake
a sum of money mistake Requisites of the bailor is the cause of the contract as to him/
Eects of Lack of Requisites
her.
Does not need to be expressly stipulated in writing Creditor is authorised to retain Borrower voluntarily paid
Concept Quintos v. Beck: In returning the object, the rules in
but usually comes in the form of a penal clause
SGS: What the law requires is that the express Refers to the loan itself
the Civil Code on where payment should be made
stipulation in writing state that THERE SHALL BE Contract OF Loan
Parties may freely stipulate the amount or rate of the should be followed (see Art. 1251), in order to be
interest, and not the amount/rate of interest per se A real contract; requires delivery for perfection
compensatory interest BUT it is subject to reduction considered to have complied with the obligation.
Requires delivery for perfection
if the court finds it to be iniquitous or An agreement/binding promise between parties to
unconscionable (Ligutan v. CA) A real contract GR: Bailor is liable since he retains ownership Delivery is made by the will of the depositor
NOTE: The legal rate of interest is 6% as per enter into a loan contract Has to have 3 essential elements to be valid:
Monetary Board Circular No. 799 consent, object and cause Also made by two or more persons, each of whom
An accessory obligation A consensual contract; perfected by mere consent Bailee devotes use of property loaned to a dierent
Definition (Art. 1968)
purpose than that agreed upon (breach of the believes himself to be entitled to the thing deposited
Stipulated Penalty, also earning legal interest (6%) Compensatory, Penalty or Indemnity Interest between parties Concept A contract for permissive use
Has Penal Clause Places an obligation upon the debtor to assume a conditions of the commodatum) with a third person, who shall deliver it in a proper
from the time it is judicially demand
greater liability in case of breach SGS: This does not yet involve delivery Kinds Loan always arises from a contract case to the one to whom it belongs
Has Stipulated Rate
Conventional Rate, also earning legal interest (6%) Penal Clauses Bailee keeps property even after accomplishment of
No Penal Clause but only Conventional Rate Sum of Money Strengthens the coercive nature of an obligation SGS on AmEx v. Pantaleon: SC is wrong in ruling Contract TO Loan One of the 'contracts of neighborliness' from the the purpose for which the property is used (delay) A valid and binding contract
from the time it is judicially demanded
that there is a contract of loan since it is only upon Roman times Contract TO Deposit
Provides liquidated damages to answer for the Bailee keeps property beyond the stipulated period Perfected by mere agreement/consent between the
6% per annum computed from judicial or the bank's payment od the money to the merchant
No Stipulation breach Creditor's primary obligation is to deliver the object of the commodatum (delay) How Constituted (Art. 1963) parties
extrajudicial demand that there is a constructive delivery; it is only at this Liability for Loss During Fortuitous Events
Eastern Shipping + Nacar Rules on Interest point that the contract of loan is perfected! of the loan. EX: Bailee is liable when...
Art. 2209: Legal interest is imposed when the debtor EX to the EX: Unless there is a stipulation that A real contract, which requires delivery for its
Interest runs from when demand was made judicially Contract OF Deposit
Liquidated Damages delays in an obligation which consists of a payment Delivery is the essential moment of the perfection of Property was delivered with appraised value exempts the bailee from loss due to FE even if value perfection
or extrajudicially The delivery of the proceeds of the loan in this case
of a sum of money, in absence of any stipulation. Siga-an v. Villanueva: Interest may be imposed as SGS: May sometimes be called as a credit line. LOAN Obligation to Deliver the contract. of the property was appraised
is called a draw down Oral
Interest runs from the date of promulgation of Award of 6% per annum on damages, at the indemnity for damages even in the absence of Rules General Concepts
Damages Not Liquidated Not a Sum of Money Art. 2212: Interest due shall earn legal interest from stipulation in 2 cases... Garcia v. Thio: Delivery is the by which the res or the Bailee lends the property to a third person who is Form (Art. 1969)
judgment discretion of the court GR: Non-consumable thing Written
time that judicial demand is made, even if the substance thereof is placed in the actual or control NOT a member of the household (breach)
obligation is silent as to this point Commodatum
NOTE: Base for the computation of legal interest EX: Consumable thing, if purpose is not of another Triple-V Food Services v. Filipino Merchants
shall be on the amount finally adjudged consumption (ex. exhibition) Bailee is able to save property loaned or his own
Refers not only to conventional interest but also Object property, the bailee chooses the latter (amounting to GR: It is a gratuitous contract Insurance Company: A deposit is a gratuitous
Art. 1935: Contract ceases to be commodatum if
includes fees, service charges, discounts, and an act of ingratitude) contract
6% per annum from finality of judgment until Money Bailor Liberality bailee pays compensation to bailor -> becomes a
Whether Sum of Money or Not Legal Interest, Applied to the Whole Award such other charges incident to the extension of Concept Finance Charges Consumable Mutuum Commodatum Consideration (Art. 1965)
satisfaction lease There is an agreement to the contrary; or,
credit, as the Monetary Board of the Central Bank of Other consumables
the Philippines may by regulation prescribe Bailee Permissive Use EX: Unless... The depositary is engaged in the business of storing
Debtor has to return the very same property Consideration
Commodatum goods
Basically, it is the lending of money at an interest rate delivered Gratuitous
higher than the ceiling prescribed by law Creditor
Loss or destruction of the thing deposited
Pay the same amount lent to him; and, Mutuum Onerous
Was prohibited by the provisions of the Civil Code Debtor has to... Money Obligation to Return or Pay How Extinguished (Art. 1995) In case of a gratuitous deposit, upon the death of
and the Usury Law (Act 2655) Concept Pay interest, if any Debtor Permissive Use
Mutuum either party
However, it is currently suspended (not repealed), by Debtor has to pay with the same amount, kind and
Other Consumables The specific manner with which the thing delivered in
virtue of the Central Bank Circ. No. 905, which lifted quality of the consumables delivered
Definition a deposit is safely kept (Editor's Note: This is my
the ceilings on interest rates own definition)
Art. 1962: An obligation constituted from the SGS: Use of the word "constituted" in Art. 1962
The provisions of the Usury Law applies only to GR: Depositary may not change the way of the
moment of delivery of the property belonging to implies that deposit does not just arise from contract
contracts that involve a loan OR a forbearance of Application deposit
another for the purpose of safekeeping and eventual
money, goods, or credit
return (as armed in BPI v. IAC and Zshornack)
Depositary can make a presumption of consent on
The increase in price by this clause in a sale on Change of the Way of the Deposit (Art. 1974) the part of the depositor, based on the
Judicially
credit transaction is NOT considered as a disguise Usury Concept and Definition circumstances
for a usurious loan Usurious Acts EX: Unless the following requisites are met:
Art. 1964: Manner of Constitution Voluntary (Art. 1967)
Extrajudicially Before such change, the depositary notifies the EX to the EX: Obligation to notify does not apply if
Such increase is not the 'interest' within the meaning On Time Price Dierential Necessary (Art. 1967) depositor and waits for his decision the delay/wait would cause danger to the object
of the Usury Law
BPI v. IAC and Zshornack: A contract of deposit Collect interest when they become due
Such clause serves only to cover expenses in a sale GR: The depositary holding certificates, bonds,
Concept involving currency is possible with banks
on credit and to encourage cash sales securities, or instruments which earn interest Take necessary measures to preserve their value and
Depositor Initiate the deposit by delivery of the property must: corresponding rights
If debtor pays under the usurious transaction, his Administration (Art. 1975)
Remedy of Debtor
remedy is to recover the amount he paid as interest Parties and Obligation Safekeeping of the property EX: This obligation does not apply if the said
Depositary certificates, etc., are kept pursuant to a contract for
This principal amount may be recovered through a Remedies Return of the property the rent of safety deposit boxes
The nullity of the usurious interest does NOT bar the
judicial action, in which case it would be considered
creditor from enforcing his right to collect the Remedy of Creditor
as to have been judicially demanded -> entitles it to GR (Art. 1966): Only movable things may be the GR: Depositary may commingle grain or other
principal amount of the obligation
earn legal interest from the date of demand object of a deposit fungible articles; various depositors shall have a
Object Commingling (Art. 1976) proportionate ownership in the mass
EX (Art. 2006): In cases of judicial deposit,
immovable property may also be a valid object EX: Unless there is a stipulation to the contrary
Also known as sequestration GR: Depositary cannot make use of the object
Concept (Art. 2005) A deposit constituted by judicial order, as a NOTE: If safekeeping is not the principal purpose,
It is an extrajudicial deposit constituted over a consequence of litigation Depositor expressly gives his permission for use then the arrangement is not a deposit and may be a
movable by a consequence of law or quasi-contract, Use (Art. 1977)
Rules loan
so that no unjust enrichment will result from a Movables EX: Unless...
Way of the Deposit
juridical relation Concepts Object (Art. 2006) Preservation of the object requires its use; use shall
Only kind of deposit that may have an immovable as
Judicial Immovables be limited only for the purpose of preservation
It is made in compliance with a legal obligation its object
Art. 1996: Deposit is necessary when... If delivered closed and sealed, depositary should
When it takes place on the occasion of any calamity Case is finally resolved; or
return it in the same condition
Extinguishment (Art. 2007)
Governed by law establishing it Court orders property's release from sequestration
If seal or lock be broken through depositary's fault,
Obligation
Rules Compliance with Legal Obligation Depositary is bound to comply, wrt the property, then he/she is liable for damages
Provisions on Voluntary Deposit are applicable Obligation (Art. 2008)
suppletorily with all the obligations of a good father of a family
Depositary is also obligated to keep the secret of the
It is a formal contract (i.e., the law provides a deposit
Governed by provisions on Voluntary Deposit and Closed and Sealed Object (Art. 1981)
Art. 2168 specific form as a requisite for its validity)
GR: Presumed to be depositary's fault
Occasion of Any Calamity As to Fault
If a person saves property on occasion of any Definition It is issued by a warehouseman, a person lawfully
EX: Unless proof to the contrary is shown
calamity without the knowledge of the owner, the Rules engaged in the business of storing goods for profit
latter is bound to pay the former just compensation If forcible opening is imputable to depositary, then Courts may however pass upon the credibility of the
It is an evidence of goods in a warehouse
As to Value the statement of the depositor as to the value shall depositor wrt the value claimed by him/her
Hotel keepers and employees must be given notice be accepted
as to the eects brought by the guests GR: May contain any terms and conditions
Art. 1998: Deposit of eects of hotel guests are GR: Depositary cannot open the locked box/
Hotel guests must follow the hotel-keepers Are contrary to the provisions of the Warehouse
considered necessary Form receptacle
precautions wrt to the care and vigilance over their Receipts Law
EX: Those that...
Coverage
eects There is express authority from the depositor
Impair the obligation to exercise due care
Opening a Locked Box or Receptacle (Art. 1982)
Art. 1999: Hotel-keeper is also liable for vehicles, Key to the lock was delivered to the depositary
Must indicate on the face of receipt that it is "non- Otherwise, it can be treated as a negotiable WR EX: Unless...
animals and articles placed in the annexes of the General Concepts
negotiable" or "not negotiable" There is presumed authority from either fact that...
hotel The instructions of the depositor cannot be executed
Necessary DEPOSIT Non-negotiable without opening the box/receptacle
Depositor
Hotel-keeper is liable for loss and/or injury to the The goods will be delivered to either...
guest's property Any other specified person on the WR CA Agro Industrial Dev't Corp. v. CA: It is still a
deposit even if the depositary did not have full
GR: Acts of thieves/robbers is not deemed force May be purchased for value control; such fact aects only the way of the
Instances
majeure Kinds of Receipt deposit
Hotel-keeper is not liable for force majeure Negotiable Bearer
Hotels or Inns
EX: Unless it was done with arms or through The goods will be delivered to either... GR: Liable when depositary deposits object with a
On Liability (Arts. 2000-2002)
irresistible force Order of any person named third person
Loss is due to act of the guests, his family, servants, Refers to any other receipt issued for the same Obligation to Safekeep Art. 1973: Assuming deposit with third persons are
Deposit with Third Person (Art. 1973)
or visitors goods allowed, depositary is liable when he/she deposits
Duplicate Receipts EX: Unless there is a stipulation which allows it
Hotel-keeper is also not liable if... the object with a person who is manifestly careless
Loss arises from the character of the eects brought All DRs must indicate on its face that it is a duplicate Failure to do so gives rise to criminal liability or unfit
into hotel
Similar to a depositary's obligation to return Liability of Depositary for Employees (Art. 1973):
Hotel-keeper cannot free himself from liability by Depositary is liable for the negligence of his/her
posting notices to the eect that they shall not be Subsists even if WR is altered or destroyed
employees
liable for the eects of the guests (as armed in YHT Obligation to Deliver
Realty Corp. v. CA) Made by holder or depositor
On Waiver (Art. 2003) GR: Depositary cannot make use of the object; he is
Arises upon valid demand
With an oer to satisfy the warehouseman's lien liable if he does
Any stipulation that exempts the hotel-keeper from Warehouse Receipt (WR)
his responsibilities in Arts. 1998-2001, or diminishes NOTE: If safekeeping is not the principal purpose,
Generally, no commingling, but also subject to
them, is considered void. Use (Art. 1977) Depositor expressly gives his permission for use then the arrangement is not a deposit and may be a
Obligations and Rights of a Warehouseman Liable to keep goods safe in the same way as a exceptions
Liability for Goods loan
depositary EX: Unless...
Governed by law on common carriers
Keep safe from levy and attachment
Check-in Luggage Preservation of the object requires its use; use shall
Common carriers must observe extraordinary be limited only for the purpose of preservation
Passengers' Baggage in a Contract of Common Similar to a depositary's right of retention, in that it is
diligence
Carriage (Art. 1754) a means to obtain payment
If delivered closed and sealed, depositary should
Governed by provisions on responsibility of hotel- Warehouseman's Lien return it in the same condition
Carry-on Luggage It is non-exclusive in nature; it entitles him to all
keepers (see above)
remedies under the law as that a creditor may have
against the debtor If seal or lock be broken through depositary's fault,
Obligation
then he/she is liable for damages
Depositary; Instances When Liable
Involves a negotiable WR
Depositary is also obligated to keep the secret of the
Negotiation Editor's Note: Sorry, the provisions in the book don't Voluntary deposit
The WR is negotiated either by delivery or by Closed and Sealed Object (Art. 1981)
define "negotiate." Personally, I understand it as
indorsement GR: Presumed to be depositary's fault
purchasing the WR for value.
Negotiation and Transfer As to Fault
May involve a negotiable or non-negotiable WR EX: Unless proof to the contrary is shown
Liability for Loss and Damage
Transfer If forcible opening is imputable to depositary, then Courts may however pass upon the credibility of the
Involves the conveyance of the WR, whether
negotiable or not, to another As to Value the statement of the depositor as to the value shall depositor wrt the value claimed by him/her
be accepted
Distinguished from the Civil Code contract of
Criminal Liability deposit, in the the WR Law provides for criminal GR: Depositary is generally not liable for a loss
liabilities for certain acts and omissions through FE
The industry of storing goods and commodities It was stipulated
require a license
Fortuitous Event (Art. 1979) He uses the object without permission
Every building/structure/other protected enclosure in EX: Depositary becomes liable in the . instances:
Warehouse Return was delayed
which commodities are kept for storage
General Bonded Warehouses He allows others to use it, even if he himself was
Any person engaged in the business of receiving
Definition of Terms Warehouseman authorised to use it
commodities for storage
Even if loss is due to FE (without his fault) or due to
Any receipt issued by a warehouseman for
Warehouse Receipt government order, the depositary is liable to deliver
commodities delivered to him Even if not liable (Art. 1990)
the money or replacement to the depositor, if any is
given
GR: Depositor becomes liable for damages to
depositary if he/she delivers a thing, whose
character causes any loss to the depositary
The depositor was not aware of the object's
dangerous character, at the time the deposit was
Depositor; Instance When Liable (Art. 1993) constituted; or,
EX: Unless... The depositor has informed the depositary of such
dangerous character; or,
The depositary was, in any case, aware of the
dangerous character of the object
Gratuitous: Depositor bears the expenses for
preservation; he is liable to reimburse the depositary
for them
Liability for Expenses (Art. 1992)
Onerous: Depositary bears the expenses for
preservation
Depositor; or
No Issues on Capacity to Contract (Art. 1972) Heirs and successors-in-interest; or
Person Designated in Contract
Guardian or administrator of depositor
Already incapacitated at the time of constitution (Art.
1970)
Depositor, if he acquires capacity
Depositor Incapacitated
Persons who may have administration of depositor's
Incapacitated after constitution (Art. 1986)
property and rights
Depositor only has a cause of action for recovery
Incapacitated Depositary in Possession while it is still in the incapacitated depositary's
Has Issues on Capacity to Contract possession
Depositor can only compel the incapacitated
Depositary Incapacitated (Art. 1971) Third Person Who Acquired in Good Faith in depositary to pay him/her the amount by which the
Possession depositary may have enriched or benefitted himself
with the thing or its price
To Whom
Third Person Who Acquired in Bad Faith in Depositor has a cause of action for the recovery of
Possession the object
Joint Depositors and Divisible Object (Art. 1985) Each depositor cannot demand more than his share
Has Stipulated Person Return to designated person
Two or more solidary depositors OR Returning an Return to co-depositor who makes a demand
Indivisible Object (Art. 1985) No Stipulated Person Return to any of the co-depositors, if no demand at
all
SGS: While the actual article says "depositor's heir,"
it should be "depositary's heir." Otherwise, the
meaning is absurd. This was an oversight in
Depositary's Heir Sold Object in Good Faith Without legislation
Knowledge That It Was Deposited (Art. 1991)
Price Paid Deliver the price to depositor
Assign to depositor the right of action to recover
Price Not Yet Paid
Obligation to Return price from buyer
Thing itself, with all products, accessories, and
accessions
Sums he applied for his own use, accruing from the
What to Return (Art. 1983)
date of use
Art 1896 applied: The depositary is liable to pay
If object is money, Art. 1896 shall apply to depositary
interest on... Sums that he still owes the depositor after the
extinguishment of the deposit
GR: Place designated, with expenses for
transportation borne by the depositor
EX: If there is no designation and provided there is
Where to Return (Art. 1987) no malice on the part of the depositary, it shall be
returned to the place where the onject deposited is,
EVEN if it was not the same place where the deposit
was made
One of the depositary's primary obligations
GR: Depositary should return the object upon
demand, even if a period was specified
Thing deposited was judicially attached while it was
in depositary's possession
Depositary was notified of a third party opposition to
EX: Depositary cannot return upon demand of
When to Return (Art. 1988) the return/removal of the thing deposited
depositor if...
NOTE: These exceptions are wrt to returning the SGS: In this cases, depositary should protect itself
object upon demand; the obligation to return the by consigning the property with the court.
object will always subsist.
Art. 1989: If deposit is gratuitous, depositary, upon If depositor refuses to accept the return, depositary
justifiable reasons for not continuing the deposit, may consign it with the court
may return the object to the depositor, even if the
period fixed had not yet elapsed
Depositary has a right to retain the thing in pledge
Right of Retention (Art. 1994) until the full payment of all amounts duly owed to
him/her
You might also like
- Rule-making power of SC under 1987 ConstitutionDocument12 pagesRule-making power of SC under 1987 ConstitutionGelo Leaño100% (1)
- MarketLineIC - PayPal Holdings Inc - Profile - 201021Document44 pagesMarketLineIC - PayPal Holdings Inc - Profile - 201021Divyang SaxenaNo ratings yet
- UV Persons and Family Relations Course SyllabusDocument46 pagesUV Persons and Family Relations Course SyllabusVal VejanteNo ratings yet
- Chart - PFRDocument12 pagesChart - PFRLei TacangNo ratings yet
- Pfda VS CaDocument1 pagePfda VS CaLarry Fritz SignabonNo ratings yet
- Civil AlbanoDocument39 pagesCivil AlbanoTyroneNo ratings yet
- Study Guide No 3 PART 2Document33 pagesStudy Guide No 3 PART 2lordonorNo ratings yet
- Civil Law marriage annulment statusDocument7 pagesCivil Law marriage annulment statusJaysonMahilumQuilbanNo ratings yet
- Test Bank: Theory of AccountsDocument241 pagesTest Bank: Theory of AccountsMa Yra YmataNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Notes 2014 - Atty. San Pedro (rAW)Document78 pagesOblicon Notes 2014 - Atty. San Pedro (rAW)Yaz CarlomanNo ratings yet
- Limited Partnership - Grp. 4Document29 pagesLimited Partnership - Grp. 4Steven Kyle PeregrinoNo ratings yet
- CLearing HouseDocument23 pagesCLearing HouseNitin KapoorNo ratings yet
- Section 3B Partnership Compilation 2017 PDFDocument59 pagesSection 3B Partnership Compilation 2017 PDFDenver Dela Cruz PadrigoNo ratings yet
- 1stweek - 2ndweekDocument7 pages1stweek - 2ndweekAmandoron Dash AdevaNo ratings yet
- Applying Laws EffectivelyDocument8 pagesApplying Laws EffectivelyKate MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Tax Law Rev Notes - Q and ADocument107 pagesTax Law Rev Notes - Q and AJohnNo ratings yet
- Case Digest 2017 2018Document292 pagesCase Digest 2017 2018Mark Anthony Ruiz Delmo0% (1)
- Conflicts of LawsDocument14 pagesConflicts of Lawscarlota ann lafuenteNo ratings yet
- Tax January 20 2021Document27 pagesTax January 20 2021Irish Bianca Usob LunaNo ratings yet
- Notarial NegligenceDocument4 pagesNotarial NegligenceJc AraojoNo ratings yet
- Persons and Family Relations MT ReviewerDocument31 pagesPersons and Family Relations MT ReviewerJohn JovesNo ratings yet
- Alba Vs CA Case DigestDocument3 pagesAlba Vs CA Case DigestNElle SAn Full100% (1)
- 04 GMA vs. People MR GR 220589 2017Document6 pages04 GMA vs. People MR GR 220589 2017nadineyagoNo ratings yet
- 5 Separate Juridical Personality and Doctrine of Piercing The Veil of Corporate Fictions PDFDocument31 pages5 Separate Juridical Personality and Doctrine of Piercing The Veil of Corporate Fictions PDFElaizaNo ratings yet
- Rev. Criminal Law and Practical ExercisesDocument11 pagesRev. Criminal Law and Practical ExercisesFranzess RicardoNo ratings yet
- Civ Pro MapDocument1 pageCiv Pro MapXavier Hawkins Lopez ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Law On Corporations Test Bank With Revised Corporate Code References - CompressDocument62 pagesLaw On Corporations Test Bank With Revised Corporate Code References - CompressCharles MateoNo ratings yet
- New Code of Judicial Conduct For The Philippine JudiciaryDocument6 pagesNew Code of Judicial Conduct For The Philippine JudiciaryMarlon CalderonNo ratings yet
- Frivaldo V COMELECDocument72 pagesFrivaldo V COMELECAU SLNo ratings yet
- History and Development of CorporationsDocument3 pagesHistory and Development of CorporationsLizbeth PucateNo ratings yet
- RA 3135 regulates property sales under mortgagesDocument3 pagesRA 3135 regulates property sales under mortgagesDonna Cel IsubolNo ratings yet
- Public Corp NotesDocument51 pagesPublic Corp NotesRaymund CallejaNo ratings yet
- Petitioner Vs VS: Third DivisionDocument8 pagesPetitioner Vs VS: Third DivisionClarence ProtacioNo ratings yet
- Story Behind SMC V KahnDocument3 pagesStory Behind SMC V KahnDonna Cel IsubolNo ratings yet
- CFA Society Boston Level III 2021 Practice Exam Morning SessionDocument53 pagesCFA Society Boston Level III 2021 Practice Exam Morning SessionSteph ONo ratings yet
- IMMOVABLE PROPERTY CLASSIFICATIONDocument66 pagesIMMOVABLE PROPERTY CLASSIFICATIONWinston YutaNo ratings yet
- #12 Ilagan Vs Enrile Digest - CastilloDocument2 pages#12 Ilagan Vs Enrile Digest - CastilloDonna Cel IsubolNo ratings yet
- Evidence Assignment 1-18 3 and 7 Not IncludedDocument143 pagesEvidence Assignment 1-18 3 and 7 Not IncludedJC HilarioNo ratings yet
- Agrobank Account StatementDocument2 pagesAgrobank Account Statementfazreina 99No ratings yet
- Estate Tax: Transfer TaxesDocument7 pagesEstate Tax: Transfer TaxesElla QuiNo ratings yet
- Heirs of Gregorio LopezDocument81 pagesHeirs of Gregorio LopezdaryllNo ratings yet
- Taxation Ii Atty. Shirley Tuazon I. Taxation Under The NircDocument5 pagesTaxation Ii Atty. Shirley Tuazon I. Taxation Under The NircRonnel DeinlaNo ratings yet
- Glenn Tuazon NotesDocument214 pagesGlenn Tuazon NotesIan LaynoNo ratings yet
- Remedial Law Review 2 Cases For MidtermsDocument13 pagesRemedial Law Review 2 Cases For Midtermskim bok jooNo ratings yet
- TRM N61 V JC OMTKD7Document8 pagesTRM N61 V JC OMTKD7Mukesh Kumar DubeyNo ratings yet
- Crimrev 2-6-20Document10 pagesCrimrev 2-6-20che doringoNo ratings yet
- Civil Law Review 2Document203 pagesCivil Law Review 2Justin YañezNo ratings yet
- (D Asia Power PointDocument42 pages(D Asia Power PointJoe Belarmino IINo ratings yet
- People v. AdrianoDocument9 pagesPeople v. AdrianoerforNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Law 103, Sales (Chan)Document17 pagesSyllabus - Law 103, Sales (Chan)DabenMendozaNo ratings yet
- The Family Code of The Philippines PDFDocument102 pagesThe Family Code of The Philippines PDFEnrryson SebastianNo ratings yet
- Psa 500Document19 pagesPsa 500Anthony FinNo ratings yet
- Legal Ethics GuideDocument46 pagesLegal Ethics GuideMariline LeeNo ratings yet
- Philippine Life Insurance Contract RulingDocument3 pagesPhilippine Life Insurance Contract Rulingsunsetsailor85No ratings yet
- Political Law Review 1 - JurisprudenceDocument79 pagesPolitical Law Review 1 - Jurisprudence刘芸No ratings yet
- PLJ Volume 1 Number 1 - 04 - Jose A. Espiritu - Parts of The Code of Commerce PDFDocument21 pagesPLJ Volume 1 Number 1 - 04 - Jose A. Espiritu - Parts of The Code of Commerce PDFiammaan214No ratings yet
- 100 Intestate Estate of Rosales v. Rosales PDFDocument2 pages100 Intestate Estate of Rosales v. Rosales PDFJuno GeronimoNo ratings yet
- POWERS OF CORPORATIONSDocument58 pagesPOWERS OF CORPORATIONSPASCUA RENALYN M.No ratings yet
- BP 22-4 CASES PRINCIPLESDocument120 pagesBP 22-4 CASES PRINCIPLESJames FrandoNo ratings yet
- Co-Ownership Not Subject to Income Tax for Resale of Real PropertyDocument1 pageCo-Ownership Not Subject to Income Tax for Resale of Real PropertyElleNo ratings yet
- Persons and Family Relations Part OneDocument47 pagesPersons and Family Relations Part OneSpartansNo ratings yet
- HR MT Slides 2016Document5 pagesHR MT Slides 2016AllisonNo ratings yet
- Torts Cases 2Document32 pagesTorts Cases 2Janice DulotanNo ratings yet
- SANTOS Vs BUENCONSEJO PDFDocument2 pagesSANTOS Vs BUENCONSEJO PDFKarlo Gonzalo Guibone BatacNo ratings yet
- Litam V EspirituDocument7 pagesLitam V EspirituElaine ChescaNo ratings yet
- ArrestDocument1 pageArrestJul A.No ratings yet
- Next-in-Rank RuleDocument43 pagesNext-in-Rank RuleAvegail Dela Cruz ValmocenaNo ratings yet
- 5 Fernando U. Juan v. Roberto U. JuanDocument3 pages5 Fernando U. Juan v. Roberto U. JuanJohn Robert BautistaNo ratings yet
- Artigo - Milestones Matrix Converter - Friedli e Kolar (2012)Document14 pagesArtigo - Milestones Matrix Converter - Friedli e Kolar (2012)lveqyopfugznlnnoijNo ratings yet
- Dlvu Lecture09Document20 pagesDlvu Lecture09Awatef MessaoudiNo ratings yet
- Grp4 Easement With AnnexesDocument10 pagesGrp4 Easement With AnnexesDonna Cel IsubolNo ratings yet
- Sample TCTDocument1 pageSample TCTDonna Cel IsubolNo ratings yet
- Memorize REM Codal SalzDocument4 pagesMemorize REM Codal SalzDonna Cel IsubolNo ratings yet
- Course Outline On Persons and Family Relations (1920-2)Document8 pagesCourse Outline On Persons and Family Relations (1920-2)Donna Cel IsubolNo ratings yet
- Atilano Till Manotok Realty DigestsDocument49 pagesAtilano Till Manotok Realty DigestsDonna Cel IsubolNo ratings yet
- Nego Course OutlineDocument5 pagesNego Course OutlineDonna Cel IsubolNo ratings yet
- AmendmentsDocument3 pagesAmendmentsDonna Cel IsubolNo ratings yet
- Malabanan 2 FullDocument26 pagesMalabanan 2 FullDonna Cel IsubolNo ratings yet
- Treatment and welfare of children under 15 facing criminal chargesDocument2 pagesTreatment and welfare of children under 15 facing criminal chargesDonna Cel IsubolNo ratings yet
- MMMDocument3 pagesMMMDonna Cel IsubolNo ratings yet
- 2016 Climate Change Negotiations Game IELDocument4 pages2016 Climate Change Negotiations Game IELDonna Cel IsubolNo ratings yet
- RA EXTENSION ACTSDocument8 pagesRA EXTENSION ACTSDonna Cel IsubolNo ratings yet
- Leonilo AntonioDocument12 pagesLeonilo AntonioDonna Cel IsubolNo ratings yet
- CREBA V SecDocument2 pagesCREBA V SecDonna Cel IsubolNo ratings yet
- Mr. OMPRAKASH JHA account statementDocument12 pagesMr. OMPRAKASH JHA account statementOmprakash JhaNo ratings yet
- Analisis Tingkat Kesehatan Bank Dengan Menggunakan Metode Camel Pada PT - Bank Syariah Mandiri (PERIODE 2001-2010) SkripsiDocument98 pagesAnalisis Tingkat Kesehatan Bank Dengan Menggunakan Metode Camel Pada PT - Bank Syariah Mandiri (PERIODE 2001-2010) SkripsiARYA AZHARI -No ratings yet
- Bahan Kuis Prak Kompak Senin SiangDocument3 pagesBahan Kuis Prak Kompak Senin SiangAkbaer EkoNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2. MIDTERM (Cash Flow Statement)Document3 pagesQuiz 2. MIDTERM (Cash Flow Statement)Gila AbrazaldoNo ratings yet
- Bule Hora University: Chapter OneDocument5 pagesBule Hora University: Chapter OneKirubel WakjiraNo ratings yet
- Example 1: SolutionDocument7 pagesExample 1: SolutionalemayehuNo ratings yet
- Final Project 200 MarksDocument62 pagesFinal Project 200 MarksPooja GolechaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Abdulrahman - Islamic Trading FinanceDocument7 pagesAssignment - Abdulrahman - Islamic Trading FinanceEmad Uddin ShahidNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis: K.R. SubramanyamDocument42 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis: K.R. Subramanyamhasan jabrNo ratings yet
- Partnership Liquidation AccountingDocument56 pagesPartnership Liquidation AccountingAj ZNo ratings yet
- Bank of America - Analyst Structured Trade ReviewDocument2 pagesBank of America - Analyst Structured Trade ReviewJigar PitrodaNo ratings yet
- CV Fifa Jaya Sport - Memorial JournalDocument6 pagesCV Fifa Jaya Sport - Memorial JournalMiskaNo ratings yet
- Pas 26Document2 pagesPas 26AnneNo ratings yet
- Module 2 FMODocument14 pagesModule 2 FMOba8477273No ratings yet
- Tata Power Q4 FY21 resultsDocument28 pagesTata Power Q4 FY21 resultspratik567No ratings yet
- Purchases Day BookDocument8 pagesPurchases Day Bookdrishti.singh0609No ratings yet
- Annex I Form ODI Part IDocument10 pagesAnnex I Form ODI Part IAbhijit ShenoyNo ratings yet
- Jedox Afp Who What and Why of Fpa enDocument50 pagesJedox Afp Who What and Why of Fpa enTech SpacexNo ratings yet
- Newman Hardware Store Completed The Following Merchandising Tran PDFDocument1 pageNewman Hardware Store Completed The Following Merchandising Tran PDFAnbu jaromiaNo ratings yet
- Gagandeep Singh AjmaniDocument2 pagesGagandeep Singh AjmaniThe Cultural CommitteeNo ratings yet
- OverallDocument8 pagesOverallKodambakkam BranchNo ratings yet
- How interest rates impact bond pricesDocument2 pagesHow interest rates impact bond pricestawhid anamNo ratings yet
- Finmar Quiz MidtermDocument1 pageFinmar Quiz MidtermNune SabanalNo ratings yet
- CMA MCQ MergedDocument224 pagesCMA MCQ Mergedsaikat karmakarNo ratings yet